You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On record heat, hurricane warnings, and electric racecars

Current conditions: Nearly 12 inches of rain fell over six hours in Mumbai this morning • Extreme storms on the South African coast are causing shipping delays • July 4 fireworks sparked a forest fire in New Jersey that burned thousands of acres.
Last month was both the hottest June ever recorded, and the 12th month in a row in which average global temperatures broke the 1.5 degrees Celsius warming threshold. Between July 2023 and June 2024, the Earth’s temperature was 1.64 degrees Celsius (or about 3 degrees Fahrenheit) warmer than the pre-industrial average. Global sea surface temperatures were also remarkably warm, averaging 20.85 degrees Celsius, or 69.53 degrees Fahrenheit.
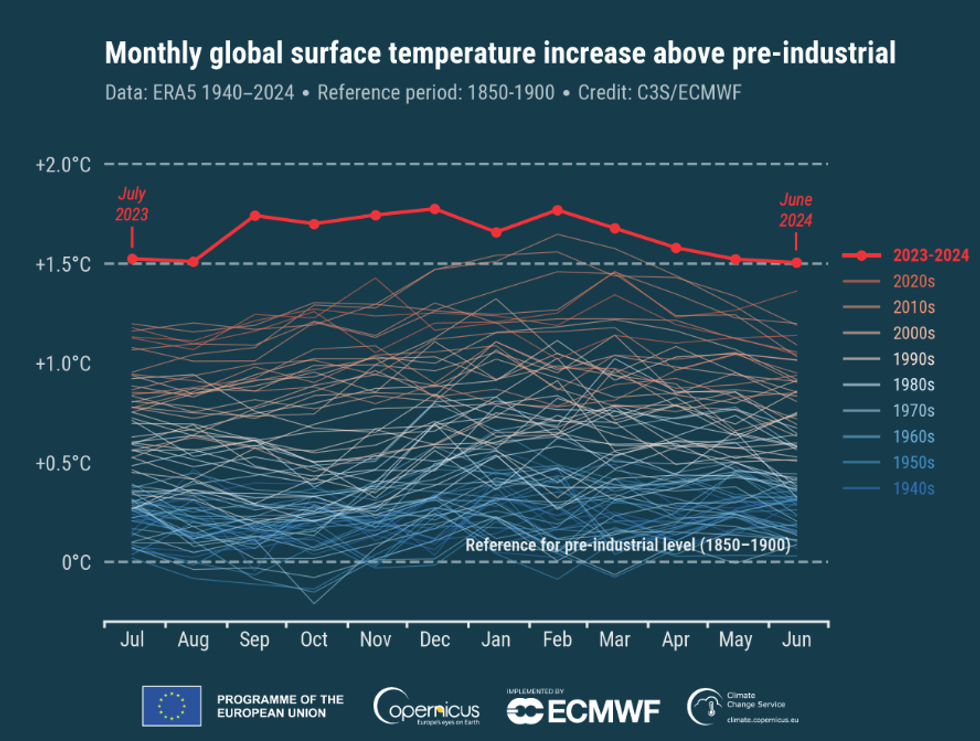
“This is more than a statistical oddity and it highlights a large and continuing shift in our climate,” said Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), which produced the data. “Even if this specific streak of extremes ends at some point, we are bound to see new records being broken as the climate continues to warm. This is inevitable, unless we stop adding greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and the oceans.”
Meanwhile, 10% of the country’s population remains under excessive heat warnings as an extreme heat wave grips states up and down the west coast. “Dozens of daily record high temperatures are forecast to be tied or broken into the work week,” the National Weather Service said. In Phoenix, Arizona, heat-related deaths have nearly doubled this year compared to last.
Hurricane Beryl made landfall on the Texas Gulf Coast this morning as a category 1 storm with top sustained winds of 80 miles per hour. Up to 15 inches of rain could fall on the region, and flooding and dangerous storm surge are expected. More than 100,000 customers are already without power. The storm is also affecting oil and gas operations: The state’s largest ports – including Corpus Christi, the top crude oil export hub in the country – halted all cargo operations and some natural gas storage facilities also closed in preparation for the storm. Beryl killed at least 11 people in the Caribbean over the last week and left islands in ruins. It became the earliest category 5 storm ever recorded in the Atlantic Ocean. Researchers published a report on Friday concluding that human driven climate change likely made Beryl stronger and wetter.
