You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On the looming climate summit, clean energy stocks, and Hurricane Rafael

Current conditions: A winter storm could bring up to 4 feet of snow to parts of Colorado and New Mexico • At least 89 people are still missing from extreme flooding in Spain • The Mountain Fire in Southern California has consumed 14,000 acres and is zero percent contained.
The world is still reeling from the results of this week’s U.S. presidential election, and everyone is trying to get some idea of what a second Trump term means for policy – both at home and abroad. Perhaps most immediately, Trump’s election is “set to cast a pall over the UN COP29 summit next week,” said the Financial Times. Already many world leaders and business executives have said they will not attend the climate talks in Azerbaijan, where countries will aim to set a new goal for climate finance. “The U.S., as the world’s richest country and key shareholder in international financial institutions, is viewed as crucial to that goal,” the FT added.
Trump has called climate change a hoax, vowed to once again remove the U.S. from the Paris Agreement, and promised to stop U.S. climate finance contributions. He has also promised to “drill, baby, drill.” Yesterday President Biden put new environmental limitations on an oil-and-gas lease sale in Alaska’s Arctic National Wildlife Refuge. The lease sale was originally required by law in 2017 by Trump himself, and Biden is trying to “narrow” the lease sale without breaking that law, according to The Washington Post. “The election results have made the threat to America's Arctic clear,” Kristen Miller, executive director of Alaska Wilderness League, told Reuters. “The fight to save the Arctic Refuge is back, and we are ready for the next four years.”
Another early effect of the decisive election result is that clean energy stocks are down. The iShares Global Clean Energy exchange traded fund, whose biggest holdings are the solar panel company First Solar and the Spanish utility and renewables developer Iberdola, is down about 6%. The iShares U.S. Energy ETF, meanwhile, whose largest holdings are Exxon and Chevron, is up over 3%. Some specific publicly traded clean energy stocks have sunk, especially residential solar companies like Sunrun, which is down about 30% compared to Tuesday. “That renewables companies are falling more than fossil energy companies are rising, however, indicates that the market is not expecting a Trump White House to do much to improve oil and gas profitability or production, which has actually increased in the Biden years thanks to the spikes in energy prices following the Russian invasion of Ukraine and continued exploitation of America’s oil and gas resources through hydraulic fracturing,” wrote Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin.
Hurricane Rafael swept through Cuba yesterday as a Category 3 storm, knocking out the power grid and leaving 10 million people without electricity. Widespread flooding is reported. The island was still recovering from last month’s Hurricane Oscar, which left at least six people dead. The electrical grid – run by oil-fired power plants – has collapsed several times over the last few weeks. Meanwhile, the U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement said yesterday that about 17% of crude oil production and 7% of natural gas output in the Gulf of Mexico was shut down because of Rafael.
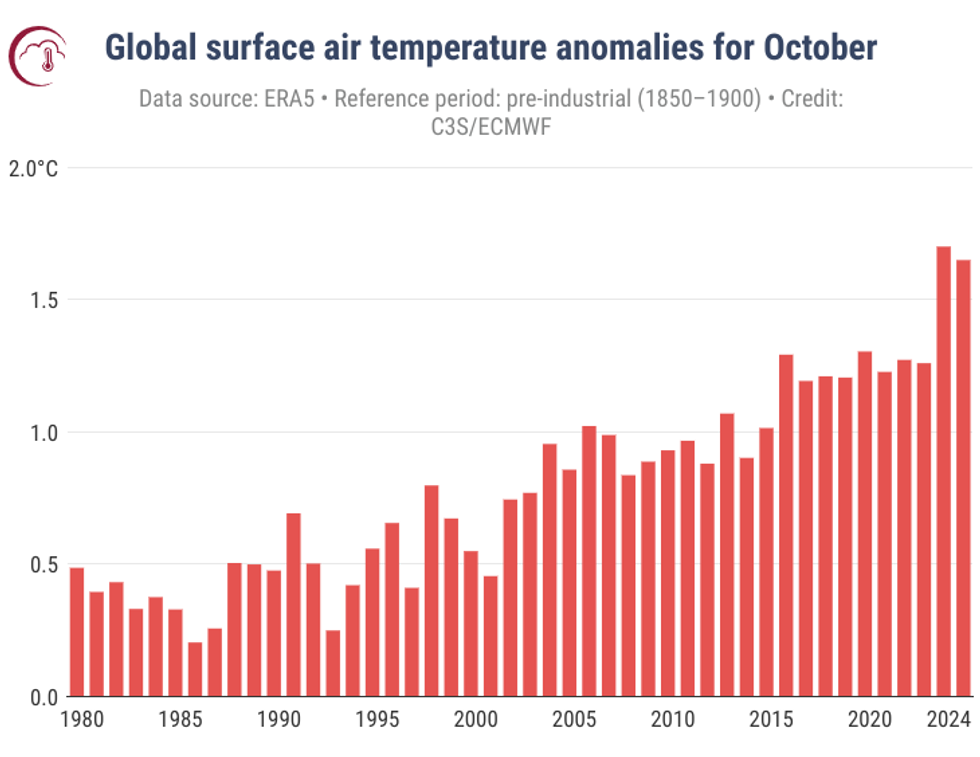
It is “virtually certain” that 2024 will be the warmest year on record, according to the European Copernicus Climate Change Service. In October, the global average surface air temperature was about 60 degrees Fahrenheit, or nearly 3 degrees Fahrenheit warmer than pre-industrial averages for that month. This year is also on track to be the first entire calendar year in which temperatures are more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. “This marks a new milestone in global temperature records and should serve as a catalyst to raise ambition for the upcoming climate change conference,” said Copernicus deputy director Dr. Samantha Burgess.
