You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On the controversial subsidies, battery production, and India's extreme weather

Current conditions: Temperatures are about 30 degrees higher in the Plains and Midwest than what’s seasonally normal • Northern Vietnam is enduring a severe cold spell • High winds from Storm Pia helped the U.K. set a new record for wind energy generation in just 30 minutes.
The Biden administration today unveiled strict rules governing the tax credits for clean hydrogen production, reports Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer. Hydrogen produces no climate pollution when burned, and could potentially replace fossil fuels in many sectors if scaled up responsibly. Under the Inflation Reduction Act, a company can get up to $3 for each kilogram of hydrogen made with clean electricity that it produces and sells. But to qualify for the subsidy, would-be hydrogen producers will have to demonstrate that they used clean, zero-carbon electricity to power their electrolyzers, the energy-hungry machines that pull hydrogen out of water or other molecules. Defining clean electricity has proven to be an enormous challenge and the subject of one of the biggest fights around the law. Under the new rules, electricity used to produce hydrogen must:
Some industry groups allege the new rules could stunt the field in its infancy. Deputy Secretary of the Treasury Wally Adeyemo was effusive about the new rules’ benefits. “We’ve developed a structure that will drive innovation and create good-paying jobs in this emerging industry while strengthening our energy security and reducing emissions in hard-to-transition sectors of the economy,” he told reporters.
New analysis from the Environmental Defense Fund, provided exclusively to Heatmap, suggests that U.S. battery production is going really well. The data shows American battery manufacturers around the country — many of them automakers — have announced over 1,000 gigawatt hours of U.S. battery production that’s slated to come online by 2028, far outpacing projected demand.
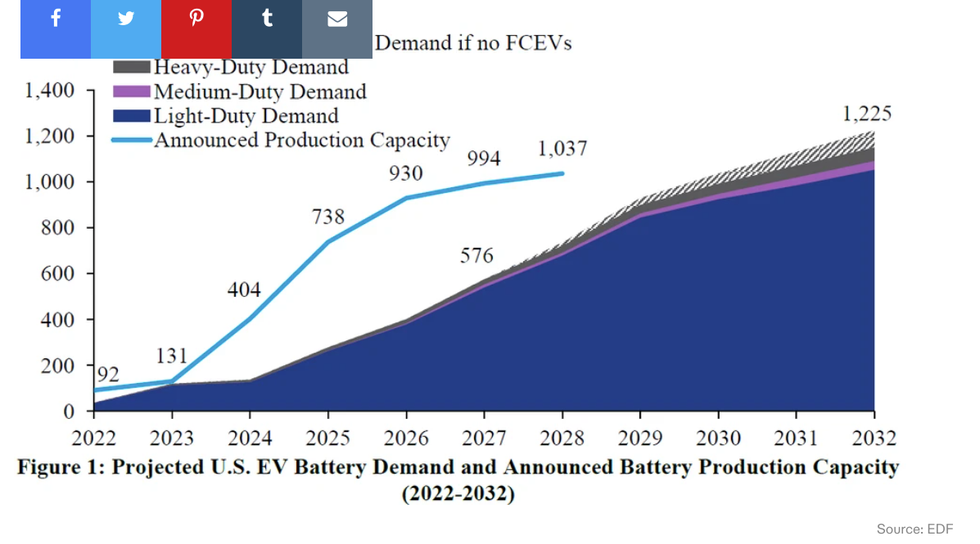
As Heatmap’s Neel Dhanesha explains, this matters because the Inflation Reduction Act stipulates that, in order to be eligible for tax credits, electric vehicle components can’t be made by a country on the U.S.’s “foreign entities of concern” list. That rules out batteries made in China. Without an increase in American battery manufacturing, we run the risk of Americans being either unwilling or unable to pay for the EVs that we’d need to hit strict new EPA vehicle emissions standards.
Let’s stick with EVs for a moment: The U.S. Treasury today announced that more than 7,000 car dealers have registered with the IRS Energy Credits Online portal. Many electric vehicles are eligible for sizable federal tax credits, and this portal, unveiled last month, helps streamline the crediting process by allowing dealers to apply the credit as a kind of discount at the point of sale. If the dealer is registered on the portal, they can submit the sales information to the IRS and receive payment for the value of the credits within 72 hours.
