You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On a very potent greenhouse gas, Florida’s flooding, and hydropower

Current conditions: Temperatures in northern China will top 107 degrees Fahrenheit today • Months-long water shortages have sparked riots in Algeria • Unseasonably cold and wet weather is being blamed for stunted economic growth in the U.K.
More than 7 million people are under flood advisories in Florida, with a tropical storm stalled over the state at least through Friday. Flooding was reported across the southern part of Florida including Fort Myers, Miami, and even farther north. In Sarasota, just south of Tampa, nearly four inches of rain fell in an hour, a new record for the area, with total rainfall reaching about 10 inches on Tuesday. The downpour was a one-in-1,000-year event. “The steadiest and heaviest rain will fall on South and central Florida through Thursday, but more spotty downpours and thunderstorms will continue to pester the region into Saturday,” AccuWeather senior meteorologist Reneé Duff said.
There has been a “downward trend” in global hydropower output over the last five years, according to the International Hydropower Association’s new 2024 World Hydropower Outlook. Hydropower is the largest renewable source of electricity, according to the International Energy Agency. It generates more electricity than all other renewable technologies combined, and plays a key role in the energy transition. But hydropower installations must double to meet net zero goals by 2050. The IEA has also projected that “without major policy changes, global hydropower expansion is expected to slow down this decade.” That may already be happening:
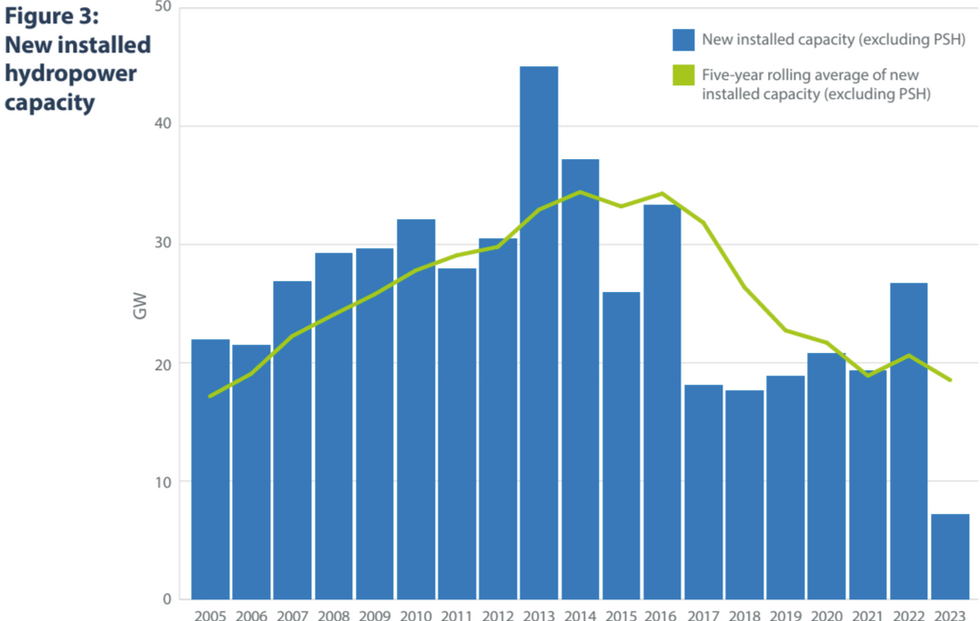
The report estimates that investment needs to double – to $130 billion per year – in order to double installed hydropower capacity by 2050.
Nitrous oxide doesn’t get as much attention as carbon dioxide or methane, but it should: This greenhouse gas is more potent than both, depletes the ozone, and is the third largest contributor to climate change, according toCarbon Brief. A new study published in the journal Earth System Science Data finds that human-caused N20 emissions rose by 40% over the past 40 years, and that most of this increase was driven by the use of nitrogen fertilizer and manure in agriculture to meet growing demand for meat and dairy. Agriculture emissions of N20 were 67% higher in 2020 than they were in 1980. The concentration of N20 in the atmosphere is now 25% higher than in pre-industrial years. “The unfettered increase in a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential approximately 300 times larger than carbon dioxide, presents dire consequences for the planet,” the researchers said in a press release.
