You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On prepurchase agreements, Al Gore, and Norway’s EVs

Current conditions: Ecuador’s government-enforced blackouts will begin tomorrow night as drought threatens hydroelectric plants • Storm Boris is causing flooding in parts of Italy • Montana could see very heavy rainfall and flash flooding today.
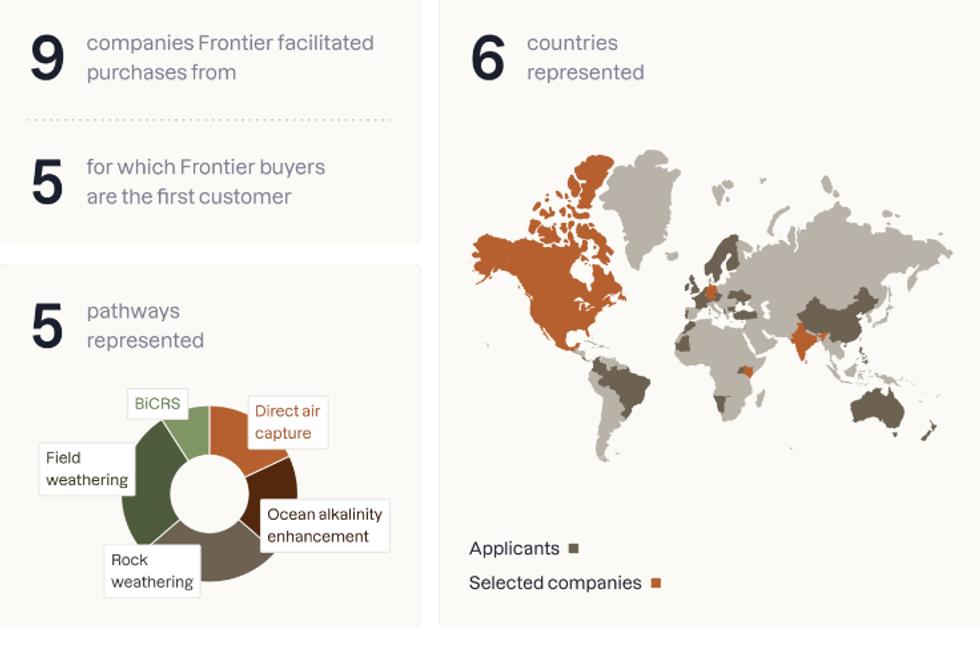
Frontier, a coalition of carbon removal buyers, announced this morning a fourth round of prepurchase agreements, worth $4.5 million. The coalition facilitated agreements with nine suppliers to remove carbon from the atmosphere on behalf of five of Frontier’s buyers: Stripe, Shopify, Alphabet, H&M Group, and Match. The removal projects are located across six countries and utilize a range of techniques, including rock weathering, direct air capture, and ocean alkalinity enhancement. In a press release, Frontier said “a significant number of companies in this purchase cycle are integrating carbon removal into existing large-scale industries. This strategy can reduce costs and accelerate scale-up relative to standalone carbon removal projects.”
Brazil’s worst drought on record, now in its second year, has caused water levels in the rivers that run through the Amazon to fall to historic lows, and some have even dried up entirely. One key tributary that supplies the mighty Amazon River, the Solimoes, has water levels that are 14 feet below average for the first half of September. The drought is fueling numerous large fires, many of which were started by humans but have plenty of dry vegetation to keep them going.
