You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Even a thousand-year rainstorm won’t cure the drought.

For the past few days, Southern Californians have found themselves living with a kind of weather one doesn’t typically associate with the region: rain. Days of rain. The kind of rain that, in the worst cases, causes flooding and landslides, and in the best cases enforces a kind of unwilling solitude. (A friend in the Los Angeles area recently sent me a video of her German Shepherd, yowling discontentedly at the falling water.) One gauge at the University of California, Los Angeles recorded more than a foot of rain in 24 hours, making it what the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration calls a “thousand-year” rainfall event.
The cause is a slow-moving atmospheric river that has essentially parked itself over the region. And yet, even with all that rain, California still won’t be able to escape the drought that’s gripped the West for years. California, it turns out, might be a bit too good at flood control.
Undeveloped floodplains act like natural speed bumps for fast-moving floods — the water spreads out over the plain, slows down, and eventually seeps into the dirt to become groundwater. But land is at a premium in Southern California, especially in the L.A. area, and for decades the prevailing wisdom was to contain rivers with concrete so they wouldn’t flood, opening the floodplains to housing development. What we still call the L.A. River is now, essentially, a concrete drain.
This creates two problems. First, there’s no natural barrier that can slow down flood waters during events like this week’s storms. And second, there’s nowhere for that water to go other than into the rivers and out to sea.
“Most of the rivers in Southern California are channelized, or concrete-lined, and most of the floodplains are developed,” Jay Famiglietti, a hydrologist at Arizona State University’s Global Futures Lab and a former member of the California State Water Board in Santa Ana and Los Angeles, told me. “When we built all that infrastructure, we really were thinking more about flooding and not thinking about saving that water.”
That’s because California has historically been pretty well-supplied with water from the Colorado River and Sierra Nevada snowpack that would melt in the spring and summer, delivering water through mountain streams. But as Ian James wrote in the Los Angeles Times last week, California is in a "snow drought," with about only about half the historical average snowpack for this point in the season. While the storms might help shore up the Sierra Nevada snowpack a bit, it still won’t be enough.
Warmer air carries more water, but it also means that less snow falls at lower elevations than before — where once we might have seen a few inches of snow, we now see a few inches of rain. During an atmospheric river in particular, so much water is dumped over such a short time period that protecting people from flooding becomes the primary concern.
“It's a difficult balance between protecting people against flooding, which I think we do a really good job at, and replenishing groundwater,” Famiglietti said. But, he told me, Californians need to start having some difficult conversations about the possibility of moving people off the floodplains — what planners called “managed retreat” — and returning riverbanks to their natural state so that floodwaters can spread out into the plains, slow down, and refill aquifers that the state can rely on throughout the year.
Managed retreat is a difficult topic — nobody ever wants to leave their home. And then there’s the problem of money; local, state, and federal government agencies would probably have to fund all those moves and the subsequent restoration of the rivers and floodplains. “We need to be spending a lot more money,” Famiglietti told me. “We’re talking trillions of dollars. And who pays for it, the federal government or the state? I don’t have the answer.”
There are some plans to reshape the L.A. River, spearheaded by none other than Frank Gehry — but Famiglietti says that instead of restoring the river’s banks and opening up floodplains, the plans call for even more development. A coalition of environmental groups opposes the plan, saying Gehry’s idea, which includes the construction of “platform parks” that would span over the canal, saying that it “stands to do particular ecological harm, create real estate speculation, and precludes future opportunities for climate resilience.”
Going in the opposite direction — less development and less concrete — is sort of antithetical to our ideas of progress. But the atmospheric rivers will keep coming, Famiglietti stressed, and it’s difficult to plan a city around unpredictable rain events.
“We did the right thing at the time [when we built flood infrastructure],” Famiglietti told me. “But now, in a sense, we have to be thinking about moving backwards.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Current conditions: Bosnia’s capital of Sarajevo is blanketed in a layer of toxic smog • Temperatures in Perth, in Western Australia, could hit 106 degrees Fahrenheit this weekend • It is cloudy in Washington, D.C., where lawmakers are scrambling to prevent a government shutdown.
The weather has gotten so weird that the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is holding internal talks about how to adjust its models to produce more accurate forecasts, the Financial Timesreported. Current models are based on temperature swings observed over one part of the Pacific Ocean that have for years correlated consistently with specific weather phenomena across the globe, but climate change seems to be disrupting that cause and effect pattern, making it harder to predict things like La Niña and El Niño. Many forecasters had expected La Niña to appear by now and help cool things down, but that has yet to happen. “It’s concerning when this region we’ve studied and written all these papers on is not related to all the impacts you’d see with [La Niña],” NOAA’s Michelle L’Heureux told the FT. “That’s when you start going ‘uh-oh’ there may be an issue here we need to resolve.”