The world is falling short of its goal to double the rate of energy efficiency improvements by 2030, the International Energy Agency said in its new Energy Efficiency 2024 report. Global primary energy intensity – which the IEA explained is a measure of efficiency – will improve by 1% this year, the same as last year. It needs to be increasing by 4% by the end of the decade to meet a goal set at last year’s COP. “Boosting energy efficiency is about getting more from everyday technologies and industrial processes for the same amount of energy input, and means more jobs, healthier cities and a range of other benefits,” the IEA said. “Improving the efficiency of buildings and vehicles, as well as in other areas, is central to clean energy transitions, since it simultaneously improves energy security, lowers energy bills for consumers and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.” The group called for more government action as well as investment in energy efficient technologies.
Deforestation in Brazil’s Amazon fell by 30.6% in the 12 months leading up to July, compared to a year earlier. It is now at the lowest levels since 2015.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Startups Airloom and Radia looked at the same set of problems and came up with very different solutions.
You’d be forgiven for assuming that wind energy is a technologically stagnant field. After all, the sleek, three-blade turbine has defined the industry for nearly half a century. But even with over 1,000 gigawatts of wind generating capacity installed worldwide, there’s a group of innovators who still see substantial room for improvement.
The problems are myriad. There are places in the world where the conditions are too windy and too volatile for conventional turbines to handle. Wind farms must be sited near existing transportation networks, accessible to the trucks delivering the massive components, leaving vast areas with fantastic wind resources underdeveloped. Today’s turbines have around 1,500 unique parts, and the infrastructure needed to assemble and stand up a turbine’s multi-hundred-foot tower and blades is expensive— giant cranes don’t come cheap.
“We’ve only really ever tried one type of technology,” Neil Rickner, the CEO of the wind power startup Airloom Energy, told me. Now, he’s one of a few entrepreneurs trying a new approach.
Airloom’s system uses much-shorter vertical blades attached to an oval track that resembles a flat rollercoaster — no climbs or drops, just a horizontal loop composed of 58 unique parts. Wind propels the blades around the track, turning a vertical shaft that’s connected to an electricity-producing generator. That differs from conventional turbines, which spin on a vertical plane around a horizontal shaft, like a ferris wheel.
The system is significantly lower to the ground than today’s turbines and has the ability to capture wind from any direction, unlike conventional turbines, allowing for deployment in areas with shifting wind patterns. It promises to be mass manufacturable, cheap, and simple to transport and install, opening up the potential to build systems in a wider variety of geographies — everywhere from airports to remote or even mountainous regions.
Airloom’s CTO, Andrew Street, brings a background in drone tech that Rickner said helped shape the architecture of Airloom’s blades. “It’s all known tech. And it’s not completely off the shelf, but Andrew’s done it on 17 other platforms,” he told me. Rickner himself spent years at GoogleX working on Makani, a now-defunct wind energy project that attempted to commercialize an airborne wind energy system. The concept involved attaching rotors to autonomous kites, which flew in high-altitude loops to capture wind energy.
That system ultimately proved too complicated, something Airloom’s founder Robert Lumley warned Rickner about a decade ago at an industry conference. As Rickner recalls, he essentially told him, “all of that flying stuff is too complicated. Put all that physics — which is great — put it on the ground, on a rail.” Rickner took the lesson to heart, and when Lumley recruited him to join Airloom’s team a few years ago, he said it felt like an ideal chance to apply all the knowledge he’d accumulated “around what it takes to bring a novel wind technology to a very stodgy market.”
