You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On a new IEA report, Hochul’s congestion pricing u-turn, and the heat dome

Current conditions: Unseasonably cool temperatures brought snow to parts of Scotland • New South Wales in Australia recorded more than a month’s worth of rain in just 12 hours • Multiple tornadoes were reported across Maryland.
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul announced yesterday that she will “indefinitely pause” the long-awaited NYC congestion pricing program that was set to start on June 30. The policy would have charged drivers for entering some of the city’s busiest areas, raising $1 billion annually for the transit authority, cutting pollution, and easing traffic congestion. It would have been the first such program in the nation. But, no more. Hochul said it risked “too many unintended consequences.”
Environmental groups, state budget hawks, and transit advocates are outraged by the u-turn. Her decision “will be a generational setback for climate policy in the United States,” wrote an incensed Robinson Meyer for Heatmap. “New York was bushwhacking a trail for everyone else to follow: If congestion policy was a success there, then other American cities could experiment with it in some form. By pausing that trial before it has even begun, Hochul has essentially frozen our ability to experiment with congestion pricing anywhere else in the country.”
Global investment in clean energy is on track to reach $2 trillion in 2024, double the $1 trillion expected to be invested in fossil fuels, according to the International Energy Agency. In its new World Energy Investment report, out today, the IEA said global spending on renewables surpassed the amount invested in fossil fuels last year for the first time. Most of the money is going toward solar power. Here’s a look at recent annual investment in solar PV (light blue) compared to all other power generation sources (dark blue):
China accounts for the largest share of clean energy investment by a long shot, and China, the U.S., and Europe make up more than two thirds of the world’s clean energy investment. “More must be done to ensure that investment reaches the places where it is needed most, in particular the developing economies where access to affordable, sustainable and secure energy is severely lacking today,” said IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol. Even as clean energy funds are flowing, spending on oil and gas is set to rise this year and remains far too high to meet the world’s climate goals, the report said. Just 4% of oil and gas companies’ 2023 investments went toward clean energy.
António Guterres yesterday urged nations to ban advertising from fossil fuel companies in a speech at the American Museum of Natural History. The UN secretary-general called the fossil fuel industry “the Godfathers of climate chaos,” and said advertising and PR agencies that take Big Oil on as clients are “enablers to planetary destruction.” He said the end of the fossil fuel age was an economic inevitability, but that global emissions need to fall 9% every year until 2030 to keep the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius alive. The next 18 months will be key to deciding our future, he said. “I call on leaders in the fossil fuel industry to understand that if you are not in the fast lane to clean energy transformation, you are driving your business into a dead end – and taking us all with you,” Guterres said.
The speech coincided with a new report from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) concluding there is an 80% chance that the global annual average temperature will exceed the 1.5C degree increase in one (or more) of the next five years. That’s up from a 66% chance last year, and as Guterres noted, “in 2015, the chance of such a breach was near zero.”
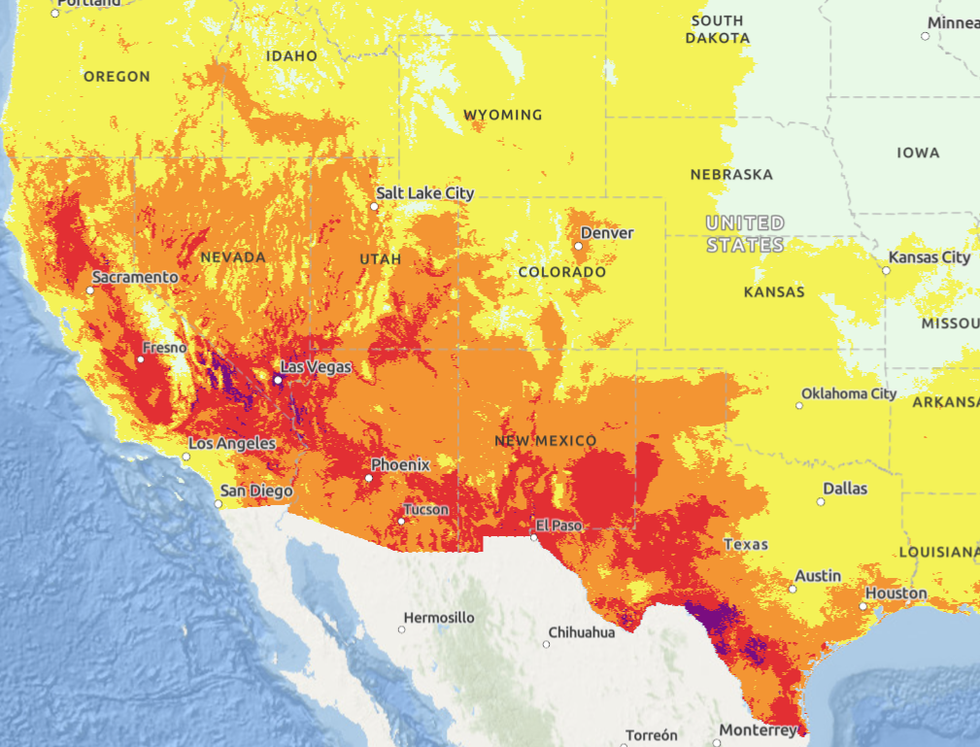
Temperatures across much of the American Southwest are between 20 and 30 degrees Fahrenheit higher than usual for this time of year, according to the National Weather Service. Residents in California, New Mexico, Nevada, Arizona, and Texas are roasting under a heat dome that has settled on the region and will likely peak in severity today. In Phoenix, where temperatures will hit 111 degrees Fahrenheit today, all fire department vehicles are being kitted out with large ice bags in which people suffering from heat stroke can be submerged to lower their temperatures. In California’s Death Valley, the mercury will hit 120 degrees today. The heat wave is expected to boost emissions from California’s power sector as customers crank up their air conditioners. Below is a snapshot of the region today from the NWS HeatRisk tool. Regions in red are experiencing “major” heat-related impacts; purple regions are under extreme heat conditions.
