You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On the latest from the campaign trail, freak storms, and the U.S. grid

Current conditions: Typhoon Jongdari is expected to bring flooding to South Korea when it makes landfall tomorrow • Wildfire smoke from North America turned the moon red for stargazers in the U.K. • California’s Park Fire, which started on July 24, is still burning.
While the Democratic National Convention got underway in Chicago yesterday, GOP presidential candidate Donald Trump and his running mate JD Vance went on the offensive in the battleground state of Pennsylvania. In separate speeches, Trump and Vance slammed Democratic presidential nominee Kamala Harris’ energy and environmental policies. Trump accused her of waging “war on American energy” and promised to “unlock American energy” if he is elected to the White House again in November. He reiterated his pledge to scrap the Biden administration’s rules limiting power plant pollution, saying Harris is on “a regulatory jihad to shut down power plants all across America.” He also hinted at giving Tesla CEO a cabinet position. Vance told a crowd: “We are going to drill, baby, drill.” In a Wall Street Journal opinion piece, Vance claimed Harris “cares more about climate change than about inflation.” A New York Times/Sienna poll last week showed Harris inching ahead of Trump in Pennsylvania, as well as in Michigan and Wisconsin.
Allies have encouraged Harris to lean into the environmental wins of the past four years, including the Inflation Reduction Act, but it’s anyone’s guess how much of her big speech on Thursday will be about climate. For his part, President Biden used his moment in the spotlight yesterday to tout emission reductions and his initiatives to expand EV charging stations across the country.
A group of climate organizations are putting out a $55 million ad campaign for Kamala Harris in swing states this week, The New York Times reported. The ads frame the current administration’s climate and energy policies as economic wins. “The goal of her presidency: strengthen America’s middle class,” one ad says. “We get there by investing in growing fields like advanced manufacturing and clean energy – good-paying jobs that don’t need a four-year degree.” The ad campaign is backed by L.C.V. Victory Fund, E.D.F. Action Votes, Climate Power Action, and the Future Forward super PAC.
The first floating offshore wind research site in the U.S. will be located in the Gulf of Maine. The Biden administration this week issued a lease for the research site, which “will inform how floating offshore wind operates and can co-exist with ocean users and ecosystems,” the Maine governor’s office said in a statement. The area is about 28 nautical miles from the shore and covers 9,700 acres, enough to accommodate 12 floating offshore wind turbines designed by the University of Maine. Floating offshore wind platforms enable wind power generation in deeper waters, and the Interior Department has a goal of deploying 15 gigawatts of floating capacity by 2035. Construction on the Maine site won’t start for another few years.
Climate change may have contributed to the freak storm that sank a luxury yacht Monday off the coast of Sicily, leaving one person dead and six missing, including British tech tycoon Mike Lynch. As rescue efforts continue, one Italian climatologist told Reuters the accident could have been caused by a water spout that produced high winds. Data suggests these weather events are becoming more frequent in Italy. “The sea surface temperature around Sicily was around 30 degrees Celsius (86 Fahrenheit), which is almost 3 degrees more than normal,” said Luca Mercalli, president of the Italian meteorological society. “This creates an enormous source of energy that contributes to these storms. So we can't say that this is all due to climate change, but we can say that it has an amplifying effect.” The Mediterranean is bracing for more intense storms today.
