This article is exclusively
for Heatmap Plus subscribers.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.

Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
And more of the week’s most important conflicts around renewable energy.
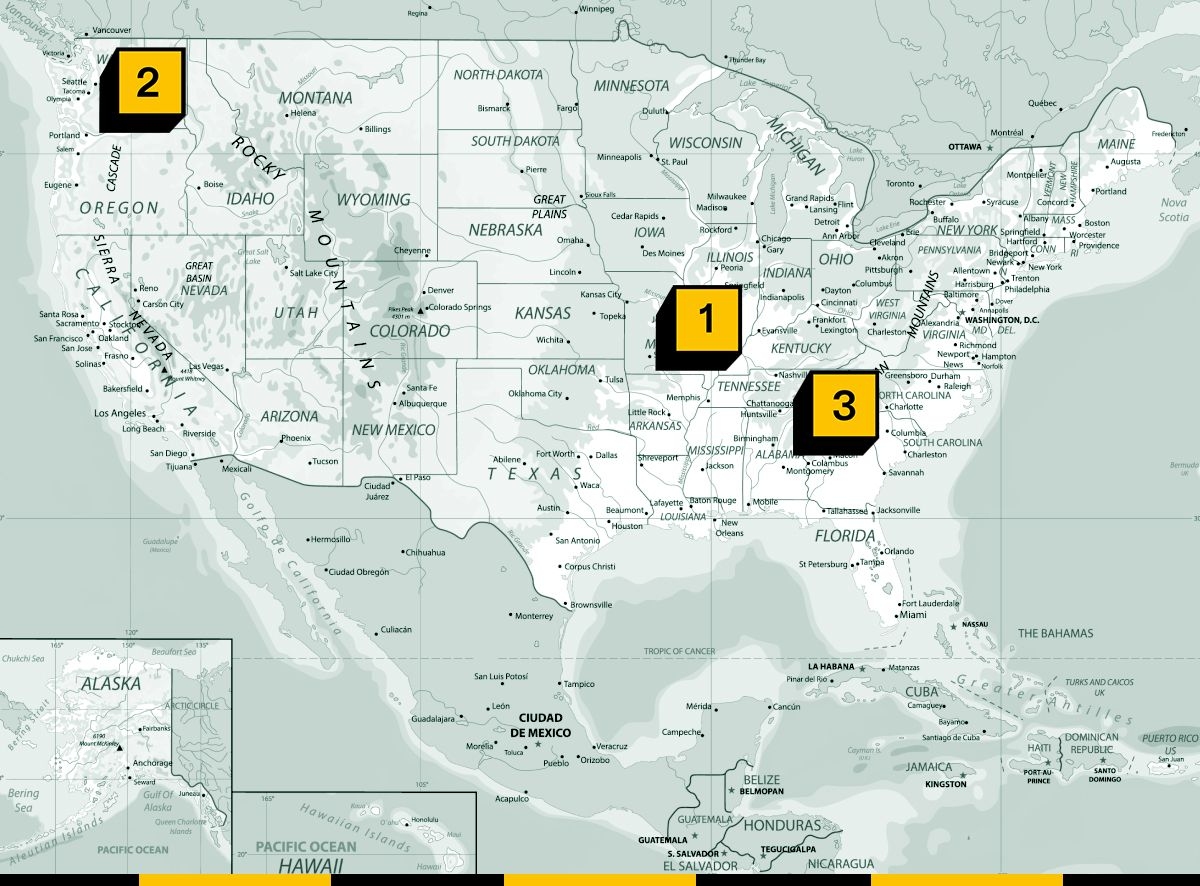
1. Madison County, Missouri – A giant battery material recycling plant owned by Critical Mineral Recovery exploded and became engulfed in flames last week, creating a potential Vineyard Wind-level PR headache for energy storage.
2. Benton County, Washington State – Governor Jay Inslee finally got state approvals finished for Scout Clean Energy’s massive Horse Heaven wind farm after a prolonged battle over project siting, cultural heritage management, and bird habitat.
3. Fulton County, Georgia – A large NextEra battery storage facility outside of Atlanta is facing a lawsuit that commingles usual conflicts over building these properties with environmental justice concerns, I’ve learned.