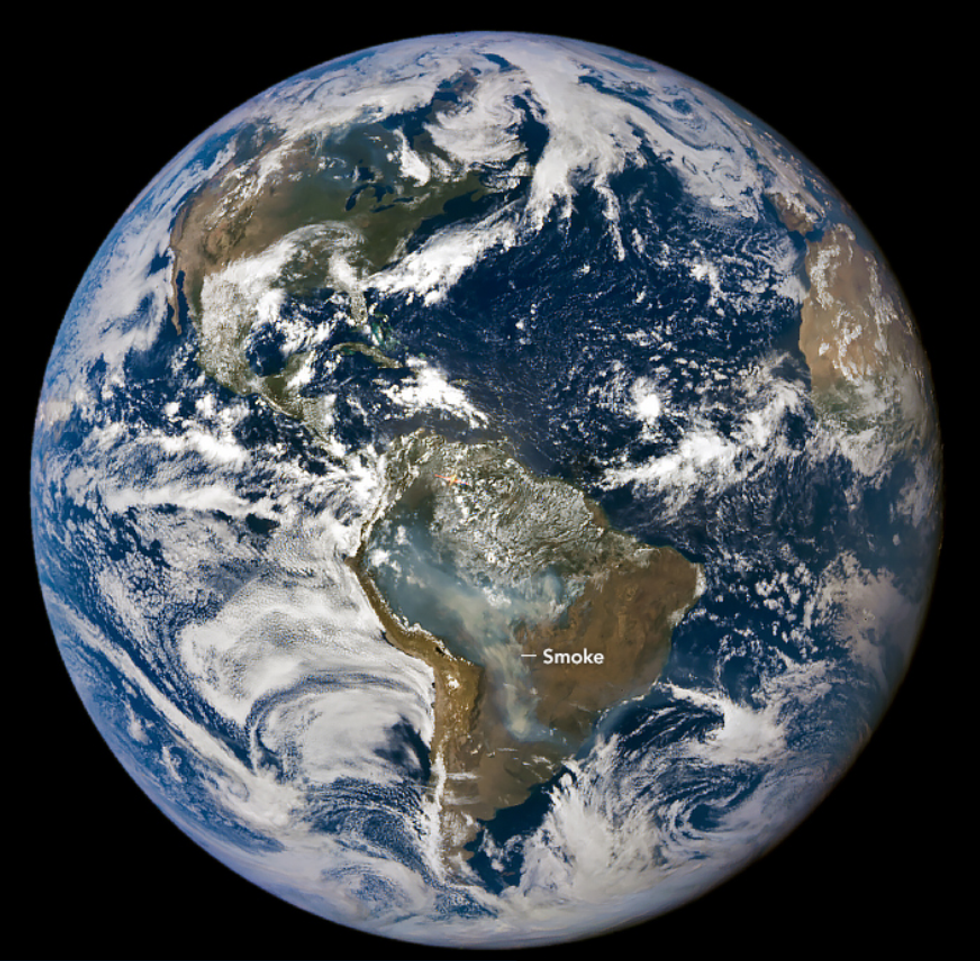

According to data from Brazil’s National Institute for Space Research, almost half of the Amazon fires are burning pristine forest. This is unusual, The New York Times reported, and “means fighting deforestation in the Amazon is no longer enough to stop fires.” The Amazon rainforest is one of the world’s most important carbon sinks. If it collapses, it could release huge amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating the climate crisis. Researchers with World Weather Attribution say climate change is the main driver of the Amazon’s ongoing drought. “Climate change is no longer something to worry about in the future, 10 or 20 years from now,” Greenpeace spokesperson Romulo Batista told Reuters. “It’s here and it’s here with much more force than we expected.”
A coalition of some of the world’s most prominent shipping and carrier companies is piloting the “first-ever U.S. over-the-road electrified corridor.” Participants include AIT Worldwide Logistics, DB Schenker, Maersk, Microsoft, and PepsiCo, who will drive their long-haul heavy-duty electric trucks along the I-10 corridor between L.A. and El Paso to identify pain points and share learnings in an effort to hasten the decarbonization of land freight. Terawatt Infrastructure will provide the charging infrastructure for the corridor with six of its own charging hubs. Terawatt’s website says it has 14 sites under development, four of which are expected to come online this year. Heavy-duty vehicles account for a quarter of transport-related greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. The new coalition is supported by the global nonprofit Smart Freight Centre.
