You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:

Current conditions: A state of emergency is in effect in Manitoba, Canada, due to multiple wildfires • 17 million people in the south-central U.S. are at risk of severe storms on Tuesday • The Interior Department has reportedly suspended air quality monitoring for National Parks, including California’s Joshua Tree, where the AQI today is moderate.
Attorneys general from 17 Democratic states and Washington, D.C., filed a lawsuit on Monday challenging President Trump’s executive order pausing approvals, permits, and loans for onshore and offshore wind projects. The lawsuit argues that Trump exceeds his authority with the indefinite pause, which threatens “thousands of good-paying jobs and billions in investments, and … is delaying our transition away from the fossil fuels that harm our health and our planet,” in the words of New York Attorney General Letitia James, who is leading the coalition.
In a response to the lawsuit, a White House spokesperson told The Associated Press that “the American people voted for the president to restore America’s energy dominance, and Americans in blue states should not have to pay the price of the Democrats’ radical climate agenda.” As my colleague Emily Pontecorvo has written, however, state climate goals “become nearly impossible if no additional [wind] projects are able to get through the permitting process until at least 2029,” with New York state’s especially in jeopardy after the administration ordered the halt of construction on the fully permitted Empire Wind project south of Long Island.
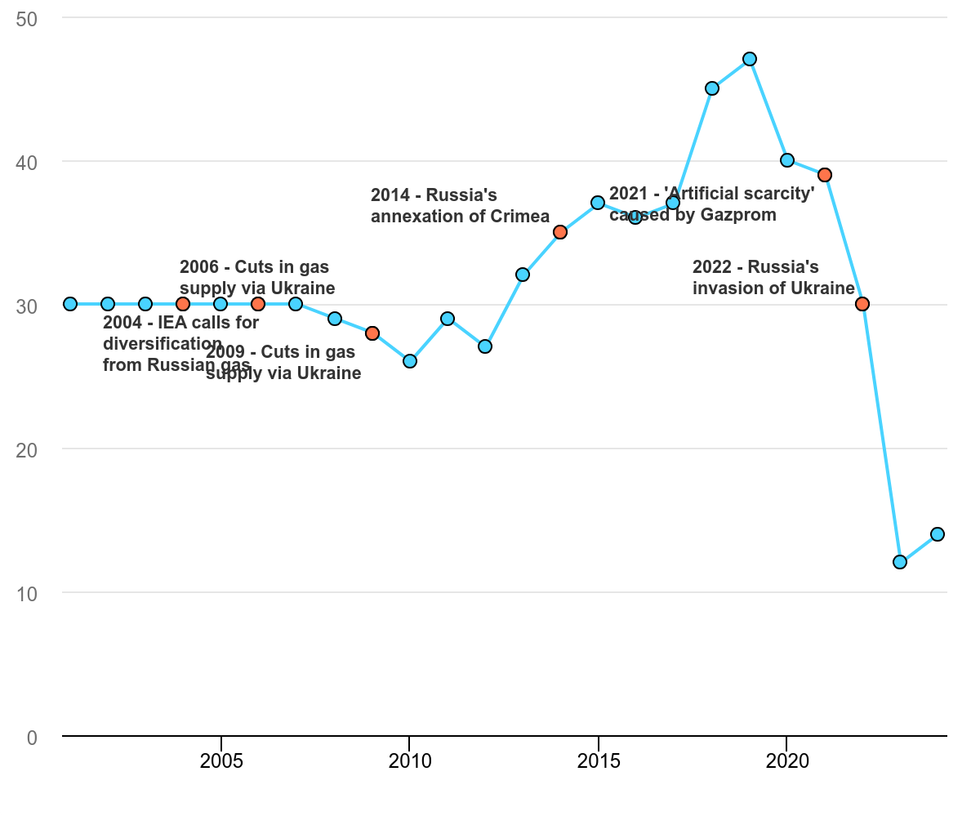
The European Union plans to announce on Tuesday a 2027 deadline for companies to end any remaining energy contracts with Russia, the Financial Times reported Monday. Though the EU’s use of Russian oil and coal virtually ended with sanctions after the invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Europe still bought 49.5 billion cubic meters of Russian gas through pipelines in 2024, and another 24.2 billion transported on ships as liquified natural gas, per Rystad Energy (though some of that LNG was resold). Another way of looking at it: “The EU purchased a total of [$26 billion] in Russian energy in 2024, exceeding its military assistance to Ukraine last year,” Bloomberg writes, with imports accounting for about 19% of the bloc’s total gas purchases.
