You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On the uncertain future of government grants and loans, a new Treasury secretary, and deadly heat

Current conditions: A major incident was declared in parts of England after Storm Herminia brought severe flooding • A 3.8-magnituted earthquake was recorded off the coast of Maine • It’s warmer than average across central and eastern states, but colder than average in the Southwest.
The Trump administration’s Office of Management and Budget issued a two-page memo temporarily suspending all federal grants and loans. “The use of Federal resources to advance Marxist equity, transgenderism, and green new deal social engineering policies is a waste of taxpayer dollars that does not improve the day-to-day lives of those we serve,” wrote the OMB’s acting director Matthew J. Vaeth. The pause will allow agencies to review grant and loan programs and make sure they align with President Trump’s many executive orders, which have sought to sharply curtail climate initiatives and clean energy spending, among other programs. Some experts say the order is too vague to be legal. Still, it triggered panic and confusion across many state and local governments and programs. “It will mean missed payrolls and rent payments and everything in between,” said Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer. “Chaos for everything from universities to non-profit charities, state disaster assistance, local law enforcement, aid to the elderly, and food for those in need.” The pause goes into effect at 5 p.m. today.
The Senate yesterday confirmed hedge fund manager Scott Bessent as Treasury secretary. As Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin has explained, Bessent has long advised Trump on the economy and has a “3-3-3” plan for the economy that involves cutting deficits in half to 3% of gross domestic product, ratcheting up GDP to 3%, and boosting oil production by three million barrels a day, a goal that Continental Resources chief executive and informal Trump advisor Harold Hamm has cast doubt on due to geologic constraints. Bessent has also suggested to the Financial Times that the Inflation Reduction Act could be one area where cuts to the federal budget could be found, telling the paper that it was “the Doomsday machine for the deficit.” He is reportedly aiming to introduce new universal tariffs on imports, starting at 2.5% and gradually rising to as high as 20%.
President Trump’s policy agenda cannot stop the global energy transition, analysts from Citigroup wrote in a note, according to Bloomberg. “Clean energy is cheaper, more widely available, and more efficient,” the note said. “For advocates of clean energy transition, the power of economics will prevail.” The analysts weren’t particularly concerned about the U.S. exodus from the Net-Zero Banking Alliance (which Citigroup itself has left), saying this “neither impedes progress nor dilutes efforts” to decarbonize investing.
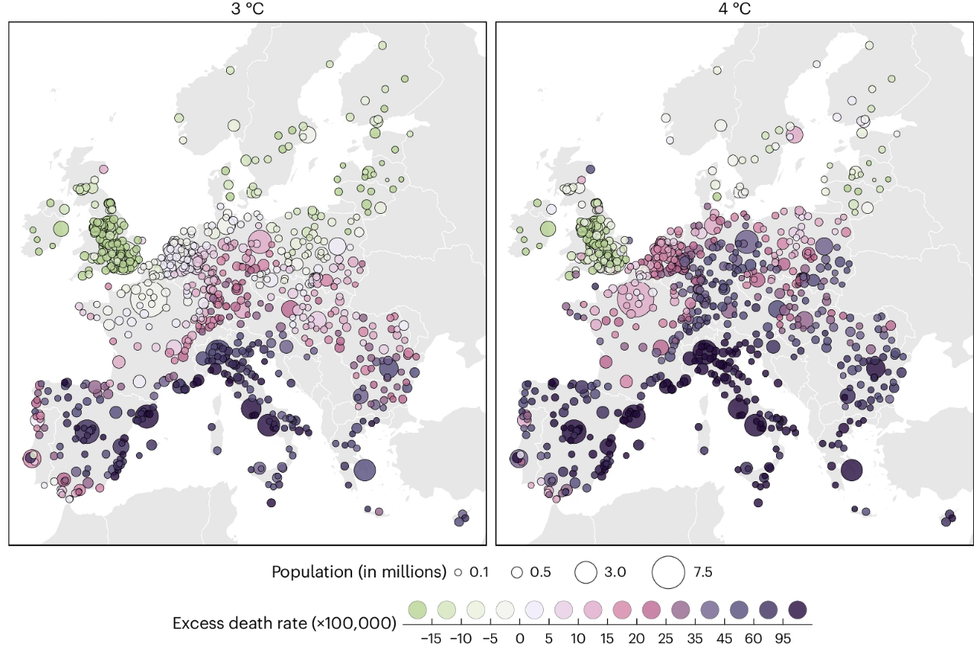
Climate change-related deaths in European cities could rise by 50% by 2099 if little is done in the way of mitigation and adaptation, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Medicine. In this scenario, some 2.3 million people in urban areas across the continent are projected to die climate-related deaths by the end of the century. “With no adaptation to heat, the increase in heat-related deaths consistently exceeds any decrease in cold-related deaths,” the authors wrote. The number of deaths could be reduced by at least two-thirds if warming peaks at 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, or at least remains below 3 degrees Celsius. The world has already warmed by 1.3 degrees Celsius. According to the Climate Action Tracker, current policies have us on a path toward roughly 2.7 degrees of warming by 2100. A separate study out today found that ocean-surface temperatures are warming more than four times faster now than they did in the late 1980s.
