You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On drinking water, a ‘rogue’ discovery, and Northwest data centers

Current conditions: Today marks the start of the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Season, and meteorologists are monitoring two potential areas of tropical development • Millions in the Great Plains and Eastern U.S. face risks of thunderstorms, large hail, and tornadoes • Steady rain continues Thursday in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo, where at least 100 people have died in flash floods.
1. Trump administration backtracks on promise to protect drinking water from forever chemicals
The Environmental Protection Agency announced Wednesday that it plans to rescind four Biden-era limitations on pollutants in drinking water. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, also called PFAS or “forever chemicals,” are linked to many serious health issues, including certain cancers; as I’ve covered, they are common in products advertised as stain-proof, nonstick, and water repellent. The EPA’s decision follows Administrator Lee Zeldin’s claim less than two weeks ago that “I have long been concerned about PFAS” and “we are tackling PFAS from all of EPA’s program offices,” E&E News reports.
In the Wednesday announcement, Zeldin backpedaled from his initial call for action, claiming the agency is looking into “common-sense flexibility in the form of additional time for compliance.” He also pushed back on claims that the agency is weakening PFAS standards, per The Washington Post, saying the EPA is looking into revising the limits and that “the number might end up going lower, not higher.” Water utilities, which have balked against the high cost and difficulty of filtering PFAS out of an estimated 158 million Americans’ drinking water, praised the EPA’s delay as “the right thing.”
2. Security experts discovered ‘unexplained’ pieces of communication equipment in Chinese-made solar power inverters
U.S. energy officials have discovered “unexplained communication equipment” in some Chinese-made solar inverters, Reuters reports. Inverters help connect solar panel systems to the electric grid and allow utilities to conduct remote updates and maintenance; because China makes most inverters, power companies typically use firewalls to prevent foreign communication with the devices.
Security experts reportedly found the rogue devices during inspections. Though the sources who spoke with Reuters did not share the manufacturers of the inverters, similar communication devices were reportedly also found in some batteries from “multiple Chinese suppliers” over the past nine months. A spokesperson at the Chinese embassy in Washington pushed back on Reuters’ report, saying, “We oppose the generalization of the concept of national security, distorting and smearing China's infrastructure achievements.”
3. Northwest data centers could ‘cannibalize’ clean power in states with lower environmental protections: report
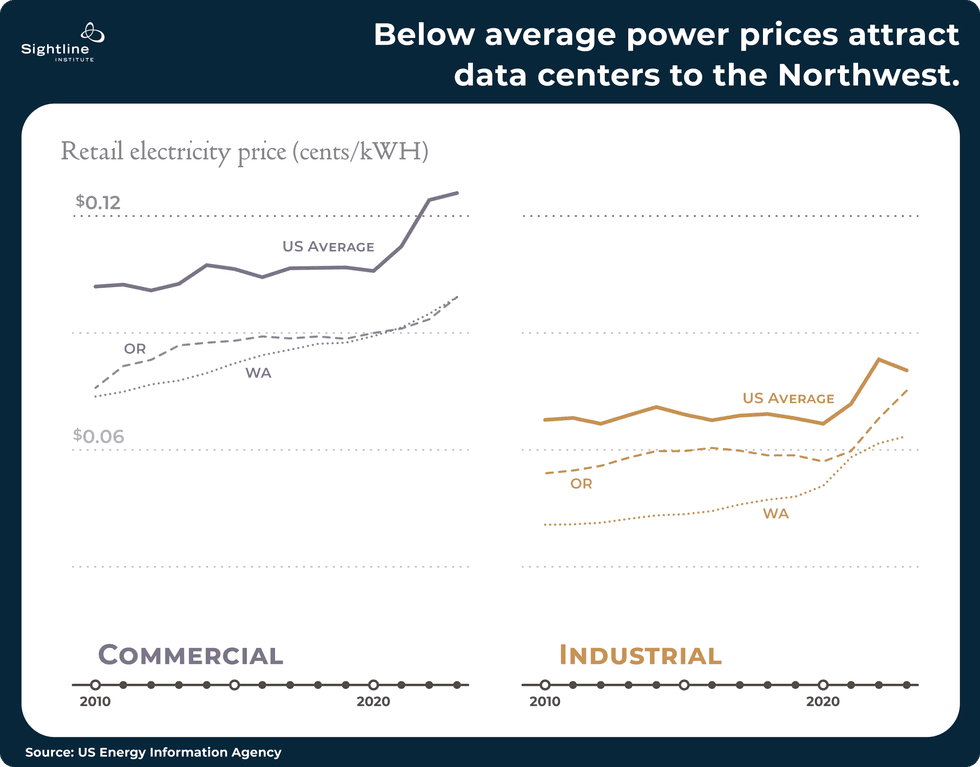
The Northwest has one of the country’s highest concentrations of data centers due to the region’s tax breaks — including low or no property taxes for many in Oregon and sales and use exemptions on equipment purchases and installations in Washington — as well as its below-average renewable power prices. But utilities “working across state lines could shift renewable resources to serve Northwest data centers, making up the difference by burning more coal and gas in places that lack strong environmental protections,” Emily Moore, the director of climate and energy at the sustainability think tank Sightline, writes in a new report.
