You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On wild February warmth, oil and gas profits, and carbon removal startups

Current conditions: The Northern Sierra mountain range could see up to 12 feet of snow • Raging bushfires are forcing 30,000 people in Australia’s Victoria state to evacuate • It will be unusually warm across much of Michigan today as voters participate in the state’s presidential primaries.
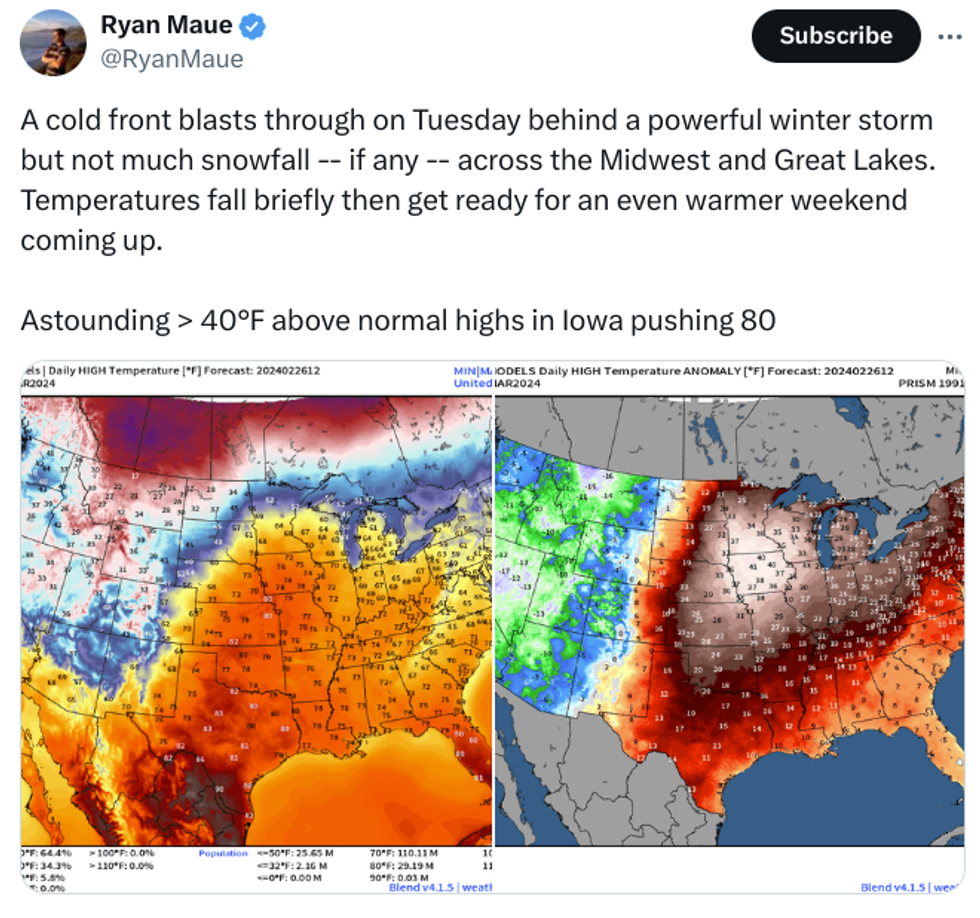
This week has already been a wild one for U.S. weather, as what is expected to be the warmest February on record comes to a close. Many states in the Midwest and South experienced a heatwave yesterday that brought record high winter temperatures. It was 65 degrees Fahrenheit in Minneapolis, for example, where the normal high is 33. Parts of Texas saw temperatures soar into the 90s. In Chicago, where February temperatures usually sit in the low 30s at best, it was a balmy 60 degrees yesterday. The warm weather brought with it wind gusts and fire risks, and red flag warnings were in place from Texas to Missouri.
But prepare for some weather whiplash: A cold front is advancing east, and will plunge some of those warmer states into frigid temperatures. Grand Forks, North Dakota, for example, won’t see temperatures rise above 9 degrees today; yesterday it was 55. In Chicago, it’ll be cold with a threat of tornadoes. Forecasters reminded Reuters climate change is making extreme and unpredictable weather more frequent.
Authorities have canceled Maine’s Can-Am Crown International Sled Dog Race, the longest such race in the eastern United States, due to lack of snow. Since 1992, the 250-mile trek has taken place in snowy northern Maine, but this year the region has seen just over half the typical amount of snowfall. “The unique challenges presented by the lack of snow have led us to conclude that moving forward with this year’s race could compromise the well-being of all involved,” wrote Can-Am President Dennis Cyr. “It is a decision made with heavy hearts but necessary caution.” National Weather Service meteorologist Joe Wegman said the lack of snow across parts of the country is creating a feedback loop: “Most of the eastern two-thirds of the country has had a relatively snow-less winter, so the ground is bare and dry. So we're getting much warmer temperatures just due to solar radiation.”