As Los Angeles starts down the long path to recovery after its devastating wildfires, a debate is growing over what to do with all the debris leftover from the blazes. Some people are considering hiring private firms to clean up their properties, but that could cost some $170,000, the Los Angeles Times reported. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers is offering to clear away the debris for free, and the Environmental Protection Agency is also working on the cleanup, but officials warned locals at a town hall meeting Sunday that the process could take up to 18 months. That timeline was met with outrage. The EPA plans to send the debris to some L.A. County’s foothill communities to be processed for disposal, but residents there aren’t happy about the idea of being dumped with toxic wildfire waste. “The potential risks associated with hazardous materials, particularly lithium electric vehicle batteries, which are highly flammable and pose environmental contamination risks, are a matter of significant concern,” said L.A. County Supervisor Hilda Solis in a statement. “The removal of these materials should not come at the cost of creating a toxic environment for communities already disproportionately impacted by pollution.”
“Blithely insisting that incredibly complex problems will be solved easily and quickly is a specialty of tech barons. And if AI itself finds the solution to our energy problems? Even better.”
–Paul Waldman writing for Heatmap on solving climate change (or not) with AI
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On Tesla’s sunny picture, Chinese nuclear, and Bad Bunny’s electric halftime show
Current conditions: The Seattle Seahawks returned home to a classically rainy, overcast city from their win in last night’s Super Bowl, though the sun is expected to come out for Wednesday's victory parade • Severe Tropical Cyclone Mitchell is pummeling Western Australia with as much as 8 inches of rain • Flash floods from Storm Marta have killed at least four in Morocco.
Orsted’s two major offshore wind projects in the United States are back on track to be completed on schedule, its chief executive said. Rasmus Errboe told the Financial Times that the Revolution Wind and Sunrise Wind projects in New England would come online in the latter half of this year and in 2027, respectively. “We are fully back to work and construction on both projects is moving forward according to plan,” Errboe said. The U.S. has lost upward of $34 billion worth of clean energy projects since President Donald Trump returned to office, as I wrote last week. A new bipartisan bill introduced in the House last week to reform the federal permitting process would bar the White House from yanking back already granted permits. For now, however, the Trump administration has signaled its plans to appeal federal courts’ decisions to rule against its actions to halt construction on offshore turbines.
The fight over the billions in federal funding the White House is holding up for the Gateway rail project between New Jersey and New York, meanwhile, heated up over the weekend. On Friday night, a federal judge ordered the Trump administration to unfreeze the nearly $16 billion to the project, just hours after construction ground to a halt as funding ran dry. In her ruling, U.S. District Judge Jeannette Vargas of the Southern District of New York wrote that “plaintiffs have adequately shown that the public interest would be harmed by a delay in a critical infrastructure project.” Trump had his own idea in mind. Over the weekend, the White House proposed releasing the money only if Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer of New York agreed to rename Penn Station after Trump.
Tesla has started hiring staff to ramp up production of solar panels as the company looks to build 100 gigawatts of panel-manufacturing capacity supplied with raw materials produced in America. In a job posting on LinkedIn, Seth Winger, Tesla’s senior manager for solar products engineering, wrote that the panel-producing buildout was “an audacious, ambitious project.” For that, he wrote, “we need audacious, ambitious engineers and scientists to help us grow to massive scale. If you want to solve tough manufacturing problems at breakneck speed and help the U.S. breakthrough on renewable energy generation, come join us.” One of the listings indicated that the target date for bringing the new factories online was the “end of 2028,” giving an indication of timing that Reuters noted had been previously absent from Elon Musk’s public statements. Bloomberg reported last week that Tesla is already looking at sites in New York, Arizona, and Idaho for its manufacturing expansion.