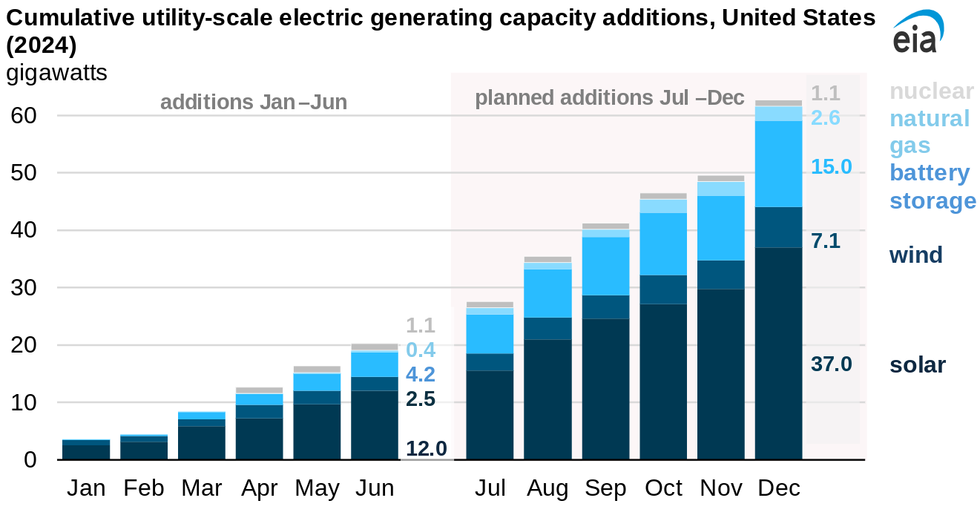
The U.S. power grid added 20.2 gigawatts of utility-scale electric generating capacity in the first half of 2024, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. That’s a 21% jump compared to the same period last year. In the second half 2024, the grid could expand capacity by another 42.6 GW “if utilities add all the solar capacity they are currently planning.” Solar accounted for 59% of additions through June this year. Battery storage made up 21% of additions, and wind power made up 12%. Meanwhile, coal and gas plant retirement has slowed.
Starting this fall, both Arizona State University and the University of California San Diego are requiring students to take a course on climate change and sustainability.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Large electricity users that employ few workers are not what America’s reindustrialization dreams are made on.
A group of local activists recently rallied against a major new industrial site in their area.
They worried the new facility was going to suck up water and electricity. They fretted about the chemicals and risky materials it might store on site. And they argued that the land’s “light industrial” zoning designation is not appropriate for the incoming tenant.
All in all, it sounded like a typical neighborhood protest against an incoming data center. As we’ve covered here at Heatmap News, local opposition to data centers has surged over the past year, ultimately playing a role in the demise of about 25 proposed projects nationwide in 2025.
But the new facility wasn’t a data center at all. It was a factory set to produce solar panel components. The proposed Silfab Solar factory in Fort Mill, South Carolina, has fought legal efforts to change local zoning rules since May 2024 as residents have fought it in a spiraling series of cases. As of January, the battle was still ongoing.
The case serves as a reminder: While the ongoing exurban land-use backlash is notionally about data centers, it will not necessarily stop there. Many of the issues that concern residents about data centers — their power use, water use, and lack of jobs — are not unique to these vast computing facilities. Data centers more closely resemble modern factories and other industrial facilities than they do the vast, job-intensive projects of last century.
One thread unites many opponents’ stated concerns: AI data centers, which consume prodigious amounts of electricity, aren’t the kind of industrial development Americans are used to. The Bethlehem Steel site or the Ford River Rouge factory used huge amounts of energy at their peak — but also employed more than 100,000 people. Although a single data center can boast dozens of megawatts of backup diesel generation — potentially turning it into an industrial-scale polluter — it is also unlikely to create few if any permanent jobs.
This isn’t to say that AI data centers create no benefits for their communities: If their community benefits or tax packages are structured well, AI data centers can lower energy costs, help local nonprofits, or generate staggering amounts of public revenue. AI data center projects also, of course, employ construction and electrical workers (and enrich local landowners). They can also generate several dozen permanent jobs, according to Matt Dunne, the founder and executive director of the Center for Rural Innovation.
“In the places where data centers are showing up, the jobs are really quite good. These are 50 really good, high-paying jobs — and in a community of 10,000 people, that’s not nothing,” Dunne told me.