But it’s not all bad news. A separate study out this week finds that atmospheric levels of ozone-depleting greenhouse gases called hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) peaked in 2021 – five years ahead of schedule – and are declining faster than expected.
UN climate finance talks in Bonn, Germany, ended on a sour note yesterday, “with negotiators from developing and developed countries blaming each other in fiery exchanges,” according toClimate Home News. The discussions were a lead-up to November’s COP29 in Azerbaijan, where countries are expected to put forward a new annual finance goal for helping vulnerable countries protect themselves from climate change and shift to clean energy. The current target, set in 2009, sits at $100 billion annually. Boosting this fund is seen as “the most important decision” expected to come out of this year’s climate summit. But so far, there has been little progress. Rich countries only managed to meet the existing $100 billion annual pledge in 2022, two years late.
One of the most important sites in Greek and Roman mythology is sinking into the sea as climate change causes water levels to rise. The tiny abandoned Greek island of Delos, in the Aegean Sea, was first settled in the third millennium BC and was once a busy port city with 30,000 occupants. In Greek mythology, it was the birthplace of Apollo and his sister Artemis. Today it is dotted with 2,000-year-old archaeological ruins and has been a UNESCO World Heritage site since 1990. But sea levels around the island have risen 66 feet in just 10 years, and archaeologists toldAFP the ruins will disappear entirely in about 50 years, eaten away by encroaching sea water and rising temperatures.

Joey Chestnut, the 16-time winner of Nathan’s Famous Hot Dog Eating Contest in Coney Island, has been banned from the competition this year because he struck a deal with plant-based food company Impossible Foods.
Editor’s note: A previous version of this articles mistakenly referred to nitrous oxide as N02 instead of N20. It has been corrected. We regret the error.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On the budget debate, MethaneSAT’s untimely demise, and Nvidia
Current conditions: The northwestern U.S. faces “above average significant wildfire potential” for July • A month’s worth of rain fell over just 12 hours in China’s Hubei province, forcing evacuations • The top floor of the Eiffel Tower is closed today due to extreme heat.
The Senate finally passed its version of Trump’s One Big Beautiful Bill Act Tuesday morning, sending the tax package back to the House in hopes of delivering it to Trump by the July 4 holiday. The excise tax on renewables that had been stuffed into the bill over the weekend was removed after Senator Lisa Murkowski of Alaska struck a deal with the Senate leadership designed to secure her vote. In her piece examining exactly what’s in the bill, Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo explains that even without the excise tax, the bill would “gum up the works for clean energy projects across the spectrum due to new phase-out schedules for tax credits and fast-approaching deadlines to meet complex foreign sourcing rules.” Debate on the legislation begins on the House floor today. House Speaker Mike Johnson has said he doesn’t like the legislation, and a handful of other Republicans have already signaled they won’t vote for it.
The Environmental Protection Agency this week sent the White House a proposal that is expected to severely weaken the federal government’s ability to rein in planet-warming pollution. Details of the proposal, titled “Greenhouse Gas Endangerment Finding and Motor Vehicle Reconsideration,” aren’t clear yet, but EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin has reportedly been urging the Trump administration to repeal the 2009 “endangerment finding,” which explicitly identified greenhouse gases as a public health threat and gave the EPA the authority to regulate them. Striking down that finding would “free EPA from the legal obligation to regulate climate pollution from most sources, including power plants, cars and trucks, and virtually any other source,” wrote Alex Guillén at Politico. The title of the proposal suggests it aims to roll back EPA tailpipe emissions standards, as well.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
So long, MethaneSAT, we hardly knew ye. The Environmental Defense Fund said Tuesday that it had lost contact with its $88 million methane-detecting satellite, and that the spacecraft was “likely not recoverable.” The team is still trying to figure out exactly what happened. MethaneSAT launched into orbit last March and was collecting data about methane pollution from global fossil fuel infrastructure. “Thanks to MethaneSAT, we have gained critical insight about the distribution and volume of methane being released from oil and gas production areas,” EDF said. “We have also developed an unprecedented capability to interpret the measurements from space and translate them into volumes of methane released. This capacity will be valuable to other missions.“ The good news is that MethaneSAT was far from the only methane-tracking satellite in orbit.