First Solar, the largest solar panel manufacturer in America, has been a boon for the nation’s economy, according to analysis from the University of Louisiana at Lafayette’s Kathleen Babineaux Blanco Public Policy Center and commissioned by the company. The report found that First Solar had 2,700 people on payroll in 2023, but because “each First Solar job ends up supporting six more jobs throughout the U.S. economy,” the company had a trickle-down effect of supporting some 16,000 jobs, Electrek’s Michelle Lewis explained. The company added $2.75 billion in value and $5.32 billion in output to the U.S. economy last year. By 2026, those numbers are expected to climb to $4.99 billion and $10.18 billion, respectively, as the company expands its solar capacity. First Solar is “a fully vertically integrated manufacturer of thin-film PV solar panels,” Lewis said. “This means they can turn a sheet of glass into a functional solar panel in about four hours, relying heavily on U.S.-sourced materials like glass and steel.”
Major U.S. oil and gas producers have seen profits nearly triple during President Biden’s presidency as production has soared, reported the Financial Times. The 10 most valuable operators – including ExxonMobil, Chevron, ConocoPhillips, and others – amassed a combined net income of $313 billion between 2020 and 2023, up from $112 billion during the same period of Donald Trump’s presidency. “The outperformance under Biden underlines the limited role of the White House in dictating the sector’s fortunes.” But it still won’t look great on his resume as he seeks to bolster support from climate-conscious progressives heading into the 2024 election. Biden ran “the most ambitious climate platform of any U.S. president in history,” and has indeed taken aim at the oil and gas industry during his tenure, the FT wrote. But he has also pushed to keep production high in the face of inflation and energy shocks.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
Carbon removal startup Equatic confirmed today that it is building a $20 million plant in Singapore to demonstrate the company’s technology, Bloomberg reported. Equatic uses electrolysis to permanently remove carbon dioxide from seawater, enabling it to absorb more of the greenhouse gas from the air. The process also creates hydrogen as a byproduct. The company already has two smaller pilot plants in operation, but the new one will be different for a few reasons: First, it’s much bigger – when complete, it could rival the annual carbon capturing capabilities of Climeworks, currently the world’s biggest carbon removal plant. Second, it will use a new proprietary process that doesn’t produce harmful chlorine gas. And third, it will mark a step toward commercialization as the company looks to scale and find more buyers. Boeing is among its most prominent customers, committing to pay the company to remove 62,000 tons of CO2 and produce 2,100 tons of hydrogen. Equatic plans to eventually build a commercial-scale plant that it claims will remove 100,000 tons of CO2 per year.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
It starts — but doesn’t end — with the Strait of Hormuz.
For the second time in a year, the United States and Israel have launched a major aerial assault on Iran. Strikes were reported across the country early Saturday, targeting Iranian leadership and military infrastructure. In retaliation, Iran has launched attacks on Israel and Gulf nations allied with the U.S., with several of the targets appearing to be American military installations. “The United States military is undertaking a massive and ongoing operation,” President Trump said in a video posted to Truth Social explaining his rationale for launching the war.
While the conflict has quickly metastasized across the region, it has the potential to affect the entire world by disrupting the production and shipment of oil and natural gas.
Iran and its neighbors on the Persian Gulf are some of the largest oil and gas producers in the world and the country has long threatened to disrupt oil exports as an act of self-defense or retaliation from attack.
That may be already happening. According to data from Bloomberg, some oil tankers are pausing or turning around outside the vital Strait of Hormuz, a narrow, deep channel between Iran and Oman that connects the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea and thus to global markets in and bordering the Indian Ocean.
The strait has been “effectively closed,” according to a report from Tasnim, a semi-official news agency linked to the Iran Revolutionary Guard Corps. British naval officials also said they had “received multiple reports” of broadcasts that “have claimed that the Strait of Hormuz (SoH) has been closed.” And a European Union naval official told Reuters that the Iranian Revolutionary Guard had been broadcasting “no ship is allowed to pass the Strait of Hormuz” to ships in the area. Some tankers are still navigating the strait, according to marine tracking data from Kpler.
But it’s questionable whether Iran can actually maintain any attempted closure of the strait, whether by laying mines or directly threatening and attacking ships.
So far, U.S. attacks are “targeting, fairly heavily, naval assets and assets that are close to the Gulf,” Greg Brew, an analyst at the Eurasia Group, told me, which “suggests that they are trying to degrade Iran’s ability to disrupt energy traffic through the Strait of Hormuz.”
The U.S. is “trying to reduce the risks of Iranian effort to close the strait as part of this operation, rather than waiting to see if the Iranians escalate in that direction. The Iranians have responded by claiming that the strait has been closed. The problem for them now, though, is that they’ll have to enforce that threat.”