Here’s what else I’m watching…
In Colorado, Weld County commissioners approved part of one of the largest solar projects in the nation proposed by Balanced Rock Power.
In New Mexico, a large solar farm in Sandoval County proposed by a subsidiary of U.S. PCR Investments on land typically used for cattle is facing consternation.
In Pennsylvania, Schuylkill County commissioners are thinking about new solar zoning restrictions.
In Kentucky, Lost City Renewables is still wrestling with local concerns surrounding a 1,300-acre solar farm in rural Muhlenberg County.
In Minnesota, Ranger Power’s Gopher State solar project is starting to go through the public hearing process.
In Texas, Trina Solar – a company media reports have linked to China – announced it sold a large battery plant the day after the election. It was acquired by Norwegian company FREYR.Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The state is poised to join a chorus of states with BYO energy policies.
With the backlash to data center development growing around the country, some states are launching a preemptive strike to shield residents from higher energy costs and environmental impacts.
A bill wending through the Washington State legislature would require data centers to pick up the tab for all of the costs associated with connecting them to the grid. It echoes laws passed in Oregon and Minnesota last year, and others currently under consideration in Florida, Georgia, Illinois, and Delaware.
Several of these bills, including Washington’s, also seek to protect state climate goals by ensuring that new or expanded data centers are powered by newly built, zero-emissions power plants. It’s a strategy that energy wonks have started referring to as BYONCE — bring your own new clean energy. Almost all of the bills also demand more transparency from data center companies about their energy and water use.
This list of state bills is by no means exhaustive. Governors in New York and Pennsylvania have declared their intent to enact similar policies this year. At least six states, including New York and Georgia, are also considering total moratoria on new data centers while regulators study the potential impacts of a computing boom.
“Potential” is a key word here. One of the main risks lawmakers are trying to circumvent is that utilities might pour money into new infrastructure to power data centers that are never built, built somewhere else, or don’t need as much energy as they initially thought.
“There’s a risk that there’s a lot of speculation driving the AI data center boom,” Emily Moore, the senior director of the climate and energy program at the nonprofit Sightline Institute, told me. “If the load growth projections — which really are projections at this point — don’t materialize, ratepayers could be stuck holding the bag for grid investments that utilities have made to serve data centers.”
Washington State, despite being in the top 10 states for data center concentration, has not exactly been a hotbed of opposition to the industry. According to Heatmap Pro data, there are no moratoria or restrictive ordinances on data centers in the state. Rural communities in Eastern Washington have also benefited enormously from hosting data centers from the earlier tech boom, using the tax revenue to fund schools, hospitals, municipal buildings, and recreation centers.
Still, concern has started to bubble up. A ProPublica report in 2024 suggested that data centers were slowing the state’s clean energy progress. It also described a contentious 2023 utility commission meeting in Grant County, which has the highest concentration of data centers in the state, where farmers and tech workers fought over rising energy costs.
But as with elsewhere in the country, it’s the eye-popping growth forecasts that are scaring people the most. Last year, the Northwest Power and Conservation Council, a group that oversees electricity planning in the region, estimated that data centers and chip fabricators could add somewhere between 1,400 megawatts and 4,500 megawatts of demand by 2030. That’s similar to saying that between one and four cities the size of Seattle will hook up to the region’s grid in the next four years.
In the face of such intimidating demand growth, Washington Governor Bob Ferguson convened a Data Center Working Group last year — made up of state officials as well as advisors from electric utilities, environmental groups, labor, and industry — to help the state formulate a game plan. After meeting for six months, the group published a report in December finding that among other things, the data center boom will challenge the state’s efforts to decarbonize its energy systems.
A supplemental opinion provided by the Washington Department of Ecology also noted that multiple data center developers had submitted proposals to use fossil fuels as their main source of power. While the state’s clean energy law requires all electricity to be carbon neutral by 2030, “very few data center developers are proposing to use clean energy to meet their energy needs over the next five years,” the department said.
The report’s top three recommendations — to maintain the integrity of Washington’s climate laws, strengthen ratepayer protections, and incentivize load flexibility and best practices for energy efficiency — are all incorporated into the bill now under discussion in the legislature. The full list was not approved by unanimous vote, however, and many of the dissenting voices are now opposing the data center bill in the legislature or asking for significant revisions.
