You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On global green energy capacity, EV charging infrastructure, and bird flu

Current conditions: The parade of winter storms continues today across much of the U.S. • The Congo River is at its highest level in more than 60 years after intense rains • This weekend's NFL game between the Kansas City Chiefs and the Miami Dolphins could be the coldest game in franchise history.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is feeling optimistic about the green energy transition. In its new Renewables 2023 report, released today, the agency says the world added 50% more renewable capacity last year than in 2022. This kind of momentum could get us close to the COP28 goal of tripling global renewable energy capacity by 2030, but governments must do more to get us across the finish line, the IEA concluded.
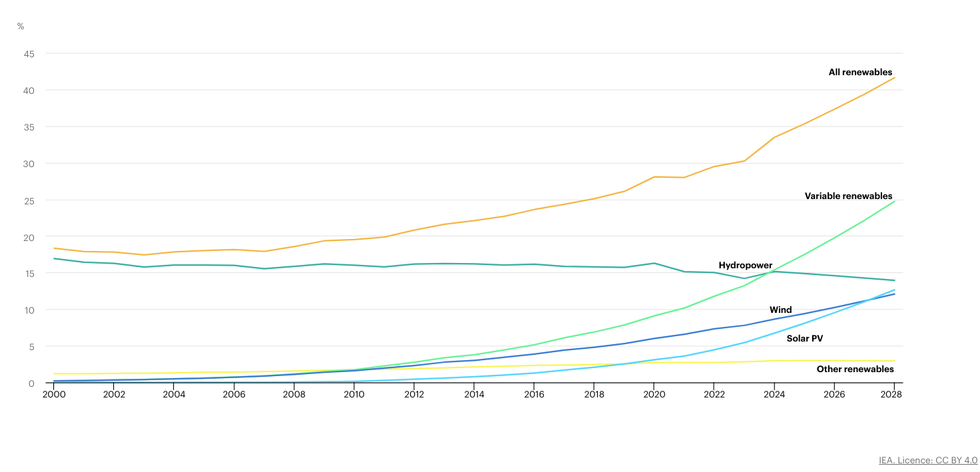
Renewable capacity hit almost 510 gigawatts (GW) in 2023, with China seeing the most explosive growth, but the U.S., Europe, and Brazil also hit all-time highs. Solar was the real workhorse, accounting for 75% of the expansion. The report includes this quite astonishing statistic: “The world is on course to add more renewable capacity in the next five years than has been installed since the first commercial renewable energy power plant was built more than 100 years ago.”
The current growth rate puts the world on course to increase renewable capacity by two-and-a-half times by 2030, said IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol. He calls on governments to prioritize policy changes that speed up renewables development, and highlights the need for more financing in developing countries to help them with the energy transition. “Success in meeting the tripling goal will hinge on this,” Birol said.
The Biden administration has announced the recipients of infrastructure grants amounting to $623 million focused heavily on expanding the national electric vehicle charging network. The administration has a goal of installing at least 500,000 public chargers by 2030 – a Department of Energy report put the number at around 140,000 at the end of 2022, installed across 53,000 stations. Huge gaps in coverage remain across the country, fueling range anxiety among would-be EV buyers. The new grants are split between 22 states and Puerto Rico and will support 47 infrastructure projects, including 7,500 charging ports. About half of the money will go to “community” projects in urban and rural communities. The other half will go to “corridor” projects along roadways that are expected to “fill gaps in the core national charging and alternative-fueling network,” according to the U.S. Department of Transportation’s press release.
It appears that Republicans have a new favorite boogeyman buzzword this election season, writes Heatmap’s Charu Sinha. The word? “Green.” It was on every Republican presidential hopeful’s lips on Wednesday, both at CNN’s debate in Iowa between Florida Governor Ron DeSantis and former UN Ambassador Nikki Haley, and at former President Donald Trump’s competing town hall on Fox News. DeSantis reiterated his promise to reverse President Biden’s clean energy policy, facetiously calling it the “Green New Deal.” Haley took her own stab at Biden’s “green subsidies” while answering a question about funding Ukraine and Israel. And for his part, Trump said Biden should “go into the energy business instead of this green new scam business that they’re in."
Sinha notes that “at no point during the fifth Republican presidential debate or Trump’s town hall was the Inflation Reduction Act mentioned by name.”
