You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On the rise of renewables, peak oil, and carbon capture

Current conditions: More than 10 inches of rain fell over nine hours in southwestern China • Wildfires are spreading in Canada, with at least 140 burning as of yesterday afternoon • The streets of Cape Town in South Africa are under water after severe storms caused widespread flooding.
More electricity was generated by wind and solar than by nuclear plants in the first half of 2024 for the first time ever in U.S. history, Reuters reported, citing data from energy think tank Ember. Solar and wind farms generated 401.4 terawatt hours (TWh) compared to 390.5 TWh generated from nuclear reactors, setting 2024 on pace to be the “first full year when more U.S. electricity will come from renewables than from any other form of clean power.” It’s helpful to compare these numbers to the same period last year, when nuclear generated 9% more power than solar and wind. Solar saw the greatest gains, with output 30% higher in the first half of 2024 compared to 2023; wind generation was up 10% and nuclear was up just 3.4%. Between 2018 and 2023, installed capacity grew by 168% for utility solar and 56% for wind. Meanwhile, nuclear generation capacity dropped by 4%.
In its latest energy outlook report, fossil fuel giant BP forecasts that global demand for oil will peak in 2025, and the related carbon emissions will, too. The analysis is based on current climate policies and pledges, growing efficiency standards for the internal combustion engine and a rise in electric vehicles, and rapid expansion of renewables. By 2050, oil’s share of the energy mix is predicted to fall to about 25%, and that would decrease even more, to just 10%, if nations strengthen (and follow through on) their climate pledges to better align with the Paris Agreement.
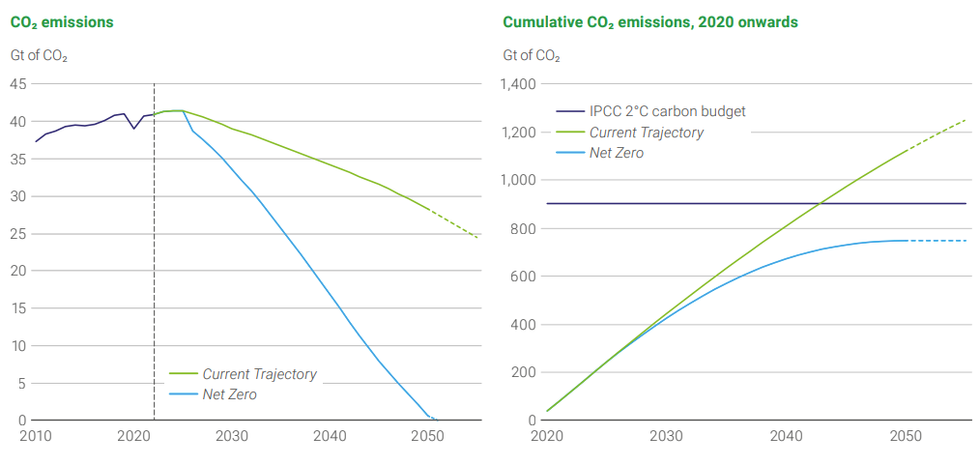
The report notes that energy demand is rising, and says the world must enter an “energy substitution” phase in which clean energy supply increases quickly to keep up while also allowing for fossil fuels to be phased out. “The longer it takes for the world to move to a rapid and sustained energy transition, the greater the risk of a costly and disorderly adjustment pathway in the future,” wrote Spencer Dale, BP’s chief economist.
More than 160 million Americans have been under excessive heat warnings this week. The heat is particularly oppressive in the West, where temperature records have been falling and heat-related deaths are rising. At least 28 people have died due to heat in the last week, and that number is expected to climb, especially as the heat wave persists into next week.
