Consider for a moment that you are deciding between two electric cars for purchase.
The first is a name-brand American-made EV.
The second is almost identical — same range, same features, same reviews — but it is $5,000 cheaper than the first vehicle, and it is made in China.
Which would you choose?
When asked a nearly identical version of this question last month, nearly four out of every five Americans — some 78% of adults — said that they would buy the more expensive, U.S.-made car, new results from the Heatmap Climate Poll have found. Only 22% of adults said that they would choose the less expensive Chinese vehicle.
The results, which arrive as the Biden administration is finalizing rules that will govern new electric-car subsidies, suggest that many Americans are willing to support costly measures to boost a home-grown EV industry. And it offers some of the first evidence that Americans — who have long told pollsters that they want to buy U.S.-made products, but that they won’t pay extra for them — may be changing their views and buying habits in light of geopolitics.
The result “highlights the opportunity under the [Inflation Reduction Act] that not only Biden has, but the broader U.S. automotive sector has,” Corey Cantor, a senior associate for electric vehicles at BloombergNEF, a clean-energy analysis group, told me. The Inflation Reduction Act, which Congress passed last year, contains what analysts have estimated at hundreds of billions of dollars in tax breaks for companies that manufacture EVs or their batteries in the United States.
The poll adds ballast to one of the law’s central ideas: that Americans would support policy to boost U.S. domestic industry as much — or more — than they would back a more straightforward decarbonization measure. “It sounds like the IRA’s theory — or Joe Manchin’s theory, or Biden’s theory — is really well supported by the American public,” Cantor said, referencing the two Democrats most often credited with the bill’s design.
The EV question united Americans across party, gender, race, age, and ideological lines. Among people who voted for Trump in 2020, 83% said that they would choose the American car; 76% of Biden voters agreed. More than 80% of white, Black, and Asian Americans each picked the domestic model. So did similar majorities of older and younger Americans, men and women, Democrats and Republicans, and college graduates and those without a college degree.
Even among prospective EV buyers — presumably the most cost-sensitive cohort — 75% said that they would choose the pricier, U.S.-made car. The Heatmap Climate Poll, a scientific survey of 1,000 American adults in all 50 states and the District of Columbia, was conducted by the Benenson Strategy Group and Heatmap News during a five-day period last month.
An opinion poll is not a guarantee of consumer behavior. But in the past, Americans have generally said they would choose U.S.-made products only if they cost about as much as foreign-made goods. In 2016, an Associated Press-GFK poll found that while about 75% of Americans wanted to buy U.S.-made products, only about 30% were willing to pay more for them. According to a Boston Consulting Group analysis, Americans tend to be willing to pay about 5% more for a domestic-made product, The Washington Post has reported. With the average price of a new car approaching $50,000, Americans now seem to say that they will pay more than double that to avoid a Chinese-made electric vehicle.
For now, that preference probably has bigger political implications than consumer ones. Although China makes more EVs than any other country and dominates global market share, relatively few Chinese-made vehicles make their way to the United States. The American government has imposed high tariffs on Chinese-made EVs and EV parts — including key minerals used in electronics such as lithium, cobalt, and cadmium — since 2018.
Probably the highest-profile Chinese-made EV now sold in the United States is the Polestar 2, a well-reviewed, roughly $50,000 sedan that gets 300 miles of range. Although Polestar is headquartered in Sweden and associated with Volvo, it is controlled by Li Shufu, a Chinese billionaire and the founder of the Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, China’s seventh-largest carmaker. Geely also owns Volvo, so some of Volvo’s electric cars — such as the XC40 Recharge, a small SUV — use the same underlying “platform,” or shared set of design and engineering components, as Geely’s cars.
But aspects of this arrangement are changing. Polestar has said that its next car, the Polestar 3 — an $83,000 SUV due to go on sale later this year — will be made in Ridgeville, South Carolina.
Chinese-made EVs have been welcomed more warmly elsewhere in the world. The five most popular EVs in Australia are all made in China. BYD, a Chinese firm that is by some measures already the world’s largest EV maker, sells cars there and across northern Europe; it plans to expand to the U.K., Japan, and Mexico this year. So do Geely and Nio, another Chinese automaker. And some American firms are deepening their China ties: Tesla’s Shanghai plant is the company’s largest factory worldwide.