The Trump administration tried to yank permits from the offshore wind projects off New England on the grounds that the towering turbines caused more ecological destruction than the electricity is worth. On Friday, however, Trump signed a proclamation reopening a giant marine preserve in the Atlantic Ocean to commercial fishing. First established at the end of the Obama administration, the Northeast Canyons and Seamounts Marine National Monument lies 130 miles off the coast of Cape Cod, encompassing what The New York Times described as “an area the size of Connecticut that is home to dolphins, endangered whales, sea turtles, and ancient deep-sea corals.” While Trump lifted the ban on commercial fishing in the zone during his first administration, President Joe Biden reinstated the restrictions. But this isn’t the first time Trump reopened a national marine national monument to fishing. In April, he ended protections for the Pacific Islands Heritage Marine National Monument located 750 miles west of Hawaii and designated by President George W. Bush in 2009.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Connecitcut’s Department of Insurance has launched a website that displays extensive information about the climate risk of every property in the state in what E&E News called “an unprecedented move to alert residents and to promote flood insurance.” The details include each property’s history of damage from floods and other events predicted to get worse as the planet warms. “A single risk score does not fully convey flood and climate risk,” department spokesperson Mary Quinn said. The department plans a marketing campaign this year with ads on radio, TV, and social media, and workshops for insurance agents on how to use the website. Nationwide, climate change is already raising household costs by $900 per year, as Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin reported last year. Wildfires have already “destroyed California’s insurance market,” according to an interview with Heatmap's Shift Key podcast last year with an expert at the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School.
Unit 1 of the Taipingling nuclear power station in China’s Guangdong has reached criticality seven years after construction began on the gigawatt-sized Hualong One reactor. The debut atom-splitting means the newest reactor is months, if not weeks, from entering into commercial operation. If that enticingly single-digit number of years to build a piece of infrastructure that takes the U.S. more than a decade wasn’t enough of a sign of China’s nuclear strengths, the country this week hit another milestone on a separate atomic station. At the Zhangzhou-3 nuclear reactor, workers last week installed the inner steel dome of the containment building.

Nearly a decade after Puerto Rico’s power grid collapsed and plunged America’s most populous territory into the second-longest blackout in world history, the island’s biggest musical star performed a Super Bowl halftime show that included linemen working on transformers. Bad Bunny’s performance, a revue of his reggaeton hits, served as an ode to what he called “my motherland, my homeland, Puerto Rico.” The grid still suffers regular outages. When it’s working, the power system sends occasional surges through wires that fry appliances. Electricity rates are higher than almost any state, despite Puerto Rico suffering worse poverty rates than Mississippi. At one point, Bad Bunny climbed a utility pole on stage waving a light-blue Puerto Rican flag, a symbol of the movement to establish the island territory as its own independent nation. It was a powerful political statement at America’s most-watched sporting event. For energy nerds, it was a rare opportunity to reflect on one of the worst, most prolonged infrastructure disasters in modern American history.
Rob talks with the lawmaker from New Mexico (and one-time mechanical engineer) about the present and future of climate policy.
The permitting reform conversation is heating up.
On this week’s episode of Shift Key, Rob talks to Senator Martin Heinrich about whether Republicans and Democrats will reach a permitting reform deal this year. They chat about what Democrats would need to see in such a deal, how it could help transmission projects, and why such a deal will ultimately need to constrain President Trump in some way.
They also discuss the future of Democratic energy and climate policy — what Heinrich learned from the Biden administration, what the Inflation Reduction Act got right (and wrong), and why data centers are becoming a new kind of energy villain.
Heinrich is the senior senator from New Mexico (and a well-known transmission policy nerd). He’s also a trained mechanical engineer and the son of a utility lineman. Shift Key is hosted by Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap, and Jesse Jenkins, a professor of energy systems engineering at Princeton University. Jesse is off this week.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from our conversation:
Robinson Meyer: There’s one bill we reported on yesterday at Heatmap called the FREEDOM Act. It just came out of the House. It has a bipartisan group behind it, including [Republican] Mike Lawler from New York and [Democrat] Adam Gray in California. It tries to prevent federal agencies from terminating work on a fully permitted project or affecting ongoing construction on a fully permitted project. And it would establish this fund that a company that has seen its permits get yanked could pull from in the Treasury Department, up to $5 million.
Does this bill meet your concerns? Have you looked at it? Is this the kind of text that you would need to see to say, okay, we could put a deal together?
Senator Martin Heinrich: We’re very intrigued in digging into that legislation right now, and I do think that anything we can do to create more certainty in the market — and that’s true for both renewables and for traditional energy. Because the truth is, we can’t have a system where, when one party controls the White House, they attack this set of energy, and then when it changes hands, that group attacks this other set of energy. We just need to set policy and then have predictable flows of capital into the market. And so I think this is a positive step forward. And we should look at all the things the House does and evaluate them on their merits.
