You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Here’s another issue with the plume of smoke blotting out the sun.

Wildfire smoke is choking renewable energy.
The plume of smoke billowing from Quebec down the East Coast of the United States isn’t just endangering people’s health, it’s reducing solar power production by darkening the sky. While the areas affected by the smoke are not greatly dependent on solar for power, both New York and New England have aggressive targets for more solar installation in the coming years, which means their grids could become more reliant on a form of generation that’s at risk during wildfires.
To find out how badly solar power was being hit, I reached out to grid operators who cover an area stretching from North Carolina to Maine, the Hamptons to Chicago. They all said something similar: the wildfire smoke meant less solar power production.
As the New England Independent System Operator put it in a release: The smoke was “significantly lowering production from solar resources in the region.”
But there was a wrinkle. The smoke isn’t just reducing the yield from photovoltaic panels, it’s also making forecasting power demand more difficult. That’s because the smoke cover also lowers temperatures, which can reduce demand for the air conditioning that is largely responsible for higher electricity usage in the summer months.
“These two factors — decreased production from solar resources and decreased consumer demand due to lower temperatures — has made forecasting demand for grid electricity challenging,” ISO New England explained, which made it hard to say exactly what factor won out over the other.
Similar effects were felt in the Midwest, Dan Lockwood, a spokesperson for the PJM Interconnection, the regional transmission organization that covers all or part of 13 states ranging from Northeast North Carolina to Chicago, told me in an email.
“Smoky conditions throughout the RTO this week have caused a reduction in visibility, reducing solar, and keeping temperatures several degrees lower than usual,” Lockwood said, although he also noted the uniqueness of the event made it “difficult to single out the effect of smoke alone.” He said the most comparable event was the summer of 2021, when western wildfire smoke floated through the Midwest and East Coast.
The New York Independent System Operator was able to put a figure on the solar production lost from the smoke. Andrew Gregory, a spokesperson for the New York ISO, said in an email that “total peak solar energy production … was 1,466 fewer megawatts than forecasted" on June 6 and 7, down about 25% from where they thought it would be. Those 1,466 megawatts would be enough to power around 250,000 homes, according to the Solar Energies Industries Association.
This is not unusual. California and Australia, which both have quickly growing solar sectors, have also experienced meaningful reductions in solar power production when they’ve been hit by severe wildfires.
One paper examining the 2020 wildfires on the West Coast found about “10%–30% reduction in solar power production during peak hours,” in California due to wildfire smoke. Not only did this mean a dirtier grid, it also wreaked havoc on planning done by the California Independent System Operation whose forecasts for electricity supply “did not include the effects of smoke and therefore overestimated the expected power production by [around] 10%–50%.”
These challenges will likely accumulate, the authors argue, as “a direct consequence of climate change is continued extreme biomass burning, which may lead to more frequent and intense smoke events.”
An Australian solar data company found that rooftop solar systems in Sydney and Canberra could see their output fall by 15 to 40 percent during hazy days. New South Wales, which includes Sydney, already gets 12.5 percent of its power from solar, according to the Australian Department of Climate Change, Energy, Environment, and Water.
While fossil fuel power is by no mean immune to extreme weather — just look at natural gas getting frozen out during cold snaps — a wide variety of carbon-free electricity can be diminished by the very climate events they are supposed to help solve, whether it’s the sun disappearing behind clouds of wildfire smoke or hydroelectric power getting choked off by drought or rivers getting too warm to cool nuclear reactors. This will only become a bigger problem as the world gets hotter.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
And more on the week’s biggest conflicts around renewable energy projects.
1. Jackson County, Kansas – A judge has rejected a Hail Mary lawsuit to kill a single solar farm over it benefiting from the Inflation Reduction Act, siding with arguments from a somewhat unexpected source — the Trump administration’s Justice Department — which argued that projects qualifying for tax credits do not require federal environmental reviews.
2. Portage County, Wisconsin – The largest solar project in the Badger State is now one step closer to construction after settling with environmentalists concerned about impacts to the Greater Prairie Chicken, an imperiled bird species beloved in wildlife conservation circles.