The proposed measures will need to be approved by a majority of EU member states and the European Parliament before they can be adopted, according to FT. Without Russian LNG, Europe is expected to turn to the U.S. to meet its energy needs.
Share of European Union gas demand met by Russian supply, 2001-2024
More than 100 employees at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory lost their jobs in a round of layoffs on Monday, Mother Jones reports. The cuts included non-probationary employees, or those who’ve worked at the Department of Energy division for over two years.
Though NREL has more than 3,000 employees on staff, sources who spoke with Mother Jones described the cuts as “rather haphazard and unorganized,” while others stressed that “if I am suddenly the only person on my team, I can’t handle that work.” The layoffs also notably come after President Trump’s “skinny” budget proposed $15 billion in cuts to Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act funding. The White House Office of Management and Budget has said that the budget aims to reorient the Department of Energy’s funding away from “unreliable renewable energy” and “toward research and development of technologies that could produce an abundance of domestic fossil energy and critical minerals, innovative concepts for nuclear reactors and advanced nuclear fuels, and technologies that promote firm baseload power.”
The Federal Emergency Management Agency plans to end door-to-door survivor outreach in disaster areas for the upcoming hurricane and wildfire seasons, Wired reported Monday, based on a FEMA memo dated May 2. Previously, the agency would canvass disaster survivors to inform them about how to register for federal aid, a policy that one emergency management coordinator told Wired was critical given how many survivors don’t get adequate information about recovery resources otherwise. Instead, FEMA’s memo said the agency will “focus survivor outreach and assistance registration capabilities in more targeted venues.”
Last year, Republicans on the Oversight Committee singled out FEMA’s outreach program over alleged “widespread discrimination against individuals displaying Trump campaign signs on their property” in the wake of Hurricane Milton. The White House’s budget has also cited FEMA for supposedly “skipping over homes when providing aid.” But the Trump administration has also sought to pare back the agency aggressively: Earlier this year, it denied a request for federal aid from Arkansas’ Republican Governor and former White House Press Secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders after severe tornadoes that left more than 40 people in the region dead, arguing the disaster was not “beyond the capabilities of the state, affected local governments, and voluntary agencies” to address.

The Los Angeles Dodgers have faced calls from activists and fans to end their sponsorship deal with Phillips 66’s 76 gas station brand — but the partnership might face a natural end due to the Olympics coming to L.A. in 2028, Legal Planet reports. Dodger Stadium will be an official Olympic venue during the summer games, and its 76 gas ads will violate the Olympic Charter prohibiting “commercial installations and advertising signs … in the stadia, venues or other sports grounds.”
The Dodgers are under mounting pressure to drop the Phillips 66 partnership even earlier. There are 76 gasoline ads “plastered throughout the ballpark, from the visiting team’s bullpen to the ribbon board screens lining the stands … Even the on-deck circles on the field, where batters prepare to hit, are orange-and-blue 76 logos,” the Los Angeles Times’ Sammy Roth wrote last year in a column calling for the team to break up with the oil company. As of November, the Houston-based energy company was facing six counts of violating the U.S. Clean Water Act by illegally discharging 790,000 gallons of wastewater from its Carson refinery into the L.A. County sewer system. “The lead up to the 2028 Olympic games period would seem to be a natural time for the Dodgers to reset a marquee sponsor for years to come — and to do so on their own terms — or else be forced to by Olympic rules,” Legal Planet writes.
“C’mon Ford, c’mon GM, c’mon Chrysler, let’s roll again/Build something useful that people need, build us a safe way for us to be/Build us something that won’t kill our kids, that runs real clean, that runs real clean.” —Lyrics to Neil Young’s new single “Let’s Roll Again.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Researchers at the hyperscaler say they can predict flash floods with a new Gemini-produced dataset.
Flash floods, when stormwater pools and rises rapidly in an area within just a few hours of a storm's onset, are one of the more dangerous hazards of a warming planet prone to heavier rainfall. They are also notoriously difficult to predict. But research out of Google on Thursday shows how artificial intelligence could unlock better forecasts and help communities prepare.
Google researchers used Gemini, the tech giant’s signature AI agent, to process millions of news articles from around the world about past floods and extract data on when and where the deluges occurred. After assembling this vast new dataset — the largest of its kind to date — they used it to train a flood prediction model that uses local, hourly meteorological data to produce 24-hour forecasts for urban flash floods in more than 150 countries.