Closing the strait was a “tail risk” that had been roiling the oil market in the lead-up to Trump’s decision to launch the attack, Rory Johnston, petroleum analyst and author of Commodity Context, told me.
Global oil prices had gotten skittish over the past weeks, with the Brent crude benchmark getting as low at $66.30 per barrel in early February and getting near $73 per barrel on Friday. Brent prices approached $80 per barrel last June during the 12 Day War between Iran and Israel.
While the market could likely weather disruption to Iran’s own exports, jumpy behavior in the market was due to pricing in an enhanced risk of a region-wide calamity. Options traders especially were “attempting to hedge that enormous tail risk,” Johnston said, and “that was really moving the market.”
And even if the strait is not directly closed off by the Iranian military, ships may find it financially onerous to attempt the passage. “Insurers told ship owners on Saturday they would cancel policies and raise coverage prices for vessels travelling through the Gulf and Strait of Hormuz after the U.S. and Israel attacked Iran,” the Financial Times reported Saturday.
Another risk to the region’s oil sector is that Iran could retaliate by striking oil production and exporting infrastructure in neighboring countries, Johnston told me. “Right next door, you’ve got Iraq, you’ve got Saudi Arabia, and you’ve got the Emirates and others who collectively are more like 20 million barrels per day. And that is obviously a much bigger deal,” Johnston said, comparing their production to Iran’s own oil industry.
Of course, Iran is still a major exporter despite U.S. sanctions; in the days running up to the U.S. attack, it was shipping out around 3 million barrels per day from Kharg Island in the Strait of Hormuz, according to data from Bloomberg, almost triple its exports from equivalent dates in January and nearly its entire daily production.
Iran’s exports “had actually surged immediately ahead of what’s gone down over the past 24 hours,” Johnston told me. “In the past couple days, you’d seen a large surge of tankers departing Kharg Island, and the inventories on Kharg Island being drawn down, which is kind of what you would do if you expected that your exports were about to get disrupted.”
To the extent Iranian oil exports are cut off, that could be a big deal for China, which has become the number one destination for Middle East oil shipments. Beijing has been building up stockpiles of oil, likely preparing for the risk that sanctioned exporters like Iran and Venezuela would go off the market, as well as wider risks to exports from the Middle East.
“China is highly concerned over the military strikes against Iran,” the Chinese foreign ministry wrote on X. “China calls for an immediate stop of the military actions, no further escalation of the tense situation, resumption of dialogue and negotiation, and efforts to uphold peace and stability in the Middle East.”
Last year, China began to substantially increase its stockpiling of oil, going from 84,000 barrels per day to 430,000 barrels per day, some 83% of the growth of its imports, according to data and estimates from Rystad Energy and Erica Downs, a senior research scholar at the Columbia University Center on Global Energy Policy.
While the U.S. is now far less reliant on oil exports from the Middle East, oil and gas is still a global market. If Middle Eastern oil and gas exports are disrupted, that will likely increase the price of energy — whether it’s gasoline, electricity, or even home heating — as American energy producers can sell their barrels and BTUs at higher prices globally.
It’s either reassure investors now or reassure voters later.
Investor-owned utilities are a funny type of company. On the one hand, they answer to their shareholders, who expect growing returns and steady dividends. But those returns are the outcome of an explicitly political process — negotiations with state regulators who approve the utilities’ requests to raise rates and to make investments, on which utilities earn a rate of return that also must be approved by regulators.
Utilities have been requesting a lot of rate increases — some $31 billion in 2025, according to the energy policy group PowerLines, more than double the amount requested the year before. At the same time, those rate increases have helped push electricity prices up over 6% in the last year, while overall prices rose just 2.4%.
Unsurprisingly, people have noticed, and unsurprisingly, politicians have responded. (After all, voters are most likely to blame electric utilities and state governments for rising electricity prices, Heatmap polling has found.) Democrat Mikie Sherrill, for instance, won the New Jersey governorship on the back of her proposal to freeze rates in the state, which has seen some of the country’s largest rate increases.
This puts utilities in an awkward position. They need to boast about earnings growth to their shareholders while also convincing Wall Street that they can avoid becoming punching bags in state capitols.
Make no mistake, the past year has been good for these companies and their shareholders. Utilities in the S&P 500 outperformed the market as a whole, and had largely good news to tell investors in the past few weeks as they reported their fourth quarter and full-year earnings. Still, many utility executives spent quite a bit of time on their most recent earnings calls talking about how committed they are to affordability.
When Exelon — which owns several utilities in PJM Interconnection, the country’s largest grid and ground zero for upset over the influx data centers and rising rates — trumpeted its growing rate base, CEO Calvin Butler argued that this “steady performance is a direct result of a continued focus on affordability.”