With limited land at their disposal to allocate for new developments, local officials typically prefer to see hundreds or even thousands of new jobs created by a new project. They imagine creating facilities like the BMW plant in Greer, South Carolina, or the Volkswagen facility in Chattanooga, Tennessee, both of which transformed their respective regions after they opened.
But AI data centers are more like wind and solar farms — or even oil or gas pipelines — than the factories or refineries of yore. They are a particularly “jobless” form of industrial development, and they seem to compare poorly with the more labor-intensive forms of economic activity that many exurban or rural communities say they crave.
The researcher Advait Arun at the Center for Public Enterprise also points out that some AI data centers take advantage of longstanding local tax incentive packages designed to help more traditional “cloud” data centers, which use less power and are less risky investments than the “neoclouds” and other more speculative proposals popping up across the U.S. No jobs and no tax revenue don’t add up to a particularly appealing package for local governments.
The challenge is that in the next few years, more forms of economic development will come to resemble AI data centers than factories or refineries. The country’s steel plants and shipyards used to employ tens of thousands of people. But SpaceX’s rocket factory near Brownsville, Texas, now employs closer to 4,000 people. Taiwanese chipmaker TSMC’s plant in Arizona — probably the country’s most advanced manufacturing facility — employs only 3,000. That number might eventually double, but it still pales in comparison to the heavy industrial sites of old.
The post-war factories of old were detrimental to their communities in any number of other ways — sending deadly particulate matter into the air, releasing chemicals into the water, and leaching contaminants into the soil — and drew their fair share of protesters as a result. These next-generation facilities share few if any of their forebears’ foibles, but that might not help them with the public, Jonas Nahm, a Johns Hopkins University professor who studies industrial policy, told me.
“The factories now being built are not the smokestack industries of the past. They are cleaner, and often among the least locally polluting facilities in the economy,” Nahm said.
“But political opposition no longer tracks pollution alone,” he added. “It increasingly tracks who bears the costs of scarce resources—electricity, water, land—and who captures the benefits. On that dimension, advanced factories can start to resemble data centers: clean in emissions, heavy in infrastructure, and relatively light on jobs.”
Silfab is not alone among manufacturers in facing local opposition — factories across the country have pushback on par with the budding data center rebellion. Rivian’s proposed 1,800-acre manufacturing facility in Stanton Springs, Georgia, has dealt with a “No2Rivian” campaign focused on “land and water preservation.” The Chinese company Gotion faced years of local opposition when it tried to build a plant in Big Rapids, Michigan, before it eventually killed the project.
Economic and national security imperatives will not ease these challenges in the near term. If America wants to compete with China’s dominant electronics or batteries industries, then its manufacturing industry must become even more capital-light. Some Chinese firms, such as the EV maker Zeeker, have begun experimenting with “lights-out factories,” where robots alone can build a product without much human involvement. Despite China’s much larger population, the country now uses more industrial robots per 10,000 workers than the United States does. (South Korea and Japan still lead in robot density.)
This isn’t the first time automation and technological change have transformed the labor market in exurban and rural communities, Dunne said.
“The great automation of agriculture is what drove a lot of people to cities in the Twenties, Thirties, and Forties — about half of Americans were employed in agriculture at that moment in time, and then these things called tractors came along,” he said. “Manufacturing today is going through the same thing.”
Manufacturing has become progressively less job-intensive over the past few decades, he added. Many companies invested in manufacturing “competitiveness” programs, he said, which “sounded great until folks realized the ‘competitiveness’ of a certain plant meant shedding 60% to 70% of its jobs.”
Nahm, the Johns Hopkins professor, agreed. “The tension is that competitiveness now requires more automation, not less,” he said. “We can’t rely indefinitely on tariffs or subsidies to make domestic production viable, and China is showing what large-scale industrial automation and AI deployment can achieve. The factories that actually make reshoring work, however, are unlikely to recreate the mass employment that once tied industrial facilities tightly to local communities.