Get Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
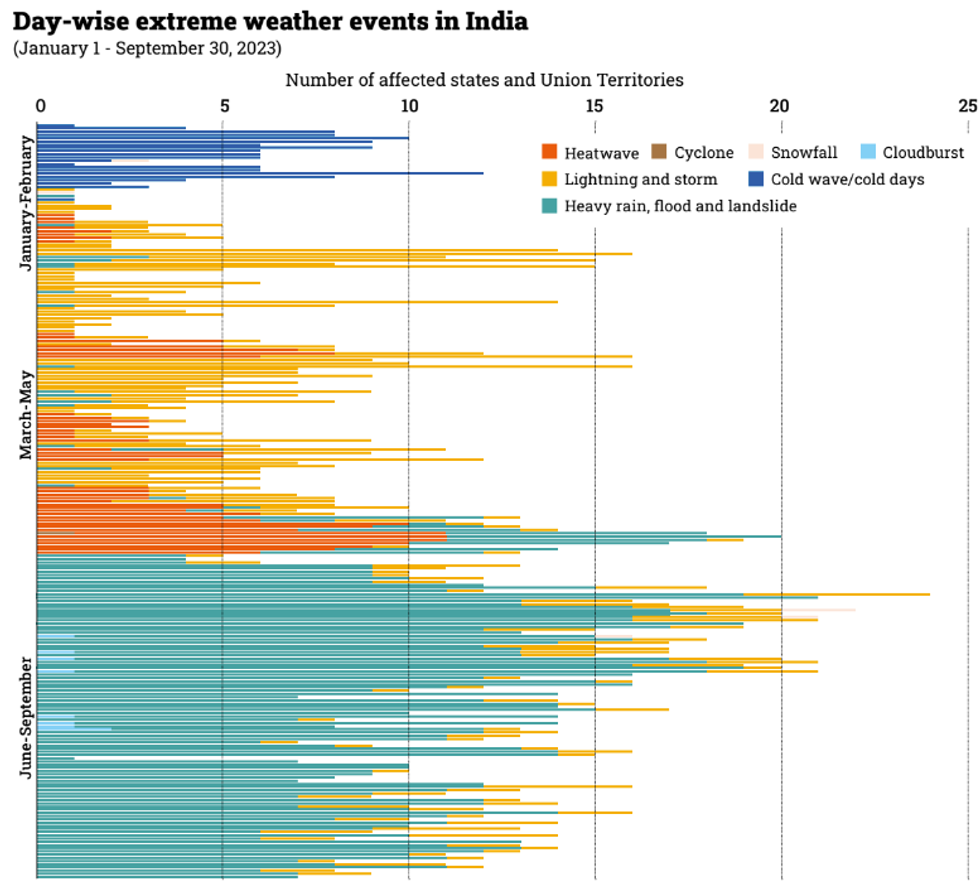
India is testing ways of incorporating artificial intelligence into weather forecasting to better prepare for extreme weather events, Reuters reports. The India Meteorological Department already uses supercomputers for weather models but “an AI model doesn't require the high cost involved in running a supercomputer,” Saurabh Rathore, an assistant professor at Indian Institute of Technology-Delhi, says. “You can even run it out of a good quality desktop.” The Centre for Science and Environment estimates that India saw almost one weather disaster per day this year, and that these events, exacerbated by global warming, have killed nearly 3,000 people. The U.K.’s Met Office is also exploring AI models that could forecast extreme weather events.
Indonesia will start fining companies that own palm oil plantations in areas designated as forests. Palm oil is widely used in foods, cosmetics, cleaning agents, and other products, and palm oil plantations are a huge culprit in deforestation and habitat loss, especially in Indonesia, which is the world’s biggest palm oil producer and exporter. Last month the country identified nearly 500,000 acres of plantations in forest areas, which will be handed over to the state and turned back into forests.
Researchers at the California Academy of Sciences discovered 153 new animal, plant, and fungi species in 2023, including 66 spiders, 13 sea stars, 12 geckos, one scorpion, and one legless skink.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Get up to speed on the SPEED Act.
After many months of will-they-won’t-they, it seems that the dream (or nightmare, to some) of getting a permitting reform bill through Congress is squarely back on the table.
