You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On the new PFAS rules, firefighters, and Tesla’s brand loyalty

Current conditions: More than 100,000 people have been evacuated in Kazakhstan and Russia due to the worst flooding in decades • The U.K. is expecting a “mini heatwave” • Multiple tornado warnings have been issued in southern Louisiana.
In an “extraordinary” move, the Environmental Protection Agency today announced limits on “forever chemicals” in drinking water. The rule means municipal water systems will have to monitor for six types of PFAS chemicals and remove them. “This is historic and monumental,” Emily Donovan, co-founder of advocacy group Clean Cape Fear, told NPR. “I didn’t think [the EPA] would ever do it.”
There are more than 12,000 known PFAS, and they are just about everywhere, including in nearly half the tap water in the U.S. PFAS exposure in humans has been linked to health problems including decreased fertility, developmental delays, metabolic disorders, and increased risk of some cancers. Utilities have five years to comply with the rule, which will cost them about $1.5 billion annually. Some money from the bipartisan infrastructure law will go toward helping states with rolling out the monitoring and filtration systems.
If you are wondering what any of this has to do with climate change, note that “these synthetic organic chemicals are typically fossil fuel derivatives,” Elsie Sunderland, an environmental chemist at Harvard, explained to Vox. “We talk about climate change and chemical exposure as two separate issues, but we should start thinking about them together. As we move away from fossil fuel combustion and towards renewable energy, the industry is going to turn their products into plastics and synthetic chemicals.”
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
Scientists have been digesting yesterday’s report from the European Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), which said that last month was the warmest March ever recorded and that temperatures have been at record highs for 10 months straight. The bleak data has some researchers worried the rate of warming is increasing and that we’re in “uncharted territory.” It’s worth compiling some of their thoughts here:
Not all experts agree the rate of warming has increased. “The world is warming AS FAST as we predicted,” said climate scientist Michael E. Mann, “and that’s bad enough.”
America’s federal wildfire officials are changing how they recruit, hire, and assign firefighting crews in response to growing wildfire threats, according toThe Associated Press. The change is “the biggest shift in wildfire management in decades.” It involves creating more leadership teams – the top-level crewmembers who take on the biggest and most complex fires – and recruiting a lot of new wildland firefighters. The Forest Service aims to hire around 11,300 firefighters this year, AP reports. While in the past many firefighting jobs were seasonal, a longer season calls for more permanent positions. Fire season is already underway. More than 2,669 square miles burned in the first three months of 2024, more than half of last year’s total.
There are more electric vehicles coming onto the American market every year, but Tesla owners can’t be lured away. A recent survey from Bloomberg Intelligence finds 87% of Tesla drivers in the U.S. say they’ll stick with the brand for their next vehicle purchase, the highest retention rate among the brands in the survey. The second-highest was for Lexus at 68%, followed by 54% for Toyota. At the bottom end was Kia at 33%. About 81% of potential Tesla drivers are switching from other EV brands. Overall, the survey found that 42% of respondents were thinking of buying an EV for their next car.
The Biden administration yesterday issued its final rule limiting dangerous air pollution from chemical plants. The new EPA regulations will require more than 200 plants to reduce emissions of several toxic chemicals, but focus heavily on two in particular that are very likely carcinogenic: ethylene oxide (used as a sterilizer) and chloroprene (used to make rubber). Manufacturers will now have to monitor their operations for emissions of these two substances and stop any leaks they find. They’ll also have to submit quarterly data from their monitoring efforts, which will be made public, The New York Timesreported. The rule is expected to reduce ethylene oxide and chloroprene emissions by 80%, and cut more than 6,200 tons of toxic air pollution every year, “dramatically reducing the number of people with elevated cancer risk,” the EPA said.
Coal power could account for less than 10% of the total U.S. electricity mix in the coming weeks, a record low.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Give the people what they want — big, family-friendly EVs.
The star of this year’s Los Angeles Auto Show was the Hyundai Ioniq 9, a rounded-off colossus of an EV that puts Hyundai’s signature EV styling on a three-row SUV cavernous enough to carry seven.
I was reminded of two years ago, when Hyundai stole the L.A. show with a different EV: The reveal of Ioniq 6, its “streamliner” aerodynamic sedan that looked like nothing else on the market. By comparison, Ioniq 9 is a little more banal. It’s a crucial vehicle that will occupy the large end of Hyundai's excellent and growing lineup of electric cars, and one that may sell in impressive numbers to large families that want to go electric. Even with all the sleek touches, though, it’s not quite interesting. But it is big, and at this moment in electric vehicles, big is what’s in.
The L.A. show is one the major events on the yearly circuit of car shows, where the car companies traditionally reveal new models for the media and show off their whole lineups of vehicles for the public. Given that California is the EV capital of America, carmakers like to talk up their electric models here.
