You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On NYC Climate Week, a brewing storm, and net zero targets

Current conditions: One of South Africa’s busiest highways has reopened after an unusual heavy snowfall • The streets of Cannes turned to rivers as heavy rains swept through southeast France • It will be about 70 degrees Fahrenheit and cloudy in New York City for most of Climate Week.
Climate Week kicked off in New York City yesterday. The event, which corresponds with the 79th United Nations General Assembly, is expected to draw some 100,000 people – including entrepreneurs, financiers, CEOs, diplomats, scientists, and creatives – to discuss climate solutions. More than 900 events are planned all over the city. Climate Week has become “the unofficial climate summit of the year,” as Bloomberg put it, not just because of its size, but also because of the low expectations going into November’s U.N. COP29 climate summit in Azerbaijan (expected to draw just 40,000 people). Climate Week organizers told The Wall Street Journal they’d seen more than 1,350 people apply to speak this year, up from 650 last year. Here’s this year’s official agenda. The event runs through September 29.
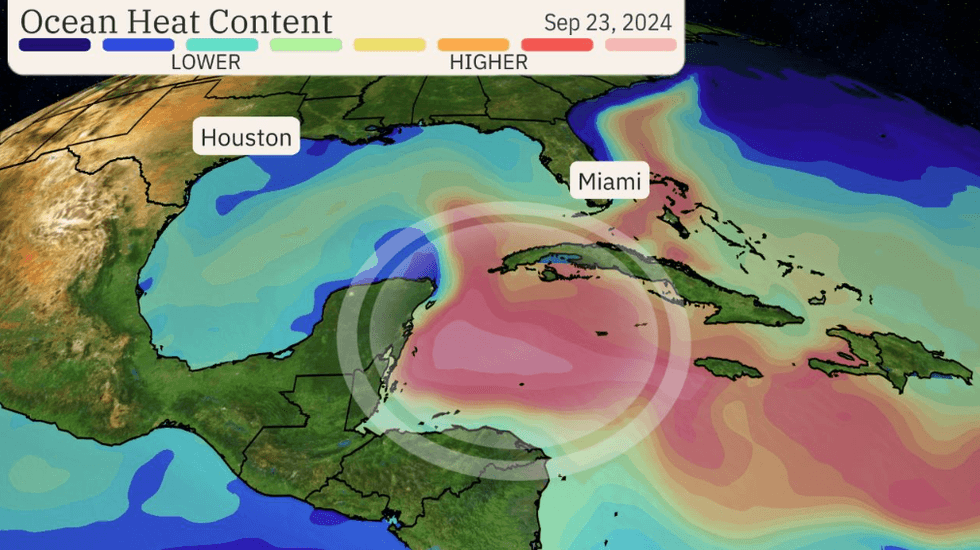
Forecasters are warning people in Florida’s Panhandle and along the eastern Gulf coast to prepare for a hurricane as a storm churns through the unusually warm Caribbean waters. It is expected to strengthen into Tropical Storm Helene today or tomorrow, and then become a hurricane Wednesday before making landfall Thursday. “Helene could become a formidably strong hurricane in the Gulf,” according to The Weather Channel. “That’s because heat content is one favorable ingredient for intensification, and the map below shows there is plenty of deep, warm water in the northwest Caribbean and parts of the Gulf of Mexico.”
The Republican-led House of Representatives on Friday passed a bill that aims to block new emissions standards for light-duty and medium vehicles that were put in place by the Environmental Protection Agency in March. The vote was 215 to 191, with eight Democrats joining 207 Republicans in support. But the bill is very unlikely to get past the Senate, and will face a veto if it somehow makes it to President Biden’s desk. The EPA estimates that the rules could see EVs make up anywhere between 30% and 56% of new light-duty sales from model years 2030 to 2032, and avoid more than 7 billion tons of carbon dioxide emissions and provide nearly $100 billion of annual net benefits to society by improving public health, and reducing fuel and maintenance costs for drivers.