“Permitting reform” has become a catch-all term for various ways of taking a machete to the thicket of bureaucracy bogging down infrastructure projects. Comprehensive permitting reform has been tried before but never quite succeeded. Now, a bipartisan group of lawmakers in the House are taking another stab at it with the SPEED Act, which passed the House Natural Resources Committee the week before Thanksgiving. The bill attempts to untangle just one portion of the permitting process — the National Environmental Policy Act, or NEPA.
There are a lot of other ways regulation and bureaucracy get in the way of innovation and clean energy development that are not related to NEPA. Some aren’t even related to permitting. The biggest barrier to building transmission lines to carry new carbon-free energy, for example, is the lack of a standard process to determine who should pay for them when they cross through multiple utility or state jurisdictions. Lawmakers on both sides of the aisle are working on additional bills to address other kinds of bottlenecks, and the SPEED Act could end up being just one piece of the pie by the time it’s brought to the floor.
But while the bill is narrow in scope, it would be sweeping in effect — and it’s highly unclear at this point whether it could garner the bipartisan support necessary to get 60 votes in the Senate. Just two of the 20 Democrats on the Natural Resources Committee voted in favor of the bill.
Still, the context for the debate has evolved significantly from a year ago, as artificial intelligence has come to dominate America’s economic prospects, raising at least some proponents’ hopes that Congress can reach a deal this time.
“We’ve got this bipartisan interest in America winning the AI race, and an understanding that to win the AI race, we’ve got to expand our power resources and our transmission network,” Jeff Dennis, the executive director of the Electricity Customer Alliance and a former official at the Department of Energy’s Grid Deployment Office, told me. “That creates, I think, a new and a different kind of energy around this conversation than we’ve had in years past.”
One thing that hasn’t changed is that the permitting reform conversation is almost impenetrably difficult to follow. Here’s a guide to the SPEED Act to help you navigate the debate as it moves through Congress.
NEPA says that before federal agencies make decisions, whether promulgating rules or approving permits, they must assess the environmental impacts of those decisions and disclose them to the public. Crucially, it does not mandate any particular action based on the outcome of these assessments — that is, agencies still have full discretion over whether to approve a permit, regardless of how risky the project is shown to be.
The perceived problem is that NEPA slows down infrastructure projects of all kinds — clean energy, dirty energy, housing, transit — beyond what should reasonably be expected, and thereby raises costs. The environmental assessments themselves take a long time, and yet third parties still often sue the federal government for not doing a thorough enough job, which can delay project development for many more years.
There’s a fair amount of disagreement over whether and how NEPA is slowing down clean energy, specifically. Some environmental and clean energy researchers have analyzed NEPA timelines for wind, solar, and transmission projects and concluded that while environmental reviews and litigation do run up the clock, that has been more the exception than the rule. Other groups have looked at the same data and seen a dire need for reform.
Part of the disconnect is about what the data doesn’t show. “What you don’t see is how little activity there is in transmission development because of the fear of not getting permits,” Michael Skelly, the CEO of Grid United, told me. “It’s so difficult to go through NEPA, it’s so costly on the front end and it’s so risky on the back end, that most people don’t even try.”
Underlying the dispute is also the fact that available data on NEPA processes and outcomes are scattered and incomplete. The Natural Resources Committee advanced two smaller complementary bills to the SPEED Act that would shine more light on NEPA’s flaws. One, called the ePermit Act, would create a centralized portal for NEPA-related documentation and data. The other directs the federal government to put out an annual report on how NEPA affects project timelines, costs, and outcomes.
During Biden’s presidency, Congress and the administration took a number of steps to reform NEPA — some more enduring than others. The biggest swing was the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023, which raised the debt ceiling. In an effort to prevent redundant analyses when a project requires approvals or input from multiple agencies, it established new rules by which one lead agency would oversee the NEPA process for a given project, set the environmental review schedule, and coordinate with other relevant agencies. It also codified new deadlines for environmental review — one year to complete environmental assessments, and two years for meatier "environmental impact statements” — and set page limits for these documents.
The 2021 bipartisan infrastructure law also established a new permitting council to streamline reviews for the largest projects.