There is quite a lot of news coming out of the Department of Energy as the year (and the Biden administration) comes to an end. A few recent updates:
Walmart, the world’s largest retailer, does not expect to meet its 2025 or 2030 emissions targets, and is putting the blame on policy, infrastructure, and technology limitations. The company previously pledged to cut its emissions by 35% by next year, and 65% by the end of the decade. Emissions in 2023 were up 4% year-over-year.
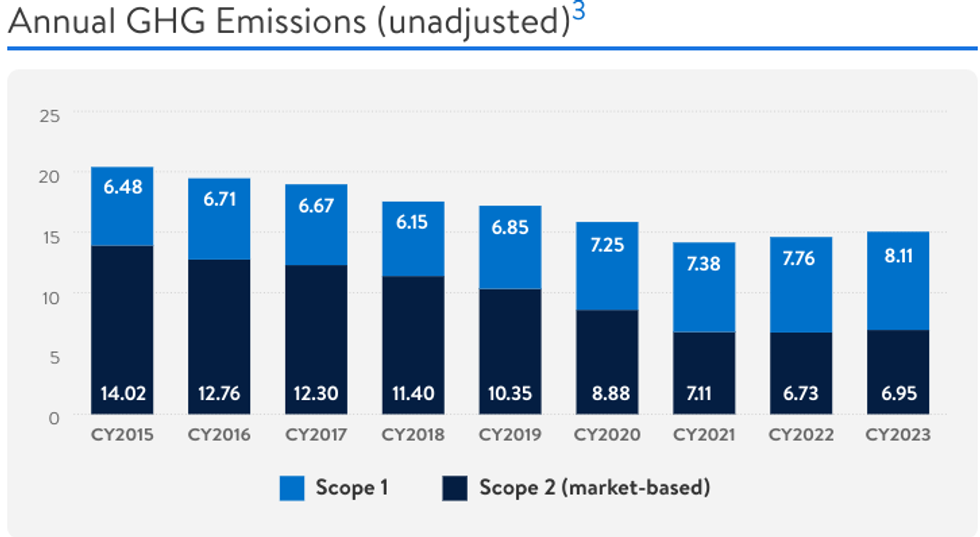
“While we continue to work toward our aspirational target of zero operational emissions by 2040, progress will not be linear … and depends not only on our own initiatives but also on factors beyond our control,” Walmart’s statement said. “These factors include energy policy and infrastructure in Walmart markets around the world, availability of more cost-effective low-GWP refrigeration and HVAC solutions, and timely emergence of cost-effective technologies for low-carbon heavy tractor transportation (which does not appear likely until the 2030s).”
BlackRock yesterday said it is writing down the value of its Global Renewable Power Fund III following the failure of Northvolt and SolarZero, two companies the fund had invested in. Its net internal rate of return was -0.3% at the end of the third quarter, way down from 11.5% in the second quarter, according toBloomberg. Sectors like EV charging, transmission, and renewable energy generation and storage have been “particularly challenged,” executives said, and some other renewables companies in the portfolio have yet to get in the black, meaning their valuations may be “more subjective and sensitive to evolving dynamics in the industry.”
Flies may be more vulnerable to climate change than bees are, according to a new study published in the Journal of Melittology. The fly haters among us might shrug at the finding, but the researchers insist flies are essential pollinators that help bolster ecosystem biodiversity and agriculture. “It’s time we gave flies some more recognition for their role as pollinators,” said lead author Margarita López-Uribe, who is the Lorenzo Langstroth Early Career Associate Professor of Entomology at Penn State. The study found bees can tolerate higher temperatures than flies, so flies are at greater risk of decline as global temperatures rise. “In alpine and subarctic environments, flies are the primary pollinator,” López-Uribe said. “This study shows us that we have entire regions that could lose their primary pollinator as the climate warms, which could be catastrophic for those ecosystems.”
“No one goes to the movies because they want to be scolded.” –Heatmap’s Jeva Lange writes about the challenges facing climate cinema, and why 2024 might be the year the climate movie grew up.
Whether you agree probably depends on how you define “climate movie” to begin with.
Climate change is the greatest story of our time — but our time doesn’t seem to invent many great stories about climate change. Maybe it’s due to the enormity and urgency of the subject matter: Climate is “important,” and therefore conscripted to the humorless realms of journalism and documentary. Or maybe it’s because of a misunderstanding on the part of producers and storytellers, rooted in an outdated belief that climate change still needs to be explained to an audience, when in reality they don’t need convincing. Maybe there’s just not a great way to have a character mention climate change and not have it feel super cringe.