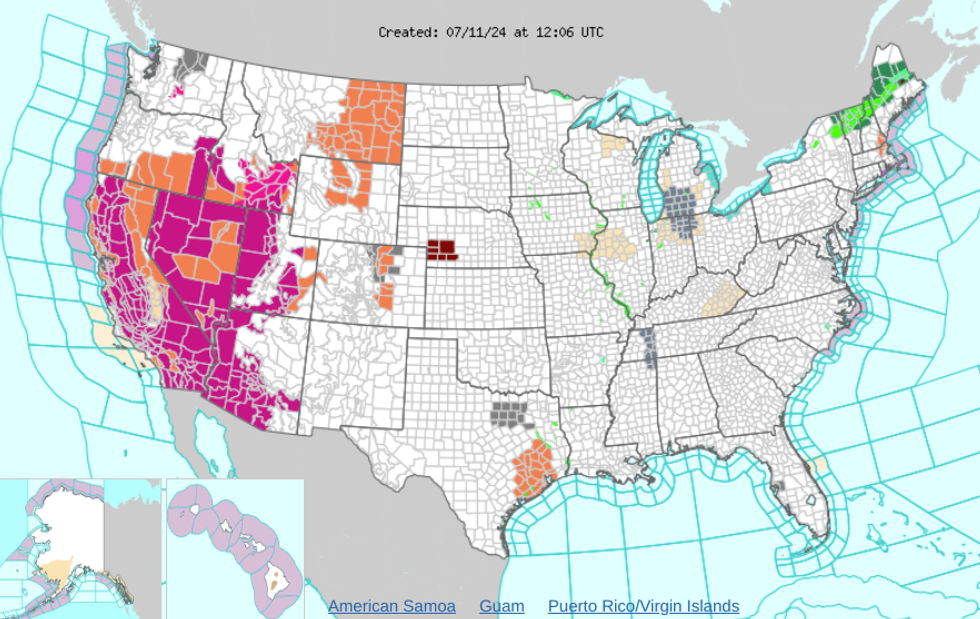
Las Vegas recorded five days a row where temperatures soared above 115 degrees Fahrenheit, breaking a record of four days set in 2005. On Sunday the city hit 120 degrees, a new record for the hottest day. It will be 118 degrees there today. “This is the most extreme heatwave in the history of record-keeping in Las Vegas since 1937,” Nevada National Weather Service meteorologist John Adair told The Associated Press. In California, the weather has been so hot that emergency rescue helicopters are struggling to fly.
Human-caused climate change is making heat waves more intense and more frequent. “While this summer is likely to be one of the hottest on record, it is important to realize that it may also be one of the coldest summers of the future,” wrote climate scientist Mathew Barlow and meteorology professor Jeffrey Basara in an essay for The Conversation.
Climate change advocacy group Evergreen Action reviewed President Biden’s record of following through on climate actions over the last four years. In 2020, the group put forward a comprehensive set of policy recommendations for Biden to use as a roadmap. The new analysis finds that the administration has “made progress” on 85% of those recommendations, including implementing new clean power policies, advancing environmental justice, the creation of the American Climate Corps, and trying to restrict liquefied natural gas exports. “The Biden-Harris administration has done more on climate than any president before,” Evergreen said. It’s worth reviewing the entire list of recommendations.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
A carbon capture company named 280 Earth has signed agreements worth $40 million to remove 61,600 tons of the greenhouse gas between now and 2030, Bloomberg reported. The company emerged from Alphabet’s moonshot factory and recently launched direct air capture operations at its plant in Oregon. The plant is located next to a Google data center and can use excess heat from that center to “improve its efficiency, while cutting the center’s cooling costs,” according to Bloomberg. The company’s website says it plans to build more facilities across the United States. It recently raised $50 million from private investors in a Series B round.
“Biden’s tremendous climate legacy rests on whether he can sell his accomplishments to the public and win the 2024 election. And that ability is faltering, to say the least.” –Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The multi-faceted investment is defense-oriented, but could also support domestic clean energy.
MP Materials is the national champion of American rare earths, and now the federal government is taking a stake.
The complex deal, announced Thursday, involves the federal government acting as a guaranteed purchaser of MP Materials’ output, a lender, and also an investor in the company. In addition, the Department of Defense agreed to a price floor for neodymium-praseodymium products of $110 per kilogram, about $50 above its current spot price.
MP Materials owns a rare earths mine and processing facility near the California-Nevada border on the edges of the Mojave National Preserve. It claims to be “the largest producer of rare earth materials in the Western Hemisphere,” with “the only rare earth mining and processing site of scale in North America.”
As part of the deal, the company will build a “10X Facility” to produce magnets, which the DOD has guaranteed will be able to sell 100% of its output to some combination of the Pentagon and commercial customers. The DOD is also kicking in $150 million worth of financing for MP Materials’ existing processing efforts in California, alongside $1 billion from Wall Street — specifically JPMorgan Chase and Goldman Sachs — for the new magnet facility. The company described the deal in total as “a multi-billion-dollar commitment to accelerate American rare earth supply chain independence.”