I will say that if the figure is $5 billion for this fund, you could exhaust that on one wind project. And thank goodness the court stepped in as quickly as they did because those offshore wind projects were on the scale of tens of billions of dollars. And effectively, if you’re going shut those off, that’s a takings, in my view. That’s like actually stealing someone’s capital, stealing someone’s money.
And we can’t — that’s third world stuff. We can’t have that in the United States of America. But I give credit to the House for coming forward with this kind of thing because we do need to constrain it.
You can find the full transcript of this episode here.
Mentioned:
SunZia: The Untold Saga of America's Biggest Power Line, by Robinson Meyer
The FREEDOM Act: New Bipartisan House Bill Would Keep President From Yanking Permits
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by ...
Accelerate your clean energy career with Yale’s online certificate programs. Explore the 10-month Financing and Deploying Clean Energy program or the 5-month Clean and Equitable Energy Development program. Use referral code HeatMap26 and get your application in by the priority deadline for $500 off tuition to one of Yale’s online certificate programs in clean energy. Learn more at cbey.yale.edu/online-learning-opportunities.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.
This transcript was automatically generated.
Robinson Meyer:
[1:25] I’m Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap News, and this is Shift Key, Heatmap’s podcast about decarbonization and the shift away from fossil fuels. It is Monday, February 9th, and I think it’s fair to say the biggest possible climate legislation that could come out of Congress this year is a permitting reform bill. This would be, let’s be clear, a compromise between Democrats and Republicans, where Democrats agree to rewrite parts of the National Environmental Policy Act, reduce some permitting barriers, maybe make it easier to build pipelines, while in exchange, Republicans would agree to change the rules on clean energy projects and transmission lines, making it easier to build wind,
Robinson Meyer:
[2:04] solar, batteries, all that good stuff. There’d be some bipartisan goals in there, too. I think there’s some lawmakers from both parties who want to make it easier to build advanced geothermal, for instance. But this would be a compromise no matter what, and nobody would be totally thrilled with it.
Robinson Meyer:
[2:18] Senator Martin Heinrich is the ranking Democratic member of the Senate Energy Committee. He’s the senior senator from New Mexico, and any permitting deal in the Senate would have to go through him. He’s also a giant transmission nerd. As I’ve written about, he was integral to reaching a deal on the Sunzia transmission line, which is a three and a half gigawatt wind farm and power line project in New Mexico. I’ll stick an article about that in the show notes. And he is our guest on Shift Key today. Senator Heinrich and I spoke last week, and you’re going to hear what he thinks the biggest obstacle to getting a permitting reform deal done is, what might need to happen for Democrats to feel good about a deal and why such a deal ultimately needs to constrain Trump in some way. He makes a little news. There was a bipartisan House bill last week that would limit executive interference on energy projects. You’ll hear what he thinks about it. And we also talk about the future of climate policy for the Democratic Party writ large, what he learned from the Biden administration, what the Inflation Reduction Act got right and what it got wrong, what a future climate law would need to do and whether energy policy needs a
Robinson Meyer:
[3:22] villain and who that villain might be. It was a great conversation. I learned a lot from it and it’s all coming up this week on Shift Key. Senator Heinrich, welcome to Shift Key.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[3:35] Great to be here.
Robinson Meyer:
[3:36] I want to start with the news. So what are the obstacles and state of play on permitting reform today?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[3:45] Well, I think the biggest obstacle is just the unwillingness of this administration to sort of play by the normal rules and laws and the order that has served our country so well for so long. There were kind of two big buckets where they were coloring outside the lines. And one that got a lot of press was the offshore wind issues. And we’ve seen the courts really do a great job with those projects that are fully permitted, at least, and are well under construction, in some cases like 80% complete. The courts have intervened and said, no, you can’t do this. These stop work orders are just illegal. So put people back to work.