One such example is what’s being done by Avista, an electricity service in eastern Washington and western Idaho. To meet the needs of a new 200 megawatt data center in Washington, as well as to comply with the state’s Clean Energy Transformation Act, “the company indicated it would add 95 megawatts of gas capacity in Idaho and then shift wind resources that would have served Idaho customers to Washington,” Moore writes. In essence, Washington is “cannibalizing” clean power currently serving Idahoans, and Avista is polluting “more in Idaho to make up the difference.” The report goes on to propose policy paths for Northwest leaders, including accelerating the buildout of the region’s congested electric transmission system, since “a right-sized modern grid could let data centers tap wind from Montana or sun from California instead of encouraging them to locate in states with no commitment to clean power.” You can read Sightline’s full report here.
4. BP chief economist warns China is winning the ‘new energy’ race
Michael Cohen, BP’s chief U.S. economist and head of oil and refining, warned this week that China is winning the “new energy” race with its clean technology supply chains and electric vehicles, Fortune reports. At the Enverus Evolve oil and gas conference in Houston, Cohen said the U.S. is at risk of failing “Econ 101” if it slow-walks on renewables due to resistance from the Trump administration, supply chain issues, and interest rates. He projected that global oil demand will peak in the next decade, with renewables rising from 15% to 30% of the global energy market between now and 2050.
A new report by Carbon Brief appears to back up Cohen’s analysis. The report says that renewable energy sources in China produced enough electricity in the first quarter of the year to “cut coal-power output even as demand surged,” with CO2 emissions down 1.6% year-on-year despite power demand growth. Carbon Brief adds that, if sustained, the findings would “herald a peak and sustained decline in China’s power-sector emissions.”
5. Trump family Bitcoin business adds personal stakes to energy policy
The Trump family is poised to have a fresh personal stake in U.S. electricity and energy policy as Eric Trump and Donald Trump, Jr. plan to take their Bitcoin mining firm public, E&E News reports. According to the announcement earlier this week, American Bitcoin — co-founded by Eric Trump — will merge with Gryphon Digital Mining Inc., which is already publicly traded.
Initially a subsidiary of Hut 8, an energy infrastructure partner with more than 1,000 megawatts of energy capacity, American Bitcoin boasted that with the merger, it will achieve “mining leadership” by leveraging Hut 8’s “energy advantage, rapid execution, and proven team.” Cryptocurrency mining is highly energy-intensive, accounting for an estimated 2.3% of the nation’s electricity use last year, and President Trump’s aspirations to have it “mined, minted, and made in the USA” are part of what his administration has used to justify its energy emergency. With American Bitcoin, the Trump family is also “delving deeper into the energy space where federal policies under Trump intersect directly with access to electricity and fuels,” E&E News writes, noting that Eric Trump stated at the launch of the company last April that “We’ve got the best energy policy in this country. That policy is only getting better.”

Nigerian author Abi Daré has won the inaugural Climate Fiction Prize for her novel And So I Roar. The book “follows fourteen-year-old Adunni from her life in Lagos, where she is excited to finally enroll in school, to her home village where she is summoned to face charges for events that are in fact caused by climate change.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The cloak-and-dagger approach is turning the business into a bogeyman.
It’s time to call it like it is: Many data center developers seem to be moving too fast to build trust in the communities where they’re siting projects.
One of the chief complaints raised by data center opponents across the country is that companies aren’t transparent about their plans, which often becomes the original sin that makes winning debates over energy or water use near-impossible. In too many cases, towns and cities neighboring a proposed data center won’t know who will wind up using the project, either because a tech giant is behind it and keeping plans secret or a real estate firm refuses to disclose to them which company it’ll be sold to.
Making matters worse, developers large and small are requiring city and county officials to be tight-lipped through non-disclosure agreements. It’s safe to say these secrecy contracts betray a basic sense of public transparency Americans expect from their elected representatives and they become a core problem that lets activists critical of the data center boom fill in gaps for the public. I mean, why trust facts and figures about energy and water if the corporations won’t be up front about their plans?