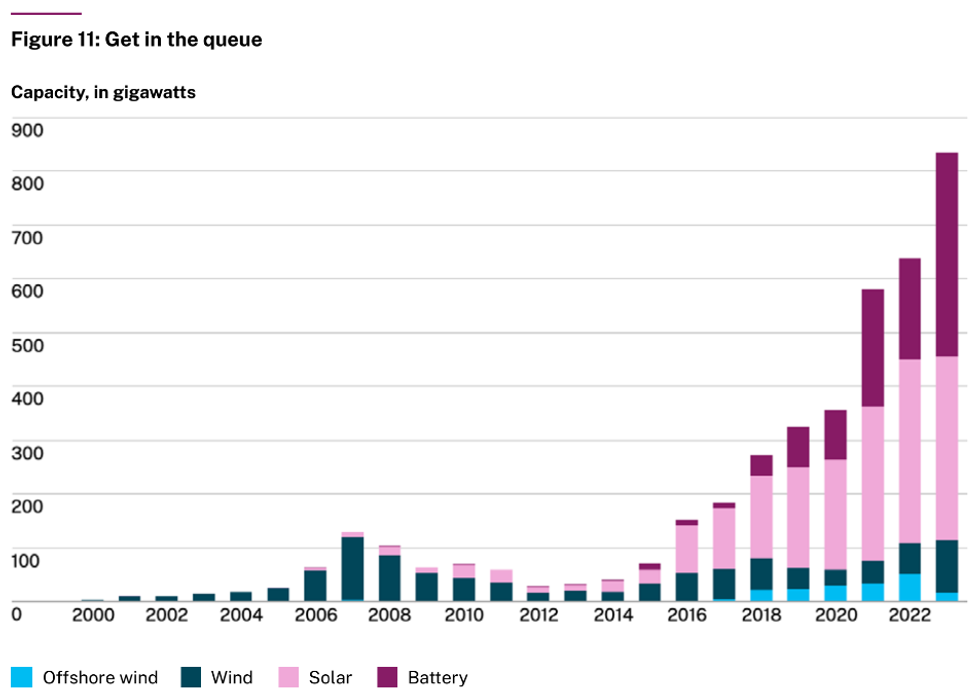
Former U.S. Vice President Al Gore’s green asset management business, Generation Investment Management, put out its eighth annual Sustainability Trends Report this week. The paper is packed full of interesting insights (both uplifting and depressing), but one stands out. It says upgrading the power grid is “the critical issue to get the energy transition moving faster in the big, developed economies.” It includes this graphic showing the cumulative backlog of renewable-energy projects wanting to connect to the grid in the U.S.:
Gore has been doing the media rounds this week. He told the Financial Times that a Trump victory in November “would be very bad.” “Most climate activists that I know in the United States believe that the single most important near-term decision America can make with regard to climate is who is the next president. It’s a bit of a Manichaean choice.” But, he added that the energy transition was, at this point, “unstoppable.”
In case you missed it: Norway has become the first country in the world to have more electric vehicles on the road than gas-powered cars. Diesel still reigns supreme in terms of registered vehicles, but the share of fully electric cars registered is now larger than the share of cars that run on gasoline. The director of the Norwegian road federation said he expects EVs will overtake diesel cars, too, by 2026. EVs already make up the vast majority (94%!) of new vehicle sales in Norway, and could very well approach 100% sometime next year.
A recent study finds that most people have a tendency to grossly underestimate the average carbon footprint of the richest individuals in society, while overestimating the carbon footprint of the poorest individuals.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
A new working paper from a trio of eminent economists tallies the effects of warming — particularly extreme weather — on Americans’ budgets.
Attempts to quantify the costs of climate change often end up as philosophical exercises in forecasting and quantifying the future. Such projects involve (at least) two difficult tasks: establishing what is the current climate “pathway” we’re on, which means projecting hard-to-predict phenomena such as future policy actions and potential climate system feedbacks; and then deciding how to value the wellbeing of those people who will be born in the decades — or centuries — to come versus those who are alive today.
But what about the climate impacts we’re paying for right now? That’s the question explored in a working paper by former Treasury Department officials Kimberley Clausing, an economist at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Catherine Wolfram, an economist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, along with Wolfram’s MIT colleague Christopher Knittel.
“We wanted to do the accounting exercise and put it all together,” Wolfram told me. Their method: Simply add up the existing harms of climate change, and boom, there’s your answer.
This approach stands in contrast to the more well-worn modeling and forecasting projects that make up much of the climate harms literature. “Projections about the future are important to make future-oriented policy,” Clausing told me. “But one of the things that’s kind of surprising and interesting to us that I don’t think has been fairly accounted for is how much climate change is already affecting household budgets.”
The paper is meant to intervene in current debates in climate and progressive policy circles over affordability — namely whether policy to address climate change should be put on the back (induction?) burner in light of concerns about how restrictions on fossil fuels or mandates for renewable energy can increase consumer costs, especially utility bills.