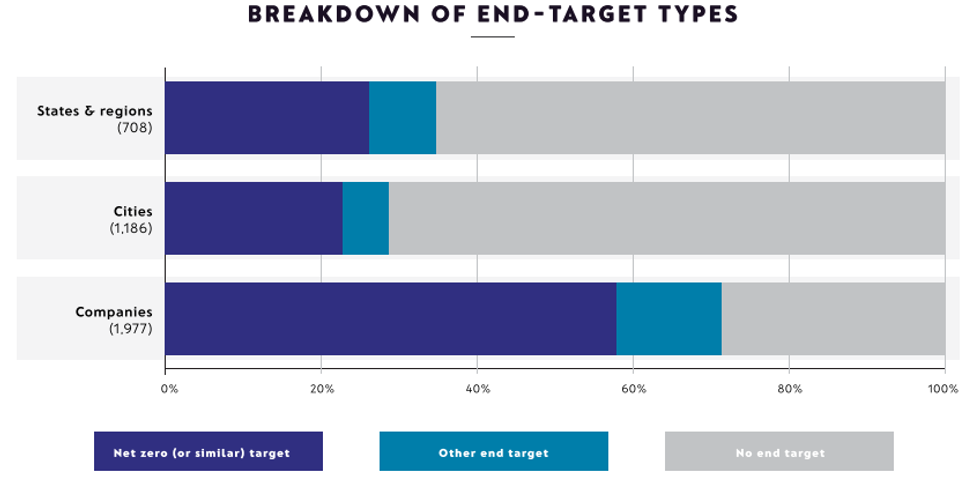
More than 40% of “non-state entities” – that is, major companies, regions, and cities – do not have targets in place for curbing greenhouse gas emissions, according to a new report from Net Zero Tracker. The group’s annual stocktake examines net zero targets “across all countries, states, regions in the largest 25-emitting countries in the world, all cities with more than 500,000 inhabitants, and the largest 2,000 publicly listed companies in the world.” It found that, while more net zero targets are being made, many of these fall short on integrity measures, like providing clarity on the use of offsets, covering all emissions scopes, annual progress reporting, and having a published implementation plan. Among the major companies that do not yet have a mitigation target are Tesla, Nintendo, and Berkshire Hathaway.
Police arrested a California firefighter on Friday suspected of igniting five brush fires while off duty over the last month or so. Robert Matthew Hernandez, a 38-year-old CAL FIRE fire apparatus engineer, is under investigation in connection with the Alexander Fire, the Windsor River Road Fire, the Geysers Fire, and the Geyser and Kinley fires. Luckily the blazes combined only burned through less than an acre, CAL FIRE said. But the strange development comes as the state’s firefighters have been battling fires that have charred almost a million acres, fueled by high temperatures and dry vegetation. “I am appalled to learn one of our employees would violate the public’s trust and attempt to tarnish the tireless work of the 12,000 women and men of CAL FIRE,” Joe Tyler, the agency’s director and fire chief, said in a statement. Some of this year’s biggest fires in the state have been linked to arson.
There were just 1,228 mentions of “climate change” in the nearly 200,000 hours of unscripted TV that aired in the U.S. in the six months between September 2022 and February 2023. Fifty-eight of those mentions were on “paranormal/mystery” programs.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Rob talks with McMaster University engineering professor Greig Mordue, then checks in with Heatmap contributor Andrew Moseman on the EVs to watch out for.
It’s been a huge few weeks for the electric vehicle industry — at least in North America.
After a major trade deal, Canada is set to import tens of thousands of new electric vehicles from China every year, and it could soon invite a Chinese automaker to build a domestic factory. General Motors has also already killed the Chevrolet Bolt, one of the most anticipated EV releases of 2026.
