The hottest new car debut of 2023 probably isn’t anything you’ve ever heard of. Unless you live in China, it’s not even something you can buy. It’s the BYD Seagull, a compact electric car from a rising giant in the EV space. And with a range of up to 252 miles and a price tag of 78,000 yuan (only $11,300), it’s expected to become China’s best-selling car within months.
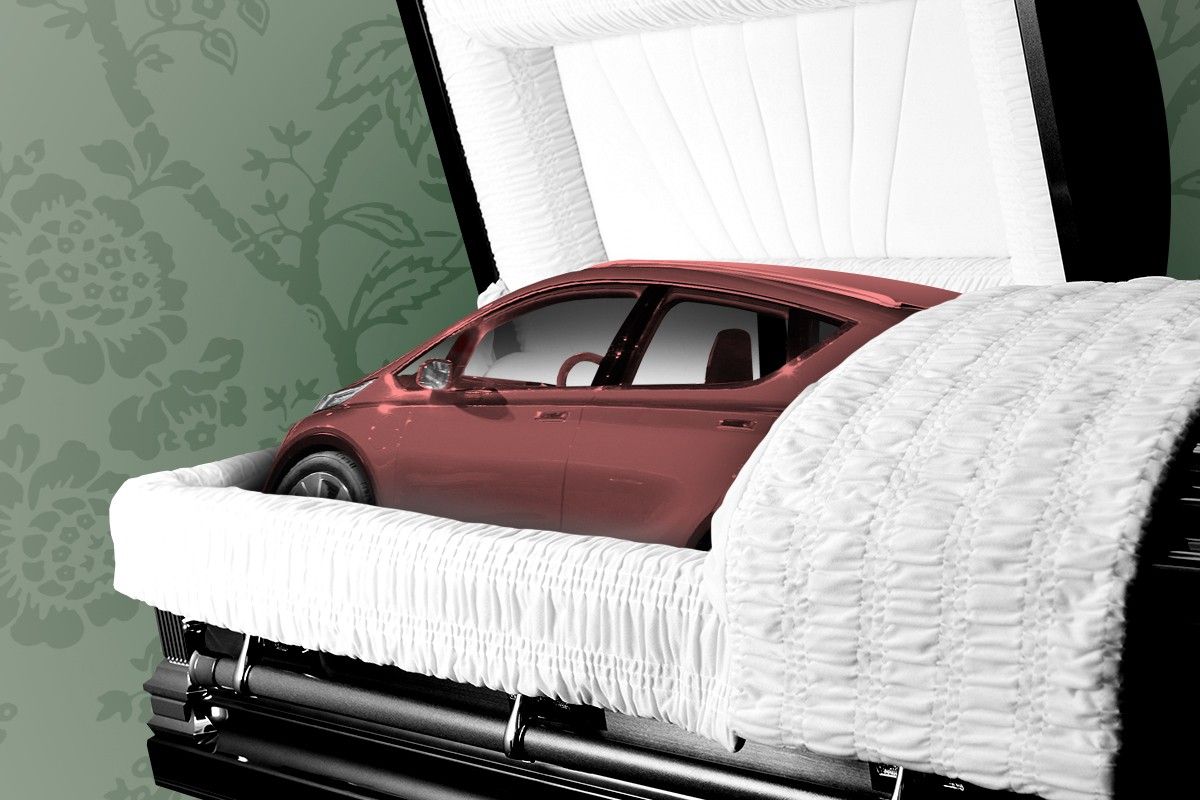
If you want anything even close to that in the United States, good luck. Your outlook got a little dimmer this week when General Motors announced the Chevrolet Bolt EV and its slightly larger sibling, the Bolt EUV, would be discontinued. The decision brings an end to a massively successful line of smaller, affordable, high-range EVs from America’s largest automaker.
Granted, the Bolt’s demise had been expected for at least a year. GM is in the midst of launching a new generation of EVs with modern hardware, software, and batteries as it aims to become an all-electric car company by 2035. And the Bolt was becoming inferior to newer cars with quicker charging times.
But what doesn’t seem to be in the cards right now is anything that will directly replace the Bolt: something small and inexpensive, as well as great on electric range.
“When the Chevrolet Bolt EV launched, it was a huge technical achievement and the first affordable EV, which set in motion GM’s all-electric future,” Chevrolet spokesman Cody Williams told CNBC in a statement. “Chevrolet will launch several new EVs later this year based on the Ultium platform in key segments, including the Silverado EV, Blazer EV, and Equinox EV. ”
The problem is that all of those vehicles are bigger and more expensive than the Bolt. GM is hinging a lot of its entry-level hopes on the Equinox EV, which should start around $30,000 before any tax incentives. But it dwarfs the compact Bolt, and further proves that America is a truck and SUV market now — and that reality will carry over into the electric era too.
Sales of small cars and sedans have been on the decline for years, thanks in part to cheap gas, changing buyer tastes, loopholes that allow larger vehicles to face less-strict fuel economy and emissions regulations, and the thirst for profit margins among car companies.