Indeed, the industry has proven difficult to disrupt. While Airloom was founded in 2014, the startup is still in its early stages, though it’s attracted backing from some climate sector heavyweights. Lowercarbon Capital led its $7.5 million seed round in 2024, which also included participation from Breakthrough Energy Ventures. The company also secured $5 million in matching funds from the state of Wyoming, where it’s based, and a $1.25 million contract with the Department of Defense.
Things are moving now. In the coming months, Airloom is preparing to bring its pilot plant online in Wyoming, closely followed by a commercial demo. Rickner told me the plan is to begin construction on a commercial facility by July 4, the deadline for wind to receive federal tax credits.
“If you could just build wind without gigantic or heavy industrial infrastructure — cranes and the like —- you will open up huge parts of the world,” Rickner told me, citing both the Global South and vast stretches of rural America as places where the roads, bridges, cranes, and port infrastructure may be insufficient for transporting and assembling conventional turbines. While modern onshore installations can exceed 600 feet from the tower’s base to the blade’s tip, Airloom’s system is about a fifth that height. Its nimble assembly would also allow turbines to be sited farther from highways, potentially enabling a more “out of sight, out of mind” attitude among residents and passersby who might otherwise resist such developments.
The company expects some of its first installations to be co-located with — you guessed it — data centers, as tech giants are increasingly looking to circumvent lengthy grid interconnection queues by sourcing power directly from onsite renewables, an option Rickner said wasn’t seriously discussed until recently.
Even considering Trump’s cuts to federal incentives for wind, “I’d much rather be doing Airloom today than even a year ago,” Rickner told me. “Now, with behind-the-meter, you’ve got different financing options. You’ve got faster buildout timelines that actually meet a venture company, like Airloom. You can see it’s still a tough road, don’t get me wrong. But a year ago, if you said we’re just going to wait around seven years for the interconnection queue, no venture company is going to survive that.”
It’s certainly not the only company in the sector looking to benefit from the data center boom. But I was still surprised when Rickner pointed out that Airloom’s fundamental value proposition — enabling wind energy in more geographies — is similar to a company that at first glance appears to be in a different category altogether: Radia.
Valued at $1 billion, this startup plans to make a plane as long as a football field to carry blades roughly 30% to 40% longer than today’s largest onshore models. Because larger blades mean more power, Radia’s strategy could make wind energy feasible in low-wind regions or simply boost output where winds are strong. And while the company isn’t looking to become a wind developer itself, “if you look at their pitch, it is the Airloom pitch,” Rickner told me.
Will Athol, Radia’s director of business development, told me that by the time the company was founded in 2016, “it was becoming clear that ground-based infrastructure — bridges, tunnels, roads, that kind of thing — was increasingly limiting where you can deploy the best turbines,” echoing Airloom’s sentiments. So competitors in the wind industry teamed up, requesting logistics input from the aviation industry. Radia responded, and has since raised over $100 million as it works to achieve its first flight by 2030.
Hopefully by that point, the federal war on wind will be a thing of the past. “We see ourselves and wind energy as a longer term play,” Athol told me. Though he acknowledged that these have certainly been “eventful times for the wind industry” in the U.S., there’s also a global market eager for this tech. He sees potential in regions such as India and North Africa, where infrastructure challenges have made it tough to deploy large-scale turbines.
Neither Radia nor Airloom thinks its approach will render today’s turbines obsolete, or that other renewable resources will be completely displaced. “I think if you look at most utilities, they want a mix,” Rickner said. But he’s still pretty confident in Airloom’s potential to seriously alter an industry that’s long been considered mature and constrained to incremental gains.
“When Airloom is 100% successful,” he told me, “we will take a huge chunk of market share.”
On electrolyzers’ decline, Anthropic’s pledge, and Syria’s oil and gas
Current conditions: Warmer air from down south is pushing the cold front in Northeast back up to Canada • Tropical Cyclone Gezani has killed at least 31 in Madagascar • The U.S. Virgin Islands are poised for two days of intense thunderstorms that threaten its grid after a major outage just days ago.
Back in November, Democrats swept to victory in Georgia’s Public Service Commission races, ousting two Republican regulators in what one expert called a sign of a “seismic shift” in the body. Now Alabama is considering legislation that would end all future elections for that state’s utility regulator. A GOP-backed bill introduced in the Alabama House Transportation, Utilities, and Infrastructure Committee would end popular voting for the commissioners and instead authorize the governor, the Alabama House speaker, and the Alabama Senate president pro tempore to appoint members of the panel. The bill, according to AL.com, states that the current regulatory approach “was established over 100 years ago and is not the best model for ensuring that Alabamians are best-served and well-positioned for future challenges,” noting that “there are dozens of regulatory bodies and agencies in Alabama and none of them are elected.”