How big a deal is the China-Canada EV trade deal, really? Will we see BYD and Xiaomi cars in Toronto and Vancouver (and Detroit and Seattle) any time soon — or is the trade deal better for Western brands like Volkswagen or Tesla which have Chinese factories but a Canadian presence? On this week’s Shift Key, Rob talks to Greig Mordue, a former Toyota executive who is now an engineering professor at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, about how the deal could shake out. Then he chats with Heatmap contributor Andrew Moseman about why the Bolt died — and the most exciting EVs we could see in 2026 anyway.
Shift Key is hosted by Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap, and Jesse Jenkins, a professor of energy systems engineering at Princeton University. Jesse is off this week.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from our conversation:
Robinson Meyer: Over the weekend there was a new tariff threat from President Trump — he seems to like to do this on Saturday when there are no futures markets open — a new tariff threat on Canada. It is kind of interesting because he initially said that he thought if Canada could make a deal with China, they should, and he thought that was good. Then over the weekend, he said that it was actually bad that Canada had made some free trade, quote-unquote, deal with China.
Do you think that these tariff threats will affect any Carney actions going forward? Is this already priced in, slash is this exactly why Carney has reached out to China in the first place?
Greig Mordue: I think it all comes under the headline of “deep sigh,” and we’ll see where this goes. But for the first 12 months of the U.S. administration, and the threat of tariffs, and the pullback, and the new threat, and this going forward, the public policy or industrial policy response from the government of Canada and the province of Ontario, where automobiles are built in this country, was to tread lightly. And tread lightly, generally means do nothing, and by doing nothing stop the challenges.
And so doing nothing led to Stellantis shutting down an assembly plant in Brampton, Ontario; General Motors shutting an assembly plant in Ingersoll, Ontario; General Motors reducing a three-shift operation in Oshawa, Ontario to two shifts; and Ford ragging the puck — Canadian term — on the launch of a new product in their Oakville, Ontario plant. So doing nothing didn’t really help Canada from a public policy perspective.
So they’re moving forward on two fronts: One is the resetting of relationships with China and the hope of some production from Chinese manufacturers. And two, the promise of automotive industrial policy in February, or at some point this spring. So we’ll see where that goes — and that may cause some more restless nights from the U.S. administration. We’ll see.
Mentioned:
Canada’s new "strategic partnership” with China
The Chevy Bolt Is Already Dead. Again.
The EVs Everyone Will Be Talking About in 2026
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by …
Heatmap Pro brings all of our research, reporting, and insights down to the local level. The software platform tracks all local opposition to clean energy and data centers, forecasts community sentiment, and guides data-driven engagement campaigns. Book a demo today to see the premier intelligence platform for project permitting and community engagement.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.
A federal judge in Massachusetts ruled that construction on Vineyard Wind could proceed.
The Vineyard Wind offshore wind project can continue construction while the company’s lawsuit challenging the Trump administration’s stop work order proceeds, judge Brian E. Murphy for the District of Massachusetts ruled on Tuesday.
That makes four offshore wind farms that have now won preliminary injunctions against Trump’s freeze on the industry. Dominion Energy’s Coastal Virginia offshore wind project, Orsted’s Revolution Wind off the coast of New England, and Equinor’s Empire Wind near Long Island, New York, have all been allowed to proceed with construction while their individual legal challenges to the stop work order play out.
The Department of the Interior attempted to pause all offshore wind construction in December, citing unspecified “national security risks identified by the Department of War.” The risks are apparently detailed in a classified report, and have been shared neither with the public nor with the offshore wind companies.
Vineyard Wind, a joint development between Avangrid Renewables and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners, has been under construction since 2021, and is already 95% built. More than that, it’s sending power to Massachusetts customers, and will produce enough electricity to power up to 400,000 homes once it’s complete.
In court filings, the developer argued it was urgent the stop work order be lifted, as it would lose access to a key construction boat required to complete the project on March 31. The company is in the process of replacing defective blades on its last handful of turbines — a defect that was discovered after one of the blades broke in 2024, scattering shards of fiberglass into the ocean. Leaving those turbine towers standing without being able to install new blades created a safety hazard, the company said.
