You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On Mission 2025, Heirloom’s new facility, and geoengineering’s unintended consequences

Excessive rainfall in the Swiss Alps triggered a landslide • Power was restored in the Balkans following a massive outage that left people sweltering • Flood waters are receding in Rock Valley, Iowa, after 1,500 people were forced to evacuate.
A group of influential leaders across business and politics have formed a new coalition, called Mission 2025, aimed at pressuring governments to “align their upcoming national climate plans with the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to 1.5°C.” These plans, known as nationally determined contributions (NDCs), outline how countries will cut their emissions. There is a February 2025 deadline for new, updated NDCs to be submitted to the United Nations, so Mission 2025 is pushing governments to set ambitious goals. The coalition points to recent data showing that more than two-thirds of annual revenues across the world’s largest companies are now aligned with net zero, which is an increase of 45% over the last two years. Backers of Mission 2025 include IKEA, Unilever, Mastercard, and the heads of C40 Cities, among others. The coalition is spearheaded by Christiana Figueres, who helped shepherd leaders toward the Paris Agreement in 2015 and is now the co-founder of nonprofit Global Optimism. “The launch of Mission 2025 today is a clear rebuttal to everyone claiming that moving faster on tackling the climate crisis is too difficult, too unpopular or too expensive,” Figueres said.
Bay Area-based carbon removal company Heirloom announced today that it’s moving its half of the Department of Energy-funded Project Cypress DAC hub from coastal Calcasieu Parish inland to Shreveport — and that it will be building a second facility, capable of removing 17,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide annually, on the same site. As Heatmap’s Kate Brigham reported, once the two facilities reach full scale, they will have the capacity to suck up a combined 317,000 metric tons of CO2 per year. Project Cypress is a partnership between Heirloom, the Swiss DAC company Climeworks, and project developer Battelle. As per the initial plan, Climeworks will still build out its portion of Project Cypress in southwest Louisiana, and together with Heirloom’s Shreveport plant, the two facilities will pull a combined megaton of CO2 out of the atmosphere every year. Heirloom expects its new 17,000 ton facility to be operational by 2026, while its larger Project Cypress plant is planned to come online in 2027. Initially, this larger facility will remove 100,000 metric tons of CO2 annually, eventually ramping up to 300,000 metric tons. For both projects, Heirloom is partnering with the carbon management company CapturePoint to permanently sequester CO2 in underground wells.
The death toll from this year’s Hajj keeps climbing. Saudi Arabia now says at least 1,300 people died during the pilgrimage, which took place during an extreme heat wave. Temperatures in the holy city of Mecca reached 125 degrees Fahrenheit at one point. “May Allah forgive and have mercy on the deceased,” Health Minister Fahd Al-Jalajel said. Meanwhile, at least 1,400 heat records were set last week as temperatures soared across five continents. In the U.S., more than 100 million people were under heat warnings as of Sunday. The East Coast is getting some relief, but a heat dome is now situated over states in the Plains and the South and the heat index could reach 110.
A new study published in the journal Nature Climate Change found that geoengineering projects off the West Coast of the U.S. could inadvertently lead to more intense heat waves over Europe. The paper examines “marine cloud brightening,” which would involve spraying aerosol particles into the atmosphere to reflect solar radiation. The researchers concluded that this process would indeed lower temperatures in Western states, but only temporarily. By 2050, if temperatures increase by 2 degrees Celsius, the researchers’ models suggest cloud brightening would be ineffective and would actually lead to temperature increases in Europe.
China and the European Union agreed during a call on Saturday to negotiate over the EU’s planned tariffs on Chinese EVs. EU Trade Commissioner Valdis Dombrovskis and his Chinese counterpart Wang Wentao had a “candid and constructive” discussion that ended with an agreement to “engage at all levels.” The EU has threatened levies as high as 48% and accused China of unfairly subsidizing its EV production. Bloombergreported that China hinted that Germany’s luxury carmakers could benefit from relaxed tariffs in China if Berlin “convinces” the EU to drop its tariffs. The discussions come weeks after President Biden announced that U.S. tariffs on electric vehicles made in China will quadruple from 25% to 100%.
Researchers have created a new kind of fabric that they claim can keep wearers up to 16 degrees Fahrenheit cooler than traditional silk.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
A little-noticed provision would make the payment option used by tax-exempt groups all but impossible to claim.
A little-noticed provision in the Senate tax bill will sabotage the efforts of tribes, rural electric cooperatives, and public power authorities to develop local affordable energy projects by striking a section of the Inflation Reduction Act that enabled tax-exempt groups to claim the clean energy tax credits as direct cash payments from the Treasury.