Nvidia is backing a D.C.-based startup called Emerald AI that “enables AI data centers to flexibly adjust their power consumption from the electricity grid on demand.” Its goal is to make the grid more reliable while still meeting the growing energy demands of AI computing. The startup emerged from stealth this week with a $24.5 million seed round led by Radical Ventures and including funding from Nvidia. Emerald AI’s platform “acts as a smart mediator between the grid and a data center,” Nvidia explains. A field test of the software during a grid stress event in Phoenix, Arizona, demonstrated a 25% reduction in the energy consumption of AI workloads over three hours. “Renewable energy, which is intermittent and variable, is easier to add to a grid if that grid has lots of shock absorbers that can shift with changes in power supply,” said Ayse Coskun, Emerald AI’s chief scientist and a professor at Boston University. “Data centers can become some of those shock absorbers.”
In case you missed it: California Governor Gavin Newsom on Monday rolled back the state’s landmark Environmental Quality Act. The law, which had been in place since 1970, required environmental reviews for construction projects and had become a target for those looking to alleviate the state’s housing crisis. The change “means most urban developers will no longer have to study, predict, and mitigate the ways that new housing might affect local traffic, air pollution, flora and fauna, noise levels, groundwater quality, and objects of historic or archeological significance,” explainedCal Matters. On the other hand, it could also mean that much-needed housing projects get approved more quickly.
Tesla is expected to report its Q2 deliveries today, and analysts are projecting a year-over-year drop somewhere from 11% to 13%.
Jesse teaches Rob the basics of energy, power, and what it all has to do with the grid.
What is the difference between energy and power? How does the power grid work? And what’s the difference between a megawatt and a megawatt-hour?
On this week’s episode, we answer those questions and many, many more. This is the start of a new series: Shift Key Summer School. It’s a series of introductory “lecture conversations” meant to cover the basics of energy and the power grid for listeners of every experience level and background. In less than an hour, we try to get you up to speed on how to think about energy, power, horsepower, volts, amps, and what uses (approximately) 1 watt-hour, 1 kilowatt-hour, 1 megawatt-hour, and 1 gigawatt-hour.
Shift Key is hosted by Jesse Jenkins, a professor of energy systems engineering at Princeton University, and Robinson Meyer, Heatmap’s executive editor.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, YouTube, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from our conversation:
Jesse Jenkins: Let’s start with the joule. The joule is the SI unit for both work and energy. And the basic definition of energy is the ability to do work — not work in a job, but like work in the physics sense, meaning we are moving or displacing an object around. So a joule is defined as 1 newton-meter, among other things. It has an electrical equivalent, too. A newton is a unit of force, and force is accelerating a mass, from basic physics, over some distance in this case. So 1 meter of distance.
So we can break that down further, right? And we can describe the newton as 1 kilogram accelerated at 1 meter per second, squared. And then the work part is over a distance of one meter. So that kind of gives us a sense of something you feel. A kilogram, right, that’s 2.2 pounds. I don’t know, it’s like … I’m trying to think of something in my life that weighs a kilogram. Rob, can you think of something? A couple pounds of food, I guess. A liter of water weighs a kilogram by definition, as well. So if you’ve got like a liter bottle of soda, there’s your kilogram.
Then I want to move it over a meter. So I have a distance I’m displacing it. And then the question is, how fast do I want to do that? How quickly do I want to accelerate that movement? And that’s the acceleration part. And so from there, you kind of get a physical sense of this. If something requires more energy, if I’m moving more mass around, or if I’m moving that mass over a longer distance — 1 meter versus 100 meters versus a kilometer, right? — or if I want to accelerate that mass faster over that distance, so zero to 60 in three seconds versus zero to 60 in 10 seconds in your car, that’s going to take more energy.
