This article is exclusively
for Heatmap Plus subscribers.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.

Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
We’re looking at battles brewing in New York and Ohio, plus there’s a bit of good news in Virginia.
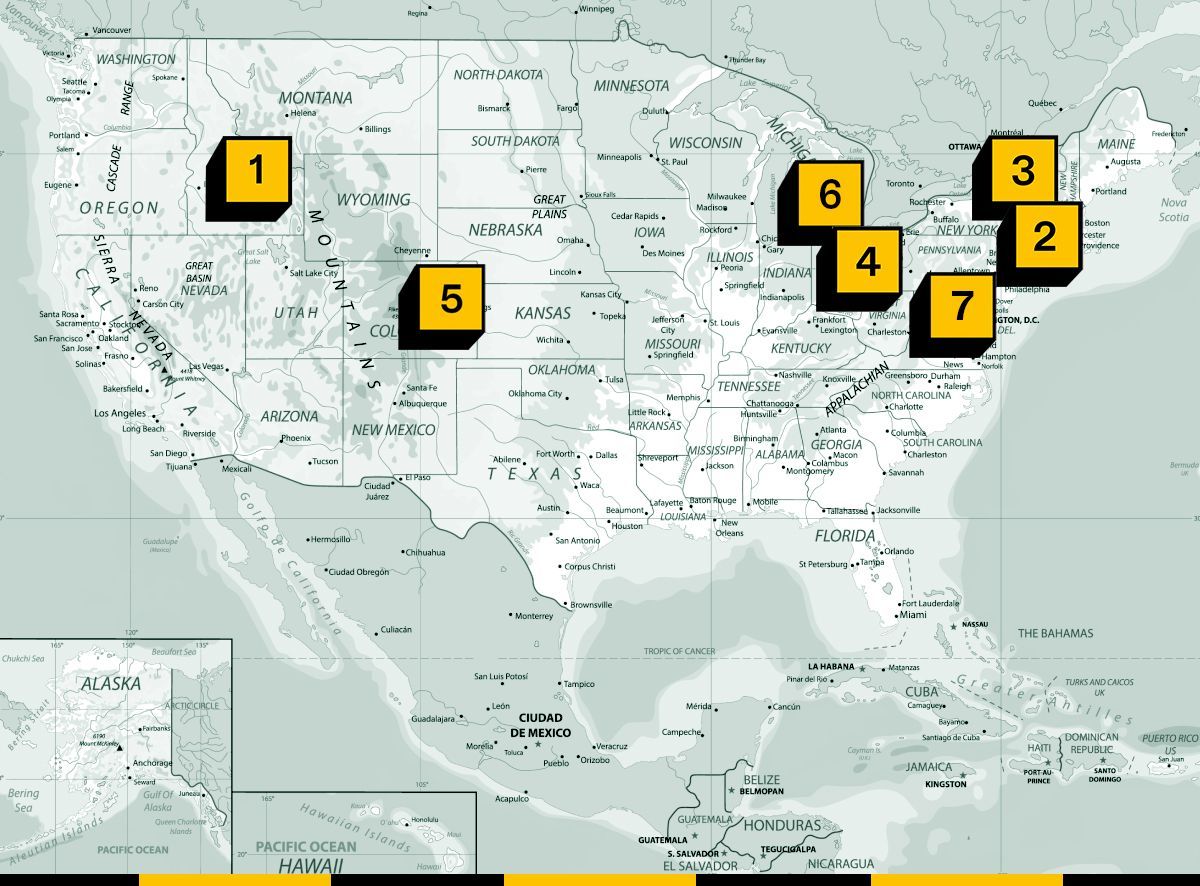
1. Idaho — The LS Power Lava Ridge wind farm is now facing a fresh assault, this time from Congress — and the Trump team now seems to want a nuclear plant there instead.
2. Suffolk County, New York — A massive fish market co-op in the Bronx is now joining the lawsuit to stop Equinor’s offshore Empire Wind project, providing anti-wind activists a powerful new ally in the public square.
3. Madison County, New York — Elsewhere in New York, a solar project upstate seems to be galvanizing opposition to the state’s permitting primacy law.
4. Fairfield County, Ohio — A trench war is now breaking out over National Grid Renewables’ Carnation Solar project, as opponents win a crucial victory at the county level.