Robinson Meyer:
[4:29] Their legal record on this is like 5-0 or something.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[4:32] Yeah, that’s exactly right. And so that’s been a great outcome for a lot of people who, you know, I had somebody in front of me testifying last week, I think it was, who said, talked about a painter who like two days before Christmas, he thought he was going to be working on this wind project for the next three years and two days before Christmas, he doesn’t have a job. So that’s outrageous, and we shouldn’t tolerate it in this country. And I think the courts are doing a good job of putting those projects back into
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[5:02] play, and those are moving forward. I think what’s gotten less coverage is this secretarial order at the Department of Interior, where there are literally 69 different things that most of which would never land on the secretary’s desk to begin with. Really minor things like rights of way and findings of no significant impact. This secretarial order has said all these things are going to land on the secretary’s desk for his approval. That’s the opposite of permitting reform. That’s intentional red tape at a scale we’ve never seen before. And so you have all of these things that oftentimes would have been handled by some bureaucrat at a local BLM office in Nevada or New Mexico or Utah. uh.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[5:51] That would have just been approved as a matter of course, unless they’re inconsistent with our laws and regulations. They’re all stacking up on Secretary Burgum’s desk and nothing is leaving his desk. And so you have roughly half the generation in the pipeline that’s trying to get plugged into the grid right now that is in permitting purgatory. We just don’t know. There’s no callback to the developers. They just don’t know when or if these projects that they’ve already invested in are going to be approved. I think that deserves a lot more attention because it is truly threatening the growth of the grid, and it is going to show up in higher and higher prices as demand continues to surge, but those generation projects are not able to put their electrons on the grid.
Robinson Meyer:
[6:45] To just dwell on that for a moment, when you talk to developers, what kind of projects are getting held up by the secretarial order? So is it projects on public land, which are obviously a huge deal out west? Or is it anything with a kind of nexus with a federal waterway? Or just like, give us a sense of which project, like, are there private projects?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[7:05] Right. It’s like across the board. It is both anything that has a nexus to public land gets caught up in this in many cases. Oftentimes you need a right of way just to be able to connect to a transmission or distribution line. It runs across the entire generation spectrum and the projects that are necessary to facilitate that generation. Things like transmission and distribution lines, roads, stuff that normally would have gotten processed as a matter of course. And so it’s hard to overstate the scale of how much things have ground to a halt. And it does go beyond Interior as well. So you have, you know, you have Fish and Wildlife Service not processing permits. You have EPA not processing permits. And so the whole ability of our country to meet our energy demand has sort of just gotten stuck in this quagmire.
Robinson Meyer:
[8:07] I want to get back to this question of executive interference, but there was a bill that came out of the House last year. There was a permitting reform bill and there were some votes on it. There was some discussion and you were among a group of senators who said, no, this would not be acceptable, this offer, because it doesn’t have any transmission in it. It doesn’t have the transmission policy we’d need to see. And so just as you understand it, what would be the key parts of a permitting reform deal across both parties and that you would need to see to get something done here?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[8:39] Well, the SPEED Act that came out of the House was very much a sort of rewrite the National Environmental Policy Act kind of permitting reform. That doesn’t live in my committee. It lives not in Energy and Natural Resources where I’m the ranking member, but it lives over in Environment and Public Works, where Sheldon Whitehouse is the ranking member. And I don’t think there is support for that legislation in that committee either. I am focused on transmission because that does live in my committee, but also because it is necessary to solve one of the fundamental, most acute problems that we have in the energy sector right now, which is the fact that we have, for the first time since air conditioning became commonplace, we have this enormous, enormous surge in demand, like something I have not seen since my dad was a lineman and I was seven years old. And so that demand, you see it in stories all over the country. But when you look at how we’re meeting that demand and you look at all the supply that is trying to be brought on the grid right now, first off, you need transmission to connect the places where you can do the generation to the places where the demand is going to be used.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[10:02] And in addition, that supply is, for the next five or six years, is 95% renewable. If you didn’t order a gas turbine multiple years ago, you’re going to be waiting five, six, seven, eight years to get that gas turbine. The stuff that is plugging into the grid right now is wind, solar, and batteries, because they’re quick to deploy. They’re fast to permit under normal conditions. You know what the costs are. You don’t have to wait in a line for five years to get pieces and parts to be able to build that. And so that’s what’s been being deployed to sort of bridge our demand. There’s a lot of neat stuff that’s out there seven years from now in terms of small modular reactors, advanced and enhanced geothermal, which I am all for. But in the meantime, we have to plug in wind, solar, and batteries. It’s the only way we can meet that demand. We don’t meet that demand. People’s electricity costs are going to go through the roof, and we’re already seeing that with about a 13% increase in retail electric costs just since this administration came into office.
Robinson Meyer:
[11:13] So transmission, so executive interference, it would be great to plug in that wind and solar and batteries. As you were saying, it’s been held up by the Trump administration. Do you think it’s possible to find some kind of bill or text or proposal that would undo the secretarial order that would allow energy projects to move in a more normal way through the Trump administration?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[11:36] We are certainly exploring that with a number of different constituencies, how you would craft something that removes executive discretion from the process and just sets a sort of performance bar. I’m a fan of that approach generally. I mean, I started my career in the city council and I dealt with land use issues all the time. I was the chair of the land use committee on Albuquerque City Council. And I found that when you had this amorphous process where you didn’t know where the bar was, that things would get caught up in litigation and just get drug out for years, where if you just set a high bar at the beginning and said, once you check these boxes, you can proceed, that that’s a much better way to do permitting to begin with.