Dan Diorio, the vice president of state policy for the Data Center Coalition, an industry trade group, warned lawmakers during a hearing on the bill that it would “significantly impact the competitiveness and viability of the Washington market,” putting jobs and tax revenue at risk. He argued that the bill inappropriately singles out data centers, when arguably any new facility with significant energy demand poses the same risks and infrastructure challenges. The onshoring of manufacturing facilities, hydrogen production, and the electrification of vehicles, buildings, and industry will have similar impacts. “It does not create a long-term durable policy to protect ratepayers from current and future sources of load growth,” he said.
Another point of contention is whether a top-down mandate from the state is necessary when utility regulators already have the authority to address the risks of growing energy demand through the ratemaking process.
Indeed, regulators all over the country are already working on it. The Smart Electric Power Alliance, a clean energy research and education nonprofit, has been tracking the special rate structures and rules that U.S. utilities have established for data centers, cryptocurrency mining facilities, and other customers with high-density energy needs, many of which are designed to protect other ratepayers from cost shifts. Its database, which was last updated in November, says that 36 such agreements have been approved by state utility regulators, mostly in the past three years, and that another 29 are proposed or pending.
Diario of the Data Center Coalition cited this trend as evidence that the Washington bill was unnecessary. “The data center industry has been an active party in many of those proceedings,” he told me in an email, and “remains committed to paying its full cost of service for the energy it uses.” (The Data Center Coalition opposed a recent utility decision in Ohio that will require data centers to pay for a minimum of 85% of their monthly energy forecast, even if they end up using less.)
One of the data center industry’s favorite counterarguments against the fear of rising electricity is that new large loads actually exert downward pressure on rates by spreading out fixed costs. Jeff Dennis, who is the executive director of the Electricity Customer Alliance and has worked for both the Department of Energy and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, told me this is something he worries about — that these potential benefits could be forfeited if data centers are isolated into their own ratemaking class. But, he said, we’re only in “version 1.5 or 2.0” when it comes to special rate structures for big energy users, known as large load tariffs.
“I think they’re going to continue to evolve as everybody learns more about how to integrate large loads, and as the large load customers themselves evolve in their operations,” he said.
The Washington bill passed the Appropriations Committee on Monday and now heads to the Rules Committee for review. A companion bill is moving through the state senate.
Plus more of the week’s top fights in renewable energy.
1. Kent County, Michigan — Yet another Michigan municipality has banned data centers — for the second time in just a few months.
2. Pima County, Arizona — Opposition groups submitted twice the required number of signatures in a petition to put a rezoning proposal for a $3.6 billion data center project on the ballot in November.
3. Columbus, Ohio — A bill proposed in the Ohio Senate could severely restrict renewables throughout the state.
4. Converse and Niobrara Counties, Wyoming — The Wyoming State Board of Land Commissioners last week rescinded the leases for two wind projects in Wyoming after a district court judge ruled against their approval in December.
A conversation with Advanced Energy United’s Trish Demeter about a new report with Synapse Energy Economics.
This week’s conversation is with Trish Demeter, a senior managing director at Advanced Energy United, a national trade group representing energy and transportation businesses. I spoke with Demeter about the group’s new report, produced by Synapse Energy Economics, which found that failing to address local moratoria and restrictive siting ordinances in Indiana could hinder efforts to reduce electricity prices in the state. Given Indiana is one of the fastest growing hubs for data center development, I wanted to talk about what policymakers could do to address this problem — and what it could mean for the rest of the country. Our conversation was edited for length and clarity.
Can you walk readers through what you found in your report on energy development in Indiana?
We started with, “What is the affordability crisis in Indiana?” And we found that between 2024 and 2025, residential consumers paid on average $28 more per month on their electric bill. Depending on their location within the state, those prices could be as much as $49 higher per month. This was a range based on all the different electric utilities in the state and how much residents’ bills are increasing. It’s pretty significant: 18% average across the state, and in some places, as high as 27% higher year over year.