3. Imperial County, California – The board of directors for the agriculture-saturated Imperial Irrigation District in southern California has approved a resolution opposing solar projects on farmland.
4. New England – Offshore wind opponents are starting to win big in state negotiations with developers, as officials once committed to the energy sources delay final decisions on maintaining contracts.
5. Barren County, Kentucky – Remember the National Park fighting the solar farm? We may see a resolution to that conflict later this month.
6. Washington County, Arkansas – It seems that RES’ efforts to build a wind farm here are leading the county to face calls for a blanket moratorium.
7. Westchester County, New York – Yet another resort town in New York may be saying “no” to battery storage over fire risks.
Solar and wind projects are getting swept up in the blowback to data center construction, presenting a risk to renewable energy companies who are hoping to ride the rise of AI in an otherwise difficult moment for the industry.
The American data center boom is going to demand an enormous amount of electricity and renewables developers believe much of it will come from solar and wind. But while these types of energy generation may be more easily constructed than, say, a fossil power plant, it doesn’t necessarily mean a connection to a data center will make a renewable project more popular. Not to mention data centers in rural areas face complaints that overlap with prominent arguments against solar and wind – like noise and impacts to water and farmland – which is leading to unfavorable outcomes for renewable energy developers more broadly when a community turns against a data center.
“This is something that we’re just starting to see,” said Matthew Eisenson, a senior fellow with the Renewable Energy Legal Defense Initiative at the Columbia University Sabin Center for Climate Change Law. “It’s one thing for environmentalists to support wind and solar projects if the idea is that those projects will eventually replace coal power plants. But it’s another thing if those projects are purely being built to meet incremental demand from data centers.”
We’ve started to see evidence of this backlash in certain resort towns fearful of a new tech industry presence and the conflicts over transmission lines in Maryland. But it is most prominent in Virginia, ground zero for American hyperscaler data centers. As we’ve previously discussed in The Fight, rural Virginia is increasingly one of the hardest places to get approval for a solar farm in the U.S., and while there are many reasons the industry is facing issues there, a significant one is the state’s data center boom.
I spent weeks digging into the example of Mecklenburg County, where the local Board of Supervisors in May indefinitely banned new solar projects and is rejecting those that were in the middle of permitting when the decision came down. It’s also the site of a growing data center footprint. Microsoft, which already had a base of operations in the county’s town of Boydton, is in the process of building a giant data center hub with three buildings and an enormous amount of energy demand. It’s this sudden buildup of tech industry infrastructure that is by all appearances driving a backlash to renewable energy in the county, a place that already had a pre-existing high opposition risk in the Heatmap Pro database.
It’s not just data centers causing the ban in Mecklenburg, but it’s worth paying attention to how the fight over Big Tech and solar has overlapped in the county, where Sierra Club’s Virginia Chapter has worked locally to fight data center growth with a grassroots citizens group, Friends of the Meherrin River, that was a key supporter of the solar moratorium, too.
In a conversation with me this week, Tim Cywinski, communications director for the state’s Sierra Club chapter, told me municipal leaders like those in Mecklenburg are starting to group together renewables and data centers because, simply put, rural communities enter into conversations with these outsider business segments with a heavy dose of skepticism. This distrust can then be compounded when errors are made, such as when one utility-scale solar farm – Geenex’s Grasshopper project – apparently polluted a nearby creek after soil erosion issues during construction, a problem project operator Dominion Energy later acknowledged and has continued to be a pain point for renewables developers in the county.
“I don’t think the planning that has been presented to rural America has been adequate enough,” the Richmond-based advocate said. “Has solar kind of messed up in a lot of areas in rural America? Yeah, and that’s given those communities an excuse to roll them in with a lot of other bad stuff.”
Cywinski – who describes himself as “not your typical environmentalist” – says the data center space has done a worse job at community engagement than renewables developers in Virginia, and that the opposition against data center projects in places like Chesapeake and Fauquier is more intense, widespread, and popular than the opposition to renewables he’s seeing play out across the Commonwealth.