Bird flu strain H5N1 has been transmitted to seals in Antarctica, scientists have confirmed, an alarming development that raises concerns about how easily the virus can spread among mammals. The virus, which has killed millions of birds across the world, was detected in elephant seals and fur seals on the sub-Antarctic island of South Georgia. Researchers believe migrating birds from South America brought the virus with them. Last week officials in Alaska confirmed a polar bear had died from the disease. “If a bird is weakened by avian influenza, or succumbs to it, polar bears aren’t fussy about what eat,” Andrew Derocher, a polar bear biologist at the University of Alberta, told Reuters. “If it’s dead and it’s edible they’ll probably eat it. There is a high likelihood of an interaction between climate change, avian influenza, bird mortality, and polar bears.”
The Northern Hemisphere is seeing less snowpack due to human-caused climate change, according to a new study published in Nature. The researchers examined data from hundreds of river basins across the U.S. and Europe and found that about 20% of them saw a decline in snowpack – which is the total mass of snow that accumulates on the ground – over the last 40 years. “We see a pattern of snow change that is only consistent with human emissions,” Alex Gottlieb, a graduate student at Dartmouth College and lead author on the new study, told The Washington Post. The researchers also seem to have discovered a snow “cliff” – a tipping point temperature of 17 degrees Fahrenheit – at which snow loss accelerates very quickly. They say more than 2 billion people who rely on snow melt as a source of water are near the cliffedge.
The cost of charging an EV in the U.S. is roughly equivalent to a gasoline price of $1 to $2 per gallon, with the national average being $1.41 per eGallon, according to Yale Climate Connections.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The lost federal grants represent about half the organization’s budget.
The Interstate Renewable Energy Council, a decades-old nonprofit that provides technical expertise to cities across the country building out renewable clean energy projects, issued a dramatic plea for private donations in order to stay afloat after it says federal funding was suddenly slashed by the Trump administration.
IREC’s executive director Chris Nichols said in an email to all of the organization’s supporters that it has “already been forced to lay off many of our high-performing staff members” after millions of federal dollars to three of its programs were eliminated in the Trump administration’s shutdown-related funding cuts last week. Nichols said the administration nixed the funding simply because the nonprofit’s corporation was registered in New York, and without regard for IREC’s work with countless cities and towns in Republican-led states. (Look no further than this map of local governments who receive the program’s zero-cost solar siting policy assistance to see just how politically diverse the recipients are.)
“Urgent: IREC Needs You Now,” begins Nichols’ email, which was also posted to the organization’s website in full. “I need to be blunt: IREC, our mission, and the clean energy progress we lead is under assault.”
In an interview this afternoon, Nichols told me the DOE funding added up to at least $8 million and was set to be doled out over multiple years. She said the organization laid off eight employees — roughly a third of the organization’s small staff of fewer than two-dozen people — because the money lost for this year represented about half of IREC’s budget. She said this came after the organization also lost more than $4 million in competitive grant funding for apprenticeship training from the Labor Department because the work “didn’t align with the administration’s priorities.”
Nichols said the renewable energy sector was losing the crucial “glue” that holds a lot of the energy transition together in the funding cuts. “I’m worried about the next generation,” she told me. “Electricity is going to be the new housing [shortage].”
IREC has been a leading resource for the entire solar and transmission industry since 1982, providing training assistance and independent analysis of the sector’s performance, and develops stuff like model interconnection standards and best practices for permitting energy storage deployment best practices. The organization boasts having worked on developing renewable energy and training local workforces in more than 35 states. In 2021, it absorbed another nonprofit, The Solar Foundation, which has put together the widely used annual Solar Jobs Census since 2010.
In other words, this isn’t something new facing a potentially fatal funding crisis — this is the sort of bedrock institutional know-how that will take a long time to rebuild should it disappear.
To be sure, IREC’s work has received some private financing — as demonstrated by its solar-centric sponsorships page — but it has also relied on funding from Energy Department grants, some of which were identified by congressional Democrats as included in DOE’s slash spree last week. In addition, IREC has previously received funding from the Labor Department and National Labs, the status of which is now unclear.
The delayed vote on a net-zero standard for the International Maritime Organization throws some of the industry’s grandest plans into chaos.
Today, members of the International Maritime Organization decided to postpone a major vote on the world’s first truly global carbon pricing scheme. The yearlong delay came in response to a pressure campaign led by the U.S.
The Net-Zero Framework — initially approved in April by an overwhelming margin and long expected to be formally adopted today — would establish a legally binding requirement for the shipping industry to cut its emissions intensity, with interim steps leading to net zero by 2050.
In the intervening months, however, U.S. opposition has gotten much louder. On Thursday, Trump posted on Truth Social that he’s “outraged that the International Maritime Organization is voting in London this week to pass a global Carbon Tax.” He also took the extraordinary step of threatening not to comply with the rules. “The United States will NOT stand for this Global Green New Scam Tax on Shipping, and will not adhere to it in any way, shape, or form.” If the framework ever does pass, noncompliance could subject U.S. vessels to fines or even denial of entry at the ports of IMO member countries, potentially setting off a cycle of retaliatory measures from all sides.