Nonetheless, it would be a mistake to think the Bolt and Bolt EUV were failures. Very much the opposite, and GM CEO Mary Barra wrote as much in a letter to shareholders about Q1 2023 results.
“In addition, we delivered more than 20,000 EVs, thanks to the third consecutive quarter of record Chevrolet Bolt EV and Bolt EUV deliveries and rising Cadillac Lyriq sales,” Barra wrote. “We are now no. 2 in the U.S. market, and we increased our EV market share by 8 percentage points.”
If you’re asking, “Why kill a car like that?,” know that it is not a crazy question. One possible answer is GM thinks it can do even better with the bigger Equinox EV, much as Tesla’s Model Y crossover is its global best-seller.
Yet it brings me no pleasure to write the eulogy for the Chevrolet Bolt. With 259 miles of electric range and a starting price of just $26,500 (and that’s before any tax incentives, which in recent months made it an almost hilarious steal), it has long been one the best cars in GM’s portfolio.
The Bolt arrived in late 2016, right as the world was only barely starting to take EVs seriously. At the same time, Tesla, which had proven its ability to make high-speed, high-end luxury cars like the Model S, was trying to become a mainstream volume-selling manufacturer with the Model 3 sedan.
For a good couple of years, the modern electric market in the U.S. was essentially just the Bolt, the Model 3, and the Nissan Leaf, another compact EV stalwart set to be discontinued so its parent company can focus on crossovers. The Bolt and the Model 3 were unlikely competitors by virtue of arriving around the same time, having the same mass-appeal mission and running on electricity. I always thought that comparison was a bit unfair; the Model 3 is a sport sedan at heart, and nobody seriously compares a BMW 3 Series to a Toyota Corolla.
The Bolt had a few other marks against it as the Model 3 increasingly took the spotlight. Admittedly, the Chevy’s tall hatchback design just wasn’t very sexy. It screamed “economy car” right as Tesla was successfully changing the golf-cart image that had dogged EVs for too long. And the front-wheel-drive Bolt simply couldn’t match the Model 3 in sheer driving dynamics. It had no “Performance” version with supercar-crushing 0-60 mph times.
But none of that takes away from how good the Bolt actually was. The range was incredible for its time and still quite respectable today. GM initially promised 200 miles of range, but the end result did even better at 238 miles. Over its life, the range was upgraded even further. And while it wasn’t the barnstormer the Model 3 was, it was surprisingly quick and fun to drive, almost on par with a hot hatchback like a Volkswagen GTI.
I remember being deeply impressed after spending a week with a Bolt in 2018 when I was editor-in-chief of the automotive website Jalopnik. (More so than some members of my staff, in fact, who thought the Bolt was ugly and that I was crazy for liking it.) EVs were much more novel five years ago than they are now, but here was something affordable, highly practical, and with enough range that it could easily fit many people’s lifestyles.
Tesla’s cars felt like spaceships; to me, the Bolt felt like proof that normal, everyday electric driving could be possible for anyone.
Certainly, its nearly eight-year run hasn’t been perfect. Bolt sales went up and down over the years (although it’s been shattering records lately thanks to the tax incentives) and it was repeatedly hit with recalls over devastating lithium-ion battery fires. Still, it had its best year ever in 2022, with nearly 40,000 sold. Sure, Tesla sells more EVs in a month in the U.S., but again, the intense demand for the Bolt lately proved there’s a place for all kinds of electric cars in our landscape.
Over its lifespan, the Bolt spawned the bigger EUV version and also became incredibly popular in municipal fleets and as delivery vehicles. How could it not? It was a near-perfect car for any city dweller looking to go green and not take up a lot of space. It’s hard to imagine the longer, taller Equinox EV filling those needs the same way.
So with the concept proven by the Bolt, what comes next? Unfortunately, the answer seems to be bigger EVs. Chevrolet itself makes very few actual cars anymore; the Bolt was one of the remaining few. Ford has stopped making cars and sedans entirely, and even the popular Mustang Mach-E is a crossover. Hyundai offers an impressive lineup of EVs, but so far only one in that family is a sedan, the Ioniq 6. And EVs in America still averaged around $60,000 at the end of last year, a far cry from the Bolt — to say nothing of BYD’s Seagull.
For critics who say that the forthcoming EV revolution will repeat many of the auto industry’s sins by putting pedestrians, cyclists, and even parking garages further at risk with massive curb weights, the death of the Bolt gives them plenty of ammunition.
On one hand, it makes sense that new technology needs to be expensive at first in order to scale; in my lifetime alone, that’s happened with everything from VHS tapes to smartphones. Automakers need hefty profit margins to pay for this EV transition. But our own buying habits, what we’ve been offered so far, and our terrible approach to regulation has made us addicted to big cars. All of it feels like a far cry from the humble, cheap, get-stuff-done Bolt.
If the Model 3 proved electric cars could be sexy and built at scale, the Bolt proved what traditional, legacy automakers could do if they actually took EVs seriously. It should be remembered as such, a game-changer in its own way. It’s just a shame that nothing seems poised to step up and take its place.









 Ember
Ember
 Sonnenkraft
Sonnenkraft
