You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Is the ocean warming up because too little dust is blowing over from the Sahara?

Lately, the North Atlantic Ocean has been more than just hot. It has been anomalously, weirdly hot. On Sunday, the ocean’s average surface temperature was 74 degrees Fahrenheit, or 23 degrees Celsius — a number normally seen a month from now, in late July. The Atlantic was warmer last month than in any previous May since 1850, according to the Met Office, the United Kingdom’s national weather service. Even more impressively, it beat the previous record by more than any previous record, for any month, has been broken. June seems virtually guaranteed to set another all-time high.
This outrageous warmth is primarily caused by climate change. And in climate science, it is generally not good news when a year’s temperature line is so immediately visible above the pack:
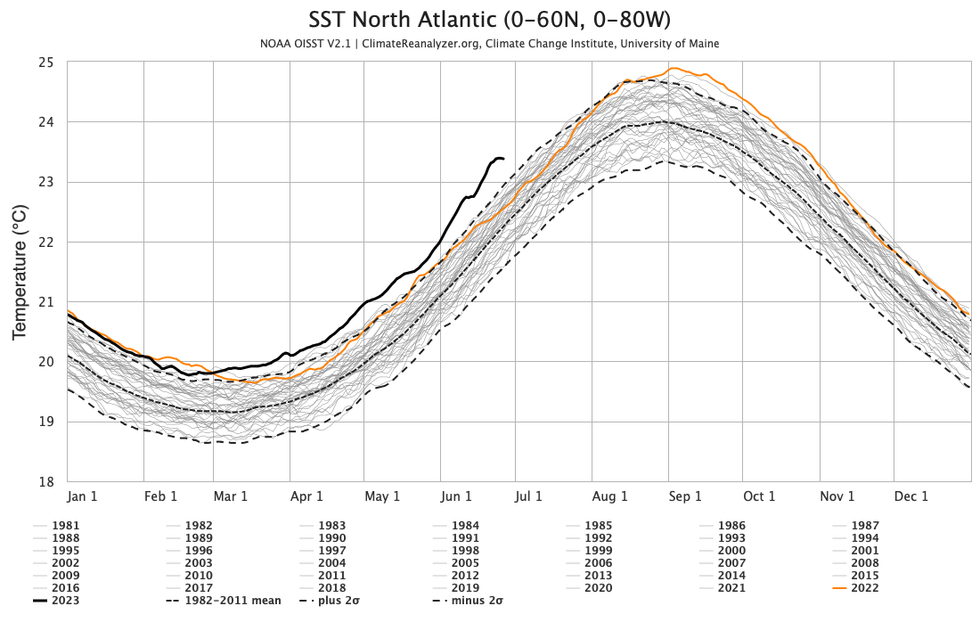
The heat wave is particularly intense in the North Atlantic’s eastern half, which runs from Mauritania to Portugal, France, and the British Isles. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the marine heat wave around the United Kingdom qualifies as a Level 5, or “beyond extreme,” event.
Such warm water would normally give rise to enormous hurricanes. And the western Atlantic has been off to a productive start, creating Tropical Storms Brett and Cindy earlier this month. But since the western Atlantic, which borders North America and the Caribbean, has been chillier, those storms have been unable to survive the journey across the ocean and have been torn apart by wind shear.
Under other circumstances, a marine heat wave of this magnitude would be dangerous for underwater animals and plants — but perhaps a curiosity for land-dwelling humans. Of course, any anomaly of this magnitude — more than two standard deviations above the trend — is extremely concerning and might raise fears that the planet has entered some kind of new normal. The Atlantic’s outrageous warmth has also attracted wider attention because it raises one of the most controversial questions in climate science: Did we accidentally stop geoengineering the oceans?
Three years ago, the United Nations agency that regulates shipping mandated that cargo ships switch from the high-sulfur form of fuel that they were previously using to a cleaner, lower-sulfur type of fuel. When burned, sulfur creates a pollutant called sulfur dioxide, which causes haze, acid rain, and health problems. The mandate worked: Ships have moved away from high-sulfur fuels, which has significantly cut aerosol emissions.