5. El Paso County, Colorado — I don’t write about Colorado often, but this situation is an interesting one.
6. St. Joseph County, Indiana — Something interesting is playing out in this county that demonstrates how it can be quite complicated to navigate municipal and county-level permitting.
7. Albemarle County, Virginia — It’s rare I get to tell a positive story about Virginia, but today we have one: It is now easier to build a solar farm in the county home to Charlottesville, one of my personal favorite small cities in our country.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
And more on the week’s biggest fights around renewable energy.
1. Benton County, Washington – The Horse Heaven wind farm in Washington State could become the next Lava Ridge — if the Federal Aviation Administration wants to take up the cause.
2. Dukes County, Massachusetts – The Trump administration signaled this week it will rescind the approvals for the New England 1 offshore wind project.
3. Washtenaw County, Michigan – Michigan attorney general Dana Nessel waded into the fight over an Oracle and OpenAI data center in a rural corner of the state, a major escalation against AI infrastructure development by a prominent Democratic official.
4. Nacogdoches County, Texas – I am eyeing the fight over a solar project in this county for potential chicanery over species and habitat protection.
5. Fulton County, Ohio – In brighter news for the solar industry, Ohio is blessing more of their projects.
A conversation with the co-chair of the House Sustainable Energy and Environment Coalition
This week’s conversation is with Rep. Sean Casten, co-chair of the House Sustainable Energy and Environment Coalition – a group of climate hawkish Democratic lawmakers in the U.S. House of Representatives. Casten and another lawmaker, Rep. Mike Levin, recently released the coalition’s priority permitting reform package known as the Cheap Energy Act, which stands in stark contrast to many of the permitting ideas gaining Republican support in Congress today. I reached out to talk about the state of play on permitting, where renewables projects fit on Democrats’ priority list in bipartisan talks, and whether lawmakers will ever address the major barrier we talk about every week here in The Fight: local control. Our chat wound up immensely informative and this is maybe my favorite Q&A I’ve had the liberty to write so far in this newsletter’s history.
The following conversation was lightly edited for clarity.
Okay, so to start, how does the Cheap Energy Act fit into the bipartisan permitting talks?
There are two separate theories about how Congress is supposed to work, and neither of these theories is universally true but I think they inform two different approaches: do you believe the purpose of Congress is to craft good policy and then put together political consensus to put that policy forward or do you think the purpose of Congress is to find where political compromise exists and then advance the policy that can proceed along that constraint?
Depending on the situation you take Door 1 or you take Door 2.
What Mike Levin and I have tried to do with our Cheap Energy Act is to say, let’s identify the barriers to deploying cheap energy in the United States, let’s try to find the policy that’ll help consumers first and then try to get that policy done. That approach – because of the way our politics is geographically sorted out in our country – implies a wealth transfer from energy producers to energy consumers. And energy producers in this country tend to be dominant in Republican areas. That’s where coal mining is, oil and gas, logging. And energy consumers are where the population is, which skews Democratic. So on a bipartisan basis you really can’t put consumers first because that is detrimental to producers.
I think that’s why you have these two different approaches going on. I guess I have a bias towards our approach but I think we have to be very candid that the other approach does not remove the barriers to cheap energy. It removes the barriers to dirty energy.
To an overwhelming degree, and I’m slightly exaggerating, but there really aren’t permitting barriers to clean energy. There are a lot of permitting barriers to dirty energy. Which is not to say you can’t weaponize the permitting system to stop clean energy from going forward. But if you’re building a solar farm and it has to have a wire that connects it to a load, your environmental footprint is very small.
Now we’ve done some things in our bill to pre-identify corridors where there is minimal species disruptions, minimal disruption of historical artifacts, and say these are corridors where you can build things fast without guessing. Let’s not kid ourselves here: the Antiquities Act exists for a reason, the Endangered Species Act exists for a reason, and the Clean Water Act exists for a reason. But the footprint of those projects environmentally is just much, much smaller than an oil rig and a pipeline and a refinery because all of those things have the potential to leak nasty chemicals that permanently defile the air, land, and water in the vicinity.
The challenge that manifests through permitting is that if I want to lower your cost of energy, that means by definition I am undercutting your current energy provider. For the most part, that provider has undue power over whether or not you get a permit. And they have an incentive to start pamphleting the neighbors around a new transmission line, for example, to say a line is going to lower people’s property values. That’s because it is an economic threat. The reason I know that’s not an issue is you never see utilities struggle to get a new wire.