“European consumers have been fairly favorable” to Chinese EVs, Cantor said. “The response has been more like, This is a cool car, they’re a cool company. There’s a more complicated geopolitical relationship for any Chinese company to come into the American market.”
Dan Wang, a technology analyst at Gavekal Dragonomics, an economic-research firm based in Beijing, said that Americans may not be ready for how different these Made-in-China EVs will initially feel. “It’s not clear that the mindset [that Chinese automakers] bring from the Chinese market — featuring greater phone connectivity and a richer infotainment experience for the rider — meets the taste of Americans,” he told me.
That said, the poll question may be unrealistic about China’s ability to make cost-efficient EVs in the American market. In addition to the high tariffs, the federal government will soon provide subsidies of up to $7,500 to EVs that meet strict U.S.-made standards; it is due to announce that program’s details later this week.
Even beyond EVs, a large majority of Americans seemed to back the IRA’s broad, industry-forward approach when it was described to them in neutral terms, the poll found. Asked to choose from a list of pro-climate policies, just under half of Americans said that they would support a carbon tax. But 69% said that they wanted the government to invest “in technologies that greatly reduce greenhouse-gas emissions,” such as renewables or carbon removal. Essentially the same share said they supported requiring businesses to buy a certain share of their energy from renewable or zero-carbon sources.
Perhaps above all, the poll hints at Americans’ deepening skepticism of what was once one of the central bargains in its global trade agreements: that the U.S. should accept less domestic manufacturing in exchange for cheaper consumer prices. Americans — at least when asked hypothetically and about their own pocketbooks — don’t seem as willing to make that exchange anymore. Will they make the same decision at the dealership? The answer will matter to more than just the auto industry.
The Heatmap Climate Poll of 1,000 American adults was conducted via online panels by Benenson Strategy Group from Feb. 15 to 20, 2023. The survey included interviews with Americans in all 50 states and Washington, D.C. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 3.02 percentage points. You can read more about the topline results here.











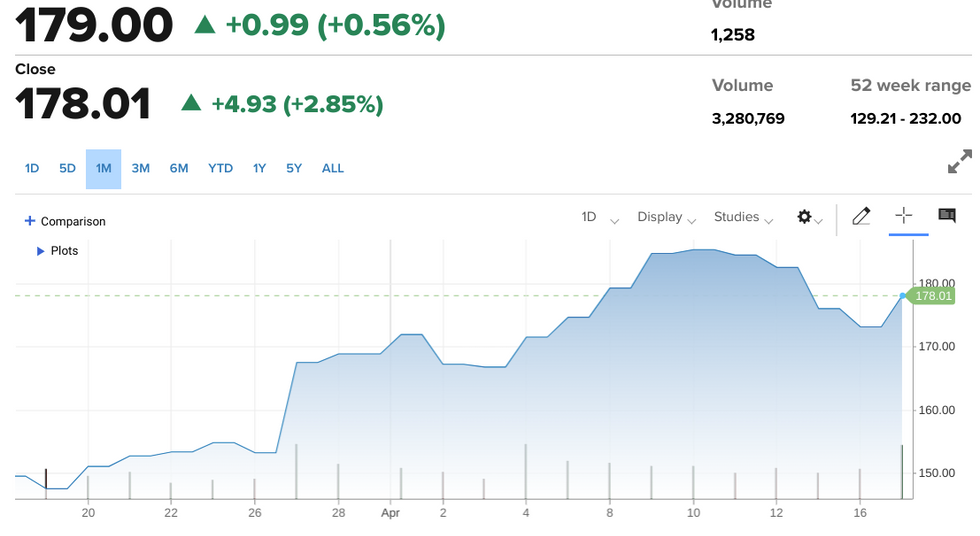 First Solar shares, up as of pre-market trading on Thursday morning.
First Solar shares, up as of pre-market trading on Thursday morning.