“What really motivated the paper, to be honest, is that we noticed that a lot of observers have made statements about climate policy action where they’re like, We’d love to do this, that, or the other thing, but it’s hard to do because the action would fall more heavily on the poor.”
The paper began its life in the fall as part of the semi-annual Brookings Papers on Economic Activity conference before being released this week as a working paper by the National Bureau of Economic Research this week.
Their research has not yet been peer reviewed, but the authors found that even using what they describe as a “narrow accounting” method — looking only at climate impacts from heat and extreme weather on household budgets and mortality — there were “sizable costs to U.S. households from recent climate change patterns.” Those started at $400 per year and went as high as $900 depending on how extreme weather were attributed to climate change, adding up to an aggregate cost of about $50 billion to $110 billion nationwide.
The direct effects of high temperatures may be easier to forecast, but the most extensive damage of climate change, in the United States, at least, runs downstream from high temperatures: storms, floods, and especially wildfires. Clausing and the authors attribute this to the fact that the United States has already made huge investments in adapting to heat in the form of air conditioning. Adaptations for natural disasters — flood walls, moving homes and businesses out of flood plains, universal indoor air purification, building codes for fire prevention — are farther behind.
Looking specifically at cost increases due to health effects from climate change, wildfires are the primary cost center.
“Wildfires have two impacts,” Wolfram told me. “One is the destruction that they cause — we see that in property insurance. The other thing, and that is probably the most surprising to us, is how bad the wildfire smoke has become.”
Those same wildfires, of course, feed into spiraling insurance costs, especially in the West.
Insurance costs top the list of household costs the authors attribute to climate change more broadly, making up more than half of the total. Citing research on homeowners insurance by University of Pennsylvania and University of Wisconsin researchers Benjamin Keys and Philip Mulder, the authors found that “average nominal premiums rose by 33% between 2020 and 2023, with disaster-prone areas experiencing particularly steep increases.”
One frequent argument against climate mitigation policies is that they cost the poor disproportionately; for example, a tax on gasoline has a bigger proportional effect on low-income drivers because a greater portion of their income is spent on fueling their car. But “if you don’t do anything, that has a disproportionate burden on the poor,” Clausing told me. That’s because the costs of dealing with climate change — higher insurance premiums, higher health insurance premiums, higher electric bills for more air conditioning — weigh more heavily on people with lower incomes, she and her co-authors found.
“Poor people may have a harder time and be more likely to be displaced by disasters,” Clausing told me.
The paper’s authors emphasized that their results show the need for climate adaptation as well as emissions-reducing policy, but also that forward-looking adaptation can’t happen if there’s insufficient information. Insufficient information appears to be exactly what some people want. Disputes over climate information have a well known political valence, with federal agencies under the current administration reducing their efforts to collect and publish climate data.
But the private sector has its own reasons not to be completely fulsome with climate-related risk data.
The New York Times reported this weekend, for instance, that the online real estate marketplace Zillow has removed climate risk scores from “more than one million home sale listings,” following complaints from real estate agents.“They’re doing people a disservice,” Clausing told me when I asked her about Zillow’s action.
“Of course, if my home’s on a floodplain, I’m not happy that this information is available to everyone on Zillow,” Clausing said. But the alternative is, “if my home’s in a floodplain, just pretending that that’s the same as if it were in a very safe place.” Which is fine, but it won’t stop your insurance bill from rising.
Current conditions: A cluster of storms from Sri Lanka to Southeast Asia triggered floods that have killed more than 900 so far • A snowstorm stretching 1,200 miles across the northern United States blanketed parts of Iowa, Illinois, and South Dakota with the white stuff • In China, 31 weather stations broke records for heat on Sunday.
The in-house market monitor at the PJM Interconnection filed a complaint last week to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission urging the agency to ban the nation’s largest grid operator from connecting any new data centers that the system can’t reliably serve. The warning from the PJM ombudsman comes as the grid operator is considering proposals to require blackouts during periods when there’s not enough electricity to meet data centers’ needs. The grid operator’s membership voted last month on a way forward, but no potential solution garnered enough votes to succeed, Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote. “That result is not consistent with the basic responsibility of PJM to maintain a reliable grid and is therefore not just and reasonable,” Monitoring Analytics said, according to Utility Dive.
The push comes as residential electricity prices continue climbing. Rates for American households spiked by an average of 7.4% in September compared to the same month in 2024, according to new data from the Energy Information Administration.