The IRA included strict domestic sourcing requirements beginning in 2026 for groups utilizing this “direct pay” option. But the law also created exceptions for cases where domestic components were not available in sufficient quantity or quality, or would increase costs by more than 25%. The Senate bill would get rid of these exceptions.
“It just makes it unlikely for those projects to go forward — or more likely for those projects to go forward with a private developer, instead of with a public utility or a tribe or a rural co-op,” Grace Henley, a tax attorney with the Natural Resources Defense Council, told me. “And so they don’t really do anything to increase the amount of domestic material that would be used, they just hurt the projects that are seeking to invest in clean energy infrastructure for these communities to lower costs.”
Public power and tribal energy advocates warn that without the exceptions, energy development will become impossible for their constituents.
Wind and solar projects being developed by these groups are already threatened by the bill’s rapid phase-out of wind and solar tax credits and its complex rules related to using materials from China. Chèri Smith, the executive director of the Alliance for Tribal Energy, told me that Tribes face longer development timelines than the average private developer. “We have multiple stages of approval that are unique to tribal energy development,” she told me, including lengthy internal consultation processes. The changes to direct pay will put these projects further out of reach, she said.
The Alliance provides free energy development consulting services to more than 100 Tribes. Smith sent me a list of projects in Alaska Native villages, Arizona, California, and Oregon that could be killed by the tax credit changes. “Alaska Native villages face some of the highest energy costs in the country,” she said, largely due to their reliance on diesel generators. Just over a third of the Hopi Tribe in Arizona lacks access to electricity, but now multiple microgrid projects meant to close the gap are at risk. Many of the projects on the list are also doubly threatened by grant cancellations and the repeal of the Tribal Energy Loan Guarantee Program.
“The bill is particularly harmful to Tribal Nations, pulling the rug out from under projects that would strengthen their energy sovereignty and power local communities,” Democratic Senators Martin Heinrich, Ron Wyden, and Brian Schatz wrote in a joint statement on Thursday. “Together, the Tribal Energy Loan Guarantee Program and our Inflation Reduction Act’s clean energy tax credits have cleared pathways and removed significant barriers for Tribes to finance and build their own resilient energy infrastructure.”
The American Public Power Association is also sounding the alarm. John Godfrey, the group’s senior government relations director, told me that in addition to wind and solar, municipal utilities and rural electric co-ops are also considering nuclear and hydropower projects. For example, Energy Northwest, a consortium of 29 public utilities in Washington State, has plans to retrofit the Columbia Generating Station nuclear plant to increase its power output. It’s also in early stages to deploy four small, modular nuclear reactors. As my colleague Matthew Zeitlin wrote a few days ago, the governor of New York has also tasked the New York Power Authority with developing a new nuclear plant in the state.
Nuclear and hydropower “are technologies where often there is not a U.S. source, but there is a good trading partner source — Canada, Germany, Japan,” Godfrey said. By tightening the domestic sourcing requirements for direct pay, the bill would “hinder the very technologies that there’s generally a bipartisan consensus we need to be developing.”
Public utilities and electric co-ops, which serve close to 30% of electric customers in the U.S., are also unfairly singled out by the provision, he said. “If my public power utility wants to develop a project and they need a Canadian turbine, they can’t get any credit. But if a taxable corporation down the street develops exactly the same project, they can.”
“If the purpose is to encourage hydropower, that’s not a good use of resources,” he said.
Senate Republicans tucked a carveout into their reconciliation bill that would allow at least one lucky renewable energy project to qualify for a major Inflation Reduction Act tax credit even after the law is all but repealed.
The only problem is, it’s near impossible to be sure right now who may actually benefit from this giveaway — and the mystery is driving me up the wall. I feel like Charlie Day in that episode of It’s Always Sunny in Philadelphia, stringing documents together and ranting like a lunatic.
The Senate bill would phase out the tech-neutral production tax credit starting next year and completely eliminate it by the start of 2028. For the past week and a half, I have been trying to solve the riddle of an exemption tucked into the language that would allow a wind or solar facility that is “part of a single project” to continue to take advantage of the tech-neutral production tax credit as it exists today, which means it would not begin to phase out until 2034.
To qualify for the exemption a project must, according to the Senate text, meet two conditions: It must produce more than 1 gigawatt of electricity, and be sited on federal lands where a “right-of-way grant or lease” had been given by the Bureau of Land Managementbefore June 16, which is the date the text was released.
Only a handful of projects in the U.S. could possibly fit that criteria. But every time I think I’ve identified one that will actually qualify, I learn a new fact that, to me, takes it out of the running.
Here’s why my head hurts so much: A renewables facility that would benefit from this language needs to be sited at least partially on federal lands. But because Trump isn’t issuing new right-of-way approvals or leases to most renewables projects right now, it likely had to get its right-of-way or its lease before he entered office. (The June 16 language feels like a bit of a red herring. Nothing that fits the other definitions has received these documents since the start of Trump 2.0.)