The dataset, which Google has named Groundsource, is free for anyone to download and use, and the forecasts are now live on Google’s Flood Hub, an online portal that also predicts river-related flood events. The tool is somewhat crude — it simply indicates whether there is a medium or high likelihood of a flash flood occurring in the next 24 hours in a given area. It only covers urban areas, and it doesn’t tell you how severe the flood could be. The resolution is also pretty coarse, indicating risks at the scale of a city rather than a street or neighborhood.
Still, the researchers said the forecasts would be useful for alerting authorities to potential risks.
“People have been very interested, even at that level of granularity,” Gila Loike, a product manager at Google Research, told reporters in a press conference this week.
According to Google, a regional disaster authority in Southern Africa caught a flash flood alert while the tool was still in beta, confirmed the flood on the ground, and then deployed a humanitarian worker to oversee the response. “We’re still in the early days of seeing the impact of Groundsource, but that chain of events from a prediction in Flood Hub to boots on the ground is exactly what Flood Hub was built for,” Juliet Rothenberg, the product director for Google’s crisis resilience work, said.
One of the key reasons it’s so hard to predict flash floods is the lack of historical data. We have decent flood models for “riverine” flooding, when rivers overflow, because of physical gauges in rivers around the world that have collected water levels for decades, but there’s no equivalent for city streets.
News articles present a largely untapped source to fill this gap. The challenge is that the key bits of information, such as where and when the flood occurred, are buried in narrative texts and expressed in wildly inconsistent formats. It would take human experts untold hours and resources to wade through each one and record the data in a standardized manner. An AI agent such as Gemini, however, can do it much faster.
Google’s research team started out by crawling the web for news articles describing flood events going back to the year 2000, gathering an initial pool of more than 9 million stories from around the world. After getting rid of ads and menus and the like and translating the articles that were in other languages to English, they fed them to Gemini.
“You are a meticulous flood event analyst,” the researchers told the AI agent. The rest of the elaborate prompt is included in a non-peer-reviewed preprint paper detailing the group’s methods for producing the dataset. In essence, they goaded Gemini to take a sentence such as “Main Street flooded on Tuesday,” and interpret where, exactly, this Main Street was located, and which Tuesday the article was referring to.
The resulting dataset contains 2.6 million historical flood events across more than 150 countries. As a comparison, the next largest public dataset, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Storm Events database, contains about 2 million storm events from 1950 to the present, only about 230,000 of which are flood events. The biggest global dataset, the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction’s DesInventar system, contains 500,000 events, only a fraction of which are records of floods. It’s also restricted to participating nations and inconsistently updated.
“Oftentimes, the first question our researchers will ask when we talk about going into a new domain within crisis resilience is, what data do you have? How many data entries do you have?” Rothenberg said. “That’s what really unlocks the ability to make breakthroughs here.”
Humberto Vergara, an assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of Iowa who studies flash floods, agreed that the lack of flood observation data has been a significant obstacle for the field. He told me the Groundsource dataset will “definitely be of great interest” and that there is “definitely great need for things like this.” Using news reports to fill out the global picture of flooding is something researchers have been thinking about doing for a while, he added.
While Vergara was cautiously optimistic the data would be useful, he was quick to note that it would take additional efforts to validate. His lab is working on its own dataset based on satellite estimates of rainfall that could be used to prove out Google’s records, he said.
The Google team already made some efforts to validate Groundsource, cross-checking it with manual annotations of the news reports as well as with other existing databases. It found that about 82% of the events were labeled with the correct location and timeframe. “From a research perspective, using an 82% accurate dataset is actually acceptable,” Loike said. “A well-trained model can smooth out the inconsistencies and thereby learn the dominant patterns while ignoring the 18% of labeling errors.”
They also validated the Flood Hub predictions by comparing its U.S. outputs to flood and flash flood warnings produced by the National Weather Service. “Achieving performance metrics comparable to such a sophisticated, instrumentation-rich framework demonstrates how AI can bridge the warning gap in underserved regions that lack equivalent infrastructure,” the researchers wrote in a second non-peer-reviewed preprint describing the model development.