The Environmental Protection Agency made some big news on Wednesday, just before much of the U.S. took off for Thanksgiving: It’s delaying a rule that would have required oil and gas companies to start reducing how much methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is released from their operations into the atmosphere. The regulation would have required oil and gas companies to start reducing how much methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is released from their operations into the atmosphere. Drillers were supposed to start tracking emissions this year. But the Trump administration is instead giving companies until January 2027 as it considers repealing the measure altogether.
The New York Power Authority, the nation’s second largest government-owned utility after the federal Tennessee Valley Authority, is staffing up in preparation for its push to build at least a gigawatt of new nuclear power generation. On Monday morning, NYPA named Todd Josifovski as its new senior vice president of nuclear energy development, tasking the veteran atomic power executive with charting the strategic direction and development of new reactor projects. Josifovski previously hailed from Ontario Power Generation, the state-owned utility in the eponymous Canadian province, which is building what is likely to be North America’s first small modular reactor project. (As Matthew wrote when NYPA first announced its plans for a new nuclear plant, the approach mirrors Ontario’s there.) NYPA is also adding Christopher Hanson, a former member of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission whom President Donald Trump abruptly fired from the federal agency this summer, as a senior consultant in charge of guiding federal financing and permitting.
The push comes as New York’s statewide grid reaches “an inflection point” as surging demand, an aging fleet, and a lack of dispatchable power puts the system at risk, according to the latest reliability report. “The margin for error is extremely narrow, and most plausible futures point to significant reliability shortfalls within the next ten years,” the report concluded. “Depending on demand growth and retirement patterns, the system may need several thousand megawatts of new dispatchable generation over that timeframe.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Zillow, the country’s largest real estate site, removed a feature from more than a million listings that showed the risks from extreme weather, The New York Times reported. The website had started including climate risk scores last year, using data from the risk-modeling company First Street. But real estate agents complained that the ratings hurt sales, and homeowners protested that there was no way to challenge the scores. Following a complaint from the California Regional Multiple Listing Service, which operates a private database of brokers and agents, Zillow stopped displaying the scores.
The European Commission unveiled a new plan to replace fossil fuels in Europe’s economy with trees. By adopting the so-called Bioeconomy Strategy, released Thursday, the continent aims to remove fossil fuels in products Politico listed as “plastics, building materials, chemicals, and fibers” with organic materials that regrow, such as trees and crops. Doing so, the bloc argued, will help to preserve Europe’s “strategic autonomy” by making the continent less dependent on imported fuels.
Canada, meanwhile, is plowing ahead with its plans to strengthen itself against the U.S. by turning into an energy superpower. Already, the Trans Mountain pipeline is earning the federal coffers nearly $1.3 billion, based on my back-of-the-napkin conversion of the Canadian loonies cited in this Globe and Mail story to U.S. dollars. Now Prime Minister Mark Carney’s government is pitching a new pipeline from Alberta to the West Coast for export to Asia, as the Financial Times reported.
Swapping bunker fuel-burning engines for nuclear propulsion units in container ships could shave up to $68 million off annual shipping expenses, a new report found. If small modular reactors designed to power a cargo vessel are commercialized within four years as expected, the shipping companies could eliminate $50 million in fuel costs each year and about $18 million in carbon penalties. That’s according to data from Lloyd’s Register and LucidCatalyst report for the Singaporean maritime services company Seaspan Corporation.
If it turns out to be a bubble, billions of dollars of energy assets will be on the line.
The data center investment boom has already transformed the American economy. It is now poised to transform the American energy system.
Hyperscalers — including tech giants such as Microsoft and Meta, as well as leaders in artificial intelligence like OpenAI and CoreWeave — are investing eyewatering amounts of capital into developing new energy resources to feed their power-hungry data infrastructure. Those data centers are already straining the existing energy grid, prompting widespread political anxiety over an energy supply crisis and a ratepayer affordability shock. Nothing in recent memory has thrown policymakers’ decades-long underinvestment in the health of our energy grid into such stark relief. The commercial potential of next-generation energy technologies such as advanced nuclear, batteries, and grid-enhancing applications now hinge on the speed and scale of the AI buildout.