Which seems like an environmental-policy success story. Except that Leon Simons, a researcher at the Dutch chapter of the Club of Rome, argues that it was a grave mistake. Aerosol pollution reflects the sun’s rays back into space: It’s not wrong to see it as a form of solar-radiation management, or geoengineering. Aerosol emissions cool the planet by about 0.5 degrees Celsius, or about 1 degree Fahrenheit, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (Aerosol pollution doesn’t just refer to sulfur dioxide, but to any small particle of a solid or liquid that is larger than a molecule but small enough to float in the air.)
When ships began burning low-sulfur fuel, they reduced some of this net cooling effect — even as they kept pouring carbon dioxide and other climate pollution into the atmosphere. Simons asserts that this inadvertent end to geoengineering is partially to blame for the ongoing heat wave afflicting the world’s oceans.
Other researchers are far less certain. Brian McNoldy, a senior research scientist at the University of Miami, told me that the low-sulfur timeline doesn’t add up. Cargo ships had to stop using high-sulfur fuels by January 1, 2020, and sulfur dioxide and aerosols only persist in the atmosphere for a few days or weeks. Those cooling aerosols rained out two and a half years ago. So why did the Atlantic Ocean start cooking in February of this year?
“I don’t totally buy the low-sulfur fuels. It doesn’t explain the past two or three months becoming abruptly record-breaking,” he said. “It might be a driver, but it’s not the reason.”
He explains the North Atlantic heat wave by looking to two other far more weather-related factors. First, he said, the Sahara Desert is generating less dust than it normally does. Every spring and summer, winds moving across northern Africa toss up enormous amounts of sand and dust from the Sahara — so much that it creates a recognizably beige haze over the North Atlantic. Like any other aerosol, that Saharan dust reflects sunlight and cools the Earth’s surface.
In a normal year, so much of that dust would have been kicked up by now that it would have blown all the way to South Florida, according to Michael Lowry, a meteorologist at ABC 10, a Miami news station. But this year, winds haven’t picked up as much dust, and the first major Saharan dust haze only appeared in the past week or so. The satellite DSCOVR picked up the first images of that dust storm on Saturday:
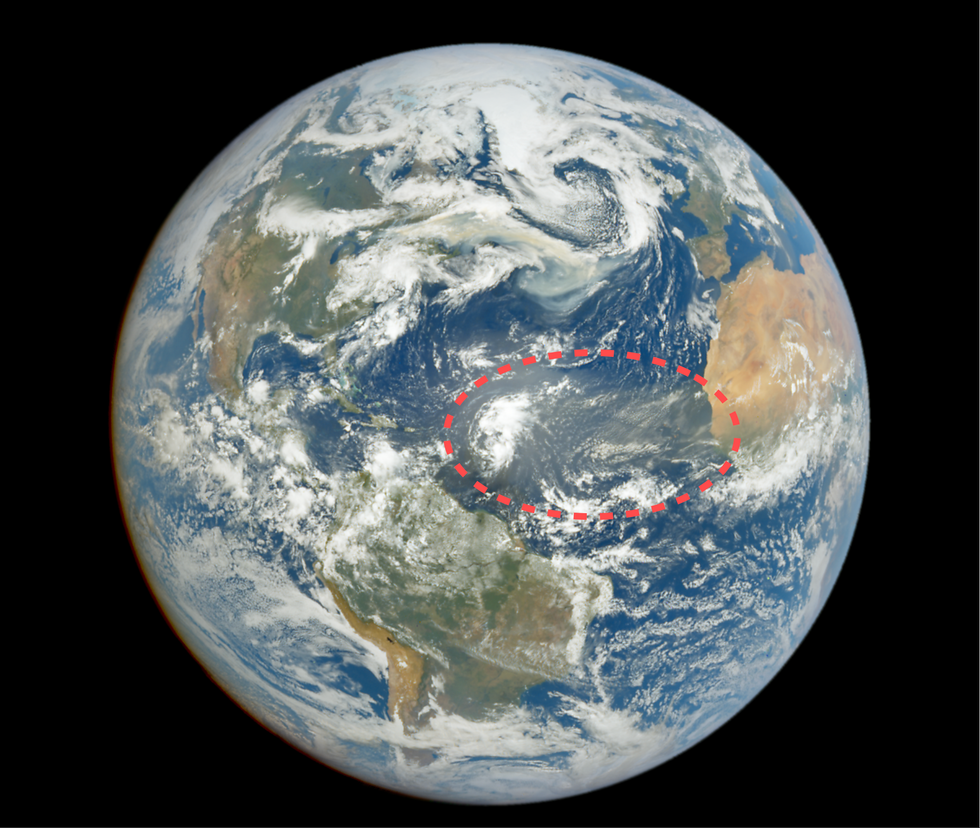
With less dust to reflect the sun’s rays, more have reached the ocean — and warmed its surface.