“If construction is not completed by that date, the partially completed wind turbines will be left in an unsafe condition and Vineyard Wind will incur a series of financial consequences that it likely could not survive,” the company wrote. The Trump administration submitted a reply denying there was any risk.
The only remaining wind farm still affected by the December pause on construction is Sunrise Wind, a 924-megawatt project being developed by Orsted and set to deliver power to New York State. A hearing for an injunction on that order is scheduled for February 2.
Noon Energy just completed a successful demonstration of its reversible solid-oxide fuel cell.
Whatever you think of as the most important topic in energy right now — whether it’s electricity affordability, grid resilience, or deep decarbonization — long-duration energy storage will be essential to achieving it. While standard lithium-ion batteries are great for smoothing out the ups and downs of wind and solar generation over shorter periods, we’ll need systems that can store energy for days or even weeks to bridge prolonged shifts and fluctuations in weather patterns.
That’s why Form Energy made such a big splash. In 2021, the startup announced its plans to commercialize a 100-plus-hour iron-air battery that charges and discharges by converting iron into rust and back again. The company’s CEO, Mateo Jaramillo, told The Wall Street Journal at the time that this was the “kind of battery you need to fully retire thermal assets like coal and natural gas power plants.” Form went on to raise a $240 million Series D that same year, and is now deploying its very first commercial batteries in Minnesota.
But it’s not the only player in the rarified space of ultra-long-duration energy storage. While so far competitor Noon Energy has gotten less attention and less funding, it was also raising money four years ago — a more humble $3 million seed round, followed by a $28 million Series A in early 2023. Like Form, it’s targeting a price of $20 per kilowatt-hour for its electricity, often considered the threshold at which this type of storage becomes economically viable and materially valuable for the grid.
Last week, Noon announced that it had completed a successful demonstration of its 100-plus-hour carbon-oxygen battery, partially funded with a grant from the California Energy Commission, which charges by breaking down CO2 and discharges by recombining it using a technology known as a reversible solid-oxide fuel cell. The system has three main components: a power block that contains the fuel cell stack, a charge tank, and a discharge tank. During charging, clean electricity flows through the power block, converting carbon dioxide from the discharge tank into solid carbon that gets stored in the charge tank. During discharge, the system recombines stored carbon with oxygen from the air to generate electricity and reform carbon dioxide.
Importantly, Noon’s system is designed to scale up cost-effectively. That’s baked into its architecture, which separates the energy storage tanks from the power generating unit. That makes it simple to increase the total amount of electricity stored independent of the power output, i.e. the rate at which that energy is delivered.
Most other batteries, including lithium-ion and Form’s iron-air system, store energy inside the battery cells themselves. Those same cells also deliver power; thus, increasing the energy capacity of the system requires adding more battery cells, which increases power whether it’s needed or not. Because lithium-ion cells are costly, this makes scaling these systems for multi-day energy storage completely uneconomical.
In concept, Noon’s ability to independently scale energy capacity is “similar to pumped hydro storage or a flow battery,” Chris Graves, the startup’s CEO, told me. “But in our case, many times higher energy density than those — 50 times higher than a flow battery, even more so than pumped hydro.” It’s also significantly more energy dense than Form’s battery, he said, likely making it cheaper to ship and install (although the dirt cheap cost of Form’s materials could offset this advantage.)
Noon’s system would be the first grid-scale deployment of reversible solid-oxide fuel cells specifically for long-duration energy storage. While the technology is well understood, historically reversible fuel cells have struggled to operate consistently and reliably, suffering from low round trip efficiency — meaning that much of the energy used to charge the battery is lost before it’s used — and high overall costs. Graves conceded Noon has implemented a “really unique twist” on this tech that’s allowed it to overcome these barriers and move toward commercialization, but that was as much as he would reveal.