But what happens if the AI boom buffers and data center investment collapses? It is not idle speculation to say that the AI boom rests on unstable financial foundations. Worse, however, is the fact that as of this year, the tech sector’s breakneck investment into data centers is the only tailwind to U.S. economic growth. If there is a market correction, there is no other growth sector that could pick up the slack.
Not only would a sudden reversal in investor sentiment make stranded assets of the data centers themselves, which will lose value as their lease revenue disappears, it also threatens to strand all the energy projects and efficiency innovations that data center demand might have called forth.
If the AI boom does not deliver, we need a backup plan for energy policy.
An analysis of the capital structure of the AI boom suggests that policymakers should be more concerned about the financial fundamentals of data centers and their tenants — the tech companies that are buoying the economy. My recent report for the Center for Public Enterprise, Bubble or Nothing, maps out how the various market actors in the AI sector interact, connecting the market structure of the AI inference sector to the economics of Nvidia’s graphics processing units, the chips known as GPUs that power AI software, to the data center real estate debt market. Spelling out the core financial relationships illuminates where the vulnerabilities lie.

First and foremost: The business model remains unprofitable. The leading AI companies ― mostly the leading tech companies, as well as some AI-specific firms such as OpenAI and Anthropic ― are all competing with each other to dominate the market for AI inference services such as large language models. None of them is returning a profit on its investments. Back-of-the-envelope math suggests that Meta, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon invested over $560 billion into AI technology and data centers through 2024 and 2025, and have reported revenues of just $35 billion.
To be sure, many new technology companies remain unprofitable for years ― including now-ubiquitous firms like Uber and Amazon. Profits are not the AI sector’s immediate goal; the sector’s high valuations reflect investors’ assumptions about future earnings potential. But while the losses pile up, the market leaders are all vying to maximize the market share of their virtually identical services ― a prisoner’s dilemma of sorts that forces down prices even as the cost of providing inference services continues to rise. Rising costs, suppressed revenues, and fuzzy measurements of real user demand are, when combined, a toxic cocktail and a reflection of the sector’s inherent uncertainty.
Second: AI companies have a capital investment problem. These are not pure software companies; to provide their inference services, AI companies must all invest in or find ways to access GPUs. In mature industries, capital assets have predictable valuations that their owners can borrow against and use as collateral to invest further in their businesses. Not here: The market value of a GPU is incredibly uncertain and, at least currently, remains suppressed due to the sector’s competitive market structure, the physical deterioration of GPUs at high utilization rates, the unclear trajectory of demand, and the value destruction that comes from Nvidia’s now-yearly release of new high-end GPU models.
The tech industry’s rush to invest in new GPUs means existing GPUs lose market value much faster. Some companies, particularly the vulnerable and debt-saddled “neocloud” companies that buy GPUs to rent their compute capacity to retail and hyperscaler consumers, are taking out tens of billions of dollars of loans to buy new GPUs backed by the value of their older GPU stock; the danger of this strategy is obvious. Others including OpenAI and xAI, having realized that GPUs are not safe to hold on one’s balance sheet, are instead renting them from Oracle and Nvidia, respectively.
To paper over the valuation uncertainty of the GPUs they do own, all the hyperscalers have changed their accounting standards for GPU valuations over the past few years to minimize their annual reported depreciation expenses. Some financial analysts don’t buy it: Last year, Barclays analysts judged GPU depreciation as risky enough to merit marking down the earnings estimates of Google (in this case its parent company, Alphabet), Microsoft, and Meta as much as 10%, arguing that consensus modeling was severely underestimating the earnings write-offs required.
Under these market dynamics, the booming demand for high-end chips looks less like a reflection of healthy growth for the tech sector and more like a scramble for high-value collateral to maintain market position among a set of firms with limited product differentiation. If high demand projections for AI technologies come true, collateral ostensibly depreciates at a manageable pace as older GPUs retain their marketable value over their useful life — but otherwise, this combination of structurally compressed profits and rapidly depreciating collateral is evidence of a snake eating its own tail.
All of these hyperscalers are tenants within data centers. Their lack of cash flow or good collateral should have their landlords worried about “tenant churn,” given the risk that many data center tenants will have to undertake multiple cycles of expensive capital expenditure on GPUs and network infrastructure within a single lease term. Data center developers take out construction (or “mini-perm”) loans of four to six years and refinance them into longer-term permanent loans, which can then be packaged into asset-backed and commercial mortgage-backed securities to sell to a wider pool of institutional investors and banks. The threat of broken leases and tenant vacancies threatens the long-term solvency of the leading data center developers ― companies like Equinix and Digital Realty ― as well as the livelihoods of the construction contractors and electricians they hire to build their facilities and manage their energy resources.
