You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Skiers, snowboarders, and cross-country athletes are in mourning for snow.

On January 15, as the first major winter storm of the season screeched across the U.S., Minneapolis’ Theodore Wirth Regional Park remained cold, hard, and — most stubbornly — brown. “We continue to be denied any measurable amount of snow,” read the park’s trail report for the day. “Frozen dandruff-covered dirt is our destiny for the time being.”
In a few weeks, over Presidents Day weekend, the park is scheduled to host the United States’ first cross country skiing World Cup in more than 20 years. For an event like that, “dandruff-covered dirt” simply will not cut it. “We’re really excited to have a great event there with tons of friends and family,” Gus Schumacher, a 2022 Winter Olympian in skiathlon, told me. While he still has hope, the Twin Cities’ snow deficit remains around 18 inches for the season. “We have to cross our fingers for some winter in the next month,” he said.
For the 30 million Americans who enjoy snow sports every year, this sort of finger-crossing has become as much of a pre-season ritual as tightening bindings and waxing skis. While scientists have long taken note of dwindling snowpack — the Fifth National Climate Assessment, released last year, specifically cited winter recreation as a pending cultural and economic victim of climate change — data had only shakily linked snow level to human-driven warming until recently. This month, a study published in Nature confirmed that it’s not all in our heads: Some parts of the U.S. are losing 10% to 20% of their snowpack per decade because of anthropogenic climate change.
Perhaps even more concerning, the study’s authors found that snow loss has a tipping point: Once the average winter temperature in a region warms beyond 17 degrees Fahrenheit (-8 degrees Celsius), snow loss rapidly accelerates, even with small temperature rises.
In spite of headlines about arctic blasts and photos of buried football fields, snow levels in many parts of the country have remained worryingly low at the midpoint of this year’s meteorological winter — and temperatures, on average, remain high. In early January, most ski areas in the U.S. were only operating half of their lifts, “which is unusual for this time of year,” Chance Keso, a senior news producer for On the Snow, which tracks ski conditions, told me. “Typically,” he explained, “we would see most resorts almost all completely open by this time of year.”
The recent storm systems have helped somewhat, Keso said — Alyeska, a ski area in Alaska, “passed the 400 inches mark a few weeks ago.” But even Buffalo, which received record snow in January, is tracking behind average when the whole season is considered. In California, where the ski industry is a $1.6 billion business, snowpack is only 57% of normal.
Likewise, meteorologist Sven Sundgaard wrote for Minneapolis’ Bring Me the News that this winter has been “pretty weak” in Minnesota. It has been cold, no doubt, and yet “nowhere in the state reached 25 [degrees Fahrenheit] below zero, which should EASILY happen in a January cold snap in northern Minnesota, even in our much warmer climate,” he said. (This week, temperatures are expected to be 10 to 15 degrees above normal across the state.) On the Snow reported that, as of Monday, “snowpack levels across Minnesota are currently 73% of normal.”
Counterintuitive as it may be, researchers expect climate change to bring more snow to certain places, as extremely cold parts of the world warm to more snow-friendly temperatures and increased precipitation from a warmer atmosphere results in more flurries. Parts of Siberia and the northern Great Plains appear to be experiencing a deepening snowpack of over 20% per decade, Justin Mankin and Alexander Gottlieb, the co-authors of the Nature paper, found in their research. But just because snow loss hasn’t hit an area yet doesn’t mean it won’t soon; “basins that are hovering right at the edge of that cliff, for whom major snow losses have not yet emerged, are about to see the snow losses emerge,” Mankin said.
Despite the worries about Minnesota’s upcoming World Cup, Susanna Sieff — the sustainability director for the Switzerland-based International Ski and Snowboard Federation (known by its French initials, FIS) — told me that event cancellations for the six Olympic snow sport disciplines this season have so far “been on par with previous seasons.” A spate of foiled World Cups in Zermatt, Italy, Beaver Creek, Colorado, and the French Alps in late 2023, she said, was “due to inclement weather and not lack of snowfall.”
Still, Sieff admitted that “for those that needed a wake-up call, the last few years have certainly provided it.” 2022 was especially bad for competitive ski and snowboarding — the organization canceled seven of its eight early-season World Cups for lack of snow. This month, FIS released an updated sustainability action plan that runs through the 2026 season and includes a particular focus on mitigation, environmental justice, and responsible stewardship. (Protect Our Winters, an environmental advocacy group that put me in touch with Schumacher, the ski athlete who serves as one of their ambassadors, has pressured FIS to be more transparent given the existential crisis facing competitive snow sports. My father is a longtime FIS event volunteer.)