Finally, the DOD will buy $400 million worth of newly issued stock in MP Materials, giving it a stake in the future production that it’s also underwriting.
Between the equity investment, the lending, and the guaranteed purchasing, the Pentagon, and by extension the federal government, has taken on considerable financial risk in casting its lot with a company whose primary asset’s previous owner went bankrupt a decade ago. But at least so far, Wall Street is happy with the deal: MP Materials’ market capitalization soared to over $7 billion on Thursday after its share price jumped over 40%, from a market capitalization of around $5 billion on Wednesday and the company is valued at around $7.5 billion as of Friday afternoon.
Despite the risk, former Biden administration officials told me they would have loved to make a deal like this.
When I asked Alex Jacquez, who worked on industrial policy for the National Economic Council in the Biden White House, whether he wished he could’ve overseen something like the DOD deal with MP Materials, he replied, “100%.” I put the same question to Ashley Zumwalt-Forbes, a former Department of Energy official who is now an investor; she said, “Absolutely.”
Rare earths and critical minerals were of intense interest to the Biden administration because of their use in renewable energy and energy storage. Magnets made with neodymium-praseodymium oxide are used in the electric motors found in EVs and wind turbines, as well as for various applications in the defense industry.
MP Materials will likely have to continue to rely on both sets of customers. Building up a real domestic market for the China-dominated industry will likely require both sets of buyers. According to a Commerce Department report issued in 2022, “despite their importance to national security, defense demand for … magnets is only a small portion of overall demand and insufficient to support an economically viable domestic industry.”
The Biden administration previously awarded MP Materials $58.5 million in 2024 through the Inflation Reduction Act’s 48C Advanced Energy Project tax credit to support the construction of a magnet facility in Fort Worth. While the deal did not come with the price guarantees and advanced commitment to purchase the facility’s output of the new agreement, GM agreed to come on as an initial buyer.
Matt Sloustcher, an MP Materials spokesperson, confirmed to me that the Texas magnet facility is on track to be fully up and running by the end of this year, and that other electric vehicle manufacturers could be customers of the new facility announced on Thursday.
At the time MP Materials received that tax credit award, the federal government was putting immense resources behind electric vehicles, which bolstered the overall supply supply chain and specifically demand for components like magnets. That support is now being slashed, however, thanks to the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, which will cancel consumer-side subsidies for electric vehicle purchases.
While the Biden tax credit deal and the DOD investment have different emphases, they both follow on years of bipartisan support for MP Materials. In 2020, the DOD used its authority under the Defense Production Act to award almost $10 million to MP Materials to support its investments in mineral refining. At the time, the company had been ailing in part due to retaliatory tariffs from China, cutting off the main market for its rare earths. The company was shipping its mined product to China to be refined, processed, and then used as a component in manufacturing.
“Currently, the Company sells the vast majority of its rare earth concentrate to Shenghe Resources,” MP Materials the company said in its 2024 annual report, referring to a Chinese rare earths company.
The Biden administration continued and deepened the federal government’s relationship with MP Materials, this time complementing the defense investments with climate-related projects. In 2022, the DOD awarded a contract worth $35 million to MP Materials for its processing project in order to “enable integration of [heavy rare earth elements] products into DoD and civilian applications, ensuring downstream [heavy rare earth elements] industries have access to a reliable feedstock supplier.”
While the DOD deal does not mean MP Materials is abandoning its energy customers or focus, the company does appear to be to the new political environment. In its February earnings release, the company mentioned “automaker” or “automotive-grade magnets” four times; in its May earnings release, that fell to zero times.
Former Biden administration officials who worked on critical minerals and energy policy are still impressed.
The deal is “a big win for the U.S. rare earths supply chain and an extremely sophisticated public-private structure giving not just capital, but strategic certainty. All the right levers are here: equity, debt, price floor, and offtake. A full-stack solution to scale a startup facility against a monopoly,” Zumwalt-Forbes, the former Department of Energy official, wrote on LinkedIn.
While the U.S. has plentiful access to rare earths in the ground, Zumwalt-Forbes told me, it has “a very underdeveloped ability to take that concentrate away from mine sites and make useful materials out of them. What this deal does is it effectively bridges that gap.”