I previously reported on how the biggest sticking point in bipartisan permitting talks underway today is whether Republicans will go for tying Trump’s hands in his pursuit to stop federal renewable energy permits. Do you think any GOP lawmakers will actually do that?
Ignore whatever politics someone might have. If you’re representing a district that had a ton of wind power, not a lot of load, and you live 200 miles from a major urban center that was paying a lot for electricity, you would probably be very supportive of making it easier to build the wire to access that market and making it easier for the wind turbines to go up.
I have just described the entire Iowa congressional delegation.
Let’s say in the next election, we flip some of those Iowa seats and now what was Republican is now a Democrat, that wouldn’t change the interests of the Iowa delegation. It would just change the party. So there’s reasons why [Iowa Republican] Randy Feenstra and I have led letters on trying to build SOO Green, this high voltage transmission line that would solve exactly the problem I described there. That’s not because he’s a Republican – it’s because it is in the interests of his community.
But then why do we see so few Republicans standing up to the president in his fight specifically against renewable energy, at least in the permitting talks?
We have a huge problem with the White House that they’ve been entirely captured by the interests of energy producers and they have a rooted interest in making the price of energy expensive. The reason why they’re blocking wind permits, and the reason why they’re accelerating oil and gas exports, is because they’re completely captured by people who want the price of oil and gas to be high and they lose money when the price is low.
But that’s a completely separate series of problems.
Within the House, the leadership of the Democratic Party represents concentrated areas that would like the price of energy to be cheap. The leadership of the Republican Party represents oil and gas extractive areas that would like the price of energy to be high. So a rank and file member of the Democratic Party has no particular problem advocating for energy consumers because they’re not crossing leadership. A rank and file member of the Republican Party has no particular problem advocating for the interests of producers because they’re not crossing leadership.
I think where there’s a slight distinction is you can identify any number of Democrats from the oil and gas patch who will regularly vote with the interests of oil and gas producers, and leadership will understand why they are doing that. But it is much harder to identify members of the Republican Party who are advocating for the interests of consumers and get a pass from leadership to do that.
Mmm. So to close the loop on this, how much of a priority is it for Democrats that whatever bipartisan permitting deal is made won’t be used to speed things up for fossil while Trump continues to put the brakes on every little thing a renewable energy permit requires?
Look, I’ve seen nothing out of the House or Senate that wouldn’t do exactly what you just said. Everything would make the price of energy more expensive and make it harder to do reasonable and thoughtful environmental review. In the House and Senate as currently constituted, we are not going to get a good bill that comes through.
I think within the House you have a growing awareness that energy prices are a problem. Certainly the recent elections in New Jersey and Virginia have made that clear. You need to have a strategy to bring energy costs down. That does create an opportunity prior to next November where folks say, can I do something to help my community?
We’ll see when this bill ultimately gets out whether we get much support. I’ll say we’ve privately found Republican support for pieces of it. The way we fix this problem is by doing what the Republican Party used to be known for, which is competition. There’s no reason why we couldn’t incentivize utilities to make money by saving their consumers money. Or incentivize various pieces of the energy industry to better interconnect their markets so you could always choose the lowest cost option because Adam Smith is a god. Those arguments play much better with Republicans in states that have heavily deregulated. There are individual pieces where we’ve found Republican support. And if you think good policy and economics wins, let’s make good policy and economics wins and build support for it.
Last thing – you said there aren’t permitting barriers to clean energy. But in my reporting, I’m constantly covering local communities opposing renewable energy projects, transmission siting, battery storage. It’s a major barrier to development.
What role do you think the federal government and Congress has in dealing with the issue of local control?
It’s an old saw: depending on the issue, I’ll tell you that I’m supportive of states rights.
There are huge chunks of our energy system that should be federalized but aren’t. As an example, it makes no sense that if you want to build a gas pipeline across multiple states in the U.S., you go to FERC and they are the sole permitting authority and they decide whether or not you get a permit. If you go to the same corridor and build an electric transmission line that has less to worry about because there’s no chance of leaks, you have a different permitting body every time you cross a state line. That’s only because of laws going back to the 1930s that gave FERC sole authority on gas but not on the electric side. Our bill would fix that.
We’ve had this legacy of local control that has – not intentionally – had the practical effect of making it much easier for communities to block electric generation and distribution than natural gas distribution. This necessarily means that we have made natural gas producers more politically powerful and electricity consumers less politically powerful. Whether it was an intentional choice or not, it was a choice.