“That gap — between national economic goals and local political buy-in — is where the next set of conflicts is likely to emerge,” he added.
Of course, AI data centers differ from factories in key ways. New data centers suck up huge amounts of electricity despite taking up a small plot of land, a concentration of power use rivaled only by a few industries, such as aluminum smelters. Factories also tend to support a network of local high-end employment — engineers, machinists, robotics specialists — even if robots themselves do much of the assembling work.
But if a future policymaker wants to revive U.S. manufacturing — as every president in recent decades has vowed to do — then they will discover a new raft of obstacles. And the employment juice of a manufacturing-focused economy might no longer deliver the benefit that it once did.
In one big way, factories and data centers present similar risks for local communities. Often a town or county will only have a few high-quality sites for economic development, Dunne, the Center for Rural Innovation director, said. Once a facility uses that land, then the community’s economic fate is tied up with that industry.
“I think we’ve all seen the story where over-dependence on a single industry — not to mention a single company — does not go well,” Dunne said. “If a data center is coming in and going to take over a huge amount of your potential developable property, you still need to be thinking about how to diversify your economy effectively.”
“The only way to do that,” he continued, “is to continue to create wealth in the community and invest in local entrepreneurship, to invest in quality-of-life amenities, in quality K-12 schools — all the things that make a place exciting for folks to want to live in.”
Alphabet and Amazon each plan to spend a small-country-GDP’s worth of money this year.
Big tech is spending big on data centers — which means it’s also spending big on power.
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, announced Wednesday that it expects to spend $175 billion to $185 billion on capital expenditures this year. That estimate is about double what it spent in 2025, far north of Wall Street’s expected $121 billion, and somewhere between the gross domestic products of Ecuador and Morocco.
This is a “a massive investment in absolute terms,” Jefferies analyst Brent Thill wrote in a note to clients Thursday. “Jarringly large,” Guggenheim analyst Michael Morris wrote. With this announcement, total expected capital expenditures by Alphabet, Microsoft and Meta for 2026 are at $459 billion, according to Jefferies calculations — roughly the GDP of South Africa. If Alphabet’s spending comes in at the top end of its projected range, that would be a third larger than the “total data center spend across the 6 largest players only 3 years ago,” according to Brian Nowak, an analyst at Morgan Stanley.
And that was before Thursday, when Amazon told investors that it expects to spend “about $200 billion” on capital expenditures this year.
For Alphabet, this growth in capital expenditure will fund data center development to serve AI demand, just as it did last year. In 2025, “the vast majority of our capex was invested in technical infrastructure, approximately 60% of that investment in servers, and 40% in data centers and networking equipment,” chief financial officer Anat Ashkenazi said on the company’s earnings call.
The ramp up in data center capacity planned by the tech giants necessarily means more power demand. Google previewed its immense power needs late last year when it acquired the renewable developer Intersect for almost $5 billion.
When asked by an analyst during the company’s Wednesday earnings call “what keeps you up at night,” Alphabet chief executive Sundar Pichai said, “I think specifically at this moment, maybe the top question is definitely around capacity — all constraints, be it power, land, supply chain constraints. How do you ramp up to meet this extraordinary demand for this moment?”
One answer is to contract with utilities to build. The utility and renewable developer NextEra said during the company’s earnings call last week that it plans to bring on 15 gigawatts worth of power to serve datacenters over the next decade, “but I'll be disappointed if we don't double our goal and deliver at least 30 gigawatts through this channel by 2035,” NextEra chief executive John Ketchum said. (A single gigawatt can power about 800,000 homes).
The largest and most well-established technology companies — the Microsofts, the Alphabets, the Metas, and the Amazons — have various sustainability and clean energy commitments, meaning that all sorts of clean power (as well as a fair amount of natural gas) are likely to get even more investment as data center investment ramps up.