“When a developer comes in and there’s going to be a project that has a huge impact on a community and the environment – a place they call home – and you’re not getting any kind of answers, you can tell they’re not being transparent with you,” Ginny Marcille-Kerslake, an organizer for Food and Water Watch in Pennsylvania, told me in an interview this week. “There’s an automatic lack of trust there. And then that extends to their own government.”
Let’s break down an example Marcille-Kerslake pointed me to, where the utility Talen Energy is seeking to rezone hundreds of acres of agricultural land in Montour County, Pennsylvania, for industrial facilities. Montour County is already a high risk area for any kind of energy or data center development, ranking in the 86th percentile nationally for withdrawn renewable energy projects (more than 10 solar facilities have been canceled here for various reasons). So it didn’t help when individuals living in the area began questioning if this was for Amazon Web Services, similar to other nearby Talen-powered data center projects in the area?
Officials wouldn’t – or couldn’t – say if the project was for Amazon, in part because one of the county commissioners signed a non-disclosure agreement binding them to silence. Subsequently, a Facebook video from an activist fighting the rezoning went viral, using emails he claimed were obtained through public records requests to declare Amazon “is likely behind the scenes” of the zoning request.
Amazon did not respond to my requests for comment. But this is a very familiar pattern to us now. Heatmap Pro data shows that a lack of transparency consistently ranks in the top five concerns people raise when they oppose data center projects, regardless of whether they are approved or canceled. Heatmap researcher Charlie Clynes explained to me that the issue routinely crops up in the myriad projects he’s tracked, down to the first data center ever logged into the platform – a $100 million proposal by a startup in Hood County, Oregon, that was pulled after a community uproar.
“At a high level, I have seen a lack of transparency become more of an issue.t makes people angry in a very unique way that other issues don’t. Not only will they think a project is going to be bad for a community, but you’re not even telling them, the key stakeholder, what is going on,” Clynes said. “It’s not a matter of, are data centers good or bad necessarily, but whether people feel like they’re being heard and considered. And transparency issues make that much more difficult..”
My interview with Marcille-Kerslake exemplified this situation. Her organization is opposed to the current rapid pace of data center build-out and is supporting opposition in various localities. When we spoke, her arguments felt archetypal and representative of how easily those who fight projects can turn secrecy into a cudgel. After addressing the trust issues with me, she immediately pivoted to saying that those exist because “at the root of it, this lack of transparency to the community” comes from “the fact that what they have planned, people don’t want.”
“The answer isn’t for these developers to come in and be fully transparent in what they want to do, which is what you’d see with other kinds of developments in your community. That doesn’t help them because what they’re building is not wanted.”
I’m not entirely convinced by her point, that the only reason data center developers are staying quiet is because of a likelihood of community opposition. In fairness, the tech sector has long operated with a “move fast, break things” approach, and Silicon Valley companies long worked in privacy in order to closely guard trade secrets in a competitive marketplace. I also know from my previous reporting that before AI, data center developers were simply focused on building projects with easy access to cheap energy.
However, in fairness to opponents, I’m also not convinced the industry is adequately addressing its trust deficit with the public. Last week, I asked Data Center Coalition vice president of state policy Dan Diorio if there was a set of “best practices” that his large data center trade organization is pointing to for community relations and transparency. His answer? People are certainly trying their best as they move quickly to build out infrastructure for AI, but no, there is no standard for such a thing.
“Each developer is different. Each company is different. There’s different sizes, different structures,” he said. “There’s common themes of open and public meetings, sharing information about water use in particular, helping put it in the proper context as well.”
He added: “I wouldn’t categorize that as industry best practice, [but] I think you’re seeing common themes emerge in developments around the country.”
Plus more of the week’s biggest renewable energy fights.
Cole County, Missouri – The Show Me State may be on the precipice of enacting the first state-wide solar moratorium.
Clark County, Ohio – This county has now voted to oppose Invenergy’s Sloopy Solar facility, passing a resolution of disapproval that usually has at least some influence over state regulator decision-making.
Millard County, Utah – Here we have a case of folks upset about solar projects specifically tied to large data centers.
Orange County, California – Compass Energy’s large battery project in San Juan Capistrano has finally died after a yearslong bout with local opposition.
Hillsdale County, Michigan – Here’s a new one: Two county commissioners here are stepping back from any decision on a solar project because they have signed agreements with the developer.
A conversation with Save Our Susquehanna’s Sandy Field.
This week’s conversation is with Sandy Field, leader of the rural Pennsylvania conservation organization Save Our Susquehanna. Field is a climate activist and anti-fossil fuel advocate who has been honored by former vice president Al Gore. Until recently, her primary focus was opposing fracking and plastics manufacturing in her community, which abuts the Susquehanna River. Her focus has shifted lately, however, to the boom in data center development.