Then Synapse looked into trends of energy deployment and made some assumptions. They used modeling to project what “business as usual” would look like if we continue on our current path and the challenges energy resources face in being built in Indiana. What if those challenges were reduced, streamlined, or alleviated to some degree, and we saw an acceleration in the deployment of wind, solar, and battery energy storage?
They found that over the next nine years, between now and 2035, consumers could save a total of $3.6 billion on their energy bills. We are truly in a supply-and-demand crunch. In the state of Indiana, there is a lot more demand for electricity than there is available electricity supply. And demand — some of it will come online, some of it won’t, depending on whose projections you’re looking at. But suffice it to say, if we’re able to reduce barriers to build new generation in the state — and the most available generation is wind, solar, and batteries — then we can actually alleviate some of the cost concerns that are falling on consumers.
How do cost concerns become a factor in local siting decisions when it comes to developing renewable energy at the utility scale?
We are focused on state decisionmakers in the legislature, the governor’s administration, and at the Indiana Utility Regulatory Commission, and there’s absolutely a conversation going on there about affordability and the trends that they’re seeing across the state in terms of how much more people are paying on their bills month to month.
But here lies the challenge with a state like Indiana. There are 92 counties in the state, and each has a different set of rules, a different process, and potentially different ways for the local community to weigh in. If you’re a wind, solar, or battery storage developer, you are tracking 92 different sets of rules and regulations. From a state law perspective, there’s little recourse for developers or folks who are proposing projects to work through appeals if their projects are denied. It’s a very risky place to propose a project because there are so many ways it can be rejected or not see action on an application for years at a time. From a business perspective, it’s a challenging place to show that bringing in supply for Indiana’s energy needs can help affordability.
To what extent do you think data centers are playing a role in these local siting conflicts over renewable energy, if any?
There are a lot of similarities with regard to the way that Indiana law is set up. It’s very much a home rule state. When development occurs, there is a complex matrix of decision-making at the local level, between a county council and municipalities with jurisdiction over data centers, renewable energy, and residential development. You also have the land planning commissions that are in every county, and then the boards of zoning appeals.
So in any given county, you have anywhere between three and four different boards or commissions or bodies that have some level of decision-making power over ordinances, over project applications and approvals, over public hearings, over imposing or setting conditions. That gives a local community a lot of levers by which a proposal can get consideration, and also be derailed or rejected.
You even have, in one instance recently, a municipality that disagreed with the county government: The municipality really wanted a solar project, and the county did not. So there can be tension between the local jurisdictions. We’re seeing the same with data centers and other types of development as well — we’ve heard of proposals such as carbon capture and sequestration for wells or test wells, or demonstration projects that have gotten caught up in the same local decision-making matrix.
Where are we at with unifying siting policy in Indiana?
At this time there is no legislative proposal to reform the process for wind, solar, and battery storage developers in Indiana. In the current legislative session, there is what we’re calling an affordability bill, House Bill 1002, that deals with how utilities set rates and how they’re incentivized to address affordability and service restoration. That bill is very much at the center of the state energy debate, and it’s likely to pass.
The biggest feature of a sound siting and permitting policy is a clear, predictable process from the outset for all involved. So whether or not a permit application for a particular project gets reviewed at a local or a state level, or even a combination of both — there should be predictability in what is required of that applicant. What do they need to disclose? When do they need to disclose it? And what is the process for reviewing that? Is there a public hearing that occurs at a certain period of time? And then, when is a decision made within a reasonable timeframe after the application is filed?
I will also mention the appeals processes: What are the steps by which a decision can be appealed, and what are the criteria under which that appeal can occur? What parameters are there around an appeal process? That's what we advocate for.
In Indiana, a tremendous step in the right direction would be to ensure predictability in how this process is handled county to county. If there is greater consistency across those jurisdictions and a way for decisions to at least explain why a proposal is rejected, that would be a great step.
It sounds like the answer, on some level, is that we don’t yet know enough. Is that right?
For us, what we’re looking for is: Let’s come up with a process that seems like it could work in terms of knowing when a community can weigh in, what the different authorities are for who gets to say yes or no to a project, and under what conditions and on what timelines. That will be a huge step in the right direction.