The issue with developing that “midstream” industry, Jacquez told me, is that China’s world-leading mining, processing, and refining capacity allows it to essentially crash the price of rare earths to see off foreign competitors and make future investment in non-Chinese mining or processing unprofitable. While rare earths are valuable strategically, China’s whip hand over the market makes them less financially valuable and deters investment.
“When they see a threat — and MP is a good example — they start ramping up production,” he said. Jacquez pointed to neodymium prices spiking in early 2022, right around when the Pentagon threw itself behind MP Materials’ processing efforts. At almost exactly the same time, several state-owned Chinese rare earth companies merged. Neodymium-praseodymium oxide prices fell throughout 2022 thanks to higher Chinese production quotas — and continued to fall for several years.
While the U.S. has plentiful access to rare earths in the ground, Zumwalt-Forbes told me, it has “a very underdeveloped ability to take that concentrate out away from mine sites and make useful materials out of them. What this deal does is it effectively bridges that gap.”
The combination of whipsawing prices and monopolistic Chinese capacity to process and refine rare earths makes the U.S.’s existing large rare earth reserves less commercially viable.
“In order to compete against that monopoly, the government needed to be fairly heavy handed in structuring a deal that would both get a magnet facility up and running and ensure that that magnet facility stays in operation and weathers the storm of Chinese price manipulation,” Zumwalt-Forbes said.
Beyond simply throwing money around, the federal government can also make long-term commitments that private companies and investors may not be willing or able to make.
“What this Department of Defense deal did is, yes, it provided much-needed cash. But it also gave them strategic certainty around getting that facility off the ground, which is almost more important,” Zumwalt-Forbes said.
“I think this won’t be the last creative critical mineral deal that we see coming out of the Department of Defense,” Zumwalt-Forbes added. They certainly are in pole position here, as opposed to the other agencies and prior administrations.”
On a new plan for an old site, tariffs on Canada, and the Grain Belt Express
Current conditions: Phoenix will “cool” to 108 degrees Fahrenheit today after hitting 118 degrees on Thursday, its hottest day of the year so far • An extreme wildfire warning is in place through the weekend in Scotland • University of Colorado forecasters decreased their outlook for the 2025 hurricane season to 16 named storms, eight hurricanes, and three major hurricanes after a quiet June and July.
President Trump threatened a 35% tariff on Canadian imports on Thursday, giving Prime Minister Mark Carney a deadline of August 1 before the levies would go into effect. The move follows months of on-again, off-again threats against Canada, with former Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau having successfully staved off the tariffs during talks in February. Despite those earlier negotiations, Trump held firm on his 50% tariff on steel and aluminum, which will have significant implications for green manufacturing.
As my colleagues Matthew Zeitlin and Robinson Meyer have written, tariffs on Canadian imports will affect the flow of oil, minerals, and lumber, as well as possibly break automobile supply chains in the United States. It was unclear as of Thursday, however, whether Trump’s tariffs “would affect all Canadian goods, or if he would follow through,” The New York Times reports. The move follows Trump’s announcement this week of tariffs on several other significant trade partners like Japan and South Korea, as well as a 50% tariff on copper.
The long beleaguered Lava Ridge Wind Project, formally halted earlier this year by an executive order from President Trump, might have a second life as the site for small modular reactors, Idaho News 6 reports. Sawtooth Energy Development Corporation has proposed installing six small nuclear power generators on the former Lava Ridge grounds in Jerome County, Idaho, drawn to the site by the power transmission infrastructure that could connect the region to the Midpoint Substation and onto the rest of the Western U.S. The proposed SMR project would be significantly smaller in scale than Lava Ridge, which would have produced 1,000 megawatts of electricity on a 200,000-acre footprint, sitting instead on 40 acres and generating 462 megawatts, enough to power 400,000 homes.
Sawtooth Energy plans to hold four public meetings on the proposal beginning July 21. The Lava Ridge Wind Project had faced strong local opposition — we named it the No. 1 most at-risk project of the energy transition last fall — due in part to concerns about the visibility of the turbines from the Minidoka National Historic Site, the site of a Japanese internment camp.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
Republican Senator Josh Hawley of Missouri said on social media Thursday that Energy Secretary Chris Wright had assured him that he will be “putting a stop to the Grain Belt Express green scam.” The Grain Belt Express is an 804-mile-long, $11 billion planned transmission line that would connect wind farms in Kansas to energy consumers in Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana, which has been nearing construction after “more than a decade of delays,” The New York Times reports. But earlier this month, Missouri Attorney General Andrew Bailey, a Republican, put in a request for the local public service commission to reconsider its approval, claiming that the project had overstated the number of jobs it would create and the cost savings for customers. Hawley has also been a vocal critic of the project and had asked the Energy Department to cancel its conditional loan guarantee for the transmission project.