Resort operators are increasingly using machine-made snow as a fall-back plan — as Schumacher told me, in cross-country, “we ski on warm, manmade snow far more than was the case 10 years ago.” It’s also common for XC events to move to alternate venues where snow can be stretched further. For example, Lillehammer, Norway has hosted a World Cup race in nine of the past 10 years. But “since I came on the World Cup in 2020, we haven’t been able to use the marquee trails built for the 1994 Olympics,” Schumacher said.
Even this “fake” snow is imperiled. “Snowmaking is not a climate solution,” the National Ski Areas Association, an industry group, has made clear. “It is an operational tool.”
It’s also expensive. Snowmaking can eat up to 15% of a ski area’s operating budget, draining the pockets of small and independent resorts. The consequence is yet another illustration of how climate change hits “the most vulnerable system and the most vulnerable people in that system,” Mankin said. “The ski industry is a really clear example of where you’re going to see consolidation onto better resourced, higher, more exclusive mountains that have the ability to produce human-made snow — and which are more difficult for the general population to access.”
Since the 1970s, ski areas in the U.S. have dwindled from roughly 1,000 locations to only about 470, according to SnowBrains, a ski and snowboard publication. It’s a trend climate change is helping to accelerate. That, of course, means fewer areas for athletes to compete and practice, as well as fewer local hills and trails for would-be athletes to fall in love with the sport.
For those in the snow sports world, this is nothing short of heartbreaking. The average American already doesn’t watch snow sports and “shouldn’t really care” whether cross-country or downhill skiing competitions survive, Schumacher told me. But the consequences are bigger than just competitive and recreational snow sports having shorter seasons of poorer quality or becoming more exclusive. A lack of snow is also about critical watersheds that are strained when snow doesn’t fall in the mountains, leaving ecosystems damaged and agriculture unirrigated. Heck, it’s about hardy, stoic Minnesotans losing what it means to be hardy, stoic Minnesotans. “What they should care about,” Schumacher said of his fellow Americans, “is the effects of climate change that come after the death of snow sport as we know it.”
Mankin told me something similar. “What happens in winter,” he warned, “doesn’t stay in winter.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
What he wants them to do is one thing. What they’ll actually do is far less certain.
Donald Trump believes that tariffs have almost magical power to bring prosperity; as he said last month, “To me, the world’s most beautiful word in the dictionary is tariffs. It’s my favorite word.” In case anyone doubted his sincerity, before Thanksgiving he announced his intention to impose 25% tariffs on everything coming from Canada and Mexico, and an additional 10% tariff on all Chinese goods.
This is just the beginning. If the trade war he launched in his first term was haphazard and accomplished very little except costing Americans money, in his second term he plans to go much further. And the effects of these on clean energy and climate change will be anything but straightforward.
The theory behind tariffs is that by raising the price of an imported good, they give a stronger footing in the market; eventually, the domestic producer may no longer need the tariff to be competitive. Imposing a tariff means we’ve decided that a particular industry is important enough that it needs this kind of support — or as some might call it, protection — even if it means higher prices for a while.
The problem with across-the-board tariffs of the kind Trump proposes is that they create higher prices even for goods that are not being produced domestically and probably never will be. If tariffs raise the price of a six-pack of tube socks at Target from $9.99 to $14.99, it won’t mean we’ll start making tube socks in America again. It just means you’ll pay more. The same is often true for domestic industries that use foreign parts in their manufacturing: If no one is producing those parts domestically, their costs will unavoidably rise.
The U.S. imported over $3 trillion worth of goods in 2023, and $426 billion from China alone, so Trump’s proposed tariffs would represent hundreds of billions of dollars of increased costs. That’s before we account for the inevitable retaliatory tariffs, which is what we saw in Trump’s first term: He imposed tariffs on China, which responded by choking off its imports of American agricultural goods. In the end, the revenue collected from Trump’s tariffs went almost entirely to bailing out farmers whose export income disappeared.