Hyundai’s brand partner, Kia, debuted a GT performance version of its EV9, adding more horsepower and flashy racing touches to a giant family SUV. Jeep reminded everyone of its upcoming forays into full-size and premium electric SUVs in the form of the Recon and the Wagoneer S. VW trumpeted the ID.Buzz, the long-promised electrified take on the classic VW Microbus that has finally gone on sale in America. The VW is the quirkiest of the lot, but it’s a design we’ve known about since 2017, when the concept version was revealed.
Boring isn’t the worst thing in the world. It can be a sign of a maturing industry. At auto shows of old, long before this current EV revolution, car companies would bring exotic, sci-fi concept cars to dial up the intrigue compared to the bread-and-butter, conservatively styled vehicles that actually made them gobs of money. During the early EV years, electrics were the shiny thing to show off at the car show. Now, something of the old dynamic has come to the electric sector.
Acura and Chrysler brought wild concepts to Los Angeles that were meant to signify the direction of their EVs to come. But most of the EVs in production looked far more familiar. Beyond the new hulking models from Hyundai and Kia, much of what’s on offer includes long-standing models, but in EV (Chevy Equinox and Blazer) or plug-in hybrid (Jeep Grand Cherokee and Wrangler) configurations. One of the most “interesting” EVs on the show floor was the Cybertruck, which sat quietly in a barely-staffed display of Tesla vehicles. (Elon Musk reveals his projects at separate Tesla events, a strategy more carmakers have begun to steal as a way to avoid sharing the spotlight at a car show.)
The other reason boring isn’t bad: It’s what the people want. The majority of drivers don’t buy an exotic, fun vehicle. They buy a handsome, spacious car they can afford. That last part, of course, is where the problem kicks in.
We don’t yet know the price of the Ioniq 9, but it’s likely to be in the neighborhood of Kia’s three-row electric, the EV9, which starts in the mid-$50,000s and can rise steeply from there. Stellantis’ forthcoming push into the EV market will start with not only pricey premium Jeep SUVs, but also some fun, though relatively expensive, vehicles like the heralded Ramcharger extended-range EV truck and the Dodge Charger Daytona, an attempt to apply machismo-oozing, alpha-male muscle-car marketing to an electric vehicle.
You can see the rationale. It costs a lot to build a battery big enough to power a big EV, so they’re going to be priced higher. Helpfully for the car brands, Americans have proven they will pay a premium for size and power. That’s not to say we’re entering an era of nothing but bloated EV battleships. Models such as the overpowered electric Dodge Charger and Kia EV9 GT will reveal the appetite for performance EVs. Smaller models like the revived Chevy Bolt and Kia’s EV3, already on sale overseas, are coming to America, tax credit or not.
The question for the legacy car companies is where to go from here. It takes years to bring a vehicle from idea to production, so the models on offer today were conceived in a time when big federal support for EVs was in place to buoy the industry through its transition. Now, though, the automakers have some clear uncertainty about what to say.
Chevy, having revealed new electrics like the Equinox EV elsewhere, did not hold a media conference at the L.A. show. Ford, which is having a hellacious time losing money on its EVs, used its time to talk up combustion vehicles including a new version of the palatial Expedition, one of the oversized gas-guzzlers that defined the first SUV craze of the 1990s.
If it’s true that the death of federal subsidies will send EV sales into a slump, we may see messaging from Detroit and elsewhere that feels decidedly retro, with very profitable combustion front-and-center and the all-electric future suddenly less of a talking point. Whatever happens at the federal level, EVs aren’t going away. But as they become a core part of the car business, they are going to get less exciting.
Current conditions: Parts of southwest France that were freezing last week are now experiencing record high temperatures • Forecasters are monitoring a storm system that could become Australia’s first named tropical cyclone of this season • The Colorado Rockies could get several feet of snow today and tomorrow.
This year’s Atlantic hurricane season caused an estimated $500 billion in damage and economic losses, according to AccuWeather. “For perspective, this would equate to nearly 2% of the nation’s gross domestic product,” said AccuWeather Chief Meteorologist Jon Porter. The figure accounts for long-term economic impacts including job losses, medical costs, drops in tourism, and recovery expenses. “The combination of extremely warm water temperatures, a shift toward a La Niña pattern and favorable conditions for development created the perfect storm for what AccuWeather experts called ‘a supercharged hurricane season,’” said AccuWeather lead hurricane expert Alex DaSilva. “This was an exceptionally powerful and destructive year for hurricanes in America, despite an unusual and historic lull during the climatological peak of the season.”