Then there’s another factor: The only projects that would benefit from this language are ones that haven't started construction yet. Even if a project doesn’t have all of its permits for federal land use, its developer can build stuff like roads on any connected private lands and technically meet the deadline to start construction laid out in the new legislation. The construction start date is what counts — it doesn’t matter whether a project is placed in service and provides power to the grid years later, as long as it began construction before that deadline.
Taken together, all this means that a project that would benefit from this language probably has to be sited on federal lands and hold permits already … but for some reason can’t start construction to qualify for the program.
When I first started hunting for an answer, many people — including renewables advocates, anti-wind activists, and even some Senate staff in conversations with me — speculated that the language was a giveaway to two wind projects under construction in Wyoming, Chokecherry and Sierra Madre, which together make up what would likely be the largest wind farm in the U.S. if completed. These two projects are largely sited on federal lands and received all their approvals before Trump entered office.
I understand why people are pointing at Chokecherry and Sierra Madre. They are not expected to be online before 2029, and the House version of the bill would have locked them out of the production tax credit because it added a requirement that projects be “placed in service” — i.e. actively providing power to the grid — by around that same period. Any slippage in construction might have really hurt their finances. They’re also backed by a powerful billionaire, GOP donor and live entertainment power-broker Phil Anschutz, a man who made his initial fortune partially from fossil fuels.
Except … my colleagues and I are still not convinced. That’s because it is not clear that these two projects are at any actual risk of losing the production tax credit. They have been actively under construction for a long time, and the Senate bill killed the House’s “placed in service” requirement.
Another project floated is the Lava Ridge wind farm in Idaho, which was fully permitted under Biden, is largely sited on federal lands, and would produce more power than necessary to qualify for the exception. Hypothetically, this project would be a great candidate for being a beneficiary of the bill because Trump banned work on the project via executive order amid opposition from Idaho politicians, making a carveout to get more time a worthwhile endeavor.
Except … Senate Finance Chair Mike Crapo, the lead author of the pertinent section of the Senate reconciliation bill, was one of those Idaho politicians who pushed Trump to kill Lava Ridge. Why would he give a tax break to a project he wanted dead?
Then there was my personal best guess for the beneficiary: Esmeralda 7, an expansive set of proposed solar farms in the Nevada desert that, as proposed, would produce more than 5 gigawatts of power and is largely sited on federal land. Construction can’t begin until Esmeralda 7 gets its federal approvals, and the Trump administration was expected to complete that work by mid-summer.
Except … I reported last week that the permitting process for Esmeralda 7 is now indefinitely stalled. The project is at best still months away from getting its right-of-way approvals from the Trump administration, which recently pushed back timelines for finishing reviews of other large Nevada solar projects, too.
Ultimately, it will be difficult to glean who the lobbyist giveaway here is for unless the legislators who wrote it disclose their intentions. I reached out to the communications director for Republicans on the Senate Finance Committee to try and find out, but so far I’ve gotten crickets.
It may be that this language is revised and that future changes lay out the true beneficiary. Sometimes lawmakers will put the wrong date or word into a bill and they’ll edit it on the floor before a vote, chalking it up to a drafting error.
If senators decide to add back the “placed in service” requirement to capitulate to the House, this would easily be the Chokecherry-Sierra Madre giveaway. If Republicans were to shift forward the deadline for getting a right-of-way, Esmeralda 7 would qualify. Or maybe they could change some secret third thing and a different project I hadn’t considered will be revealed as the mastermind in the shadows.
Until then, I’ll be in my basement poring over more maps and going slowly insane.
Additional reporting was provided by Emily Pontecorvo.
On resuming rare earth shipments, hurricane tracking, and EV tax credits
Current conditions: The Ohio Valley is still sweltering through the last remnants of this week’s brutal heat wave • The death toll from recent floods in South Africa has risen to 101 • It’s 90 degrees in Venice, Italy, where the world’s rich and famous are gathering for the wedding of Jeff Bezos and Lauren Sanchez.
The U.S. and China have hammered out the details of a trade deal, including an agreement that China will resume rare earth shipments to the U.S. Rare earth materials are essential for everything from planes to EVs to wind turbines. China controls most of the world’s rare earth production and halted exports in April in response to President Trump’s tariff hike, and China’s chokehold on rare earths threatened to derail trade talks between the two countries altogether. Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick said a deal has now been “signed and sealed.” “They’re going to deliver rare earths to us,” Lutnick said, adding that the U.S. will then “take down our countermeasures.” Lutnick also indicated that Trump plans to announce further trade deals with other nations in the coming two weeks.