I reached out to Field because I’ve been quite interested in better understanding how data centers may be seen by climate-conscious conservation advocates. Our conversation led me to a crucial conclusion: Areas with historic energy development are rife with opposition to new tech infrastructure. It will require legwork for data centers – or renewable energy projects, for that matter – to ever win support in places still reeling from legacies of petroleum pollution.
The following conversation has been lightly edited for clarity.
Given your background, tell me about how you wound up focusing on data centers?
We won a fight against a gas plant in fall of 2023. We started saying, Instead of focusing on what we don’t want, we’re going to start focusing on what we do want. We were focusing on supporting recreational projects in our area, because this is an area where people come to hike and camp and fish. It’s a great place to ride your bike.
Then, all of the sudden, people were saying, What about these data centers?
At first, it seemed benign. It’s like a warehouse, who cares? But we started to learn about the water use concerns, the energy use concerns. We learned about the Amazon one that’s connected to Three Mile Island, which is responsible for turning it back on. We learned about one in Homer, Pennsylvania, where they’re taking a former coal plant and converting it into the largest gas plant in the country in order to power a data center. The people in that area are going to get the pollution from the enormous power plant but none of the power. It started to be clear to us that, again, behind these projects is a push to build out more fracking and gas in Pennsylvania.
From a climate change point of view, this is exactly the wrong perspective. We’re running in the wrong direction. Between water usage, and this energy usage, people are becoming alarmed that the burden will be on us and data centers will be just another boondoggle.
The last thing I’ll say is that there is nothing right now in American politics that is reaching across the aisle. Our communities are coming together. Everybody – Democrats, Republicans – to fight these things.
This is also the only thing I’ve ever worked on that people hate more than plastics.
It sounds like how you learned about these projects was, it began as an anodyne issue but you began to hear about impacts on water and energy use. When I talk to people in the development space, some will call anybody who opposes development NIMBYs. But I’m feeling like this is an oversimplification of the problem here. If you had to identify a principle reason so many people are opposing data centers, what would be the big overarching motive?
I think it seems rushed. People are concerned because it's like a gold rush.
A gas-fired power plant takes five years to build. They’re talking about data centers right now. Where is that power coming from? The whole thing feels like a bubble, and we’re concerned that people are going to invest into communities, and communities will be accepting them only to be left with stranded assets.
When I hear you bring up the principle reason being speed, I hear you. Power plants take years. Mines take years. So do renewable energy projects. Help me get a better understanding though, how much of this is purely the speed –
They’re taking people by surprise.
Take into account where we are. We live by the Susquehanna River, the longest non-navigable river in the world. It doesn’t have a lot of industry on it because it’s too shallow, but we drink from the river and we’ve just gotten it clean. The river was so low this past year that historic structures were beginning to be visible that I’ve never seen, the entire time I have lived here. That was because of a drought.
Now, add to that a couple of data centers pulling millions of gallons of water a day and only putting a portion back in, with who knows what in there. People here are saying that back in the day this river was filled with coal dust, and then we had fracking, so its… enough is enough. Let’s put something into rural communities that will actually benefit us.
The small townships [deciding] don’t know enough about data centers to plan for them. So we’re trying to make sure they’re prepared for managing them. We go to these townships being approached and encourage them to have a protective ordinance that allows them to define parameters for these things. Setbacks, water use rules, things like that.
To your point about NIMBYs – there are a few around here who really are. But there are others who really do just have concerns about how this is a bad idea and we’re rushing in a direction we don’t want to go for our state. They felt this way about fracking, about advanced plastics recycling too, for example. It wasn’t that people didn’t want the projects in their backyards – it’s that they didn’t want them anywhere. Labeling us as NIMBYs or whiners or gripers is unfair.
On that note, I can’t help but notice that these efforts to get protective ordinances on data centers are happening as opponents of renewable energy are doing the same thing. Are you at all concerned that this increased scrutiny towards land use will lead to greater restrictions on renewables alongside data centers?
You’re right that a lot of this is about land use and there are similar arguments about renewable energy. Some of these arguments are being fed by the fossil fuel industry and its allies, and a lot of it is baseless. They’re feeding in concerns about glare and noise and whatever else that don’t even really exist about solar panels.
But it is, yes, often the same people talking about protecting their land. It does have similar elements, especially because of the agricultural land use being proposed in many cases.
We need to meet the concerns about renewable energy head-on. If you talk to people and show them a picture of solar panels with sheep grazing underneath and the land can be conserved for many years, this starts to be a different argument than building a data center for Amazon or someone else that people don’t even like, using the water and all that.