In case you missed it: General Motors just had its best month ever in terms of EV sales. During a shareholder meeting on Tuesday, CEO Mary Barra said May was the company’s “best month ever for EV sales in North America,” adding that “we’re seeing profit improvement in our EV portfolio as we scale production of the broadest EV portfolio on the market, a portfolio purposely built to win new customers.” Demand was particularly strong for the Cadillac Lyric and the new Chevrolet Blazer EV. The news would have been unfathomable even last year, when GM reported cratering EV sales after it discontinued the Chevy Bolt EV, wrote Patrick George at Inside EVs. The new numbers are “an outstanding development for GM and for the wider EV market,” he said.
A Department of Energy initiative will repurpose two former nuclear test sites in Idaho by using the land to install 400 megawatts of solar power with battery storage.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Whether any of them will hold up in court is now the big question.
Environmental lawyers are in for years of déjà vu as the Trump administration relitigates questions that many believed were settled by the Supreme Court nearly 20 years ago.
On Thursday, Trump rescinded the “endangerment finding,” the Environmental Protection Agency’s 2009 determination that greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles threaten Americans’ public health and welfare and should be regulated. In the short term, the move repeals existing vehicle emissions standards and prevents future administrations from replacing them. In the longer term, what matters is whether any of the administration’s justifications hold up in court.
In its final rule, the EPA abandoned its attempt to back the move using a bespoke climate science report published by the Department of Energy last year. The report was created by a working group assembled in secret by the department and made up of five scientists who have a track record of pushing back on mainstream climate science. Not only was the report widely refuted by scientists, but the assembly of the working group itself broke federal law, a judge ruled in late January.
“The science is clear that climate change is creating a risk for the public and public health, and so I think it’s significant that they realized that it creates a legal risk if they were to try to assert otherwise,” Carrie Jenks, the executive director of Harvard’s Environmental and Energy Law Program, told me.
Instead, the EPA came up with three arguments to justify its decision, each of which will no doubt have to be defended in court. The agency claims that each of them can stand alone, but that they also reinforce each other. Whether that proves to be true, of course, has yet to be determined.
Here’s what they are:
Congress never specifically told the EPA to regulate greenhouse gas emissions. If it did, maybe we would have accomplished more on climate change by now.
What happened instead was that in 1999, a coalition of environmental and solar energy groups asked the EPA to regulate emissions from cars, arguing that greenhouse gases should be considered pollutants under the federal Clean Air Act. In 2007, in a case called Massachusetts v. EPA, the Supreme Court agreed with the second part. That led the EPA to consider whether these gases posed enough of a danger to public health to warrant regulation. In 2009, it concluded they did — that’s what’s known as the endangerment finding. After reaching that finding, the EPA went ahead and developed standards to limit emissions from vehicles. It later followed that up with rules for power plants and oil and gas operations.
Now Trump’s EPA is arguing that this three-step progression — categorizing greenhouse gases as pollutants under the Clean Air Act, making a scientific finding that they endanger public health, and setting regulations — was all wrong. Instead, the agency now believes, it’s necessary to consider all three at once.