Last week’s demonstration, however, is a big step toward validating this approach. “They’re one of the first ones to get to this stage,” Alexander Hogeveen Rutter, a manager at the climate tech accelerator Third Derivative, told me. “There’s certainly many other companies that are working on a variance of this,” he said, referring to reversible fuel cell systems overall. But none have done this much to show that the technology can be viable for long-duration storage.
One of Noon’s initial target markets is — surprise, surprise — data centers, where Graves said its system will complement lithium-ion batteries. “Lithium ion is very good for peak hours and fast response times, and our system is complementary in that it handles the bulk of the energy capacity,” Graves explained, saying that Noon could provide up to 98% of a system’s total energy storage needs, with lithium-ion delivering shorter streams of high power.
Graves expects that initial commercial deployments — projected to come online as soon as next year — will be behind-the-meter, meaning data centers or other large loads will draw power directly from Noon’s batteries rather than the grid. That stands in contrast to Form’s approach, which is building projects in tandem with utilities such as Great River Energy in Minnesota and PG&E in California.
Hogeveen Rutter, of Third Derivative, called Noon’s strategy “super logical” given the lengthy grid interconnection queue as well as the recent order from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission intended to make it easier for data centers to co-locate with power plants. Essentially, he told me, FERC demanded a loosening of the reins. “If you’re a data center or any large load, you can go build whatever you want, and if you just don’t connect to the grid, that’s fine,” Hogeveen Rutter said. “Just don’t bother us, and we won’t bother you.”
Building behind-the-meter also solves a key challenge for ultra-long-duration storage — the fact that in most regions, renewables comprise too small a share of the grid to make long-duration energy storage critical for the system’s resilience. Because fossil fuels still meet the majority of the U.S.’s electricity needs, grids can typically handle a few days without sun or wind. In a world where renewables play a larger role, long-duration storage would be critical to bridging those gaps — we’re just not there yet. But when a battery is paired with an off-grid wind or solar plant, that effectively creates a microgrid with 100% renewables penetration, providing a raison d’être for the long-duration storage system.
“Utility costs are going up often because of transmission and distribution costs — mainly distribution — and there’s a crossover point where it becomes cheaper to just tell the utility to go pound sand and build your power plant,” Richard Swanson, the founder of SunPower and an independent board observer at Noon, told me. Data centers in some geographies might have already reached that juncture. “So I think you’re simply going to see it slowly become cost effective to self generate bigger and bigger sizes in more and more applications and in more and more locations over time.”
As renewables penetration on the grid rises and long-duration storage becomes an increasing necessity, Swanson expects we’ll see more batteries like Noon’s getting grid connected, where they’ll help to increase the grid’s capacity factor without the need to build more poles and wires. “We’re really talking about something that’s going to happen over the next century,” he told me.
Noon’s initial demo has been operational for months, cycling for thousands of hours and achieving discharge durations of over 200 hours. The company is now fundraising for its Series B round, while a larger demo, already built and backed by another California Energy Commission grant, is set to come online soon.
While Graves would not reveal the size of the pilot that’s wrapping up now, this subsequent demo is set to deliver up to 100 kilowatts of power at once while storing 10 megawatt-hours of energy, enough to operate at full power for 100 hours. Noon’s full-scale commercial system is designed to deliver the same 100-hour discharge duration while increasing the power output to 300 kilowatts and the energy storage capacity to 30 megawatt-hours.
This standard commercial-scale unit will be shipping container-sized, making it simple to add capacity by deploying additional modules. Noon says it already has a large customer pipeline, though these agreements have yet to be announced. Those deals should come to light soon though, as Swanson says this technology represents the “missing link” for achieving full decarbonization of the electricity sector.
Or as Hogeveen Rutter put it, “When people talk about, I’m gonna get rid of all my fossil fuels by 2030 or 2035 — like the United Kingdom and California — well this is what you need to do that.”