The Inflation Reduction Act allocated more than $750 million for NEPA implementation across the federal government so that agencies would have more resources to conduct reviews. Biden’s Council of Environmental Quality also issued new regulations outlining how agencies should comply with NEPA, but those were vacated by a court decision that held that CEQ does not have authority to issue NEPA regulations.
Trump’s One Big Beautiful Bill Act, which he signed in early July, created a new process under NEPA by which developers could pay a fee to the government to guarantee a faster environmental review process.
None of these laws directly affected NEPA litigation, which many proponents of reform say is the biggest cause of delay and uncertainty in the process.
The most positive comments I heard about the SPEED Act from clean energy proponents were that it was a promising, though flawed, opening salvo for permitting reform.
Dennis told me it was “incredibly important” that the bill had bipartisan support and that it clarified the boundaries for what agencies should consider in environmental reviews. Marc Levitt, the director of regulatory reform at the Breakthrough Institute and a former Environmental Protection Agency staffer, said it addresses many of the right problems — especially the issue of litigation — although the provisions as written are “a bit too extreme.” (More on that in a minute.)
Skelly liked the 150-day statute of limitations on challenging agency decisions in court. In general, speeding up the NEPA process is crucial, he said, not just because time is money. When it takes five years to get a project permitted, “by the time you come out the other side, the world has changed and you might want to change your project,” but going through it all over again is too arduous to be worth it.
Industry associations for both oil and gas and clean energy have applauded the bill, with the American Clean Power Association joining the American Petroleum Institute and other groups in signing a letter urging lawmakers to pass it. The American Council on Renewable Energy also applauded the bill’s passage, but advised that funding and staffing permitting agencies was also crucial.
Many environmental groups fundamentally oppose the bill — both the provisions in it, and the overall premise that NEPA requires reform. “If you look at what’s causing delay at large,” Stephen Schima, senior legislative council for Earthjustice Action, told me, “it’s things like changes in project design, local and state regulations, failures of applicants to provide necessary information, lack of funding, lack of staff and resources at the agencies. It’s not the law itself.”
Schima and Levitt both told me that the language in the bill that’s supposed to prevent Trump from revoking previously approved permits is toothless — all of the exceptions listed “mirror almost precisely the conditions under which Trump and his administration are currently taking away permits,” Levitt said. The Solar Energy Industry Association criticized the bill for not addressing the “core problem” of the Trump administration’s “ongoing permitting moratorium” on clean energy projects.
Perhaps the biggest problem people have with the bill, which came up in my interviews and during a separate roundtable hosted by the Bipartisan Policy Center, is the way it prevents courts from stopping projects. An agency could do a slapdash environmental review, miss significant risks to the public, and there would be no remedy other than that the agency has to update its review — the project could move forward as-is.
Those are far from the only red flags. During a Heatmap event on Thursday, Ted Kelly, the director and lead counsel for U.S. energy at the Environmental Defense Fund, told me one of his biggest concerns was the part about ignoring new scientific research. “That just really is insisting the government shut its eyes to new information,” he said. Schima pointed to the injustice of limiting lawsuits to individuals who submitted public comments, when under the Trump administration, agencies have stopped taking public comments on environmental reviews. The language around considering effects that are “separate in time or place from the project or action” is also dangerous, Levitt said. It limits an agency’s discretion over what effects are relevant to consider, including cumulative effects like pollution and noise from neighboring projects.
The SPEED Act is expected to come to a vote on the House floor in the next few weeks. Then the Senate will likely put forward its own version.
As my colleague Jael Holzman wrote last month, Trump himself remains the biggest wildcard in permitting reform. Democrats have said they won’t agree to a deal that doesn’t bar the president from pulling previously-approved permits or otherwise level the playing field for renewable energy. Whether Trump would ever sign a bill with that kind of language is not a question we have much insight into yet.
And more on the week’s biggest fights around renewable energy.
1. Benton County, Washington – The Horse Heaven wind farm in Washington State could become the next Lava Ridge — if the Federal Aviation Administration wants to take up the cause.
2. Dukes County, Massachusetts – The Trump administration signaled this week it will rescind the approvals for the New England 1 offshore wind project.
3. Washtenaw County, Michigan – Michigan attorney general Dana Nessel waded into the fight over an Oracle and OpenAI data center in a rural corner of the state, a major escalation against AI infrastructure development by a prominent Democratic official.