The past almost-four years under Joe Biden have seen a series of back-and-forth moves in which new tariffs were announced, other tariffs were increased, exemptions were removed and reinstated. For instance, this May Biden increased the tariff on Chinese electric vehicles to over 100% while adding tariffs on certain EV batteries. But some of the provisions didn’t take effect right away, and only certain products were affected, so the net economic impact was minimal. And there’s been nothing like an across-the-board tariff.
It’s reasonable to criticize Biden’s tariff policies related to climate. But his administration was trying to navigate a dilemma, serving two goals at once: reducing emissions and promoting the development of domestic clean energy technology. Those goals are not always in alignment, at least in the short run, which we can see in the conflict within the solar industry. Companies that sell and install solar equipment benefit from cheap Chinese imports and therefore oppose tariffs, while domestic manufacturers want the tariffs to continue so they can be more competitive. The administration has attempted to accommodate both interests with a combination of subsidies to manufacturers and tariffs on certain kinds of imports — with exemptions peppered here and there. It’s been a difficult balancing act.
Then there are electric vehicles. The world’s largest EV manufacturer is Chinese company BYD, but if you haven’t seen any of their cars on the road, it’s because existing tariffs make it virtually impossible to import Chinese EVs to the United States. That will continue to be the case under Trump, and it would have been the case if Kamala Harris had been elected.
On one hand, it’s important for America to have the strongest possible green industries to insulate us from future supply shocks and create as many jobs-of-the-future as possible. On the other hand, that isn’t necessarily the fastest route to emissions reductions. In a world where we’ve eliminated all tariffs on EVs, the U.S. market would be flooded with inexpensive, high-quality Chinese EVs. That would dramatically accelerate adoption, which would be good for the climate.
But that would also deal a crushing blow to the American car industry, which is why neither party will allow it. What may happen, though, is that Chinese car companies may build factories in Mexico, or even here in the U.S., just as many European and Japanese companies have, so that their cars wouldn’t be subject to tariffs. That will take time.
Of course, whatever happens will depend on Trump following through with his tariff promise. We’ve seen before how he declares victory even when he only does part of what he promised, which could happen here. Once he begins implementing his tariffs, his administration will be immediately besieged by a thousand industries demanding exemptions, carve-outs, and delays in the tariffs that affect them. Many will have powerful advocates — members of Congress, big donors, and large groups of constituents — behind them. It’s easy to imagine how “across-the-board” tariffs could, in practice, turn into Swiss cheese.
There’s no way to know yet which parts of the energy transition will be in the cheese, and which parts will be in the holes. The manufacturers can say that helping them will stick it to China; the installers may not get as friendly an audience with Trump and his team. And the EV tariffs certainly aren’t going anywhere.
There’s a great deal of uncertainty, but one thing is clear: This is a fight that will continue for the entirety of Trump’s term, and beyond.
Give the people what they want — big, family-friendly EVs.
The star of this year’s Los Angeles Auto Show was the Hyundai Ioniq 9, a rounded-off colossus of an EV that puts Hyundai’s signature EV styling on a three-row SUV cavernous enough to carry seven.
I was reminded of two years ago, when Hyundai stole the L.A. show with a different EV: The reveal of Ioniq 6, its “streamliner” aerodynamic sedan that looked like nothing else on the market. By comparison, Ioniq 9 is a little more banal. It’s a crucial vehicle that will occupy the large end of Hyundai's excellent and growing lineup of electric cars, and one that may sell in impressive numbers to large families that want to go electric. Even with all the sleek touches, though, it’s not quite interesting. But it is big, and at this moment in electric vehicles, big is what’s in.
The L.A. show is one the major events on the yearly circuit of car shows, where the car companies traditionally reveal new models for the media and show off their whole lineups of vehicles for the public. Given that California is the EV capital of America, carmakers like to talk up their electric models here.
Hyundai’s brand partner, Kia, debuted a GT performance version of its EV9, adding more horsepower and flashy racing touches to a giant family SUV. Jeep reminded everyone of its upcoming forays into full-size and premium electric SUVs in the form of the Recon and the Wagoneer S. VW trumpeted the ID.Buzz, the long-promised electrified take on the classic VW Microbus that has finally gone on sale in America. The VW is the quirkiest of the lot, but it’s a design we’ve known about since 2017, when the concept version was revealed.