Jefferies analyst Julien Dumoulin-Smith described the Alphabet capex figure as “a utility tailwind,” specifically calling out NextEra, renewable developer Clearway Energy (which struck a $2.4 billion deal with Google for 1.2 gigawatts worth of projects earlier this year), utility Entergy (which is Google’s partner for $4 billion worth of projects in Arkansas), Kansas-based utility Evergy (which is working on a data center project in Kansas City with Google), and Wisconsin-based utility Alliant (which is working on data center projects with Google in Iowa).
If getting power for its data centers keeps Pichai up at night, there’s no lack of utility executives willing to answer his calls.
Current conditions: The snow squalls and cold air headed from the Ohio Valley to the Northeast are coming with winds of up to 55 miles per hour • A “western disturbance,” an extratropical storm that originates in the Mediterranean and travels eastward, is set to arrive in India and bring heavy snow to the Himalayas • Tropical Storm Basyang made landfall over the Philippines this morning, forcing Cebu City to cancel all in-person classes for public school students.
Vice President JD Vance delivered a 40-minute speech Wednesday appealing to 54 countries and the European Union to join a trading alliance led by the United States to establish a supply of critical minerals that could meaningfully rival China. The agreement would create a “preferential trade zone” meant to be “protected from disruptions through enforceable price floors.” The effort comes in response to years of export controls from Beijing that have sent the prices of key minerals over which China has near monopolies skyrocketing. “This morning, the Trump administration is proposing a concrete mechanism to return the global critical minerals market to a healthier, more competitive state,” Vance said at the State Department’s inaugural Critical Minerals Ministerial in Washington.
Under the Biden administration, the U.S. attempted to coordinate a network of trading partners, to make up for the minerals American mines no longer produced. The Treasury Department allowed automakers that sourced battery minerals to countries with which the U.S. had a free trade agreement to benefit from the most valuable version of the landmark electric vehicle tax credit reserved for power packs made with domestically-sourced metals. The White House worked with Republicans in Congress to eliminate the tax credit last year, demonstrating what Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin referred to as the “paradox” of Trump’s push for more domestic mining: A push to increase supply while eliminating one of the biggest sources of demand. The on-again, off-again tariff wars with allies haven’t done much to rally the spirit of camaraderie among America’s traditional trade partners either. Since then, as I have covered repeatedly in this newsletter, Trump has gone on a shopping spree for equity stakes in mining companies, shelled out grants through the military to mineral startups, and, most recently, created a $12 billion federal stockpile. Yet it’s come with plenty of missteps, as a former Department of Energy official told our colleague Robinson Meyer in his latest Shift Key podcast. Still, Congress is backing up the mining push. The House voted 224-195 Wednesday to approve legislation meant to speed up mining on federal lands.
Despite President Donald Trump’s threats to eliminate its funding, Congress has spared the long-running federal program that helps low-income Americans pay for heating and electric bills. The budget deal the president signed Tuesday to fund most federal agencies through September added $20 million to the Low Income Energy Assistance Program, bringing the total funding to just over $4 billion. It’s a full reversal of Trump’s position in May, when the administration asked Congress to completely eliminate the funding, Utility Dive reported. A second appropriations package Trump signed last month also included a small increase in funding for a separate program that subsidizes weatherization projects and other energy efficiency renovations for low- and moderate-income households.

Last week, I told you about copper prices soaring to a record — and seemingly unsustainable — high. While Goldman Sachs analysts expected the price for the metal needed for virtually anything electric to fall, it was still forecast to level off well above the average for the past few years. Well, that’s good news José Antonio Kast, the far-right leader scheduled to be inaugurated president of Chile next month. His incoming finance minister told the Financial Times the government plans to deliver economic growth rates of 4% and balance the country’s budget by 2029. If that proves possible, it’s only because Chile is the world’s largest producer of the red metal.