Part of the reason Vergara was cautious in praising the effort is that predicting flash floods is challenging for reasons beyond the lack of historical data. “Most of the driving force is rainfall,” he said. “Everybody in the community knows that predicting rainfall is extremely difficult. The best models out there cannot predict rainfall with the accuracy that is needed for flash floods with more than one or two hours of lead time.”
The utility of Google’s Flood Hub depends on who will be consuming the information, he said. It’s probably not high-resolution enough to be useful for emergency responders, but there might be agencies at the city or regional level that can use it as a situational awareness tool.
Rothenberg, of Google, is optimistic that this same method can produce useful predictions for other kinds of extreme events.
“Applying this methodology to flash flood reports is just the beginning,” Juliet Rothenberg, the product director for Google’s crisis resilience work, told reporters at the press conference. “We think there’s an immense opportunity in thinking about how we could use publicly available information to help predict heat waves or landslides, for example — other events that are hard to predict because the data hasn’t been centralized or it doesn’t exist.”
Current conditions: A tornado that formed amid the storms pummeling the Midwest touched down in northwest Indiana and killed two • The Philippines’ Mount Kanlaon erupted 150 meters into the air in at least the fourth eruption on the archipelago this month • The swarm of earthquakes that started rattling northern Louisiana last week is continuing.
Oil prices surged 8% as Iran refused to start ceasefire talks with the United States and vowed to drive oil prices up by more than 100%. In a statement, Ebrahim Zolfaqari, a spokesperson for Iran’s Khatam al-Anbiya military command headquarters, said the world should “get ready for oil to be $200 a barrel” as “we will never allow even a liter of oil to pass through the Strait of Hormuz for the benefit of the United States, the Zionist regime, or their partners.” Living up to its threat, Iranian missiles struck three ships Wednesday attempting to cross the narrow channel in the Persian Gulf through which about one-fifth of the world’s hydrocarbons typically flow. The U.S. military, after vowing to safely shepherd ships via the waterway, turned down requests yesterday for an escort, The Wall Street Journal reported. During a televised appearance Wednesday with Fox News’ Laura Ingraham, Secretary of Energy Chris Wright said the Strait would reopen “hopefully in the next few weeks.” Later that evening, during an interview that aired on CNN, President Donald Trump said the strait was in “great shape,” promising, “We’re going to look very strongly at the strait.”

In the meantime, the International Energy Agency agreed to release more than 400 million barrels of oil from the world’s strategic reserve, by far the largest disbursement in history. Wright’s Department of Energy, too, will release 172 million barrels onto the market to keep prices down. The U.S. just refilled the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, which the Biden administration tapped to battle surging inflation a few years ago. In fact, U.S. crude exports fell last year for the first time since 2021, in large part due to efforts to redirect flows to the national stockpile, according to analysis the Energy Information Administration just released. All that stored oil will only cover about a month of global demand, Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote yesterday, succinctly summarizing the stakes like this: “This oil supply shock is very, very bad.”
Big money is pouring into the U.S. congressional race to replace former Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene in her conservative district in northwest Georgia. The first big spend came from Leading the Future, a super PAC backed by artificial intelligence companies that raised more than $125 million last year. According to Atlanta Journal-Constitution reporter Greg Bluestein, the group is spending $500,000 to back Republican Clay Fuller, Trump’s favored candidate, ahead of next month’s special runoff election. Taylor Greene, a right-wing populist who resigned from office following a public fallout with the president, emerged as a fierce critic of the AI industry’s data center buildout. Georgia led the nationwide push to ban data centers, with a state lawmaker introducing what The Guardian called one of the country’s first bills to put a moratorium on the buildout.
With copper prices at a record high, shifting political winds in major mining countries matter more than ever. All eyes, as I told you last month, are now on one of South America’s richest countries. On Wednesday, Chile inaugurated José Antonio Kast as its new president, replacing the copper- and lithium-rich nation’s most left-wing leader in half a century with its farthest-right head of state since the fall of former dictator Augusto Pinochet. The sea change comes just a month after Chile became the latest country to sign onto an 11-nation minerals accord with Washington, according to Buenos Aires Times. One of the first moves Kast is expected to make is placing mining under the country’s economic development ministry, and appointing Daniel Mas — an agribusiness executive with no background in mining — to be in charge. “Supporters of the model argue that tighter alignment between mining and economic policy could improve coordination on investment and competitiveness,” reporter Agustín de Vicente wrote in the Valparaíso-based mining trade publication Reporte Minero. “Critics, however, warn that mining’s technical complexity, long project cycles and strategic importance require dedicated expertise and institutional focus.” The next big priority will be permitting reform for the mining industry. The prospects for the green hydrogen industry are less clear. Under leftist President Gabriel Boric, the government last year approved a $423 million green hydrogen project, part of a burgeoning industry in the country. The Boric administration unveiled a finalized national strategy for green hydrogen just a week before the inauguration. Whether Kast holds to that plan remains to be seen, but it’s more likely he’ll overhaul the policy.