A lawsuit playing out this week in a New Orleans appeals court could be the first test of how courts will treat regulations set by federal agencies after the Supreme Court overturned a 40-year-old precedent, known as the Chevron deference, that deferred to agencies’ interpretations of their own mandates. In this particular case, 25 Republican-led states are challenging a rule from the U.S. Department of Labor that says employee retirement plans can consider ESG factors when deciding where to invest. Conservatives have argued this amounts to politicizing investment decisions. A Texas judge refused to block the rule in 2022, citing Chevron, but now the landscape looks very different. “The trial court expressly relying on Chevron in upholding the ESG regulation ... puts this case on track to be an early harbinger of how courts will address pending cases,” said Julie Stapel, a lawyer with the firm Morgan Lewis & Bockius. The court will begin to hear arguments tomorrow. The fall of Chevron is expected to make it harder for federal agencies to regulate environmental hazards like air and water pollution.
The U.K. has scrapped its ban on onshore wind farms just days after a new Labour government came into power. The ban came into effect in 2015, and was part of a planning policy that required onshore wind projects to prove local communities did not object to new turbines. The new chancellor, Rachel Reeves, called the rule “absurd.” The Labour Party has pledged to double onshore wind energy by 2030 and decarbonize the power sector completely on that same time frame.
How and when Britain goes green matters on a global scale. “Britain is one of history’s major climate polluters,” as The New York Times explained. “It’s where the Industrial Revolution began in the 18th century, giving rise to a global economy driven by coal, oil and gas and with it, the emissions of planet-heating greenhouse gases. So the speed and scale of Britain’s energy transition is likely to be closely watched by other industrialized countries and emerging economies alike.”
NASCAR showed off its first electric racecar in Chicago over the weekend. The ABB NASCAR EV Prototype was developed as part of a partnership between NASCAR, Chevrolet, Ford, Toyota, and electrification company ABB. It hasn’t been driven much yet, and there’s no plan to get rid of gas-powered racers any time soon (in fact NASCAR says it is “committed to the historic role of the combustion engine in racing”), but the prototype is intended to “gauge fan interest in electric racing,” according to The Associated Press. “As more and more customers are buying all-electric vehicles, there will be, we believe, a growing number of people that want to watch full electric racing,” said Mark Rushbrook, global director of Ford Performance Motorsports.

There are now more than 800 carbon removal startups.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
It’s either reassure investors now or reassure voters later.
Investor-owned utilities are a funny type of company. On the one hand, they answer to their shareholders, who expect growing returns and steady dividends. But those returns are the outcome of an explicitly political process — negotiations with state regulators who approve the utilities’ requests to raise rates and to make investments, on which utilities earn a rate of return that also must be approved by regulators.
Utilities have been requesting a lot of rate increases — some $31 billion in 2025, according to the energy policy group PowerLines, more than double the amount requested the year before. At the same time, those rate increases have helped push electricity prices up over 6% in the last year, while overall prices rose just 2.4%.
Unsurprisingly, people have noticed, and unsurprisingly, politicians have responded. (After all, voters are most likely to blame electric utilities and state governments for rising electricity prices, Heatmap polling has found.) Democrat Mikie Sherrill, for instance, won the New Jersey governorship on the back of her proposal to freeze rates in the state, which has seen some of the country’s largest rate increases.
This puts utilities in an awkward position. They need to boast about earnings growth to their shareholders while also convincing Wall Street that they can avoid becoming punching bags in state capitols.
Make no mistake, the past year has been good for these companies and their shareholders. Utilities in the S&P 500 outperformed the market as a whole, and had largely good news to tell investors in the past few weeks as they reported their fourth quarter and full-year earnings. Still, many utility executives spent quite a bit of time on their most recent earnings calls talking about how committed they are to affordability.
When Exelon — which owns several utilities in PJM Interconnection, the country’s largest grid and ground zero for upset over the influx data centers and rising rates — trumpeted its growing rate base, CEO Calvin Butler argued that this “steady performance is a direct result of a continued focus on affordability.”
But, a Wells Fargo analyst cautioned, there is a growing number of “affordability things out there,” as they put it, “whether you are looking at Maryland, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware.” To name just one, Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro said in a speech earlier this month that investor-owned utilities “make billions of dollars every year … with too little public accountability or transparency.” Pennsylvania’s Exelon-owned utility, PECO, won approval at the end of 2024 to hike rates by 10%.