The U.S., meanwhile, is seeing early fruits of its global mineral diplomacy. The federal government’s International Development Finance Corporation said Wednesday that a U.S.-backed venture will begin shipping 50,000 tons of copper from the Democratic Republic of the Congo to Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. The export package comes a month after the same Congolese project pledged to send 100,000 tons to the U.S. The lending agency’s chief executive, Ben Black, said the partnership between Washington and Kinshasa “ensures valuable critical minerals are directed to the U.S. and our allies.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Newcleo, the best-known European nuclear startup promising to build fourth-generation small modular reactors, just netted $85 million in its latest financing round, bringing its total fundraising for the past 12 months to more than $125 million. The financing round includes venture funds Kairos and Indaco Ventures, asset manager Azimut Investments, the CERN pension fund, and industrial giants such as steelmaker Danieli, concrete manufacturer Cementir Holding, and components producers such as Walter Tosto and Orion Valves. The money will “accelerate our expansion into the U.S.,” a nascent effort that has included brokering a partnership with fellow next-generation reactor startup Oklo. Unlike the California company, whose microreactor design uses liquid sodium instead of water as a coolant, Paris-based Newcleo has proposed building a lead-cooled unit. The design has already gained approval in the United Kingdom. “Our ability to deliver impactful low-carbon energy solutions for energy-intensive firms is proving an attractive investment rationale for both industrial and financial investors,” said Newcleo CEO Stefano Buono.
Last week, I told you about the trouble brewing for the controversial wood-pellet giant Drax, which built its business on government subsidies predicated on the idea that burning felled trees for electricity could somehow provide a low-carbon alternative to fossil fuels. Facing overdue scrutiny of its green credentials, the British company had hoped Japan, the world’s No. 2 importer of wood pellets, would provide a growth market. But Tokyo indicated it’s cutting off the subsidy spigot. Then, two days ago, I told you that a former Drax employee admitted the company misled the public when claiming it wasn’t felling old-growth trees to make its wood pellets. Now the union that represents its British workers, Unite, has blasted Drax for the “shameful betrayal” of threatening to cut as many as 350 jobs. That could total up to 10% of the workforce. “It is shameful that a firm making billions such as Drax is choosing to target its staff,” Sharon Graham, Unite’s general secretary, said, according to Energy Voice. “It is morally wrong that workers, their families, and local communities pay the price for corporate greed.”
Over at The Washington Post, billionaire owner Jeff Bezos’ management team just gutted the newspaper's Pulitzer Prize-winning climate desk. The paper sent layoff notices to at least 14 climate journalists, newsroom sources told veteran beat reporter Sammy Roth for his Climate-Colored Goggles newsletter. The pink slips included eight writers and reporters, an editor, and several video, data, and graphics journalists. I’ll echo Sammy’s sentiment with the highest compliment I can give: I was routinely jealous of the top-notch reporting the climate team published at the Post. Losing that nuanced, complex reporting, at this particular juncture in the history of our nation and our atmosphere, is devastating. It’s also infuriating when you read the back-of-the-napkin math New York Times reporter Peter Baker posted on X yesterday: “Last reported annual losses of Post: $100 million,” he wrote. “Number of years Bezos could absorb those losses with what he makes in a single week: 5.”
Take a guess who wrote this on X yesterday morning: “Solar energy is the energy of the future. Giant fusion reactor up there in the sky — we must rapidly expand solar to compete with China.” Go ahead, I’ll wait. Whomever you were going to name, you’re probably wrong. The answer, astonishingly, is Katie Miller, the right-wing influencer wife of top Trump adviser Stephen Miller. A regular feature of White House social media content, Katie Miller posted her praise for an industry her husband’s boss has done much to stymie in response to an Axios article on a poll that found strong support for solar among GOP voters. The survey, commissioned by the panel manufacturer First Solar, comes as the solar industry says that the administration is throttling its permitting. While Trump seems unlikely to let up on wind, it could be a sign of a brighter future for America’s fastest-growing source of electricity.