No specific date has yet been scheduled for the forthcoming vote, which will be taken again a year from now. That throws plans for the world’s largest shipping companies — some of which have already taken expensive measures to decarbonize their fleets — into turmoil. The framework would have marked a major turning point for a sector that’s responsible for 3% of global emissions, of course. But even more importantly, it would have made a range of decarbonization technologies — from advanced batteries and clean fuels to wind-assisted propulsion and onboard carbon capture — far more viable and attractive to investors.
Kate Danaher, managing director of the oceans team at S2G Investments, has a vested interest in the frameworks’ eventual passage. “Over the past two years people have really started investing around the anticipation of something like the Net-Zero Framework being adopted,” Danaher told me. For its part, S2G has invested in Sofar Ocean, which focuses on fuel savings through route optimization, battery company Echandia which is aiming to electrify smaller vessels, and ocean data and monitoring companies Xocean and Apeiron Lab.
The new rules were originally set to take effect in 2028, and would apply to large vessels — ships of 5,000 gross tonnage or more — involved in international voyages. Qualifying ships would be assigned a base target for emissions intensity and a stricter “direct compliance target.” For every metric ton of CO2 equivalent that exceeds the compliance target but falls below the base target, ships must pay $100. For all emissions that exceed the base target, ships must pay $380 per metric ton. Noncompliant ships would pay these penalties by purchasing so-called “remedial units” from a central IMO registry, while the cleanest vessels — those performing better than their compliance targets — would earn surplus units they can sell to others or bank for future use.
Green shipping fuels such as e-methanol, e-hydrogen, and e-ammonia — all produced from green hydrogen using renewable electricity — stand to be the biggest winners, she said. “A new fuel would completely decarbonize the industry. That is 10 years out, and is completely contingent on the IMO,” Danaher said, explaining that if the framework ultimately fails, there’s no economic incentive to adopt these more expensive fuels, which also require costly retrofits for existing fleets. But the framework would effectively cause the cost of conventional fuel to rise just as alternative fuels are scaling up, which would allow them to reach parity around 2035, she said.
A specialized agency within the United Nations, the IMO gets its power to set global regulations from the vastness of the ocean itself. Most of the world’s waters exist outside the jurisdiction of any national government. Because of that, IMO member states — which represent the vast majority of global shipping tonnage — have ratified treaties that empower the organization to set safety, security, and environmental standards on the high seas, which members then implement and enforce through their own national laws. Only member states have a stake in IMO policy. Furthermore, vessels that aren’t IMO-compliant face penalties such as fees and even possible detentions when entering the ports of IMO countries.
While IMO decisions are typically made via negotiated consensus, the contentious nature of these new regulations necessitates a vote. U.S. officials celebrated the delay. U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio posted on X that the postponement represents “another HUGE win for @POTUS,” going on to say that “the United States prevented a massive UN tax hike on American consumers that would have funded progressive climate pet projects.”
Along with Secretary of Energy Chris Wright, and Secretary of Transportation Sean Duffy, Rubio last week issued a statement threatening to punish nations that voted in favor of these “activist-driven climate policies” with actions such as banning their ships from U.S. ports, imposing vessel fees, and even leveling sanctions on officials supportive of the regulations.
Saudi Arabia — the world’s second largest oil producer after the U.S. — also strongly opposed the framework, as did a host of other oil-producing Middle Eastern countries, Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Thailand, Russia and Venezuela. Singapore ultimately put forth the motion to delay the adoption vote for a full year and Saudi Arabia called it to a vote. It passed with a simple majority, with 57 countries approving and 49 opposed.
When it comes to costs, Trump officials might actually have a point, Danaher conceded. “Once alternative fuels come online and people are actively paying penalties, it gets a lot more expensive,” she told me. “I don’t see how this isn’t incredibly inflationary to the global market in 10 years.”
Today’s standard low-sulfur fuel, she explained, costs about $500 per metric ton. But reaching the same energy density with e-methanol, for example, could push the price to around $2,000 a metric ton. “That is all going to get passed on, essentially, to the consumer,” she said.
Even so, the framework has the backing of major shipping trade organizations and industry giants alike, from the International Chamber of Shipping to Maersk. As a group of leading international maritime associations put it in an open letter last week, “Only global rules will decarbonise a global industry. Without the Framework, shipping would risk a growing patchwork of unilateral regulations, increasing costs without effectively contributing to decarbonisation.”