The Tennessee Valley Authority, meanwhile, announced plans to keep two coal-fired plants operating beyond their planned retirement dates. In a move that seems laser-targeted at the White House, the federally-owned utility’s board of directors — or at least those that are left after President Donald Trump fired most of them last year — voted Wednesday — voted Wednesday to keep the Kingston and Cumberland coal stations open for longer. “TVA is building America’s energy future while keeping the lights on today,” TVA CEO Don Moul said in a statement. “Taking steps to continue operations at Cumberland and Kingston and completing new generation under construction are essential to meet surging demand and power our region’s growing economy.”
Secretary of the Interior Doug Burgum said the Trump administration plans to appeal a series of court rulings that blocked federal efforts to halt construction on offshore wind farms. “Absolutely we are,” the agency chief said Wednesday on Bloomberg TV. “There will be further discussion on this.” The statement comes a week after Burgum suggested on Fox Business News that the Supreme Court would break offshore wind developers’ perfect winning streak and overturn federal judges’ decisions invalidating the Trump administration’s orders to stop work on turbines off the East Coast on hotly-contested national security, environmental, and public health grounds. It’s worth reviewing my colleague Jael Holzman’s explanation of how the administration lost its highest profile case against the Danish wind giant Orsted.
Thyssenkrupp Nucera’s sales of electrolyzers for green hydrogen projects halved in the first quarter of 2026 compared to the same period last year. It’s part of what Hydrogen Insight referred to as a “continued slowdown.” Several major projects to generate the zero-carbon fuel with renewable electricity went under last year in Europe, Australia, and the United States. The Trump administration emphasized the U.S. turn away from green hydrogen by canceling the two regional hubs on the West Coast that were supposed to establish nascent supply chains for producing and using green hydrogen — more on that from Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo. Another potential drag on the German manufacturer’s sales: China’s rise as the world’s preeminent manufacturer of electrolyzers.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
The artificial intelligence giant Anthropic said Wednesday it would work with utilities to figure out how much its data centers were driving up electricity prices and pay a rate high enough to avoid passing the costs onto ratepayers. The announcement came as part of a multi-pronged energy strategy to ease public concerns over its data centers at a moment when the server farms’ effect on power prices and local water supplies is driving a political backlash. As part of the plan, Anthropic would cover 100% of the costs of upgrading the grid to bring data centers online, and said it would “work to bring net-new power generation online to match our data centers’ electricity needs.” Where that isn’t possible, the company said it would “work with utilities and external experts to estimate and cover demand-driven price effects from our data centers.” The maker of ChatGPT rival Claude also said it would establish demand response programs to power down its data centers when demand on the grid is high, and deploy other “grid optimization” tools.
“Of course, company-level action isn’t enough. Keeping electricity affordable also requires systemic change,” the company said in a blog post. “We support federal policies — including permitting reform and efforts to speed up transmission development and grid interconnection — that make it faster and cheaper to bring new energy online for everyone.”

Syria’s oil reserves are opening to business, and Western oil giants are in line for exploration contracts. In an interview with the Financial Times, the head of the state-owned Syrian Petroleum Company listed France’s TotalEnergies, Italy’s Eni, and the American Chevron and ConocoPhillips as oil majors poised to receive exploration licenses. “Maybe more than a quarter, or less than a third, has been explored,” said Youssef Qablawi, chief executive of the Syrian Petroleum Company. “There is a lot of land in the country that has not been touched yet. There are trillions of cubic meters of gas.” Chevron and Qatar’s Power International Holding inked a deal just last week to explore an offshore block in the Mediterranean. Work is expected to begin “within two months.”
At the same time, Indonesia is showing the world just how important it’s become for a key metal. Nickel prices surged to $17,900 per ton this week after Indonesia ordered steep cuts to protection at the world’s biggest mine, highlighting the fast-growing Southeast Asian nation’s grip over the global supply of a metal needed for making batteries, chemicals, and stainless steel. The spike followed Jakarta’s order to cut production in the world’s biggest nickel mine, Weda Bay, to 12 million metric tons this year from 42 million metric tons in 2025. The government slashed the nationwide quota by 100 million metric tons to between 260 million and 270 million metric tons this year from 376 million metric tons in 2025. The effect on the global price average showed how dominant Indonesia has become in the nickel trade over the past decade. According to another Financial Times story, the country now accounts for two-thirds of global output.