Boring isn’t the worst thing in the world. It can be a sign of a maturing industry. At auto shows of old, long before this current EV revolution, car companies would bring exotic, sci-fi concept cars to dial up the intrigue compared to the bread-and-butter, conservatively styled vehicles that actually made them gobs of money. During the early EV years, electrics were the shiny thing to show off at the car show. Now, something of the old dynamic has come to the electric sector.
Acura and Chrysler brought wild concepts to Los Angeles that were meant to signify the direction of their EVs to come. But most of the EVs in production looked far more familiar. Beyond the new hulking models from Hyundai and Kia, much of what’s on offer includes long-standing models, but in EV (Chevy Equinox and Blazer) or plug-in hybrid (Jeep Grand Cherokee and Wrangler) configurations. One of the most “interesting” EVs on the show floor was the Cybertruck, which sat quietly in a barely-staffed display of Tesla vehicles. (Elon Musk reveals his projects at separate Tesla events, a strategy more carmakers have begun to steal as a way to avoid sharing the spotlight at a car show.)
The other reason boring isn’t bad: It’s what the people want. The majority of drivers don’t buy an exotic, fun vehicle. They buy a handsome, spacious car they can afford. That last part, of course, is where the problem kicks in.
We don’t yet know the price of the Ioniq 9, but it’s likely to be in the neighborhood of Kia’s three-row electric, the EV9, which starts in the mid-$50,000s and can rise steeply from there. Stellantis’ forthcoming push into the EV market will start with not only pricey premium Jeep SUVs, but also some fun, though relatively expensive, vehicles like the heralded Ramcharger extended-range EV truck and the Dodge Charger Daytona, an attempt to apply machismo-oozing, alpha-male muscle-car marketing to an electric vehicle.
You can see the rationale. It costs a lot to build a battery big enough to power a big EV, so they’re going to be priced higher. Helpfully for the car brands, Americans have proven they will pay a premium for size and power. That’s not to say we’re entering an era of nothing but bloated EV battleships. Models such as the overpowered electric Dodge Charger and Kia EV9 GT will reveal the appetite for performance EVs. Smaller models like the revived Chevy Bolt and Kia’s EV3, already on sale overseas, are coming to America, tax credit or not.
The question for the legacy car companies is where to go from here. It takes years to bring a vehicle from idea to production, so the models on offer today were conceived in a time when big federal support for EVs was in place to buoy the industry through its transition. Now, though, the automakers have some clear uncertainty about what to say.
Chevy, having revealed new electrics like the Equinox EV elsewhere, did not hold a media conference at the L.A. show. Ford, which is having a hellacious time losing money on its EVs, used its time to talk up combustion vehicles including a new version of the palatial Expedition, one of the oversized gas-guzzlers that defined the first SUV craze of the 1990s.
If it’s true that the death of federal subsidies will send EV sales into a slump, we may see messaging from Detroit and elsewhere that feels decidedly retro, with very profitable combustion front-and-center and the all-electric future suddenly less of a talking point. Whatever happens at the federal level, EVs aren’t going away. But as they become a core part of the car business, they are going to get less exciting.
Current conditions: Parts of southwest France that were freezing last week are now experiencing record high temperatures • Forecasters are monitoring a storm system that could become Australia’s first named tropical cyclone of this season • The Colorado Rockies could get several feet of snow today and tomorrow.
This year’s Atlantic hurricane season caused an estimated $500 billion in damage and economic losses, according to AccuWeather. “For perspective, this would equate to nearly 2% of the nation’s gross domestic product,” said AccuWeather Chief Meteorologist Jon Porter. The figure accounts for long-term economic impacts including job losses, medical costs, drops in tourism, and recovery expenses. “The combination of extremely warm water temperatures, a shift toward a La Niña pattern and favorable conditions for development created the perfect storm for what AccuWeather experts called ‘a supercharged hurricane season,’” said AccuWeather lead hurricane expert Alex DaSilva. “This was an exceptionally powerful and destructive year for hurricanes in America, despite an unusual and historic lull during the climatological peak of the season.”