Indeed, a universal set of coherent rules is what many in the sector want most, Danaher affirmed. Some voting bodies, such as the EU and Singapore, have already set their own shipping-related emissions requirements, creating a regulatory patchwork that’s both costly and confusing for companies to comply with. “I think most people are like, let’s just do this. Let’s rip the Band-Aid off, and let’s get clarity,” Danaher told me.
In a statement released after the vote’s delay and the conclusion of the IMO’s days-long meeting in London, Thomas A. Kazakos, the shipping chamber’s secretary general, said, “We are disappointed that member states have not been able to agree a way forward at this meeting. Industry needs clarity to be able to make the investments needed to decarbonise the maritime sector, in line with the goals set out in the IMO GHG strategy.”
The delay also risks delegitimizing the power of the IMO as a whole, something the organization’s Secretary-General, Arsenio Dominguez, warned about in the meeting’s opening remarks on Tuesday, when he stated that “Prolonged uncertainty will put off investments and diminish confidence in IMO.”
There would be other ways for shippers to comply with the framework besides switching to e-fuels, Danaher told me. For example, S2G’s portfolio company Sofar Ocean operates a network of ocean sensors designed to improve marine weather predictions and power a route optimization platform that can help ships save time, fuel, and ultimately, emissions.
Software solutions have a pretty low barrier to adoption. But a step up in complexity — and cost — would involve a technology such as wind-assisted propulsion. The companies Norsepower and Anemoi, for example, use a cylindrical “rotor sail” that creates a powerful thrust as it spins, which they say allows for up to 25% to 30% fuel savings. Another approach is the “rigid wing sail,” such as that developed by Bar Technologies. This generates lift in the direction of the ship’s movement with less drag than a normal sail — similar to how an airplane wing works.
Pairing route optimization with wind-assisted propulsion will generate even greater emissions savings, as the software can direct ships towards areas with the most advantageous winds. Given the obvious co-benefits and cost savings stemming from lower fuel use, Danaher thinks this tech could gain traction even if the regulations ultimately fail to pass next year. “I think the adoption curve will still continue without IMO [Net-Zero Framework], but I think it'll be slower,” she told me.
One approach she doesn’t think will be economically viable without the framework is onboard carbon capture. This tech, which traps carbon dioxide from a ship’s exhaust system before it’s released into the atmosphere, is being explored by startups including Seabound — which I reported on last year — and Value Maritime, as well as more established companies such as Mitsubishi and Wartsila. “A lot of the carbon capture technologies have not yet solved for how to turn that captured carbon into a valuable resource, and how to get it off the boat, put it in a pipeline, and sell it,” Danaher told me.” The economic incentive just isn't there without the IMO.”
At the same time, when I talked to one of Seabound’s backers — Clea Kolster, of Lowercarbon Capital — last year, she told me that when it comes to cargo shipping, “carbon capture is probably the only way that you can get a meaningful amount of emissions reductions in any near term way.” And it’s true that alternative fuels will take a while to scale up, so if the framework is ultimately adopted, carbon capture may still have an important role to play — at least that’s what investors and startups alike are banking on. “Everybody's talking about carbon capture in anticipation of this getting adopted,” Danaher told me. “All these vessels are going to be old, they’re going to need to comply, and they’re not going to be able to comply fast enough,” she said.
Amidst the turmoil, one silver lining is that interest in maritime innovation and efficiency appears to be increasing regardless of global frameworks. For one, the surge in global military spending has underscored this tech’s potential for dual-use applications. “A lot of wars happen in and around the oceans, because that’s where we intersect each other the most.” Danaher told me. Many of S2G’s investments in ocean tech have received additional backing from governments and defense agencies looking to make their fleets more efficient, energy resilient, and secure. “Every single one of our ocean tech companies, one of their customers is the government, or many governments,” she said.
It’s an important reminder that there are many practical reasons for investors and states alike to support a decarbonization agenda, regardless of whether the U.S. is on board or not. But a global system of carrots and sticks sure wouldn’t hurt either. And now, we face the uneasy prospect of waiting another year to see whether the shipping industry will resist the Trump-era pushback or abandon its collective ambitions for a decarbonized future.
Amarillo-area residents successfully beat back a $600 million project from Xcel Energy that would have provided useful tax revenue.
Power giant Xcel Energy just suffered a major public relations flap in the Texas Panhandle, scrubbing plans for a solar project amidst harsh backlash from local residents.
