Numerous investors did say, however, that they thought a Republican-controlled White House and perhaps Congress would affect the investment landscape overall. “The real answer is, it will impact,” Rajesh Swaminathan, a partner at Khosla Ventures, told me. “I don’t expect everybody that came in when the going was great to remain when and if the going gets tough with any kind of administration shift,” Juan Muldoon, a partner at the climate software VC Energize Capital, told me.
A Trump presidency puts $1 trillion in overall energy investments at risk, according to a May report from energy consultancy Wood Mackenzie. Much of this depends on whether Trump would take a scalpel or a hammer to IRA incentives, which is difficult to predict. Republican rhetoric is often extreme — gut the IRA, gut the Environmental Protection Agency, maximize fossil fuel production. If actions align with words, climate tech investors ought to have plenty of reasons to be fearful, as the startups they support often owe part of their success to government grants and incentives.
As it stands, there’s widespread agreement that mature technologies like solar and wind will survive and potentially even thrive no matter the changing political tides. But tech that’s yet to come down the cost curve could surely see less investment. This includes electric vehicles, which Trump has alternately derided and praised, though this isn’t really the domain of VCs. Newer technologies that benefit from the tech-neutral clean electricity investment and production tax credits could be at risk, especially energy storage in any form, as the GOP has already introduced a bill that would eliminate these credits. Tech for hard-to-decarbonize industrial sectors such as steel, cement and chemicals production could also take a hit, as emergent solutions are often simply much pricier than business-as-usual.
Some cleantech does benefit from bipartisan support. This includes nuclear — both fission and fusion — as well as technologies that stand to enrich the oil and gas industry, such as advanced geothermal and geologic hydrogen, both of which require drilling expertise. And considering the largest direct air capture deal to date is Occidental Petroleum’s $1.1 billion acquisition of Carbon Engineering, DAC, as well as point source carbon capture and storage, could also grow under Trump, as the oil and gas industry essentially views CCS as a pathway towards the continued production of fossil fuels.
The rest of the hydrogen industry is a jump ball. Green hydrogen made from renewable-powered electrolyzers is expensive and the proposed strict rules that would allow it to qualify for the most generous tax credit are likely goners. But a fossil-fuel based hydrogen economy is certainly an option — although not one that will do much for the climate.
Essentially, though, a number of investors and policy wonks told me that they simply don’t expect the GOP’s bark to match its bite when it comes to completely repealing or seriously altering many of the IRA’s key provisions, instead trusting that legislators will recognize the law’s economic benefits, even if they’re not advertising them.
Although the first Trump administration was undoubtedly disastrous for climate policy, it’s true that many of Trump’s more extreme ambitions never materialized. His budget proposals regularly recommended major funding cuts to the EPA as well as the Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, and called for eliminating key DOE agencies like the Loan Programs Office and the energy tech-focused ARPA-E. But Congress ultimately rejected all these proposals. Funding for both the EPA and EEREtrended upwards, as did funding for clean energy research and development more broadly.
But the IRA didn’t exist then, and now that it does, the bill has become a major recipient of Republican ire. “Precedent tells you it might not be as drastic as you think,” Ben Brenner, senior vice president at the climate-focused government affairs and advisory firm Boundary Stone Partners, told me. “But the environment is very target rich now.”
Brenner noted that the 45X advanced manufacturing production tax credit, for instance, has helped incentivize the expansion of the largest solar manufacturing facility in the U.S. in Dalton, Georgia, Representative Marjorie Taylor-Greene’s territory. Were Republicans to bring it up for full or partial repeal, Brenner thinks results would fall along partisan lines. “If we’re banking on the fact that Marjorie Taylor Greene is going to vote with Democrats on this, we’re fooling ourselves, right? That is not a real viable political strategy.”
In the end, elected officials are responsible to voters. You might think that, because IRA benefits are largely flowing to red states, that will lead to a groundswell of citizen support, but Brenner told me that’s a risky assumption to make. “Wow, it would be nice to think, in theory, that people respond to political incentives in that way,” he said. But “there’s a plenty broad and big enough body of data to show that isn’t necessarily how people react politically.”
That matters for venture capitalists, because while they might view themselves as insulated from the whims of government, a 2023 analysis by ImpactAlpha shows how interconnected the ecosystems are. The analysis, which groups climate tech investors into clusters based on who they frequently co-invest with, found that two of the most central climate “investors” in the network are the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy, which provide grants to climate-focused startups. It also showed that government grants markedly increase a startup’s chance of survival and ability to raise additional capital in early funding rounds.