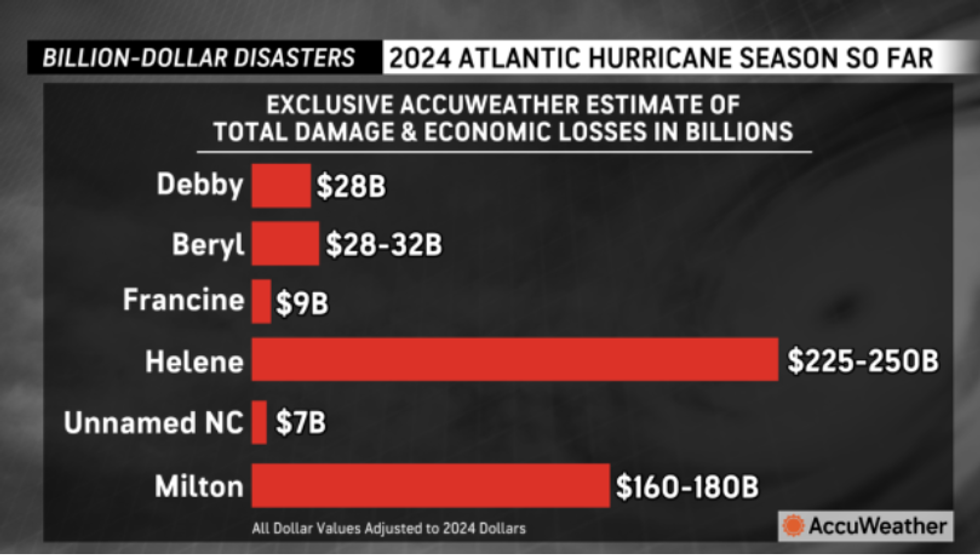
This year’s hurricane season produced 18 named storms and 11 hurricanes. Five hurricanes made landfall, two of which were major storms. According to NOAA, an “average” season produces 14 named storms, seven hurricanes, and three major hurricanes. The season comes to an end on November 30.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom announced yesterday that if President-elect Donald Trump scraps the $7,500 EV tax credit, California will consider reviving its Clean Vehicle Rebate Program. The CVRP ran from 2010 to 2023 and helped fund nearly 600,000 EV purchases by offering rebates that started at $5,000 and increased to $7,500. But the program as it is now would exclude Tesla’s vehicles, because it is aimed at encouraging market competition, and Tesla already has a large share of the California market. Tesla CEO Elon Musk, who has cozied up to Trump, called California’s potential exclusion of Tesla “insane,” though he has said he’s okay with Trump nixing the federal subsidies. Newsom would need to go through the State Legislature to revive the program.
President-elect Donald Trump said yesterday he would impose steep new tariffs on all goods imported from China, Canada, and Mexico on day one of his presidency in a bid to stop “drugs” and “illegal aliens” from entering the United States. Specifically, Trump threatened Canada and Mexico each with a 25% tariff, and China with a 10% hike on existing levies. Such moves against three key U.S. trade partners would have major ramifications across many sectors, including the auto industry. Many car companies import vehicles and parts from plants in Mexico. The Canadian government responded with a statement reminding everyone that “Canada is essential to U.S. domestic energy supply, and last year 60% of U.S. crude oil imports originated in Canada.” Tariffs would be paid by U.S. companies buying the imported goods, and those costs would likely trickle down to consumers.
Amazon workers across the world plan to begin striking and protesting on Black Friday “to demand justice, fairness, and accountability” from the online retail giant. The protests are organized by the UNI Global Union’s Make Amazon Pay Campaign, which calls for better working conditions for employees and a commitment to “real environmental sustainability.” Workers in more than 20 countries including the U.S. are expected to join the protests, which will continue through Cyber Monday. Amazon’s carbon emissions last year totalled 68.8 million metric tons. That’s about 3% below 2022 levels, but more than 30% above 2019 levels.
Researchers from MIT have developed an AI tool called the “Earth Intelligence Engine” that can simulate realistic satellite images to show people what an area would look like if flooded by extreme weather. “Visualizing the potential impacts of a hurricane on people’s homes before it hits can help residents prepare and decide whether to evacuate,” wrote Jennifer Chu at MIT News. The team found that AI alone tended to “hallucinate,” generating images of flooding in areas that aren’t actually susceptible to a deluge. But when combined with a science-backed flood model, the tool became more accurate. “One of the biggest challenges is encouraging people to evacuate when they are at risk,” said MIT’s Björn Lütjens, who led the research. “Maybe this could be another visualization to help increase that readiness.” The tool is still in development and is available online. Here is an image it generated of flooding in Texas:

A new installation at the Centre Pompidou in Paris lets visitors listen to the sounds of endangered and extinct animals – along with the voice of the artist behind the piece, the one and only Björk.