When asked specifically about its regulatory strategy in Pennsylvania and when it intended to file a new rate case, Butler said that, “with affordability front and center in all of our jurisdictions, we lean into that first,” but cautioned that “we also recognize that we have to maintain a reliable and resilient grid.” In other words, Exelon knows that it’s under the microscope from the public.
Butler went on to neatly lay out the dilemma for utilities: “Everything centers on affordability and maintaining a reliable system,” he said. Or to put it slightly differently: Rate increases are justified by bolstering reliability, but they’re often opposed by the public because of how they impact affordability.
Of the large investor-owned utilities, it was probably Duke Energy, which owns electrical utilities in the Carolinas, Florida, Kentucky, Indiana, and Ohio, that had to most carefully navigate the politics of higher rates, assuring Wall Street over and over how committed it was to affordability. “We will never waver on our commitment to value and affordability,” Duke chief executive Harry Sideris said on the company’s February 10 earnings call.
In November, Duke requested a $1.7 billion revenue increase over the course of 2027 and 2028 for two North Carolina utilities, Duke Energy Carolinas and Duke Energy Progress — a 15% hike. The typical residential customer Duke Energy Carolinas customer would see $17.22 added onto their monthly bill in 2027, while Duke Energy Progress ratepayers would be responsible for $23.11 more, with smaller increases in 2028.
These rate cases come “amid acute affordability scrutiny, making regulatory outcomes the decisive variable for the earnings trajectory,” Julien Dumoulin-Smith, an analyst at Jefferies, wrote in a note to clients. In other words, in order to continue to grow earnings, Duke needs to convince regulators and a skeptical public that the rate increases are necessary.
“Our customers remain our top priority, and we will never waver on our commitment to value and affordability,” Sideris told investors. “We continue to challenge ourselves to find new ways to deliver affordable energy for our customers.”
All in all, “affordability” and “affordable” came up 15 times on the call. A year earlier, they came up just three times.
When asked by a Jefferies analyst about how Duke could hit its forecasted earnings growth through 2029, Sideris zeroed in on the regulatory side: “We are very confident in our regulatory outcomes,” he said.
At the same time, Duke told investors that it planned to increase its five-year capital spending plan to $103 billion — “the largest fully regulated capital plan in the industry,” Sideris said.
As far as utilities are concerned, with their multiyear planning and spending cycles, we are only at the beginning of the affordability story.
“The 2026 utility narrative is shifting from ‘capex growth at all costs’ to ‘capex growth with a customer permission slip,’” Dumoulin-Smith wrote in a separate note on Thursday. “We believe it is no longer enough for utilities to say they care about affordability; regulators and investors are demanding proof of proactive behavior.”
If they can’t come up with answers that satisfy their investors, ultimately they’ll have to answer to the voters. Last fall, two Republican utility regulators in Georgia lost their reelection bids by huge margins thanks in part to a backlash over years of rate increases they’d approved.
“Especially as the November 2026 elections approach, utilities that fail to demonstrate concrete mitigants face political and reputational risk and may warrant a credibility discount in valuations, in our view,” Dumoulin wrote.
At the same time, utilities are dealing with increased demand for electricity, which almost necessarily means making more investments to better serve that new load, which can in the short turn translate to higher prices. While large technology companies and the White House are making public commitments to shield existing customers from higher costs, utility rates are determined in rate cases, not in press releases.
“As the issue of rising utility bills has become a greater economic and political concern, investors are paying attention,” Charles Hua, the founder and executive director of PowerLines, told me. “Rising utility bills are impacting the investor landscape just as they have reshaped the political landscape.”
Plus more of the week’s top fights in data centers and clean energy.
1. Osage County, Kansas – A wind project years in the making is dead — finally.
2. Franklin County, Missouri – Hundreds of Franklin County residents showed up to a public meeting this week to hear about a $16 billion data center proposed in Pacific, Missouri, only for the city’s planning commission to announce that the issue had been tabled because the developer still hadn’t finalized its funding agreement.
3. Hood County, Texas – Officials in this Texas County voted for the second time this month to reject a moratorium on data centers, citing the risk of litigation.
4. Nantucket County, Massachusetts – On the bright side, one of the nation’s most beleaguered wind projects appears ready to be completed any day now.
Talking with Climate Power senior advisor Jesse Lee.