Robinson Meyer: I am looking up what weighs … Oh, here we go: A 13-inch MacBook Air weighs about, a little more than a kilogram.
Jenkins: So your laptop. If you want to throw your laptop over a meter, accelerating at a pace of 1 meter per second, squared …
Meyer: That’s about a joule.
Jenkins: … that’s about a joule.
Mentioned:
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by …
The Yale Center for Business and the Environment’s online clean energy programs equip you with tangible skills and powerful networks—and you can continue working while learning. In just five hours a week, propel your career and make a difference.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.
If the Senate reconciliation bill gets enacted as written, you’ve got about 92 days left to seal the deal.
If you were thinking about buying or leasing an electric vehicle at some point, you should probably get on it like, right now. Because while it is not guaranteed that the House will approve the budget reconciliation bill that cleared the Senate Tuesday, it is highly likely. Assuming the bill as it’s currently written becomes law, EV tax credits will be gone as of October 1.
The Senate bill guts the subsidies for consumer purchases of electric vehicles, a longstanding goal of the Trump administration. Specifically, it would scrap the 30D tax credit by September 30 of this year, a harsher cut-off than the version of the bill that passed the House, which would have axed the credit by the end of 2025 except for automakers that had sold fewer than 200,000 electric vehicles. The credit as it exists now is worth up to $7,500 for cars with an MSRP below $55,000 (and trucks and sports utility vehicles under $80,000), and, under the Inflation Reduction Act, would have lasted through the end of 2032. The Senate bill also axes the $4,000 used EV tax credit at the end of September.
“Long story short, the credits under the current legislation are only going to be on the books through the end of September,” Corey Cantor, the research director of the Zero Emission Transportation Association, told me. “Now is definitely a good time, if you’re interested in an EV, to look at the market.”
The Senate applied the same strict timeline to credits for clean commercial vehicles, both new and used. For home EV chargers, the tax credit will now expire at the end of June next year.
While EVs were on the road well before the 2022 passage of the Inflation Reduction Act, what the new tax credit did was help build out a truly domestic electric vehicle market, Cantor said. “You have a bunch of refreshed EV models from major automakers,” Cantor told me, including “more affordable models in different segments, and many of them qualify for the credit.”
These include cars produceddomestically by Kia,Hyundai, and Chevrolet. But of course, the biggest winner from the credit is Tesla, whose Model Y was the best-selling car in the world in 2023.
Tesla shares were down over 5.5% in Tuesday afternoon trading, though not just because of Congress. JPMorgan also released an analyst report Monday arguing that the decline in sales seen in the first quarter would accelerate in the second quarter. President Trump, with whom Tesla CEO Elon Musk had an extremely public falling out last month, suggested on social media Monday night that the government efficiency department Musk himself formerly led should “take a good, hard, look” at the subsidies Musk receives across his many businesses. Trump also said that he would “take a look” at Musk’s United States citizenship in response to reporters’ questions about it.
Cantor told me that he expects a surge of consumer attention to the EV market if the bill passes in its current form. “You’ve seen more customers pull their purchase ahead” when subsidies cut-offs are imminent, he said.
But overall, the end of the subsidy is likely to reduce EV sales from their previously expected levels.
Harvard researchers have estimated that the termination of the EV tax credit “would cut the EV share of new vehicle sales in 2030 by 6.0 percentage points,” from 48% of new sales by 2030 to 42%. Combined with other Trump initiatives such as terminating the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure program for publicly funded chargers (currently being litigated) and eliminating California’s waiver under the Clean Air Act that allowed it to set tighter vehicle emissions standards, the share of new car sales that are electric could fall to 32% in 2030.
But not all government support for electric vehicles will end by October 1, even if the bill gets the president’s signature in its current form.
“It’s important for consumers to know there are many states that offer subsidies, such as New York, and Colorado,” Cantor told me. That also goes for California, New Jersey, Nevada, and New Mexico. You can find the full list here.
Editor’s note: This story has been edited to include a higher cost limit for trucks and SUVs.