Whatever the reason, between 2016 and 2020, less than 3% of film and TV scripts used climate-related keywords during their runtime, according to an analysis by media researchers at the University of Southern California. (The situation isn’t as bad in literature, where cli-fi has been going strong since at least 2013.) At least on the surface, this on-screen avoidance of climate change continued in 2024. One of the biggest movies of the summer, Twisters, had an extreme weather angle sitting right there, but its director, Lee Isaac Chung, went out of his way to ensure the film didn’t have a climate change “message.”
I have a slightly different take on the situation, though — that 2024 was actuallyfull of climate movies, and, I’d argue, that they’re getting much closer to the kinds of stories a climate-concerned individual should want on screen.
That’s because for the most part, when movies and TV shows have tackled the topic of climate change in the past, it’s been with the sort of “simplistic anger-stoking and pathos-wringing” that The New Yorker’s Richard Brody identified in 2022’s Don’t Look Up, the Adam McKay satire that became the primary touchpoint for scripted climate stories. At least it was kind of funny: More overt climate stories like last year’s Foe, starring Saoirse Ronan and Paul Mescal, and Extrapolations, the Apple TV+ show in which Meryl Streep voices a whale, are so self-righteous as to be unwatchable (not to mention, no fun).
But what if we widened our lens and weren’t so prescriptive? Then maybe Furiosa, this spring’s Mad Max prequel, becomes a climate change movie. The film is set during a “near future” ecological collapse, and it certainly makes you think about water scarcity and our overreliance on a finite extracted resource — but it also makes you think about how badass the Octoboss’ kite is. The same goes for Dune: Part Two, which made over $82 million in its opening weekend and is also a recognizable environmental allegory featuring some cool worms. Even Ghostbusters: Frozen Empire, a flop that most people have already memory-holed, revisitedThe Day After Tomorrow’s question of, “What if New York City got really, really, really cold?”
Two 2024 animated films with climate themes could even compete against each other at the Academy Awards next year. Dreamworks Animation’s The Wild Robot, one of the centerpiece films at this fall’s inaugural Climate Film Festival, is set in a world where sea levels have risen to submerge the Golden Gate Bridge, and it impresses on its audience the importance of protecting the natural world. And in Gints Zilbalodis’ Flow, one of my favorite films of the year, a cat must band together with other animals to survive a flood.
Flow also raises the question of whether a project can unintentionally be a climate movie. Zilbalodis told me that making a point about environmental catastrophe wasn’t his intention — “I can’t really start with the message, I have to start with the character,” he said — and to him, the water is a visual metaphor in an allegory about overcoming your fears.
But watching the movie in a year when more than a thousand people worldwide have died in floods, and with images of inundated towns in North Carolina still fresh in mind, it’s actually climate change itself that makes one watch Flow as a movie about climate change. (I’m not the only one with this interpretation, either: Zilbalodis told me he’d been asked by one young audience member if the flood depicted in his film is “the future.”)
Perhaps this is how we should also consider Chung’s comments about Twisters. While nobody in the film says the words “climate change” or “global warming,” the characters note that storms are becoming exceptional — “we've never seen tornadoes like this before,” one says. Despite the director’s stated intention not to make the movie “about” climate change, it becomes a climate movie by virtue of what its audiences have experienced in their own lives.
Still, there’s that niggling question: Do movies like these, which approach climate themes slant-wise, really count? To help me decide, I turned to Sam Read, the executive director of the Sustainable Entertainment Alliance, an advocacy consortium that encourages environmental awareness both on set and on screen. He told me that to qualify something as a “climate” movie or TV show, some research groups look to see if climate change exists in the world of the story or whether the characters acknowledge it. Other groups consider climate in tiers, such as whether a project has a climate premise, theme, or simply a moment.
The Sustainable Entertainment Alliance, however, has no hard rules. “We want to make sure that we support creatives in integrating these stories in whatever way works for them,” Read told me.
Read also confirmed my belief that there seemed to be an uptick in movies this year that were “not about climate change but still deal with things that feel very climate-related, like resource extraction.” There was even more progress on this front in television, he pointed out: True Detective: Night Country wove in themes of environmentalism, pollution, mining, and Indigenous stewardship; the Max comedy Hacks featured an episode about climate change this season; and Industry involved a storyline about taking a clean energy company public, with some of the characters even attending COP. Even Doctor Odyssey, a cruise ship medical drama that airs on USA, worked climate change into its script, albeit in ridiculous ways. (Also worth mentioning: The Netflix dating show Love is Blind cast Taylor Krause, who works on decarbonizing heavy industry at RMI.)
We can certainly do more. As many critics before me have written, it’s still important to draw a connection between things like environmental catastrophes and the real-world human causes of global warming. But the difference between something being “a climate movie” and propaganda — however true its message, or however well-intentioned — is thin. Besides, no one goes to the movies because they want to be scolded; we want to be moved and distracted and entertained.