For this week's Q&A I hopped on the phone with Jesse Lee, a senior advisor at the strategic communications organization Climate Power. Last week, his team released new polling showing that while voters oppose the construction of data centers powered by fossil fuels by a 16-point margin, that flips to a 25-point margin of support when the hypothetical data centers are powered by renewable energy sources instead.
I was eager to speak with Lee because of Heatmap’s own polling on this issue, as well as President Trump’s State of the Union this week, in which he pitched Americans on his negotiations with tech companies to provide their own power for data centers. Our conversation has been lightly edited for length and clarity.
What does your research and polling show when it comes to the tension between data centers, renewable energy development, and affordability?
The huge spike in utility bills under Trump has shaken up how people perceive clean energy and data centers. But it’s gone in two separate directions. They see data centers as a cause of high utility prices, one that’s either already taken effect or is coming to town when a new data center is being built. At the same time, we’ve seen rising support for clean energy.
As we’ve seen in our own polling, nobody is coming out looking golden with the public amidst these utility bill hikes — not Republicans, not Democrats, and certainly not oil and gas executives or data center developers. But clean energy comes out positive; it’s viewed as part of the solution here. And we’ve seen that even in recent MAGA polls — Kellyanne Conway had one; Fabrizio, Lee & Associates had one; and both showed positive support for large-scale solar even among Republicans and MAGA voters. And it’s way high once it’s established that they’d be built here in America.
A year or two ago, if you went to a town hall about a new potential solar project along the highway, it was fertile ground for astroturf folks to come in and spread flies around. There wasn’t much on the other side — maybe there was some talk about local jobs, but unemployment was really low, so it didn’t feel super salient. Now there’s an energy affordability crisis; utility bills had been stable for 20 years, but suddenly they’re not. And I think if you go to the town hall and there’s one person spewing political talking points that they've been fed, and then there’s somebody who says, “Hey, man, my utility bills are out of control, and we have to do something about it,” that’s the person who’s going to win out.
The polling you’ve released shows that 52% of people oppose data center construction altogether, but that there’s more limited local awareness: Only 45% have heard about data center construction in their own communities. What’s happening here?
There’s been a fair amount of coverage of [data center construction] in the press, but it’s definitely been playing catch-up with the electric energy the story has on social media. I think many in the press are not even aware of the fiasco in Memphis over Elon Musk’s natural gas plant. But people have seen the visuals. I mean, imagine a little farmhouse that somebody bought, and there’s a giant, 5-mile-long building full of computers next to it. It’s got an almost dystopian feel to it. And then you hear that the building is using more electricity than New York City.
The big takeaway of the poll for me is that coal and natural gas are an anchor on any data center project, and reinforce the worst fears about it. What you see is that when you attach clean energy [to a data center project], it actually brings them above the majority of support. It’s not just paranoia: We are seeing the effects on utility rates and on air pollution — there was a big study just two days ago on the effects of air pollution from data centers. This is something that people in rural, urban, or suburban communities are hearing about.
Do you see a difference in your polling between natural gas-powered and coal-powered data centers? In our own research, coal is incredibly unpopular, but voters seem more positive about natural gas. I wonder if that narrows the gap.
I think if you polled them individually, you would see some distinction there. But again, things like the Elon Musk fiasco in Memphis have circulated, and people are aware of the sheer volume of power being demanded. Coal is about the dirtiest possible way you can do it. But if it’s natural gas, and it’s next door all the time just to power these computers — that’s not going to be welcome to people.
I'm sure if you disentangle it, you’d see some distinction, but I also think it might not be that much. I’ll put it this way: If you look at the default opposition to data centers coming to town, it’s not actually that different from just the coal and gas numbers. Coal and gas reinforce the default opposition. The big difference is when you have clean energy — that bumps it up a lot. But if you say, “It’s a data center, but what if it were powered by natural gas?” I don’t think that would get anybody excited or change their opinion in a positive way.
Transparency with local communities is key when it comes to questions of renewable buildout, affordability, and powering data centers. What is the message you want to leave people with about Climate Power’s research in this area?
Contrary to this dystopian vision of power, people do have control over their own destinies here. If people speak out and demand that data centers be powered by clean energy, they can get those data centers to commit to it. In the end, there’s going to be a squeeze, and something is going to have to give in terms of Trump having his foot on the back of clean energy — I think something will give.
Demand transparency in terms of what kind of pollution to expect. Demand transparency in terms of what kind of power there’s going to be, and if it’s not going to be clean energy, people are understandably going to oppose it and make their voices heard.