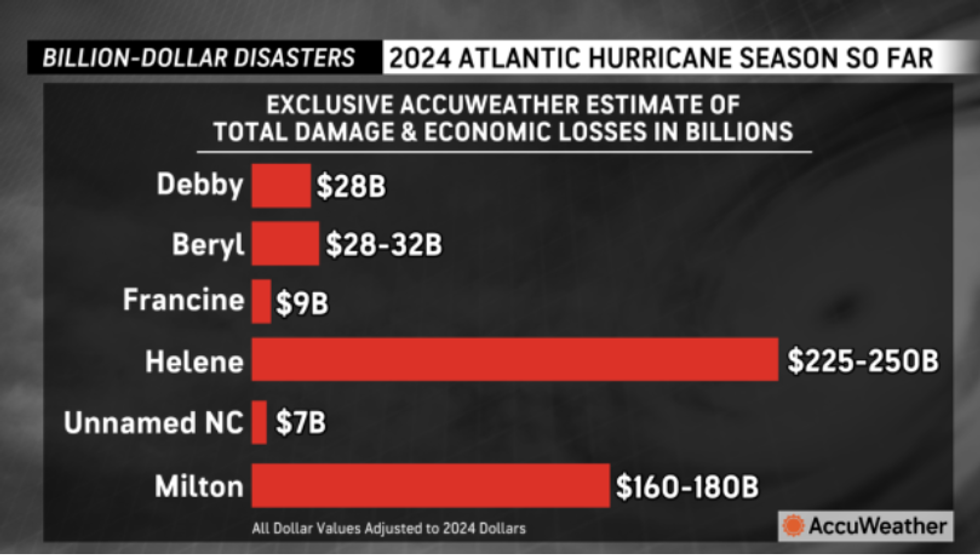
This year’s hurricane season produced 18 named storms and 11 hurricanes. Five hurricanes made landfall, two of which were major storms. According to NOAA, an “average” season produces 14 named storms, seven hurricanes, and three major hurricanes. The season comes to an end on November 30.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom announced yesterday that if President-elect Donald Trump scraps the $7,500 EV tax credit, California will consider reviving its Clean Vehicle Rebate Program. The CVRP ran from 2010 to 2023 and helped fund nearly 600,000 EV purchases by offering rebates that started at $5,000 and increased to $7,500. But the program as it is now would exclude Tesla’s vehicles, because it is aimed at encouraging market competition, and Tesla already has a large share of the California market. Tesla CEO Elon Musk, who has cozied up to Trump, called California’s potential exclusion of Tesla “insane,” though he has said he’s okay with Trump nixing the federal subsidies. Newsom would need to go through the State Legislature to revive the program.
President-elect Donald Trump said yesterday he would impose steep new tariffs on all goods imported from China, Canada, and Mexico on day one of his presidency in a bid to stop “drugs” and “illegal aliens” from entering the United States. Specifically, Trump threatened Canada and Mexico each with a 25% tariff, and China with a 10% hike on existing levies. Such moves against three key U.S. trade partners would have major ramifications across many sectors, including the auto industry. Many car companies import vehicles and parts from plants in Mexico. The Canadian government responded with a statement reminding everyone that “Canada is essential to U.S. domestic energy supply, and last year 60% of U.S. crude oil imports originated in Canada.” Tariffs would be paid by U.S. companies buying the imported goods, and those costs would likely trickle down to consumers.
Amazon workers across the world plan to begin striking and protesting on Black Friday “to demand justice, fairness, and accountability” from the online retail giant. The protests are organized by the UNI Global Union’s Make Amazon Pay Campaign, which calls for better working conditions for employees and a commitment to “real environmental sustainability.” Workers in more than 20 countries including the U.S. are expected to join the protests, which will continue through Cyber Monday. Amazon’s carbon emissions last year totalled 68.8 million metric tons. That’s about 3% below 2022 levels, but more than 30% above 2019 levels.
Researchers from MIT have developed an AI tool called the “Earth Intelligence Engine” that can simulate realistic satellite images to show people what an area would look like if flooded by extreme weather. “Visualizing the potential impacts of a hurricane on people’s homes before it hits can help residents prepare and decide whether to evacuate,” wrote Jennifer Chu at MIT News. The team found that AI alone tended to “hallucinate,” generating images of flooding in areas that aren’t actually susceptible to a deluge. But when combined with a science-backed flood model, the tool became more accurate. “One of the biggest challenges is encouraging people to evacuate when they are at risk,” said MIT’s Björn Lütjens, who led the research. “Maybe this could be another visualization to help increase that readiness.” The tool is still in development and is available online. Here is an image it generated of flooding in Texas:

A new installation at the Centre Pompidou in Paris lets visitors listen to the sounds of endangered and extinct animals – along with the voice of the artist behind the piece, the one and only Björk.
How Hurricane Helene is still putting the Southeast at risk.