On the opposite side of the global copper supply chain, Mongolia is demanding earlier payments and a larger share of the sweeping Oyu Tolgoi copper mine the country co-owns with Rio Tinto. The government of President Ukhnaagiin Khürelsükh, which owns a 34% stake through the state-owned Erdenes Mongol LLC, said it considers the current agreement unfair and wants dividend payments on a faster schedule in addition to a 60% share of returns. “These discussions reflect our continued commitment to working together to achieve Oyu Tolgoi’s full potential for the benefit of all partners,” Rio Tinto told Mining.com.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Dajin Heavy Industry, a Chinese manufacturer of offshore wind foundations, has begun promoting its plans to go public on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, offshoreWIND.biz reported. The privately-owned Beijing-based company has so far self-funded its expansion, including a new assembly plant in Tangshan, the development of a fleet of deck carriers for transporting turbine components, and direct investments into wind and solar projects across China. It’s a sign of how much China’s wind industry is growing. As I reported in Monday’s newsletter, global wind installations hit a record high last year as Chinese companies surged into dominance, seizing eight of the top 10 manufacturer slots. Last October, Matthew wrote that a Chinese company’s new factory in Scotland augured the eventual takeover of one of Europe’s few strong domestic energy industries.
The Canadian mining startup Myriad Uranium has announced plans to double the size of its Copper Mountain Uranium Project in Wyoming, increasing the total holdings from about 9,439 acres to 18,351 acres. The expansion, the company said, came after a recent “high-resolution radiometric and magnetic survey” revealed that the deposit likely stretches east of where the existing project has already explored. “Confidence is increasing that we now have one of the largest uranium projects in the United States,” Myriad CEO Thomas Lamb said in a statement. “As uranium prices rise, a progressively larger share of our endowment will transition into economic viability, offering strong leverage to the steadily increasing price of uranium.”
If I were a cornier writer, I would earnestly try to come up with a Sonic pun. University of Oxford researchers found that ultrasound-repellers could save hedgehogs from cars. A study published Wednesday in Biology Letters demonstrates for the first time that hedgehogs can hear high-frequency ultrasound, highlighting the possibility that repellers could deter the mammals from scurrying into roads where they’re frequently killed by cars. “Having discovered that hedgehogs can hear in ultrasound, the next stage will be to find collaborators within the car industry to fund and design sound repellents for cars,” Sophie Lund Rasmussen, the assistant professor who served as lead researcher on the paper, said in a press release. “If our future research shows that it proves possible to design an effective device to keep hedgehogs away from cars, this could have a significant impact in reducing the threat of road traffic to the declining European hedgehog.”
Even releasing hundreds of millions of barrels from the world’s strategic reserves will only cover about a month of missing supply.
Every day the Strait of Hormuz remains closed, the global oil supply deficit increases by millions of barrels. So far, even the biggest responses to the crisis are at best short-term and partial.
Today the International Energy Agency announced a coordinated deployment of 400 million barrels from its member states’ strategic reserves. The United States, which has a 414 million-barrel Strategic Petroleum Reserve, has yet to detail its plans to deploy reserves. President Trump appeared to confirm, however, that the U.S. would release some oil from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. “Right now, we’ll reduce it a little bit, and that brings the prices down,” he told a Cincinnati television station Wednesday.
Four-hundred-million barrels may sound like a lot, but even the back-of-the-envelope math about how far that will go is unforgiving.
Around 20 million barrels per day of oil were going through the Strait of Hormuz last year, according to the IEA, representing about a quarter of the world’s seaborne oil trade. Since its effective closure starting February 28 in response to the U.S. and Israeli strikes on Iran, some oil that would otherwise transit the strait is still getting out: The Saudi pipeline to the Red Sea can handle up to 7 million barrels per day; an Emirati pipeline can transit up to 2 million barrels per day; and Iran itself is still managing to export oil. That leaves some 10 million barrels not making it to the market, according to Greg Brew, an analyst at the Eurasia Group.