But, he added, he doesn’t believe the fight against data centers is “mutually exclusive” from conflicts over solar. “I’m not going to tout the gospel of solar while I’m trying to fight a data center for these people because it’s about listening to them, hearing their concerns, and then not telling them what to say but trying to help them elevate their perspective and their concerns,” Cywinski said.
As someone who spends a lot of time speaking with communities resisting solar and trying to best understand their concerns, I agree with Cywinksi: the conflict over data centers speaks to the heart of the rural vs. renewables divide, and it offers a warning shot to anyone thinking AI will help make solar and wind more popular.
The One Big Beautiful Bill Act is one signature away from becoming law and drastically changing the economics of renewables development in the U.S. That doesn’t mean decarbonization is over, experts told Heatmap, but it certainly doesn’t help.
What do we do now?
That’s the question people across the climate change and clean energy communities are asking themselves now that Congress has passed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, which would slash most of the tax credits and subsidies for clean energy established under the Inflation Reduction Act.
Preliminary data from Princeton University’s REPEAT Project (led by Heatmap contributor Jesse Jenkins) forecasts that said bill will have a dramatic effect on the deployment of clean energy in the U.S., including reducing new solar and wind capacity additions by almost over 40 gigawatts over the next five years, and by about 300 gigawatts over the next 10. That would be enough to power 150 of Meta’s largest planned data centers by 2035.
But clean energy development will hardly grind to a halt. While much of the bill’s implementation is in question, the bill as written allows for several more years of tax credit eligibility for wind and solar projects and another year to qualify for them by starting construction. Nuclear, geothermal, and batteries can claim tax credits into the 2030s.
Shares in NextEra, which has one of the largest clean energy development businesses, have risen slightly this year and are down just 6% since the 2024 election. Shares in First Solar, the American solar manufacturer, are up substantially Thursday from a day prior and are about flat for the year, which may be a sign of investors’ belief that buyer demand for solar panels will persist — or optimism that the OBBBA’s punishing foreign entity of concern requirements will drive developers into the company’s arms.
Partisan reversals are hardly new to climate policy. The first Trump administration gleefully pulled the rug from under the Obama administration’s power plant emissions rules, and the second has been thorough so far in its assault on Biden’s attempt to replace them, along with tailpipe emissions standards and mileage standards for vehicles, and of course, the IRA.
Even so, there are ways the U.S. can reduce the volatility for businesses that are caught in the undertow. “Over the past 10 to 20 years, climate advocates have focused very heavily on D.C. as the driver of climate action and, to a lesser extent, California as a back-stop,” Hannah Safford, who was director for transportation and resilience in the Biden White House and is now associate director of climate and environment at the Federation of American Scientists, told Heatmap. “Pursuing a top down approach — some of that has worked, a lot of it hasn’t.”
In today’s environment, especially, where recognition of the need for action on climate change is so politically one-sided, it “makes sense for subnational, non-regulatory forces and market forces to drive progress,” Safford said. As an example, she pointed to the fall in emissions from the power sector since the late 2000s, despite no power plant emissions rule ever actually being in force.
“That tells you something about the capacity to deliver progress on outcomes you want,” she said.
Still, industry groups worry that after the wild swing between the 2022 IRA and the 2025 OBBBA, the U.S. has done permanent damage to its reputation as a business-friendly environment. Since continued swings at the federal level may be inevitable, building back that trust and creating certainty is “about finding ballasts,” Harry Godfrey, the managing director for Advanced Energy United’s federal priorities team, told Heatmap.
The first ballast groups like AEU will be looking to shore up is state policy. “States have to step up and take a leadership role,” he said, particularly in the areas that were gutted by Trump’s tax bill — residential energy efficiency and electrification, transportation and electric vehicles, and transmission.
State support could come in the form of tax credits, but that’s not the only tool that would create more certainty for businesses — considering the budget cuts states will face as a result of Trump’s tax bill, it also might not be an option. But a lot can be accomplished through legislative action, executive action, regulatory reform, and utility ratemaking, Godfrey said. He cited new virtual power plant pilot programs in Virginia and Colorado, which will require further regulatory work to “to get that market right.”