Robinson Meyer:
[12:22] There’s one bill we reported on yesterday at Heatmap called the FREEDOM Act. It just came out of the House. It has a bipartisan group behind it, including Mike Lawler from New York, Adam Gray in California. It tries to prevent federal agencies from terminating work on a fully permitted project or affecting ongoing construction on a fully permitted project. And it would establish this fund that a company that has seen its permits get yanked could pull from in the Treasury Department up to $5 million. Does this bill meet your concerns? Have you looked at it? Is this the kind of text that you would need to see to say, okay, we could put a deal together?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[13:00] We’re very intrigued and digging into that legislation right now. And I do think that anything we can do to create more certainty in the market, and that’s true for both renewables and for traditional energy, because the truth is, we can’t have a system where when one party controls the White House, they attack this set of energy. And then when it changes hands, that group attacks this other set of energy. We just need to set policy and then have predictable flows of capital into the market. And so I think this is a positive step forward. And we should look at all the things the House does and evaluate them on their merits. I will say that if the figure is $5 billion for this fund, you could exhaust that on one wind project. And thank goodness the courts stepped in as quickly as they did because those offshore wind projects were on the scale of tens of billions of dollars.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[14:08] And effectively, if you’re going to shut those off, that’s a takings in my view. That’s like actually stealing someone’s capital, stealing someone’s money. And we can’t like that’s third world stuff. We can’t have that in the United States of America. But I give credit to the House for coming forward with this kind of thing because we do need to constrain it.
Robinson Meyer:
[14:31] Well, if you sign on to it, let us know at Heatmap. I want to zoom out and talk about climate policy more broadly. So permitting reform obviously fits into this. But we just came out of an administration that did a lot on the climate, passed the Inflation Reduction Act, and frankly, had a tough time of it with voters, and even had a tough time of it, I think, with some environmental groups and maybe didn’t find the support that they expected. So how are you thinking about the future of democratic climate policy? And do you think we’ll ever see another administration that prioritizes the issue in the same way the Biden administration did?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[15:04] I certainly hope so. I think the mistake that was made, it’s true of the Biden administration, but it’s true of a lot of members who were involved in the creation of the IRA too. We did not tell the story well enough. And it wasn’t because there wasn’t a story to tell so in new mexico i made i was up for election last year and I made a very concerted effort to put the things that we did that created new jobs new manufacturing and new projects at the center of my communication because people are busy like you can’t just think that you’re going to change a policy and people are going to figure out how to connect the dots between what you did and what the impacts were. But I found if I told that story as part of my campaign, and it was central to my paid media strategy and everything we did, that people got it. They connected the dots because we told a story. And that’s a lesson. You have to do that. You also have to move fast. And I think we made a number of mistakes in being.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[16:18] Willing to accept a kind of cumbersome process that already existed that kept things from moving at a pace where we could demonstrate actual results. And this is a lesson I’ve learned over the years. Just like when we did Obamacare, like all the bad stuff was up front and all the good stuff was five years later. That’s a bad recipe because people have now figured out that, oh, oh, I need Obamacare, but it took years to get there. We can learn those lessons in terms of any climate policy to front load things like tax benefits are relatively quick. There’s a process to write the rules, but those things can take effect almost immediately. If you had something like the green bank that lived at EPA, it took too long to set that up. And by the time cash was moving, a new administration was in and said, nope, we’re going to stop, full stop on all that stuff. So that should inform, you know, speed to market is going to need to be absolutely critical in any sort of climate policy.
Robinson Meyer:
[17:27] So I’m happy to hear you say this. And it’s something that I think your other colleagues have said as well, that there was too much process. It took too long to end things up. I do want to push on it because I think we’re about as far now from a democratic legislative process as it is possible to be. It’s been a few years since the IRA. It’s like at least a few years until the possibility of another trifecta. And if there were to be a bill in the future... The people who want process don’t come to the negotiations, or they don’t advocate and say, we really want process. What they say is, well, this needs to be careful. We don’t want the benefits to go to people who don’t need the benefits. We need more planning here. We need to make sure that the stakeholders who fought for this coalition actually get the benefits. And we don’t want the market to decide that. So it’s great that at this moment, people are like, we need to go faster. But in the heat of a bill legislating process, how is that actually going to pan out?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[18:31] I think it means that you have to understand what your goals are, what you’re trying to accomplish, and think through how you set a high bar for... You need to think through that ahead of time and incorporate it into the legislation, as opposed to defer to some agency who’s going to go through a very cumbersome regulatory process to figure that out. So you need you need to work, do the work on the front end, basically. And I think that’s where we did that things moved quickly and where we didn’t, things moved painfully slowly.