New electric vehicles sold in Europe are significantly more environmentally friendly than gas cars, even when battery production is taken into consideration, according to a new study by the International Council on Clean Transportation. Per the report, EVs produce 73% less life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions than combustion engine cars, even considering production — a 24% improvement over 2021 estimates. The gains are also owed to the large share of renewable energy sources in Europe, and factor in that “cars sold today typically remain on the road for about 20 years, [and] continued improvement of the electricity mix will only widen the climate benefits of battery electric cars.” The gains are exclusive to battery electric cars, however; “other powertrains, including hybrids and plug-in hybrids, show only marginal or no progress in reducing their climate impacts,” the report found.

With the United Kingdom staring down its third heatwave in a month this week, a new study warns of dire consequences if homes and cities do not adapt to the new climate reality. According to researchers at the University College London and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, heat-related deaths in England and Wales could rise 50-fold by the 2070s, jumping from a baseline of 634 deaths to 34,027 in a worst-case scenario of 4.3 degrees Celsius warming, a high-emissions pathway.
The report specifically cited the aging populations of England and Wales, as older people become more vulnerable to the impacts of extreme heat. Low adoption of air conditioning is also a factor: only 2% to 5% of English households use air conditioning, although that number may grow to 32% by 2050. “We can mitigate [the] severity” of the health impacts of heat “by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and with carefully planned adaptations, but we have to start now,” UCL researcher Clare Heaviside told Sky News.
This week, Centerville, Ohio, rolled out high-tech recycling trucks that will use AI to scan the contents of residents’ bins and flag when items have been improperly sorted. “Reducing contamination in our recycling system lowers processing costs and improves the overall efficiency of our collection,” City Manager Wayne Davis said in a statement about the AI pilot program, per the Dayton Daily News.
Or at least the team at Emerald AI is going to try.
Everyone’s worried about the ravenous energy needs of AI data centers, which the International Energy Agency projects will help catalyze nearly 4% growth in global electricity demand this year and next, hitting the U.S. power sector particularly hard. On Monday, the Department of Energy released a report adding fuel to that fire, warning that blackouts in the U.S. could become 100 times more common by 2030 in large part due to data centers for AI.
The report stirred controversy among clean energy advocates, who cast doubt on that topline number and thus the paper’s justification for a significant fossil fuel buildout. But no matter how the AI revolution is powered, there’s widespread agreement that it’s going to require major infrastructure development of some form or another.
Not so fast, says Emerald AI, which emerged from stealth last week with $24.5 million in seed funding led by Radical Ventures along with a slew of other big name backers, including Nvidia’s venture arm as well as former Secretary of State John Kerry, Google’s chief scientist Jeff Dean, and Kleiner Perkins chair John Doerr. The startup, founded and led by Orsted’s former chief strategy and innovation officer Varun Sivaram, was built to turn data centers from “grid liabilities into flexible assets” by slowing, pausing, or redirecting AI workloads during times of peak energy demand.
Research shows this type of data center load flexibility could unleash nearly 100 gigawatts of grid capacity — the equivalent of four or five Project Stargates and enough to power about 83 million U.S. homes for a year. Such adjustments, Sivaram told me, would be necessary for only about 0.5% of a data center’s total operating time, a fragment so tiny that he says it renders any resulting training or operating performance dips for AI models essentially negligible.
As impressive as that hypothetical potential is, whether a software product can actually reduce the pressures facing the grid is a high stakes question. The U.S. urgently needs enough energy to serve that data center growth, both to ensure its economic competitiveness and to keep electricity bills affordable for Americans. If an algorithm could help alleviate even some of the urgency of an unprecedented buildout of power plants and transmission infrastructure, well, that’d be a big deal.
While Emerald AI will by no means negate the need to expand and upgrade our energy system, Sivaram told me, the software alone “materially changes the build out needs to meet massive demand expansion,” he said. “It unleashes energy abundance using our existing system.”