A lot of work can be done within states, as well, to make their deployment of clean energy more efficient and faster. Tyler Norris, a fellow at Duke University's Nicholas School of the Environment, pointed to Texas’ “connect and manage” model for connecting renewables to the grid, which allows projects to come online much more quickly than in the rest of the country. That’s because the state’s electricity market, ERCOT, does a much more limited study of what grid upgrades are needed to connect a project to the grid, and is generally more tolerant of curtailing generation (i.e. not letting power get to the grid at certain times) than other markets.
“As Texas continues to outpace other markets in generator and load interconnections, even in the absence of renewable tax credits, it seems increasingly plausible that developers and policymakers may conclude that deeper reform is needed to the non-ERCOT electricity markets,” Norris told Heatmap in an email.
At the federal level, there’s still a chance for, yes, bipartisan permitting reform, which could accelerate the buildout of all kinds of energy projects by shortening their development timelines and helping bring down costs, Xan Fishman, senior managing director of the energy program at the Bipartisan Policy Center, told Heatmap. “Whether you care about energy and costs and affordability and reliability or you care about emissions, the next priority should be permitting reform,” he said.
And Godfrey hasn’t given up on tax credits as a viable tool at the federal level, either. “If you told me in mid-November what this bill would look like today, while I’d still be like, Ugh, that hurts, and that hurts, and that hurts, I would say I would have expected more rollbacks. I would have expected deeper cuts,” he told Heatmap. Ultimately, many of the Inflation Reduction Act’s tax credits will stick around in some form, although we’ve yet to see how hard the new foreign sourcing requirements will hit prospective projects.
While many observers ruefully predicted that the letter-writing moderate Republicans in the House and Senate would fold and support whatever their respective majorities came up with — which they did, with the sole exception of Pennsylvania Republican Brian Fitzpatrick — the bill also evolved over time with input from those in the GOP who are not openly hostile to the clean energy industry.
“You are already seeing people take real risk on the Republican side pushing for clean energy,” Safford said, pointing to Alaska Republican Senator Lisa Murkowski, who opposed the new excise tax on wind and solar added to the Senate bill, which earned her vote after it was removed.
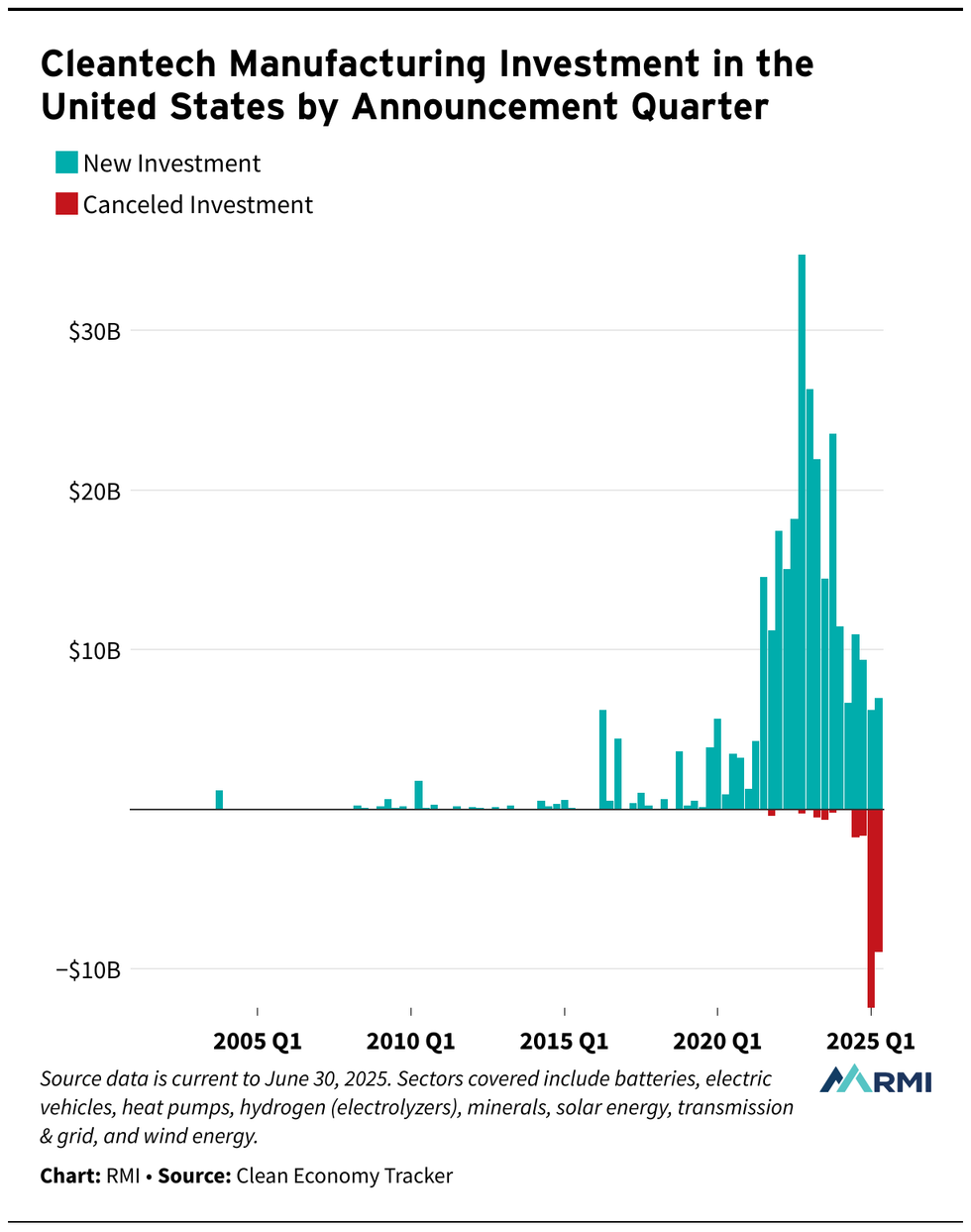