On Friday, Xcel Energy withdrew plans to build a $600 million solar project right outside of Rolling Hills, a small, relatively isolated residential neighborhood just north of the city of Amarillo, Texas. The project was part of several solar farms it had proposed to the Texas Public Utilities Commission to meet the load growth created by the state’s AI data center boom. As we’ve covered in The Fight, Texas should’ve been an easier place to do this, and there were few if any legal obstacles standing in the way of the project, dubbed Oneida 2. It was sited on private lands, and Texas counties lack the sort of authority to veto projects you’re used to seeing in, say, Ohio or California.
But a full-on revolt from homeowners and realtors apparently created a public relations crisis.
Mere weeks ago, shortly after word of the project made its way through the small community that is Rolling Hills, more than 60 complaints were filed to the Texas Public Utilities Commission in protest. When Xcel organized a public forum to try and educate the public about the project’s potential benefits, at least 150 residents turned out, overwhelmingly to oppose its construction. This led the Minnesota-based power company to say it would scrap the project entirely.
Xcel has tried to put a happy face on the situation. “We are grateful that so many people from the Rolling Hills neighborhood shared their concerns about this project because it gives us an opportunity to better serve our communities,” the company said in a statement to me. “Moving forward, we will ask for regulatory approval to build more generation sources to meet the needs of our growing economy, but we are taking the lessons from this project seriously.”
But what lessons, exactly, could Xcel have learned? What seems to have happened is that it simply tried to put a solar project in the wrong place, prizing convenience and proximity to an existing electrical grid over the risk of backlash in an area with a conservative, older population that is resistant to change.
Just ask John Coffee, one of the commissioners for Potter County, which includes Amarillo, Rolling Hills, and a lot of characteristically barren Texas landscape. As he told me over the phone this week, this solar farm would’ve been the first utility-scale project in the county. For years, he said, renewable energy developers have explored potentially building a project in the area. He’s entertained those conversations for two big reasons – the potential tax revenue benefits he’s seen elsewhere in Texas; and because ordinarily, a project like Oneida 2 would’ve been welcomed in any of the pockets of brush and plain where people don’t actually live.
“We’re struggling with tax rates and increases and stuff. In the proper location, it would be well-received,” he told me. “The issue is, it’s right next to a residential area.”
Indeed, Oneida 2 would’ve been smack dab up against Rolling Hills, occupying what project maps show would be the land surrounding the neighborhood’s southeast perimeter – truly the sort of encompassing adjacency that anti-solar advocates like to describe as a bogeyman.
Cotton also told me he wasn’t notified about the project’s existence until a few weeks ago, at the same time resident complaints began to reach a fever pitch. He recalled hearing from homeowners who were worried that they’d no longer be able to sell their properties. When I asked him if there was any data backing up the solar farm’s potential damage to home prices, he said he didn’t have hard numbers, but that the concerns he heard directly from the head of Amarillo’s Realtors Association should be evidence enough.
Many of the complaints against Oneida 2 were the sort of stuff we’re used to at The Fight, including fears of fires and stormwater runoff. But Cotton said it really boiled down to property values – and the likelihood that the solar farm would change the cultural fabric in Rolling Hills.
“This is a rural area. There are about 300 homes out there. Everybody sitting out there has half an acre, an acre, two acres, and they like to enjoy the quiet, look out their windows and doors, and see some distance,” he said.
Ironically, Cotton opposed the project on the urging of his constituents, but is now publicly asking Xcel to continue to develop solar in the county. “Hopefully they’ll look at other areas in Potter County,” he told me, adding that at least one resident has already come to him with potential properties the company could acquire. “We could really use the tax money from it. But you just can’t harm a community for tax dollars. That’s not what I’m about.”
I asked Xcel how all this happened and what their plans are next. A spokesperson repeatedly denied my requests to discuss Oneida 2 in any capacity. In a statement, the company told me it “will provide updates if the project is moved to another site,” and that “the company will continue to evaluate whether there is another location within Potter County, or elsewhere, to locate the solar project.”
Meanwhile, Amarillo may be about to welcome data center development because of course, and there’s speculation the first AI Stargate facility may be sited near Amarillo, as well.
City officials will decide in the coming weeks on whether to finalize a key water agreement with a 5,600-acre private “hypergrid” project from Fermi America, a new company cofounded by former Texas governor Rick Perry, says will provide upwards of 11 gigawatts to help fuel artificial intelligence services. Fermi claims that at least 1 gigawatt of power will be available by the end of next year – a lot of power.
The company promises that its “hypergrid” AI campus will use on-site gas and nuclear generation, as well as contracted gas and solar capacity. One thing’s for sure – it definitely won’t be benefiting from a large solar farm nearby anytime soon.