4. Nacogdoches County, Texas – I am eyeing the fight over a solar project in this county for potential chicanery over species and habitat protection.
5. Fulton County, Ohio – In brighter news for the solar industry, Ohio is blessing more of their projects.
A conversation with the co-chair of the House Sustainable Energy and Environment Coalition
This week’s conversation is with Rep. Sean Casten, co-chair of the House Sustainable Energy and Environment Coalition – a group of climate hawkish Democratic lawmakers in the U.S. House of Representatives. Casten and another lawmaker, Rep. Mike Levin, recently released the coalition’s priority permitting reform package known as the Cheap Energy Act, which stands in stark contrast to many of the permitting ideas gaining Republican support in Congress today. I reached out to talk about the state of play on permitting, where renewables projects fit on Democrats’ priority list in bipartisan talks, and whether lawmakers will ever address the major barrier we talk about every week here in The Fight: local control. Our chat wound up immensely informative and this is maybe my favorite Q&A I’ve had the liberty to write so far in this newsletter’s history.
The following conversation was lightly edited for clarity.
Okay, so to start, how does the Cheap Energy Act fit into the bipartisan permitting talks?
There are two separate theories about how Congress is supposed to work, and neither of these theories is universally true but I think they inform two different approaches: do you believe the purpose of Congress is to craft good policy and then put together political consensus to put that policy forward or do you think the purpose of Congress is to find where political compromise exists and then advance the policy that can proceed along that constraint?
Depending on the situation you take Door 1 or you take Door 2.
What Mike Levin and I have tried to do with our Cheap Energy Act is to say, let’s identify the barriers to deploying cheap energy in the United States, let’s try to find the policy that’ll help consumers first and then try to get that policy done. That approach – because of the way our politics is geographically sorted out in our country – implies a wealth transfer from energy producers to energy consumers. And energy producers in this country tend to be dominant in Republican areas. That’s where coal mining is, oil and gas, logging. And energy consumers are where the population is, which skews Democratic. So on a bipartisan basis you really can’t put consumers first because that is detrimental to producers.
I think that’s why you have these two different approaches going on. I guess I have a bias towards our approach but I think we have to be very candid that the other approach does not remove the barriers to cheap energy. It removes the barriers to dirty energy.
To an overwhelming degree, and I’m slightly exaggerating, but there really aren’t permitting barriers to clean energy. There are a lot of permitting barriers to dirty energy. Which is not to say you can’t weaponize the permitting system to stop clean energy from going forward. But if you’re building a solar farm and it has to have a wire that connects it to a load, your environmental footprint is very small.
Now we’ve done some things in our bill to pre-identify corridors where there is minimal species disruptions, minimal disruption of historical artifacts, and say these are corridors where you can build things fast without guessing. Let’s not kid ourselves here: the Antiquities Act exists for a reason, the Endangered Species Act exists for a reason, and the Clean Water Act exists for a reason. But the footprint of those projects environmentally is just much, much smaller than an oil rig and a pipeline and a refinery because all of those things have the potential to leak nasty chemicals that permanently defile the air, land, and water in the vicinity.
The challenge that manifests through permitting is that if I want to lower your cost of energy, that means by definition I am undercutting your current energy provider. For the most part, that provider has undue power over whether or not you get a permit. And they have an incentive to start pamphleting the neighbors around a new transmission line, for example, to say a line is going to lower people’s property values. That’s because it is an economic threat. The reason I know that’s not an issue is you never see utilities struggle to get a new wire.
I previously reported on how the biggest sticking point in bipartisan permitting talks underway today is whether Republicans will go for tying Trump’s hands in his pursuit to stop federal renewable energy permits. Do you think any GOP lawmakers will actually do that?
Ignore whatever politics someone might have. If you’re representing a district that had a ton of wind power, not a lot of load, and you live 200 miles from a major urban center that was paying a lot for electricity, you would probably be very supportive of making it easier to build the wire to access that market and making it easier for the wind turbines to go up.
I have just described the entire Iowa congressional delegation.
Let’s say in the next election, we flip some of those Iowa seats and now what was Republican is now a Democrat, that wouldn’t change the interests of the Iowa delegation. It would just change the party. So there’s reasons why [Iowa Republican] Randy Feenstra and I have led letters on trying to build SOO Green, this high voltage transmission line that would solve exactly the problem I described there. That’s not because he’s a Republican – it’s because it is in the interests of his community.