I’ve done my fair share of complaining over the past few years about how climate storytelling needs to grow up. But lately I’ve been coming around to the idea that it’s not the words “climate change” appearing in a script that we need to be so focused on. As 2024’s slate of films has proven to me — or, perhaps, as this year’s extreme weather events have thrown into relief — there are climate movies everywhere.
Keep ‘em coming.
They might not be worried now, but Democrats made the same mistake earlier this year.
Permitting reform is dead in the 118th Congress.
It died earlier this week, although you could be forgiven for missing it. On Tuesday, bipartisan talks among lawmakers fell apart over a bid to rewrite parts of the National Environmental Policy Act. The changes — pushed for by Representative Bruce Westerman, chairman of the House Natural Resources Committee — would have made it harder for outside groups to sue to block energy projects under NEPA, a 1970 law that governs the country’s process for environmental decisionmaking.
When those talks died, they also killed a separate deal over permitting struck earlier this year between Senator Joe Manchin of West Virginia and Senator John Barrasso of Wyoming. That deal, as I detailed last week, would have loosened some federal rules around oil and gas drilling in exchange for a new, quasi-mandatory scheme to build huge amounts of long-distance transmission.
Rest in peace, I suppose. Even if lawmakers could not agree on NEPA changes, I think Republicans made a mistake by not moving forward with the Manchin-Barrasso deal. (I still believe that the standalone deal could have passed the Senate and the House if put to a vote.) At this point, I do not think we will see another shot at bipartisan permitting reform until at least late 2026, when the federal highway law will need fresh funding.
But it is difficult to get too upset about this failure because larger mistakes have since compounded the initial one. On Wednesday, Republican Speaker Mike Johnson’s bipartisan deal to fund the government — which is, after all, a much more fundamental task of governance than rewriting some federal permitting laws — fell apart, seemingly because Donald Trump and Elon Musk decided they didn’t like it. If I can indulge in the subjunctive for a moment: That breakdown might have likely killed any potential permitting deal, too. So even in a world where lawmakers somehow did strike a deal earlier this week, it might already be dead. (As I write this, the House GOP has reportedly reached a new deal to fund the government through March, which has weakened or removed provisions governing pharmacy benefit managers and limiting American investments in China.)
The facile reading of this situation is that Republicans now hold the advantage. The Trump administration will soon be able to implement some of the fossil fuel provisions in the Manchin-Barrasso deal through the administrative state. Trump will likely expand onshore and offshore drilling, will lease the government’s best acreage to oil and gas companies, and will approve as many liquified natural gas export terminals as possible. His administration will do so, however, without the enhanced legal protection that the deal would have provided — and while those protections are not a must-have, especially with a friendly Supreme Court, their absence will still allow environmental groups to try to run down the clock on some of Trump’s more ambitious initiatives.
Republicans believe that they will be able to get parts of permitting reform done in a partisan reconciliation bill next year. These efforts seem quite likely to run aground, at least as long as something like the current rules governing reconciliation bills hold. I have heard some crazy proposals on this topic — what if skipping a permitting fight somehow became a revenue-raiser for the federal government? — but even they do not touch the deep structure of NEPA in the way a bipartisan compromise could. As Westerman toldPolitico’s Josh Siegel: “We need 60 votes in the Senate to get real permitting reform … People are just going to have to come to an agreement on what permitting reform is.” In any case, Manchin and the Democrats already tried to reform the permitting system via a partisan reconciliation bill and found it essentially impossible.
Even if reconciliation fails, Republicans say, they will still be in a better negotiating position next year than this year because the party will control a few more Senate votes. But will they? The GOP will just have come off a difficult fight over tax reform. Twelve or 24 months from now, demands on the country’s electricity grid are likely to be higher than they are today, and the risk of blackouts will be higher than before. The lack of a robust transmission network will hinder the ability to build a massive new AI infrastructure, as some of Trump’s tech industry backers hope. But 12 or 24 months from now, too, Democrats — furious at Trump — are not going to be in a dealmaking mood, and Republicans have relatively few ways to bring them to the table.
In any case, savvy Republicans should have realized that it is important to get supply-side economic reforms done as early in a president’s four-year term as possible. Such changes take time to filter through the system and turn into real projects and real economic activity; passing the law as early as possible means that the president’s party can enjoy them and campaign on them.
All of it starts to seem more and more familiar. When Manchin and Barrasso unveiled their compromise earlier this year, Democrats didn’t act quickly on it. They felt confident that the window for a deal wouldn’t close — and they looked forward to a potential trifecta, when they would be able to get even more done (and reject some of Manchin’s fossil fuel-friendly compromises).
Democrats, I think, wound up regretting the cavalier attitude that they brought to permitting reform before Trump’s win. But now the GOP is acting the same way: It is rejecting compromises, believing that it will be able to strike a better deal on permitting issues during its forthcoming trifecta. That was a mistake when Democrats did it. I think it will be a mistake for Republicans, too.