Using the EPA’s logic, the argument comes out something like this: If we consider that U.S. cars are a small sliver of global emissions, and that limiting those emissions will not materially change the trajectory of global warming or the impacts of climate change on Americans, then we must conclude that Congress did not intend for greenhouse gases to be regulated when it enacted the Clean Air Act.
“They are trying to merge it all together and say, because we can’t do that last thing in a way that we think is reasonable, we can’t do the first thing,” Jenks said.
The agency is not explicitly asking for Massachusetts v. EPA to be overturned, Jenks said. But if its current argument wins in court, that would be the effective outcome, preventing future administrations from issuing greenhouse gas standards unless Congress passed a law explicitly telling it to do so. While it's rare for the Supreme Court to reverse course, none of the five justices who were in the majority on that case remain, and the makeup of the court is now far more conservative than in 2007.
The EPA also asserted that the “major questions doctrine,” a legal principle that says federal agencies cannot set policies of major economic and political significance without explicit direction from Congress, means the EPA cannot “decide the Nation’s policy response to global climate change concerns.”
The Supreme Court has used the major questions doctrine to overturn EPA’s regulations in the past, most notably in West Virginia v. EPA, which ruled that President Obama’s Clean Power Plan failed this constitutional test. But that case was not about EPA’s authority to regulate greenhouse gases, the court solely struck down the particular approach the EPA took to those regulations. Nevertheless, the EPA now argues that any climate regulation at all would be a violation.
The EPA’s final argument is about the “futility” of vehicle emissions standards. It echoes a portion of the first justification, arguing that the point alone is enough of a reason to revoke the endangerment finding absent any other reason.
The endangerment finding had “severed the consideration of endangerment from the consideration of contribution” of emissions, the agency wrote. The Clean Air Act “instructs the EPA to regulate in furtherance of public health and welfare, not to reduce emissions regardless [of] whether such reductions have any material health and welfare impact.”
Funnily enough, to reach this conclusion, the agency had to use climate models developed by past administrations, including the EPA’s Optimization Model for reducing Emissions of GHGs from Automobiles, as well as some developed by outside scientists, such as the Finite amplitude Impulse Response climate emulator model — though it did so begrudgingly.
The agency “recognizes that there is still significant dispute regarding climate science and modeling,” it wrote. “However, the EPA is utilizing the climate modeling provided within this section to help illustrate” that zero-ing out emissions from vehicles “would not materially address the health and welfare dangers attributed to global climate change concerns in the Endangerment Finding.”
I have yet to hear back from outside experts about the EPA’s modeling here, so I can’t say what assumptions the agency made to reach this conclusion or estimate how well it will hold up to scrutiny. We’ll be talking to more legal scholars and scientists in the coming days as they digest the rule and dig into which of these arguments — if any — has a chance to prevail.
The state is poised to join a chorus of states with BYO energy policies.
With the backlash to data center development growing around the country, some states are launching a preemptive strike to shield residents from higher energy costs and environmental impacts.
A bill wending through the Washington State legislature would require data centers to pick up the tab for all of the costs associated with connecting them to the grid. It echoes laws passed in Oregon and Minnesota last year, and others currently under consideration in Florida, Georgia, Illinois, and Delaware.
Several of these bills, including Washington’s, also seek to protect state climate goals by ensuring that new or expanded data centers are powered by newly built, zero-emissions power plants. It’s a strategy that energy wonks have started referring to as BYONCE — bring your own new clean energy. Almost all of the bills also demand more transparency from data center companies about their energy and water use.
This list of state bills is by no means exhaustive. Governors in New York and Pennsylvania have declared their intent to enact similar policies this year. At least six states, including New York and Georgia, are also considering total moratoria on new data centers while regulators study the potential impacts of a computing boom.
“Potential” is a key word here. One of the main risks lawmakers are trying to circumvent is that utilities might pour money into new infrastructure to power data centers that are never built, built somewhere else, or don’t need as much energy as they initially thought.
“There’s a risk that there’s a lot of speculation driving the AI data center boom,” Emily Moore, the senior director of the climate and energy program at the nonprofit Sightline Institute, told me. “If the load growth projections — which really are projections at this point — don’t materialize, ratepayers could be stuck holding the bag for grid investments that utilities have made to serve data centers.”
Washington State, despite being in the top 10 states for data center concentration, has not exactly been a hotbed of opposition to the industry. According to Heatmap Pro data, there are no moratoria or restrictive ordinances on data centers in the state. Rural communities in Eastern Washington have also benefited enormously from hosting data centers from the earlier tech boom, using the tax revenue to fund schools, hospitals, municipal buildings, and recreation centers.