Less than two months after Hurricane Helene cut a historically devastating course up into the southeastern U.S. from Florida’s Big Bend, drenching a wide swath of states with 20 trillion gallons of rainfall in just five days, experts are warning of another potential threat. The National Interagency Fire Center’s forecast of fire-risk conditions for the coming months has the footprint of Helene highlighted in red, with the heightened concern stretching into the new year.
While the flip from intense precipitation to wildfire warnings might seem strange, experts say it speaks to the weather whiplash we’re now seeing regularly. “What we expect from climate change is this layering of weather extremes creating really dangerous situations,” Robert Scheller, a professor of forestry and environmental resources at North Carolina State University, explained to me.
Scheuller said North Carolina had been experiencing drought conditions early in the year, followed by intense rain leading up to Helene’s landfall. Then it went dry again — according to the U.S. Drought Monitor, much of the state was back to some level of drought condition as of mid-November. The NIFC forecast report says the same is true for much of the region, including Florida, despite its having been hit by Hurricane Milton soon after Helene.
That dryness is a particular concern due to the amount of debris left in Helene’s wake — another major risk factor for fire. The storm’s winds, which reached more than 100 miles per hour in some areas, wreaked havoc on millions of acres of forested land. In North Carolina alone, the state’s Forest Service estimates over 820,000 acres of timberland were damaged.
“When you have a catastrophic storm like [Helene], all of the stuff that was standing upright — your trees — they might be snapped off or blown over,” fire ecologist David Godwin told me. “All of a sudden, that material is now on the forest floor, and so you have a really tremendous rearrangement of the fuels and the vegetation within ecosystems that can change the dynamics of how fire behaves in those sites.”
Godwin is the director of the Southern Fire Exchange for the University of Florida, a program that connects wildland firefighters, prescribed burners, and natural resources managers across the Southeast with fire science and tools. He says the Southeast sees frequent, unplanned fires, but that active ecosystem management helps keep the fires that do spark from becoming conflagrations. But an increase like this in fallen or dead vegetation — what Godwin refers to as fire “fuel” — can take this risk to the next level, particularly as it dries out.
Godwin offered an example from another storm, 2018’s Hurricane Michael, which rapidly intensified before making landfall in Northern Florida and continuing inland, similar to Hurricane Helene. In its aftermath, there was a 10-fold increase in the amount of fuel on the ground, with 72 million tons of timber damaged in Florida. Three years later, the Bertha Swamp Road Fire filled the storm’s Florida footprint with flames, which consumed more than 30,000 acres filled with dried out forest fuel. One Florida official called the wildfire the “ghost” of Michael, nodding to the overlap of the impacted areas and speaking to the environmental threat the storm posed even years later.
Not only does this fuel increase the risk of fire, it changes the character of the fires that do ignite, Godwin said. Given ample ground fuel, flame lengths can grow longer, allowing them to burn higher into the canopy. That’s why people setting prescribed fires will take steps like raking leaf piles, which helps keep the fire intensity low.
These fires can also produce more smoke, Godwin said, which can mix with the mountainous fog in the region to deadly effect. According to the NIFC, mountainous areas incurred the most damage from Helene, not only due to downed vegetation, but also because of “washed out roads and trails” and “slope destabilization” from the winds and rain. If there is a fire in these areas, all these factors will also make it more challenging for firefighters to address it, the report adds.
In addition to the natural debris fire experts worry about, Helene caused extensive damage to the built environment, wrecking homes, businesses, and other infrastructure. Try imagining four-and-a-half football fields stacked 10 feet tall with debris — that’s what officials have removed so far just in Asheville, North Carolina. In Florida’s Treasure Island, there were piles 50 feet high of assorted scrap materials. Officials have warned that some common household items, such as the lithium-ion batteries used in e-bikes and electric vehicles, can be particularly flammable after exposure to floodwaters. They are also advising against burning debris as a means of managing it due to all the compounding risks.
Larry Pierson, deputy chief of the Swannanoa Fire Department in North Carolina, told Blueridge Public Radio that his department’s work has “grown exponentially since the storm.” While cooler, wetter winter weather could offer some relief, Scheuller said the area will likely see heightened fire behavior for years after the storm, particularly if the swings between particularly wet and particularly dry periods continue.
Part of the challenge moving forward, then, is to find ways to mitigate risk on this now-hazardous terrain. For homeowners, that might mean exercising caution when dealing with debris and considering wildfire risk as part of rebuilding plans, particularly in more wooded areas. On a larger forest management scale, this means prioritizing safe debris collection and finding ways to continue the practice of prescribed burns, which are utilized more in the Southeast than in any other U.S. region. Without focused mitigation efforts, Godwin told me the area’s overall fire outlook would be much different.
“We would have a really big wildfire issue,” he said, “perhaps even bigger than what we might see in parts of the West.”