Much ink has already been spilled on how the hyperscalers are “roundabouting” each other, or engaging in circular financing: They are making billions of dollars of long-term purchase commitments, equity investments, and project co-development agreements with one another. OpenAI, Oracle, CoreWeave, and Nvidia are at the center of this web. Nvidia has invested $100 billion in OpenAI, to be repaid over time through OpenAI’s lease of Nvidia GPUs. Oracle is spending $40 billion on Nvidia GPUs to power a data center it has leased for 15 years to support OpenAI, for which OpenAI is paying Oracle $300 billion over the next five years. OpenAI is paying CoreWeave over the next five years to rent its Nvidia GPUs; the contract is valued at $11.9 billion, and OpenAI has committed to spending at least $4 billion through April 2029. OpenAI already has a $350 million equity stake in CoreWeave. Nvidia has committed to buying CoreWeave’s unsold cloud computing capacity by 2032 for $6.3 billion, after it already took a 7% stake in CoreWeave when the latter went public. If you’re feeling dizzy, count yourself lucky: These deals represent only a fraction of the available examples of circular financing.
These companies are all betting on each others’ growth; their growth projections and purchase commitments are all dependent on their peers’ growth projections and purchase commitments. Optimistically, this roundabouting represents a kind of “risk mutualism,” which, at least for now, ends up supporting greater capital expenditures. Pessimistically, roundabouting is a way for these companies to pay each other for goods and services in any way except cash — shares, warrants, purchase commitments, token reservations, backstop commitments, and accounts receivable, but not U.S. dollars. The second any one of these companies decides it wants cash rather than a commitment is when the music stops. Chances are, that company needs cash to pay a commitment of its own, likely involving a lender.
Lenders are the final piece of the puzzle. Contrary to the notion that cash-rich hyperscalers can finance their own data center buildout, there has been a record volume of debt issuance this year from companies such as Oracle and CoreWeave, as well as private credit giants like Blue Owl and Apollo, which are lending into the boom. The debt may not go directly onto hyperscalers’ balance sheets, but their purchase commitments are the collateral against which data center developers, neocloud companies like CoreWeave, and private credit firms raise capital. While debt is not inherently something to shy away from ― it’s how infrastructure gets built ― it’s worth raising eyebrows at the role private credit firms are playing at the center of this revenue-free investment boom. They are exposed to GPU financing and to data center financing, although not the GPU producers themselves. They have capped upside and unlimited downside. If they stop lending, the rest of the sector’s risks look a lot more risky.

A market correction starts when any one of the AI companies can’t scrounge up the cash to meet its liabilities and can no longer keep borrowing money to delay paying for its leases and its debts. A sudden stop in lending to any of these companies would be a big deal ― it would force AI companies to sell their assets, particularly GPUs, into a potentially adverse market in order to meet refinancing deadlines. A fire sale of GPUs hurts not just the long-term earnings potential of the AI companies themselves, but also producers such as Nvidia and AMD, since even they would be selling their GPUs into a soft market.
For the tech industry, the likely outcome of a market correction is consolidation. Any widespread defaults among AI-related businesses and special purpose vehicles will leave capital assets like GPUs and energy technologies like supercapacitors stranded, losing their market value in the absence of demand ― the perfect targets for a rollup. Indeed, it stands to reason that the tech giants’ dominance over the cloud and web services sectors, not to mention advertising, will allow them to continue leading the market. They can regain monopolistic control over the remaining consumer demand in the AI services sector; their access to more certain cash flows eases their leverage constraints over the longer term as the economy recovers.
A market correction, then, is hardly the end of the tech industry ― but it still leaves a lot of data center investments stranded. What does that mean for the energy buildout that data centers are directly and indirectly financing?