Still, concern has started to bubble up. A ProPublica report in 2024 suggested that data centers were slowing the state’s clean energy progress. It also described a contentious 2023 utility commission meeting in Grant County, which has the highest concentration of data centers in the state, where farmers and tech workers fought over rising energy costs.
But as with elsewhere in the country, it’s the eye-popping growth forecasts that are scaring people the most. Last year, the Northwest Power and Conservation Council, a group that oversees electricity planning in the region, estimated that data centers and chip fabricators could add somewhere between 1,400 megawatts and 4,500 megawatts of demand by 2030. That’s similar to saying that between one and four cities the size of Seattle will hook up to the region’s grid in the next four years.
In the face of such intimidating demand growth, Washington Governor Bob Ferguson convened a Data Center Working Group last year — made up of state officials as well as advisors from electric utilities, environmental groups, labor, and industry — to help the state formulate a game plan. After meeting for six months, the group published a report in December finding that among other things, the data center boom will challenge the state’s efforts to decarbonize its energy systems.
A supplemental opinion provided by the Washington Department of Ecology also noted that multiple data center developers had submitted proposals to use fossil fuels as their main source of power. While the state’s clean energy law requires all electricity to be carbon neutral by 2030, “very few data center developers are proposing to use clean energy to meet their energy needs over the next five years,” the department said.
The report’s top three recommendations — to maintain the integrity of Washington’s climate laws, strengthen ratepayer protections, and incentivize load flexibility and best practices for energy efficiency — are all incorporated into the bill now under discussion in the legislature. The full list was not approved by unanimous vote, however, and many of the dissenting voices are now opposing the data center bill in the legislature or asking for significant revisions.
Dan Diorio, the vice president of state policy for the Data Center Coalition, an industry trade group, warned lawmakers during a hearing on the bill that it would “significantly impact the competitiveness and viability of the Washington market,” putting jobs and tax revenue at risk. He argued that the bill inappropriately singles out data centers, when arguably any new facility with significant energy demand poses the same risks and infrastructure challenges. The onshoring of manufacturing facilities, hydrogen production, and the electrification of vehicles, buildings, and industry will have similar impacts. “It does not create a long-term durable policy to protect ratepayers from current and future sources of load growth,” he said.
Another point of contention is whether a top-down mandate from the state is necessary when utility regulators already have the authority to address the risks of growing energy demand through the ratemaking process.
Indeed, regulators all over the country are already working on it. The Smart Electric Power Alliance, a clean energy research and education nonprofit, has been tracking the special rate structures and rules that U.S. utilities have established for data centers, cryptocurrency mining facilities, and other customers with high-density energy needs, many of which are designed to protect other ratepayers from cost shifts. Its database, which was last updated in November, says that 36 such agreements have been approved by state utility regulators, mostly in the past three years, and that another 29 are proposed or pending.
Diario of the Data Center Coalition cited this trend as evidence that the Washington bill was unnecessary. “The data center industry has been an active party in many of those proceedings,” he told me in an email, and “remains committed to paying its full cost of service for the energy it uses.” (The Data Center Coalition opposed a recent utility decision in Ohio that will require data centers to pay for a minimum of 85% of their monthly energy forecast, even if they end up using less.)
One of the data center industry’s favorite counterarguments against the fear of rising electricity is that new large loads actually exert downward pressure on rates by spreading out fixed costs. Jeff Dennis, who is the executive director of the Electricity Customer Alliance and has worked for both the Department of Energy and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, told me this is something he worries about — that these potential benefits could be forfeited if data centers are isolated into their own ratemaking class. But, he said, we’re only in “version 1.5 or 2.0” when it comes to special rate structures for big energy users, known as large load tariffs.
“I think they’re going to continue to evolve as everybody learns more about how to integrate large loads, and as the large load customers themselves evolve in their operations,” he said.
The Washington bill passed the Appropriations Committee on Monday and now heads to the Rules Committee for review. A companion bill is moving through the state senate.
Plus more of the week’s top fights in renewable energy.
1. Kent County, Michigan — Yet another Michigan municipality has banned data centers — for the second time in just a few months.
2. Pima County, Arizona — Opposition groups submitted twice the required number of signatures in a petition to put a rezoning proposal for a $3.6 billion data center project on the ballot in November.
3. Columbus, Ohio — A bill proposed in the Ohio Senate could severely restrict renewables throughout the state.
4. Converse and Niobrara Counties, Wyoming — The Wyoming State Board of Land Commissioners last week rescinded the leases for two wind projects in Wyoming after a district court judge ruled against their approval in December.