Second, the weather over the North Atlantic has been unusually stagnant. The wind plays a big role in warming up or cooling down the ocean surface: When winds push the oceans around a lot, surface water tends to mix with deeper water and the air, producing a cooling effect; when winds slacken, the sea sits stagnant and heats up.
The winds have been still lately. There’s a “large-scale blocking pattern” in the jet stream that is preventing storms from moving across the North Atlantic, and generally discouraging winds from pushing around the sea surface, McNoldy said.
The cause of all this stagnation is an atypically weak “Azores High,” a quasi-permanent high pressure system that sits over the North Atlantic throughout the year. It hasn’t drawn in Saharan dust or generated winds to push ocean water around, turning the western Atlantic into the planetary equivalent of a kiddie pool on a hot day. “It’s allowing the ocean to really cook,” McNoldy said.
The warmth is now so pronounced that even a change in weather won’t drive it out for some time. Even if the circumstances causing the warming were to fade now, McNoldy told me, the ocean is “not gonna get back to normal any time soon.”
That could eventually cause problems for folks in the Americas. Right now, the western Atlantic is generating storms like it’s the late summer, while the cooler eastern Atlantic is tearing them apart. Were the eastern Atlantic to get just a little warmer, it might let those storms survive or even strengthen them — leading to an unusually strong hurricane season.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The attacks on Iran have not redounded to renewables’ benefit. Here are three reasons why.
The fragility of the global fossil fuel complex has been put on full display. The Strait of Hormuz has been effectively closed, causing a shock to oil and natural gas prices, putting fuel supplies from Incheon to Karachi at risk. American drivers are already paying more at the pump, despite the United States’s much-vaunted energy independence. Never has the case for a transition to renewable energy been more urgent, clear, and necessary.
So despite the stock market overall being down, clean energy companies’ shares are soaring, right?
Wrong.
First Solar: down over 1% on the day. Enphase: down over 3%. Sunrun: down almost 8%; Tesla: down around 2.5%.
Why the slump? There are a few big reasons:
Several analysts described the market action today as “risk-off,” where traders sell almost anything to raise cash. Even safe haven assets like U.S. Treasuries sold off earlier today while the U.S. dollar strengthened.
“A lot of things that worked well recently, they’re taking a big beating,” Gautam Jain, a senior research scholar at the Columbia University Center on Global Energy Policy, told me. “It’s mostly risk aversion.”
Several trackers of clean energy stocks, including the S&P Global Clean Energy Transition Index (down 3% today) or the iShares Global Clean Energy ETF (down over 3%) have actually outperformed the broader market so far this year, making them potentially attractive to sell off for cash.
And some clean energy stocks are just volatile and tend to magnify broader market movements. The iShares Global Clean Energy ETF has a beta — a measure of how a stock’s movements compare with the overall market — higher than 1, which means it has tended to move more than the market up or down.
Then there’s the actual news. After President Trump announced Tuesday afternoon that the United States Development Finance Corporation would be insuring maritime trade “for a very reasonable price,” and that “if necessary” the U.S. would escort ships through the Strait of Hormuz, the overall market picked up slightly and oil prices dropped.
It’s often said that what makes renewables so special is that they don’t rely on fuel. The sun or the wind can’t be trapped in a Middle Eastern strait because insurers refuse to cover the boats it arrives on.
But what renewables do need is cash. The overwhelming share of the lifetime expense of a renewable project is upfront capital expenditure, not ongoing operational expenditures like fuel. This makes renewables very sensitive to interest rates because they rely on borrowed money to get built. If snarled supply chains translate to higher inflation, that could send interest rates higher, or at the very least delay expected interest rate cuts from central banks.
Sustained inflation due to high energy prices “likely pushes interest rate cuts out,” Jain told me, which means higher costs for renewables projects.
While in the long run it may make sense to respond to an oil or natural gas supply shock by diversifying your energy supply into renewables, political leaders often opt to try to maintain stability, even if it’s very expensive.