Robinson Meyer:
[19:07] What’s the policy that you think worked best in the bill?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[19:10] I think that, you know, tax credits, definitely. And some of those survived and are, you know, one of the things people need to understand is that clean energy is the dominant energy. Now, It’s not alternative. It is the dominant energy in our country, and it is continuing to expand its dominance. And we have a situation where the things that did survive, the incentives for energy storage and batteries, the incentives for nuclear, the incentives for geothermal, those things did survive. And they’re going to continue to drive innovation in the market. I’m really excited about the things that we’re seeing in small modular fission, in advanced and enhanced geothermal. I’m seeing stuff in my state that 10 years ago just did not exist. It’s going to be five years before that stuff is plugged into the grid, but it’s game-changing, and we’re just going to continue to expand the places where the clean energy sector is market-dominant.
[AD BREAK]
Robinson Meyer:
[21:53] So you come from an oil and gas state, and there have been some calls for Democrats to look for places they can ally with the oil and gas industry or oil and gas interests. I think we’ve seen from one state over, Senator Gallego has made some noise in this direction. Do you think Democrats need a different oil and gas policy than the one they had during the Biden administration? And what do you hear from your constituents?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[22:15] Well, I think it can’t be supply You can’t tell people that you can’t burn gasoline in your car before you have an alternative, right? That mistake has been made in many countries over the years. It sort of led to some of the protests we saw in France a few years ago. You have to build a better mousetrap. And I do think there are, you know, one of the reasons why, if we can deal with the administrative stall out on permitting, that you can build alliances between clean energy and traditional molecules-based energy around the certainty of the permitting process. That’s a place where both sides don’t want to live in a world where their capital can be held at gunpoint by some hostile administration. And so there are some opportunities there. And I think it’s important to explore those. That’s how you build a permitting package that can actually pass. And I think that was done well in the permitting package that we passed out of committee two years ago that I certainly supported.
Robinson Meyer:
[23:26] Do you think a future president should talk about these things a little differently? I think, I don’t know, I think back to the Biden administration and when he approved Willow, for instance, he got all this blowback from it, from green groups, from environmentalists. And it was an export project, so it wasn’t quite the same story. But there was no, he didn’t try to sell the benefits at all. And he had to live with the consequences anyway. He wasn’t like, oh, this is going to make us richer because we’re selling oil into the world. He was just like, I’m sorry, I have to do this. And he got beat up for it anyway. Do you think that they’re like, you know, I think one
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[24:01] Of the weird things about the oil and gas markets is that we have put so much capital into exporting American oil and gas to the world because we haven’t put capital into the kind of refining technology that would allow it to be used here and lower people’s prices. And so that creates a lot of sort of strange gymnastics in the market. You know, we export so much crude oil and we’re now, because this administration has taken a no holds barred, we’re going to export any gas permit that comes our way. We’re going to approve it all, despite the fact that there is a requirement in the law that it’s in the best interest of the country and DOE is supposed to certify that. They’ve just said, we’re going to export it all. If you do that and you’re not careful about taking each incremental project, on its own merits and how it’s going to impact the market.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[25:08] That is part of the reason we’ve seen natural gas prices double in the last few years. And in addition to that really hurting consumers, it also hurts for those manufacturing businesses that have been really dependent on gas for heat in the manufacturing process. It’s really hard on them, too. So it puts us at a disadvantage with other international manufacturers. So all of this stuff, the details really do matter. It’s why like bumper stickers don’t make good energy policy. You really do need to understand the capital flows and the energy flows to be able to protect the consumer.