As climate talks in Bonn, Germany, wind down, negotiators there have agreed to increase the budget for the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change by 10% over the next two years to 81.5 million euros ($95.4 million). The UNFCCC runs some of the world’s largest climate negotiations and tries to ensure countries follow through on their climate commitments. Its budget is funded by government contributions. China will account for 20% of the new budget, Reuters reported. The U.S. is supposed to cover 22%, but President Trump has pulled international climate funding. Former New York Mayor Michael Bloomberg’s philanthropic arm has stepped in to cover the missing U.S. contributions. UN climate chief Simon Stiell said the budget increase was “a clear signal that governments continue to see UN-convened climate cooperation as essential, even in difficult times.”
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
Hurricane forecasting is about to get a little bit more difficult. At the end of June, the federal government is going to stop distributing readings from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, a tool forecasters all over the world have been using to track and predict hurricane development. As retired federal meteorologist Alan Gerard told Bloomberg, this particular satellite program is unique because it lets forecasters peer inside storms and monitor for rapid intensification. As the planet warms, hurricanes are strengthening much faster than they did in recent decades. Hurricane expert Michael Lowry says the Department of Defense seems to be concerned that the satellite data poses a security concern. Its termination “will severely impede and degrade hurricane forecasts for this season and beyond, affecting tens of millions of Americans who live along its hurricane-prone shorelines,” Lowry wrote.
A group of U.S. car dealers penned a letter urging senators to “reject provisions in the budget reconciliation process that would abruptly eliminate EV-related tax credits from the Inflation Reduction Act,” warning that sudden changes would bring about market uncertainty, damage businesses, and hurt Americans. The signatories – including EV Auto, Carmax, and Caravan – instead call for a “gradual sunset” of the EV tax credits to avoid disruption to the used car market. “A multi-year transitional period would also provide the opportunity for Americans to continue adopting cleaner vehicles more affordably,” they add. The tax and budget bill put forward by Senate Republicans would end the $7,500 EV tax credit within 180 days after the law’s passage.
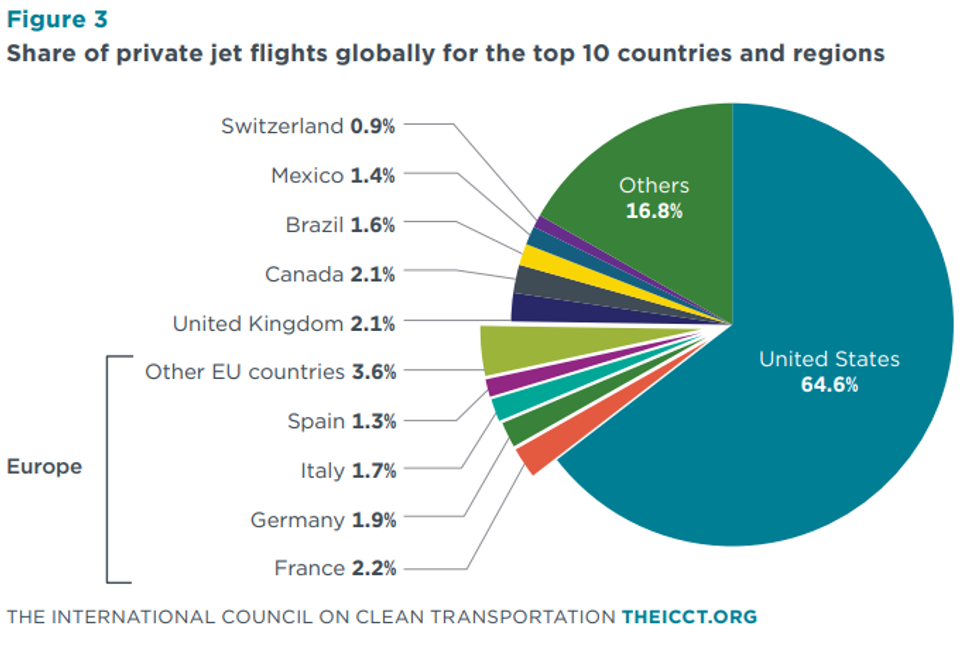
A report out today from the International Council on Clean Transportation estimates that the world’s private jets produced more greenhouse gas emissions in 2023 than all the flights that took off from Heathrow Airport — the world’s fourth busiest airport — that same year. Emissions from private jets increased 25% over the past decade. A few more interesting (though perhaps not surprising) tidbits from the report:
Solar power accounted for more than 10% of U.S. electrical output in April, while wind provided about 14%. As Michelle Lewis at Electreknotes, “solar is now producing more electricity than hydropower, biomass, and geothermal combined.”