A market correction would likely compel vertically integrated utilities to cancel plans to develop new combined-cycle gas turbines and expensive clean firm resources such as nuclear energy. Developers on wholesale markets have it worse: It’s not clear how new and expensive firm resources compete if demand shrinks. Grid managers would have to call up more expensive units less frequently. Doing so would constrain the revenue-generating potential of those generators relative to the resources that can meet marginal load more cheaply — namely solar, storage, peaker gas, and demand-response systems. Combined-cycle gas turbines co-located with data centers might be stranded; at the very least, they wouldn’t be used very often. (Peaker gas plants, used to manage load fluctuation, might still get built over the medium term.) And the flight to quality and flexibility would consign coal power back to its own ash heaps. Ultimately, a market correction does not change the broader trend toward electrification.
A market correction that stabilizes the data center investment trajectory would make it easier for utilities to conduct integrated resource planning. But it would not necessarily simplify grid planners’ ability to plan their interconnection queues — phantom projects dropping out of the queue requires grid planners to redo all their studies. Regardless of the health of the investment boom, we still need to reform our grid interconnection processes.
The biggest risk is that ratepayers will be on the hook for assets that sit underutilized in the absence of tech companies’ large load requirements, especially those served by utilities that might be building power in advance of committed contracts with large load customers like data center developers. The energy assets they build might remain useful for grid stability and could still participate in capacity markets. But generation assets built close to data center sites to serve those sites cheaply might not be able to provision the broader energy grid cost-efficiently due to higher grid transport costs incurred when serving more distant sources of load.
These energy projects need not be albatrosses.
Many of these data centers being planned are in the process of securing permits and grid interconnection rights. Those interconnection rights are scarce and valuable; if a data center gets stranded, policymakers should consider purchasing those rights and incentivizing new businesses or manufacturing industries to build on that land and take advantage of those rights. Doing so would provide offtake for nearby energy assets and avoid displacing their costs onto other ratepayers. That being said, new users of that land may not be able to pay anywhere near as much as hyperscalers could for interconnection or for power. Policymakers seeking to capture value from stranded interconnection points must ensure that new projects pencil out at a lower price point.
Policymakers should also consider backstopping the development of critical and innovative energy projects and the firms contracted to build them. I mean this in the most expansive way possible: Policymakers should not just backstop the completion of the solar and storage assets built to serve new load, but also provide exigent purchase guarantees to the firms that are prototyping the flow batteries, supercapacitors, cooling systems, and uninterruptible power systems that data center developers are increasingly interested in. Without these interventions, a market correction would otherwise destroy the value of many of those projects and the earnings potential of their developers, to say nothing of arresting progress on incredibly promising and commercializable technologies.
Policymakers can capture long-term value for the taxpayer by making investments in these distressed projects and developers. This is already what the New York Power Authority has done by taking ownership and backstopping the development of over 7 gigawatts of energy projects ― most of which were at risk of being abandoned by a private sponsor.
The market might not immediately welcome risky bets like these. It is unclear, for instance, what industries could use the interconnection or energy provided to a stranded gigawatt-scale data center. Some of the more promising options ― take aluminum or green steel ― do not have a viable domestic market. Policy uncertainty, tariffs, and tax credit changes in the One Big Beautiful Bill Act have all suppressed the growth of clean manufacturing and metals refining industries like these. The rest of the economy is also deteriorating. The fact that the data center boom is threatened by, at its core, a lack of consumer demand and the resulting unstable investment pathways is itself an ironic miniature of the U.S. economy as a whole.
As analysts at Employ America put it, “The losses in a [tech sector] bust will simply be too large and swift to be neatly offset by an imminent and symmetric boom elsewhere. Even as housing and consumer durables ultimately did well following the bust of the 90s tech boom, there was a one- to two-year lag, as it took time for long-term rates to fall and investors to shift their focus.” This is the issue with having only one growth sector in the economy. And without a more holistic industrial policy, we cannot spur any others.
Questions like these ― questions about what comes next ― suggest that the messy details of data center project finance should not be the sole purview of investors. After all, our exposure to the sector only grows more concentrated by the day. More precisely mapping out how capital flows through the sector should help financial policymakers and industrial policy thinkers understand the risks of a market correction. Political leaders should be prepared to tackle the downside distributional challenges raised by the instability of this data center boom ― challenges to consumer wealth, public budgets, and our energy system.
This sparkling sector is no replacement for industrial policy and macroeconomic investment conditions that create broad-based sources of demand growth and prosperity. But in their absence, policymakers can still treat the challenge of a market correction as an opportunity to think ahead about the nation’s industrial future.