The IEA’s 400 million barrels therefore add up to just about 40 more days of missing supply — and that doesn’t take into account the matter of actually getting those barrels to market.
That will still take some time, Ben Cahill, a senior associate at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, explained to me.
“The question is how much of that volume can be offset by a stock release, and when. The timing really matters,” he said. “The U.S. SPR, for example, takes 13 days to hit the market from the time of a presidential order, according to the DOE. So we still have a period of big potential supply shortfalls.”
Then there are the shut-ins, oil wells that are no longer being pumped across the Gulf region due to the conflict, which add up to around 6 million to 7 million barrels per day across Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, and Iraq.
That’s “barrels gone now and barrels gone in the future,” Brew told me. Oil that was loaded on ships or put into storage before the closure could still end up on the market. “But the shut-ins are barrels that have disappeared.”
Prices also spiked after Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022, leading the U.S. to sell around 180 million barrels of oil from the SPR. Then, however, Russia was able to continue selling its oil on the world market, though the United States and its allies implemented a price cap.
This time, explained Employ America’s managing director of policy implementation, Arnab Datta, the price action has been more restrained even as the real supply hit has been far greater.
“It’s important to understand the scale of this supply shortage versus what we had then, which was a speculative supply shortage,” Datta said, comparing the response to the Ukraine invasion with the current conflict in the Persian Gulf. “This one is a physical supply shortage that's not being realized necessarily in prices.”
Exactly how much oil could be drawn out of the U.S. Strategic Petroleum Reserve is unclear. While its legal drawdown limit is 4.4 million barrels per day, it may not be physically able to hit that even if the U.S. wanted to. The four salt caverns where the oil is stored are likely at different levels of operational readiness, Datta explained, with only some of them having completed modernization operations that have been underway for nearly a decade. It’s also possible some are offline entirely. When oil was drawn from the SPR in 2022, outflows were around a million barrels per day.
Datta told me that it’s “unlikely” SPR’s actual drawdown capacity is much higher than that, and that he’d be “surprised if it was higher than two [million barrels per day].”
Other analysts were even more pessimistic. “Realistic U.S. SPR releases today are likely below the 1.0 [million barrels per day] pace averaged in 2022,” J.P. Morgan analyst Natasha Kaneva wrote in a note to clients Tuesday. The combined expected release rate from the IEA countries “would not materially ease” the shortfall, she wrote.
At best, the IEA release can help keep a lid on price increase, Ryan Cummings, a former economist at the White House Council of Economic Advisors and the chief of staff of the Stanford Institute for Economic Policymaking, told me. “But it’s not big enough to fully offset the current supply gap. And as time goes on, this supply gap will only get worse as there’s more shuttered production.”
Datta and his Employ America colleague Skanda Amarnath have called on the administration to at least clarify what the SPR is currently capable of even if they hold off on releases.
“Regardless of when or under what conditions a release occurs, we encourage the administration to take this moment to announce the operational status of the SPR,” Employ America said in a statement Wednesday.
Salt caverns are not the only place there’s oil underground in the United States, however.
While many rich countries have sizable reserves — Japan, which is heavily dependent on oil imports, maintains private and public stockpiles of about 440 million barrels — the United States is unique in its combination of reserves and production capacity, a legacy of the 1970s oil shock and the 2010s shale boom, making it into an exporting powerhouse.
But even if U.S. producers were to respond by ramping up output substantially (which their investors would almost certainly not want them to do) any new supply would not hit the market quickly enough to meet the physical shortage at play now.
“You can’t pull supply forward in a matter of weeks,” Cahill told me. “The only countries that can typically do that are those with spare production capacity.” And the countries with spare capacity that can ramp up production quickly? They’re “almost exclusively in the Gulf,” Cahill said.
While President Trump has trumpeted a new refinery project in Texas, its developers have said they don’t expect it to be operational until next year. That would process some 160,000 barrels per day, not nearly enough to make a dent in the supply shortage currently confronting the world right now.
The solution to the current shortfall therefore lies in the Persian Gulf, not the Gulf of Mexico.
“Policy measures may have limited impact on oil prices unless safe passage through the Strait of Hormuz is assured,” Kaneva wrote.
Absent a ceasefire between the U.S., Israel, and Iran, that day is likely still far off. After all, how can tankers be expected to sail through the strait when, Brew observed, “the U.S. Navy is saying we’re not even sending our ships?”