Some damage has already been done, however. Canceled clean energy investments adds up to $23 billion so far this year, compared to just $3 billion in all of 2024, according to the decarbonization think tank RMI. And that’s before OBBBA hits Trump’s desk.
The start-and-stop nature of the Inflation Reduction Act may lead some companies, states, local government and nonprofits to become leery of engaging with a big federal government climate policy again.
“People are going to be nervous about it for sure,” Safford said. “The climate policy of the future has to be polycentric. Even if you have the political opportunity to make a big swing again, people will be pretty gun shy. You will need to pursue a polycentric approach.”
But to Godfrey, all the back and forth over the tax credits, plus the fact that Republicans stood up to defend them in the 11th hour, indicates that there is a broader bipartisan consensus emerging around using them as a tool for certain energy and domestic manufacturing goals. A future administration should think about refinements that will create more enduring policy but not set out in a totally new direction, he said.
Albert Gore, the executive director of the Zero Emissions Transportation Association, was similarly optimistic that tax credits or similar incentives could work again in the future — especially as more people gain experience with electric vehicles, batteries, and other advanced clean energy technologies in their daily lives. “The question is, how do you generate sufficient political will to implement that and defend it?” he told Heatmap. “And that depends on how big of an economic impact does it have, and what does it mean to the American people?”
Ultimately, Fishman said, the subsidy on-off switch is the risk that comes with doing major policy on a strictly partisan basis.
“There was a lot of value in these 10-year timelines [for tax credits in the IRA] in terms of business certainty, instead of one- or two- year extensions,” Fishman told Heatmap. “The downside that came with that is that it became affiliated with one party. It was seen as a partisan effort, and it took something that was bipartisan and put a partisan sheen on it.”
The fight for tax credits may also not be over yet. Before passage of the IRA, tax credits for wind and solar were often extended in a herky-jerky bipartisan fashion, where Democrats who supported clean energy in general and Republicans who supported it in their districts could team up to extend them.
“You can see a world where we have more action on clean energy tax credits to enhance, extend and expand them in a future congress,” Fishman told Heatmap. “The starting point for Republican leadership, it seemed, was completely eliminating the tax credits in this bill. That’s not what they ended up doing.”