The small-scale solar industry is singing a Peter Tosh tune: Legalize it. Twenty-four states — funny enough, the same number that now allow the legal purchase of marijuana — are currently considering legislation that would allow people to hook up small solar systems on balconies, porches, and backyards. Stringent permitting rules already drive up the cost of rooftop solar in the U.S. But systems small enough for an apartment to generate some power from a balcony have largely been barred in key markets. Utah became the first state to vote unanimously last year to pass a law allowing residents to plug small solar systems straight into wall sockets, providing enough electricity to power a laptop or small refrigerator, according to The New York Times.
The maker of the Prius is finally embracing batteries — just as the rest of the industry retreats.
Selling an electric version of a widely known car model is no guarantee of success. Just look at the Ford F-150 Lightning, a great electric truck that, thanks to its high sticker price, soon will be no more. But the Toyota Highlander EV, announced Tuesday as a new vehicle for the 2027 model year, certainly has a chance to succeed given America’s love for cavernous SUVs.
Highlander is Toyota’s flagship titan, a three-row SUV with loads of room for seven people. It doesn’t sell in quite the staggering numbers of the two-row RAV4, which became the third-best-selling vehicle of any kind in America last year. Still, the Highlander is so popular as a big family ride that Toyota recently introduced an even bigger version, the Grand Highlander. Now, at last, comes the battery-powered version. (It’s just called Highlander and not “Highlander EV,” by the way. The Highlander nameplate will be electric-only, while gas and hybrid SUVs will fly the Grand Highlander flag.)
The American-made electric Highlander comes with a max range of 287 miles in its less expensive form and 320 in its more expensive form. The SUV comes with the NACS port to charge at Tesla Superchargers and vehicle-to-load capability that lets the driver use their battery power for applications like backing up the home’s power supply. Six seats come standard, but the upgraded Highlander comes with the option to go to seven. The interior is appropriately high-tech.
Toyota will begin to build this EV later this year at a factory in Kentucky and start sales late in the year. We don’t know the price yet, but industry experts expect Highlander to start around $55,000 — in the same ballpark as big three-row SUVs like the Kia EV9 and Hyundai Ioniq 9 — and go up from there.
The most important point of the electric Highlander’s arrival, however, is that it signals a sea change for the world’s largest automaker. Toyota was decidedly not all in on the first wave (or two) of modern electric cars. The Japanese giant was content to make money hand over first while the rest of the industry struggled, losing billions trying to catch up to Tesla and deal with an unpredictable market for electrics.
A change was long overdue. This year, Toyota was slated to introduce better EVs to replace the lackluster bZ4x, which had been its sole battery-only model. That included an electrified version of the C-HR small crossover. Now comes the electrified Highlander, marking a much bigger step into the EV market at a time when other automakers are reining in their battery-powered ambitions. (Fellow Japanese brand Subaru, which sold a version of bZ4x rebadged as the Solterra, seems likely to do the same with the electric Highlander and sell a Subaru-labeled version of essentially the same vehicle.)
The Highlander EV matters to a lot of people simply because it’s a Toyota, and they buy Toyotas. This pattern was clear with the success of the Honda Prelude. Under the skin that car was built on General Motors’ electric vehicle platform, but plenty of people bought it because they were simply waiting for their brand, Honda, to put out an EV. Toyota sells more cars than anyone in the world. Its act of putting out a big family EV might signal to some of its customers that, yeah, it’s time to go electric.
Highlander’s hefty size matters, too. The five-seater, two-row crossover took over as America’s default family car in the past few decades. There are good EVs in this space, most notably the Tesla Model Y that has led the world in sales for a long time. By contrast, the lineup of true three-row SUVs that can seat six, seven, or even eight adults has been comparatively lacking. Tesla will cram two seats in the back of the Model Y to make room for seven people, but this is not a true third row. The excellent Rivian R1S is big, but expensive. Otherwise, the Ioniq 9 and EV9 are left to populate the category.
And if nothing else, the electrified Highlander is a symbolic victory. After releasing an era-defining auto with the Prius hybrid, Toyota arguably had been the biggest heel-dragger about EVs among the major automakers. It waited while others acted; its leadership issued skeptical statements about battery power. Highlander’s arrival is a statement that those days are done. Weirdly, the game plan feels like an announcement from the go-go electrification days of the Biden administration — a huge automaker going out of its way to build an important EV in America.
If it succeeds, this could be the start of something big. Why not fully electrify the RAV4, whose gas-powered version sells in the hundreds of thousands in America every year?