“The moment you start thinking about energy security, renewables jump up as a priority,” Jain said. “Most countries realize how important it is to be independent of the global supply chain. In the long term it works in favor of renewables. The problem is the short term.”
In the short term, governments often try to mitigate spiking fuel prices by subsidizing fossil fuels and locking in supply contracts to reinforce their countries’ energy supplies. Renewables may thereby lose out on investment that might more logically flow their way.
The other issue is that the same fractured supply chain that drives up oil and gas prices also affects renewables, which are still often dependent on imports for components. “Freight costs go up,” Jain said. “That impacts clean energy industry more.”
As for the Strait of Hormuz, Trump said the Navy would start escorting ships “as soon as possible.”
“It is difficult to imagine more arbitrary and capricious decisionmaking than that at issue here.”
A federal court shot down President Trump’s attempt to kill New York City’s congestion pricing program on Tuesday, allowing the city’s $9 toll on cars entering downtown Manhattan during peak hours to remain in effect.
Judge Lewis Liman of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York ruled that the Trump administration’s termination of the program was illegal, writing, “It is difficult to imagine more arbitrary and capricious decisionmaking than that at issue here.”
So concludes a fight that began almost exactly one year ago, just after Trump returned to the White House. On February 19, 2025, the newly minted Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy sent a letter to Kathy Hochul, the governor of New York, rescinding the federal government’s approval of the congestion pricing fee. President Trump had expressed concerns about the program, Duffy said, leading his department to review its agreement with the state and determine that the program did not adhere to the federal statute under which it was approved.
Duffy argued that the city was not allowed to cordon off part of the city and not provide any toll-free options for drivers to enter it. He also asserted that the program had to be designed solely to relieve congestion — and that New York’s explicit secondary goal of raising money to improve public transit was a violation.
Trump, meanwhile, likened himself to a monarch who had risen to power just in time to rescue New Yorkers from tyranny. That same day, the White House posted an image to social media of Trump standing in front of the New York City skyline donning a gold crown, with the caption, "CONGESTION PRICING IS DEAD. Manhattan, and all of New York, is SAVED. LONG LIVE THE KING!"
New York had only just launched the tolling program a month earlier after nearly 20 years of deliberation — or, as reporter and Hell Gate cofounder Christopher Robbins put it in his account of those years for Heatmap, “procrastination.” The program was supposed to go into effect months earlier before, at the last minute, Hochul tried to delay the program indefinitely, claiming it was too much of a burden on New Yorkers’ wallets. She ultimately allowed congestion pricing to proceed with the fee reduced from $15 during peak hours to $9, and thereafter became one of its champions. The state immediately challenged Duffy’s termination order in court and defied the agency’s instruction to shut down the program, keeping the toll in place for the entirety of the court case.
In May, Judge Liman issued a preliminary injunction prohibiting the DOT from terminating the agreement, noting that New York was likely to succeed in demonstrating that Duffy had exceeded his authority in rescinding it.
After the first full year the program was operating, the state reported 27 million fewer vehicles entering lower Manhattan and a 7% boost to transit ridership. Bus speeds were also up, traffic noise complaints were down, and the program raised $550 million in net revenue.
The final court order issued Tuesday rejected Duffy’s initial arguments for terminating the program, as well as additional justifications he supplied later in the case.
“We disagree with the court’s ruling,” a spokesperson for the Transportation Department told me, adding that congestion pricing imposes a “massive tax on every New Yorker” and has “made federally funded roads inaccessible to commuters without providing a toll-free alternative.” The Department is “reviewing all legal options — including an appeal — with the Justice Department,” they said.
Current conditions: A cluster of thunderstorms is moving northeast across the middle of the United States, from San Antonio to Cincinnati • Thailand’s disaster agency has put 62 provinces, including Bangkok, on alert for severe summer storms through the end of the week • The American Samoan capital of Pago Pago is in the midst of days of intense thunderstorms.
We are only four days into the bombing campaign the United States and Israel began Saturday in a bid to topple the Islamic Republic’s regime. Oil prices closed Monday nearly 9% higher than where trading started last Friday. Natural gas prices, meanwhile, spiked by 5% in the U.S. and 45% in Europe after Qatar announced a halt to shipments of liquified natural gas through the Strait of Hormuz, which tapers at its narrowest point to just 20 miles between the shores of Iran and the United Arab Emirates. It’s a sign that the war “isn’t just an oil story,” Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote yesterday. Like any good tale, it has some irony: “The one U.S. natural gas export project scheduled to start up soon is, of all things, a QatarEnergy-ExxonMobil joint venture.” Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer further explored the LNG angle with Eurasia Group analyst Gregory Brew on the latest episode of Shift Key.