But then why do we see so few Republicans standing up to the president in his fight specifically against renewable energy, at least in the permitting talks?
We have a huge problem with the White House that they’ve been entirely captured by the interests of energy producers and they have a rooted interest in making the price of energy expensive. The reason why they’re blocking wind permits, and the reason why they’re accelerating oil and gas exports, is because they’re completely captured by people who want the price of oil and gas to be high and they lose money when the price is low.
But that’s a completely separate series of problems.
Within the House, the leadership of the Democratic Party represents concentrated areas that would like the price of energy to be cheap. The leadership of the Republican Party represents oil and gas extractive areas that would like the price of energy to be high. So a rank and file member of the Democratic Party has no particular problem advocating for energy consumers because they’re not crossing leadership. A rank and file member of the Republican Party has no particular problem advocating for the interests of producers because they’re not crossing leadership.
I think where there’s a slight distinction is you can identify any number of Democrats from the oil and gas patch who will regularly vote with the interests of oil and gas producers, and leadership will understand why they are doing that. But it is much harder to identify members of the Republican Party who are advocating for the interests of consumers and get a pass from leadership to do that.
Mmm. So to close the loop on this, how much of a priority is it for Democrats that whatever bipartisan permitting deal is made won’t be used to speed things up for fossil while Trump continues to put the brakes on every little thing a renewable energy permit requires?
Look, I’ve seen nothing out of the House or Senate that wouldn’t do exactly what you just said. Everything would make the price of energy more expensive and make it harder to do reasonable and thoughtful environmental review. In the House and Senate as currently constituted, we are not going to get a good bill that comes through.
I think within the House you have a growing awareness that energy prices are a problem. Certainly the recent elections in New Jersey and Virginia have made that clear. You need to have a strategy to bring energy costs down. That does create an opportunity prior to next November where folks say, can I do something to help my community?
We’ll see when this bill ultimately gets out whether we get much support. I’ll say we’ve privately found Republican support for pieces of it. The way we fix this problem is by doing what the Republican Party used to be known for, which is competition. There’s no reason why we couldn’t incentivize utilities to make money by saving their consumers money. Or incentivize various pieces of the energy industry to better interconnect their markets so you could always choose the lowest cost option because Adam Smith is a god. Those arguments play much better with Republicans in states that have heavily deregulated. There are individual pieces where we’ve found Republican support. And if you think good policy and economics wins, let’s make good policy and economics wins and build support for it.
Last thing – you said there aren’t permitting barriers to clean energy. But in my reporting, I’m constantly covering local communities opposing renewable energy projects, transmission siting, battery storage. It’s a major barrier to development.
What role do you think the federal government and Congress has in dealing with the issue of local control?
It’s an old saw: depending on the issue, I’ll tell you that I’m supportive of states rights.
There are huge chunks of our energy system that should be federalized but aren’t. As an example, it makes no sense that if you want to build a gas pipeline across multiple states in the U.S., you go to FERC and they are the sole permitting authority and they decide whether or not you get a permit. If you go to the same corridor and build an electric transmission line that has less to worry about because there’s no chance of leaks, you have a different permitting body every time you cross a state line. That’s only because of laws going back to the 1930s that gave FERC sole authority on gas but not on the electric side. Our bill would fix that.
We’ve had this legacy of local control that has – not intentionally – had the practical effect of making it much easier for communities to block electric generation and distribution than natural gas distribution. This necessarily means that we have made natural gas producers more politically powerful and electricity consumers less politically powerful. Whether it was an intentional choice or not, it was a choice.
There are ways consistent with energy policy and congressional law where we can rationalize and have more parity across the energy system to make sure we make the right decision every time.
I also think at the end of the day, markets win. West Virginia one hundred years ago was the place to site your energy-intensive manufacturer because they had a ton of hydro and a ton of coal. They’ve tapped out the hydro, the coal is no longer cheap, and the economy is not good anymore. Then shift to Texas which has built more wind and solar than any state in the country and unusually for a red state has been much more pro-competition in how they regulate their energy markets, that has given them more dynamic electricity costs. Those are two different red states and sets of policy choices.