But, a Wells Fargo analyst cautioned, there is a growing number of “affordability things out there,” as they put it, “whether you are looking at Maryland, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware.” To name just one, Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro said in a speech earlier this month that investor-owned utilities “make billions of dollars every year … with too little public accountability or transparency.” Pennsylvania’s Exelon-owned utility, PECO, won approval at the end of 2024 to hike rates by 10%.
When asked specifically about its regulatory strategy in Pennsylvania and when it intended to file a new rate case, Butler said that, “with affordability front and center in all of our jurisdictions, we lean into that first,” but cautioned that “we also recognize that we have to maintain a reliable and resilient grid.” In other words, Exelon knows that it’s under the microscope from the public.
Butler went on to neatly lay out the dilemma for utilities: “Everything centers on affordability and maintaining a reliable system,” he said. Or to put it slightly differently: Rate increases are justified by bolstering reliability, but they’re often opposed by the public because of how they impact affordability.
Of the large investor-owned utilities, it was probably Duke Energy, which owns electrical utilities in the Carolinas, Florida, Kentucky, Indiana, and Ohio, that had to most carefully navigate the politics of higher rates, assuring Wall Street over and over how committed it was to affordability. “We will never waver on our commitment to value and affordability,” Duke chief executive Harry Sideris said on the company’s February 10 earnings call.
In November, Duke requested a $1.7 billion revenue increase over the course of 2027 and 2028 for two North Carolina utilities, Duke Energy Carolinas and Duke Energy Progress — a 15% hike. The typical residential customer Duke Energy Carolinas customer would see $17.22 added onto their monthly bill in 2027, while Duke Energy Progress ratepayers would be responsible for $23.11 more, with smaller increases in 2028.
These rate cases come “amid acute affordability scrutiny, making regulatory outcomes the decisive variable for the earnings trajectory,” Julien Dumoulin-Smith, an analyst at Jefferies, wrote in a note to clients. In other words, in order to continue to grow earnings, Duke needs to convince regulators and a skeptical public that the rate increases are necessary.
“Our customers remain our top priority, and we will never waver on our commitment to value and affordability,” Sideris told investors. “We continue to challenge ourselves to find new ways to deliver affordable energy for our customers.”
All in all, “affordability” and “affordable” came up 15 times on the call. A year earlier, they came up just three times.
When asked by a Jefferies analyst about how Duke could hit its forecasted earnings growth through 2029, Sideris zeroed in on the regulatory side: “We are very confident in our regulatory outcomes,” he said.
At the same time, Duke told investors that it planned to increase its five-year capital spending plan to $103 billion — “the largest fully regulated capital plan in the industry,” Sideris said.
As far as utilities are concerned, with their multiyear planning and spending cycles, we are only at the beginning of the affordability story.
“The 2026 utility narrative is shifting from ‘capex growth at all costs’ to ‘capex growth with a customer permission slip,’” Dumoulin-Smith wrote in a separate note on Thursday. “We believe it is no longer enough for utilities to say they care about affordability; regulators and investors are demanding proof of proactive behavior.”
If they can’t come up with answers that satisfy their investors, ultimately they’ll have to answer to the voters. Last fall, two Republican utility regulators in Georgia lost their reelection bids by huge margins thanks in part to a backlash over years of rate increases they’d approved.
“Especially as the November 2026 elections approach, utilities that fail to demonstrate concrete mitigants face political and reputational risk and may warrant a credibility discount in valuations, in our view,” Dumoulin wrote.
At the same time, utilities are dealing with increased demand for electricity, which almost necessarily means making more investments to better serve that new load, which can in the short turn translate to higher prices. While large technology companies and the White House are making public commitments to shield existing customers from higher costs, utility rates are determined in rate cases, not in press releases.
“As the issue of rising utility bills has become a greater economic and political concern, investors are paying attention,” Charles Hua, the founder and executive director of PowerLines, told me. “Rising utility bills are impacting the investor landscape just as they have reshaped the political landscape.”
Plus more of the week’s top fights in data centers and clean energy.
1. Osage County, Kansas – A wind project years in the making is dead — finally.
2. Franklin County, Missouri – Hundreds of Franklin County residents showed up to a public meeting this week to hear about a $16 billion data center proposed in Pacific, Missouri, only for the city’s planning commission to announce that the issue had been tabled because the developer still hadn’t finalized its funding agreement.
3. Hood County, Texas – Officials in this Texas County voted for the second time this month to reject a moratorium on data centers, citing the risk of litigation.
4. Nantucket County, Massachusetts – On the bright side, one of the nation’s most beleaguered wind projects appears ready to be completed any day now.