At least for now, the bombing of Iranian nuclear enrichment sites hasn’t led to any detectable increase in radiation levels in countries bordering Iran, the International Atomic Energy Agency said Monday. That includes the Bushehr nuclear power plant, the Tehran research reactor, and other facilities. “So far, no elevation of radiation levels above the usual background levels has been detected in countries bordering Iran,” Director General Rafael Grossi said in a statement.
Financial giants are once again buying a utility in a bet on electricity growth. A consortium led by BlackRock subsidiary Global Infrastructure Partners and Swedish private equity heavyweight EQT announced a deal Monday to buy utility giant AES Corp. The acquisition was valued at more than $33 billion and is expected to close by early next year at the latest. “AES is a leader in competitive generation,” Bayo Ogunlesi, the chief executive officer of BlackRock’s Global Infrastructure Partners, said in a statement. “At a time in which there is a need for significant investments in new capacity in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution, especially in the United States of America, we look forward to utilizing GIP’s experience in energy infrastructure investing, as well as our operational capabilities to help accelerate AES’ commitment to serve the market needs for affordable, safe and reliable power.” The move comes almost exactly a year after the infrastructure divisions at Blackstone, the world’s largest alternative asset manager, bought the Albuquerque-based utility TXNM Energy in an $11.5 billion gamble on surging power demand.
China’s output of solar power surpassed that of wind for the first time last year as cheap panels flooded the market at home and abroad. The country produced nearly 1.2 million gigawatt-hours of electricity from solar power in 2025, up 40% from a year earlier, according to a Bloomberg analysis of National Bureau of Statistics data published Saturday. Wind generation increased just 13% to more than 1.1 gigawatt-hours. The solar boom comes as Beijing bolsters spending on green industry across the board. China went from spending virtually nothing on fusion energy development to investing more in one year than the entire rest of the world combined, as I have previously reported. To some, China is — despite its continued heavy use of coal — a climate hero, as Heatmap’s Katie Brigham has written.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:

Canada and India have a longstanding special friendship on nuclear power. Both countries — two of the juggernauts of the 56-country Commonwealth of Nations — operate fleets that rely heavily on pressurized heavy water reactors, a very different design than the light water reactors that make up the vast majority of the fleets in Europe and the United States. Ottawa helped New Delhi build its first nuclear plants. Now the two countries have renewed their atomic ties in what the BBC called a “landmark” deal Monday. As part of the pact, India signed a nine-year agreement with Canada’s largest uranium miner, Cameco, to supply fuel to New Delhi’s growing fleet of seven nuclear plants. The $1.9 billion deal opens a new market for Canada’s expanding production of uranium ore and gives India, which has long worried about its lack of domestic deposits, a stable supply of fuel.
India, meanwhile, is charging ahead with two new reactors at the Kaiga atomic power station in the southwestern state of Karnataka. The units are set to be IPHWR-700, natively designed pressurized heavy water reactors. Last week, the Nuclear Power Corporation of India poured the first concrete on the new pair of reactors, NucNet reported Monday.
The Spanish refiner Moeve has decided to move forward with an investment into building what Hydrogen Insight called “a scaled-back version” of the first phase of its giant 2-gigawatt Andalusian Green Hydrogen Valley project. Even in a less ambitious form, Reuters pegged the total value of the project at $1.2 billion. Meanwhile in the U.S., as I wrote yesterday, is losing major projects right as big production facilities planned before Trump returned to office come online.
Speaking of building, the LEGO Group is investing another $2.8 million into carbon dioxide removal. The Danish toymaker had already pumped money into carbon-removal projects overseen by Climate Impact Partners and ClimeFi. At this point, LEGO has committed $8.5 million to sucking planet-heating carbon out of the atmosphere, where it circulates for centuries. “As the program expands, it is helping to strengthen our understanding of different approaches and inform future decision-making on how carbon removal may complement our wider climate goals,” Annette Stube, LEGO’s chief sustainability officer, told Carbon Herald.