If government can’t be a reliable partner to private industry, Aliya Haq, vice president of U.S. policy and advocacy at Breakthrough Energy, told me, “the private sector can’t move forward. Companies can’t figure out what facilities they can build, investors don’t know what actually makes sense to put money into.” (Breakthrough Energy is the umbrella organization for the climate tech VC firm Breakthrough Energy Ventures.)
On an individual level, though, many investors beg to differ, saying that as accelerative as government support can be, they invest in companies that can weather the inevitable vagaries of politics. “The most important climate investing is investing in assets that are long lived, and those things have to be durable across administrations,” Jonah Goldman, head of external affairs and impact at the sustainable infrastructure investment firm Generate Capital, told me.
That was a common refrain. “We’ve invested under a Republican president, a Democratic president,”Muldoon told me. “When we talk about a transition, it needs to span changes in political regimes.”
Clay Dumas, a founding partner at Lowercarbon Capital who used to work in the Obama White House, agreed. “If you were depending on a big premium to sell your products at scale, you were in trouble before the IRA, and you’re going to be in trouble no matter who is president next year,” he told me.
At the same time, there’s no denying that investment is down. A recent report from the market intelligence firm Sightline Climate indicated that climate tech funding in the first half of 2024 fell to 2020 levels, which aligns with a downturn in the VC market at large. The assumption is that it’s at least partially due to investors taking a “wait-and-see” approach ahead of November, although other factors such as high interest rates and continued inflation could also be playing a role. The landscape has been especially tough for startups that have already raised a few rounds, as it now takes about 2.5 times longer to raise a Series B as it did in 2021, when the climate tech market was white hot.
“Those emerging technologies absolutely need government partnership to be able to get across the Valley of Death, to be able to scale, to be able to compete on a level playing field with fossil fuels,” Haq told me.
Even if government does pull way back, Muldoon told me that other sources of funding could step in — universities, private research organizations, family offices and other forms of philanthropic dollars might turn to support climate tech. Still though, he admits that “it doesn’t necessarily fill the void.”
But Haq and many of the investors I spoke with are hanging onto the belief that there won’t necessarily be a void to fill — that the benefits of government investment in climate tech will prevail in the face of deep partisan divides, giving private investors the confidence they need to keep the money coming.
“I hold out hope that there’s enough rationality still left in politics, despite the messaging but in the reality of policymaking, that it doesn’t matter what color your shirt is,” Haq told me. “What matters is whether or not there are jobs in your district, whether there is strong U.S. competitiveness, whether the communities in your state have a strong tax base.”
Fingers crossed.
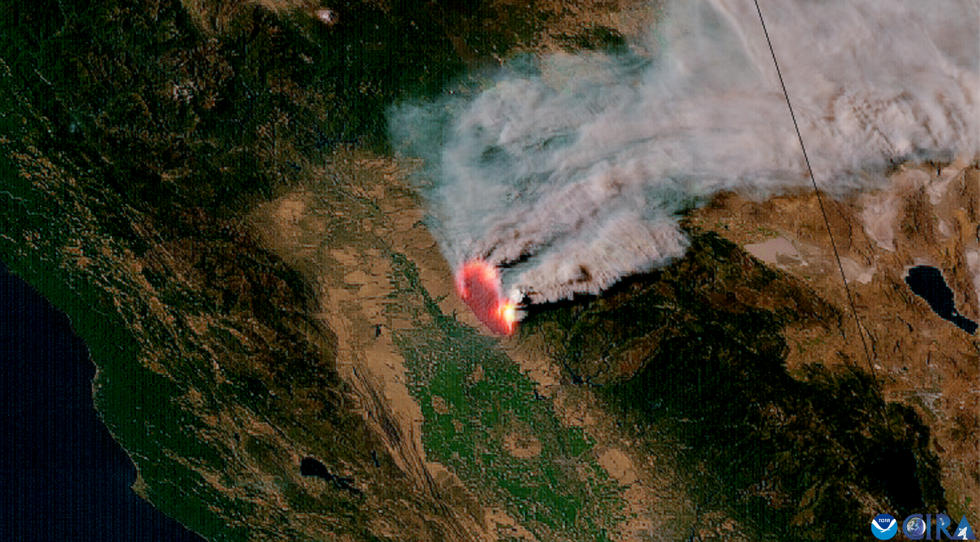




 The Park Fire burns in California.
The Park Fire burns in California.