There are ways consistent with energy policy and congressional law where we can rationalize and have more parity across the energy system to make sure we make the right decision every time.
I also think at the end of the day, markets win. West Virginia one hundred years ago was the place to site your energy-intensive manufacturer because they had a ton of hydro and a ton of coal. They’ve tapped out the hydro, the coal is no longer cheap, and the economy is not good anymore. Then shift to Texas which has built more wind and solar than any state in the country and unusually for a red state has been much more pro-competition in how they regulate their energy markets, that has given them more dynamic electricity costs. Those are two different red states and sets of policy choices.
A renewables project runs into trouble — and wins.
It turns out that in order to get a wind farm approved in Trump’s America, you have to treat the project like a local election. One developer working in North Dakota showed the blueprint.
Earlier this year, we chronicled the Longspur wind project, a 200-megawatt project in North Dakota that would primarily feed energy west to Minnesota. In Morton County where it would be built, local zoning officials seemed prepared to reject the project – a significant turn given the region’s history of supporting wind energy development. Based on testimony at the zoning hearing about Longspur, it was clear this was because there’s already lots of turbines spinning in Morton County and there was a danger of oversaturation that could tip one of the few friendly places for wind power against its growth. Longspur is backed by Allete, a subsidiary of Minnesota Power, and is supposed to help the utility meet its decarbonization targets.
Except by the time the zoning officials’ decision came before the full county commission, the winds were once again blowing at Longspur’s back and county officials denied the denial. Then a few weeks later, the zoning board reconsidered Longspur and opted to approve it. Now Longspur has the permits it needs from the county.
“They have the right to put the towers on their land,” Morton County commission vice chair Jackie Buckley told me. “And Longspur has crossed their Ts and dotted their Is.”
I investigated what happened here and it turns out, Allete saw what happened at the hearing and worked extremely hard to bring supporters out when the zoning officials’ decision came before the full Morton County commission. They brought with them a bevy of landowners with a future Longspur turbine sited on their property to speak, so many that it severely outnumbered the opposition. One after another, residents spoke out against the anti-wind naysayers, a phenomenon I rarely see in fights over renewable energy projects in the United States. One resident called the wind turbines “a windfall” that was ensuring their family’s “retirement plans.” Another compared it to neighbors denying a farm the right to build a barn. Multiple people said if coal mining could happen in Morton County, why couldn’t wind?
“We just tried to understand, even internally. We asked, ‘Why didn’t we have more proponents speaking?’” Todd Simmons, Allete’s vice president of generation operations, told me in an interview this week about the project’s initial rejection. He said after the initial zoning rejection, the company then went door to door asking supporters to come testify. “We tried to make sure that landowners knew that you may have to show up and be more than present. We wanted a civil meeting, and we did not want an argumentative meeting, [but] they were not coached.”
Candidly, this style of outreach reminds me a lot of door-to-door campaign canvassing and a well-worn phrase in professional politics: it all comes down to turnout. And Allete treated the situation that way, telling me that the initial rejection to them was because of an absence, not conflict. “When the folks who were anti- spoke, and the rest of the crowd did not say anything, there was a belief that silence was [an] agreement by the rest,” Simmons told me.
Buckley told me that some of these supporters were actually at the zoning hearing too, but did not want to speak up because “they wouldn’t talk against their neighbor.” Out in rural communities like Morton County, “they all know each other – it’s all one neighborhood community.” In the end, the county commission felt it couldn’t deny people’s property rights, let alone invite whatever legal ramifications would arrive from denying the project in spite of the support from these property owners. “I think it had to do more with private property rights and the people that were in favor of it have property rights, same as do the people in opposition,” Simmons said.
I think there’s an important conclusion to be drawn from what happened in Morton County for any renewable energy project developer out there dealing with local opposition. Too often I watch and listen to local permitting hearings where the dissenting voices are the only ones raised. There are obvious risks for anyone in a small community who does speak up, as I’ve heard of threats against people who come out in support of a project, from anti-renewables homeowners. But it’s clear from what happened to Longspur there is strength in numbers when supporters are mobilized to speak up.
Allete told me they saw an education in the Longspur permitting process too. “It doesn’t matter where you’re building,” SImmons said. “Working with the landowners, and the public agencies…. The sooner you can help them understand what the project is actually about, the better you are.”