Robinson Meyer:
[25:52] Do you think the energy policy, environmental policy, is like an area where it’s good to have villains? I mean, we used to talk about oil and gas companies. I would say green groups, there’s a lot of focus on oil and gas companies as villains. And true to form, Trump’s administration has knocked a lot of clean energy projects back. Now we’re talking about utilities as villains. Are the utilities villains going forward? Are the oil and gas companies villains?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[26:14] If they’re not careful, the entities that are going to be portrayed as villains, and depending on how they manage their community engagement and their sort of benefit to local communities, they could be villains, but they don’t have to be, are going to be the hyperscalers and the data center developers.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[26:39] And unfortunately, a lot of what I am seeing is move fast and break things. Like it’s a very top-down Silicon Valley kind of process where they come into a community and say, hey, you should be really glad we’re here and we’re going to tell you exactly how we’re going to do things. And that’s a recipe for failure. It’s no different than what I saw 20 years ago in the transmission sector when transmission companies thought they could do the same thing in local communities. What they need to do is go into communities and engage and listen. And the first thing people will tell you is, if you’re going to build this data center, don’t raise my rates. And that’s a very reasonable request. They also want good jobs, not crappy jobs. They want you to use water responsibly. And in many communities, they want clean energy as the source of energy for those data centers. And if if developers would approach that process by actually listening at the front end and working with local communities i think you would see a much faster rate of adoption and because frankly many of them some of them are being arrogant it puts at risk a lot of capital and a lot of compute so don’t, you know, like, don’t let yourself be painted as a villain by behaving responsibly
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[28:04] and listening to local communities.
Robinson Meyer:
[28:06] How are data centers playing into this evolving energy politics story? You just gave us a taste, but do you think they’re going to make transmission reform, permitting reform easier or harder in the next few years?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[28:17] I think it depends on whether they get off their rear ends and actually get involved in that conversation. You cannot have the scale and number of data centers that the hyperscalers want without building a lot more transmission and having a more robust grid. That said, they have not been active in these conversations, and that’s a giant mistake. Republicans are just coming around to the fact that they generally, in the past, have not been that interested in transmission, but they’re starting to realize that if they want the benefits and the investment, of these data centers that you kind of have to do the transmission. And that’s a good dynamic because it means that when both sides want something, we can figure out how to write a policy that satisfies both sides.
Robinson Meyer:
[29:12] What are you hearing from Republicans about data centers? Because we notice at Heatmap that it’s a major issue for their constituents and there’s a lot of backlash. You started to hear that from them. And you recently did this electricity affordability roundtable? What were you being told about the effect of data centers on the grid?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[29:29] Well, if you’re not careful with how you structure incremental demand and rates, I think you’re going to see a huge backlash, and Republicans understand that. The key is to actually engage and do good policy so that you’re not passing those incremental costs on to rate payers, customers. They should not bear those costs. The smart thing to do is to say, if we’re going to build this data center, they’re going to pay a premium for the power so that they’re not raising rates on the surrounding community. And if you do it that way, you can build a win-win situation where you have community support. We’ve seen a lot of mistakes out of the gate. And I think it’s for the developers who figure this out and do it in a way that treats local communities with respect and doesn’t raise their rates and sort of checks those other boxes I talked about in terms of quality of workforce and water efficiency, they’re going to have an unending supply of very profitable work. But if you think you’re going to run roughshod over some county and.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[30:48] The truth is, if you’re in a county commission and they have to permit you, and there are five people on the county commission and three are against it, your project’s going away. It’s not getting built. So the lesson there should be genuinely get involved with that local community and figure out what a win-win looks like.
Robinson Meyer:
[31:09] Last question. Can you give us quickly your hit list for transmission reform in a future permitting reform package? Like what is the checklist of things you’d like to see and things you think we can get?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[31:21] I would love to see regional planning that really works. I would love to see grid enhancing technologies incentivized because there’s a lot more we can get out of the existing grid. And that buys us some time for the new big build kind of transmission projects that we need to do. So those are some of the things that I think are really critical.
Robinson Meyer:
[31:43] And those would be like a mandate or a tax credit or something?
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[31:46] I would love to see a tax credit for building in a regional transmission. That would create some economic incentive and some certainty where these are patient capital projects. So anything you can do to incentivize the value stack there gives people the
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[32:02] patience to get through what is often a very long process.
Robinson Meyer:
[32:05] Okay, I know you have to go vote. Thank you, Senator Heinrich. Always good to talk.
Senator Martin Heinrich:
[32:09] Thanks, Rob.
Robinson Meyer:
[32:13] That will do it for us this week. Thank you so much for listening to Shift Key. You can follow me on X at at Robinson Meyer or more actively on Blue Sky or LinkedIn at my name, Robinson Meyer. If you enjoyed Shift Key, please leave us a review on your favorite podcast app or send this episode to your friends. Jesse, I promise, is returning soon. He’s not gone forever. We’ll be back later this week, actually, with another episode of Shift Key. Until then, Shift Key is a production of Heatmap News. Our editors are Jillian Goodman and Nico Loricella. Multimedia editing and audio engineering is by Jacob Lambert and by Nick Woodbury. Our music is by Adam Kromelow. Thank you so much for listening and see you next week.