Grand as that sounds, the fundamental idea is nothing new. It’s the same concept as a virtual power plant, which coordinates distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar panels, smart thermostats, and electric vehicles to ramp energy supply either up or down in accordance with the grid’s needs.
Adoption of VPPs has lagged far behind their technical potential, however. That’s due to a whole host of policy, regulatory, and market barriers such as a lack of state and utility-level rules around payment structures, insufficient participation incentives for customers and utilities, and limited access to wholesale electricity markets. These programs also depend on widespread customer opt-in to make a real impact on the grid.
“It’s really hard to aggregate enough Nest thermostats to make any kind of dent,”” Sivaram told me. Data centers are different, he said, simply because “they’re enormous, they’re a small city.” They’re also, by nature, virtually controllable and often already interconnected if they’re owned by the same company. Sivaram thinks the potential of flexible data center loads is so promising and the assets themselves so valuable that governments and utilities will opt to organize “bespoke arrangements for data centers to provide their services.”
Sivaram told me he’s also optimistic that utilities will offer data center operators with flexible loads the option to skip the ever-growing interconnection queue, helping hyperscalers get online and turn a profit more quickly.
The potential to jump the queue is not something that utilities have formally advertised as an option, however, although there appears to be growing interest in the idea. An incentive like this will be core to making Emerald AI’s business case work, transmission advocate and president of Grid Strategies Rob Gramlich told me.
Data center developers are spending billions every year on the semiconductor chips powering their AI models, so the typical demand response value proposition — earn a small sum by turning off appliances when the grid is strained — doesn’t apply here. “There’s just not anywhere near enough money in that for a hyperscaler to say, Oh yeah, I’m gonna not run my Nvidia chips for a while to make $200 a megawatt hour. That’s peanuts compared to the bazillions [they] just spent,” Gramlich explained.
For Emerald AI to make a real dent in energy supply and blunt the need for an immediate and enormous grid buildout, a significant number of data center operators will have to adopt the platform. That’s where the partnership with Nvidia comes in handy, Sivaram told me, as the startup is “working with them on the reference architecture” for future AI data centers. “The goal is for all [data centers] to be potentially flexible in the future because there will be a standard reference design,” Sivaram said.
Whether or not data centers will go all in on Nvidia’s design remains to be seen, of course. Hyperscalers have not typically thought of data centers as a flexible asset. Right now, Gramlich said, most are still in the mindset that they need to be operating all 8,760 hours of the year to reach their performance targets.
“Two or three years ago, when we first noticed the surge in AI-driven demand, I talked to every hyperscaler about how flexible they thought they could be, because it seemed intuitive that machine learning might be more flexible than search and streaming,” Gramlich told me. By and large, the response was that while these companies might be interested in exploring flexibility “potentially, maybe, someday,” they were mostly focused on their mandate to get huge amounts of gigawatts online, with little time to explore new data center models.
“Even the ones that are talking about flexibility now, in terms of what they’re actually doing in the market today, they all are demanding 8,760 [hours of operation per year],” Gramlich told me.
Emerald AI is well aware that its business depends on proving to hyperscalers that a degree of flexibility won’t materially impact their operations. Last week, the startup released the results of a pilot demonstration that it ran at an Oracle data center in Phoenix, which proved it was able to reduce power consumption by 25% for three hours during a period of grid stress while still “assuring acceptable customer performance for AI workloads.”
It achieved this by categorizing specific AI tasks — think everything from model training and fine tuning to conversations with chatbots — from high to low priority, indicating the degree to which operations could be slowed while still meeting Oracle’s performance targets. Now, Emerald AI is planning additional, larger-scale demonstrations to showcase its capacity to handle more complex scenarios, such as responding to unexpected grid emergencies.
As transmission planners and hyperscalers alike wait to see more proof validating Emerald AI’s vision of the future, Sivaram is careful to note that his company is not advocating for a halt to energy system expansion. In an increasingly electrified economy, expanding and upgrading the grid will be essential — even if every data center in the world has a flexible load profile.
’We should be building a nationwide transmission system. We should be building out generation. We should be doing grid modernization with grid enhancing technologies,” Sivaram told me. “We just don’t need to overdo it. We don’t need the particularly massive projections that you’re seeing that are going to cause your grandmother’s electricity rates to spike. We can avoid that.”