You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The Environmental Protection Agency is feeling a calendar crunch.

Since President Joe Biden took office more than two years ago, the Environmental Protection Agency has been something of a sleeping giant.
Once central to President Barack Obama’s climate policy, the EPA seemed to take a backseat under Biden. As the Department of Treasury wrote rules for a dizzying number of new tax credits, and the Department of Energy became a de facto industrial-planning organization, the EPA seemed to wallow.
Then a few weeks ago, the agency came alive.
Last week, it proposed requiring that most new cars sold in the United States — and one quarter of all heavy-duty trucks — be powered solely by electricity. A week before, it tightened limits on the amount of brain-damaging mercury that coal-burning power plants can release. In March, it instructed nearly two dozen states to clean up pollution from their factories and power plants, and it slashed the amount of toxic air pollution that buses, vans, and heavy-duty trucks can legally produce.
This sudden burst of activity is in some ways just the appetizer. Within the next few weeks, the EPA is expected to propose restricting climate-warming pollution from new and existing power plants. This set of draft rules will aim to rapidly eliminate greenhouse-gas pollution from the power sector, one of the most carbon-intensive parts of the economy, in order to meet Biden’s goal of producing 100% zero-carbon electricity by 2035.
It will also face an immediate challenge in the Supreme Court, which has blocked a similar effort in the past even as it has preserved the EPA’s broad power to issue rules about the power sector.
This sudden flurry of productivity may seem to have come out of nowhere.
So why is the EPA publishing so many of these rules now?
The same reason that any of us suddenly become productive: It’s under deadline pressure. For the EPA, and for every other executive agency, the effective beginning of the end of Biden’s first term is as little as a few weeks away. Here’s why.
Under a law called the Congressional Review Act, Congress can overturn new federal rules by a simple majority vote and with the president’s signature. Most of the time, that power doesn’t matter, because presidents rarely want to repeal rules that their own administration has issued. (Last month, Biden vetoed a CRA resolution for this reason.)
But it becomes important when a new White House and Congress take over from a president of the opposite party. In 2017, a newly elected President Donald Trump and a Republican Congress repealed 16 Obama-era rules. In 2021, the new Democratic trifecta overturned three of Trump’s rules.
Biden would like to avoid the same fate befalling his own administration’s climate rules, so he’s moving fast. The key is that Congress can only activate the CRA for new rules — which, under the law, means rules that were finalized during the past 60 “legislative days,” or days when the House or Senate was in session. Because Congress isn’t in session every day, that’s a much longer period of time than it may seem — it can stretch four or five months into the past. When Biden took office in early January 2021, for instance, Congress could use the CRA on any rules that the Trump administration finalized after August 21, 2020.
“It is difficult to know with any specificity what the ‘lookback window’ will look like in 2024,” because it depends on what “the actual session of Congress looks like,” Dan Goldbeck, the director of regulatory policy at the American Action Forum, a center-right think tank, told me. In recent years, the deadline has tended to fall sometime in the late summer, but there’s no guarantee this pattern will hold next year, he said.
Let’s figure it does, though, and that the administration must finalize rules before about August 1, 2024, in order to protect them from the CRA.
We can backfill the calendar from there. As of today, the EPA has only started to circulate drafts of its most important rules, such as the clean-cars mandate. It has yet to publish these drafts in the Federal Register, the government’s official journal of rules and regulations. When they are published, the agency will open a 60-day comment period when the public can respond to any facet of the rules; it will probably extend this to 90 days as a show of good faith.
So if the EPA publishes its draft rule in the Federal Register soon — on May 1, say — then the public comment period will end three months later, on August 1. Then the agency must go over its draft again, double check its math, and respond to every public comment that it has received. This process of finalizing the rule can take about a year. Assuming it does, then suddenly it’s August 1, 2024 — and we’re at the (approximate) deadline.
In other words, the EPA must publish as many rules as possible now in order to protect them from quick repeal if, say, Ron DeSantis is inaugurated in 2025. This is part of why the EPA is moving with such haste now — and why the Biden administration’s climate policy has entered a new and more aggressive phase.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Current conditions: The remnants of Tropical Storm Chantal will bring heavy rain and potential flash floods to the Carolinas, southeastern Virginia, and southern Delaware through Monday night • Two people are dead and 300 injured after Typhoon Danas hit Taiwan • Life-threatening rainfall is expected to last through Monday in Central Texas.
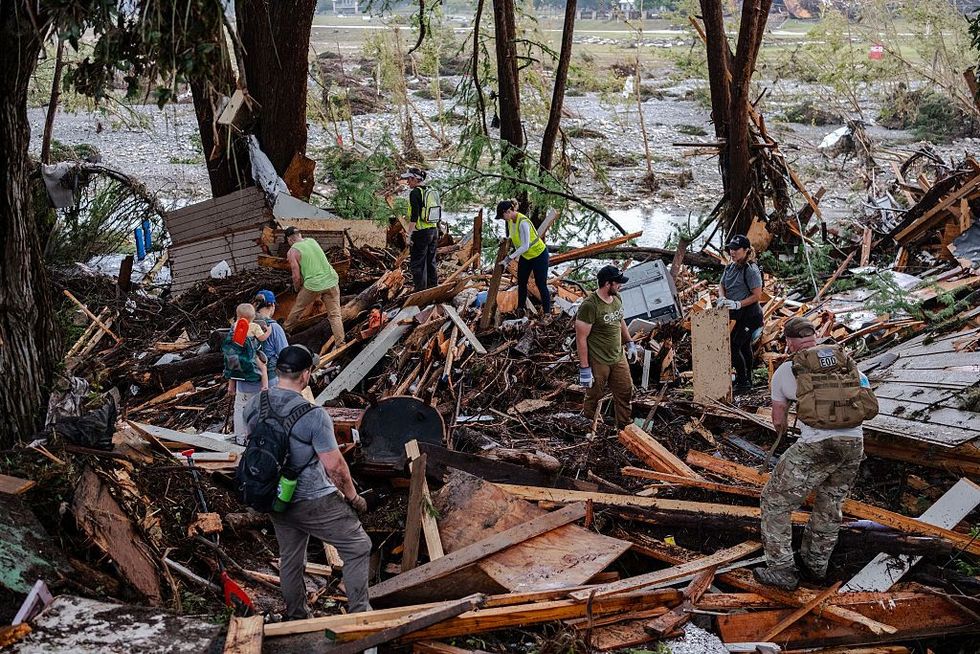

The flash floods in Central Texas are expected to become one of the deadliest such events in the past 100 years, with authorities updating the death toll to 82 people on Sunday night. Another 41 people are still missing after the storms, which began Thursday night and raised the Guadalupe River some 26 feet in less than an hour, providing little chance for holiday weekend campers and RVers to escape.
Although it’s far too soon to definitively attribute the disaster to climate change, a warmer atmosphere is capable of holding more moisture and producing heavy bursts of life-threatening rainfall. Disasters like the one in Texas are one of the “hardest things to predict that’s becoming worse faster than almost anything else in a warming climate, and it’s at a moment where we’re defunding the ability of meteorologists and emergency managers to coordinate,” Daniel Swain of the University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources told the Los Angeles Times. Meteorologists who spoke to Wired argued that the National Weather Service “accurately predicted the risk of flooding in Texas and could not have foreseen the extreme severity of the storm” ahead of the event, while The New York Times noted that staffing shortages at the agency following President Trump’s layoffs potentially resulted in “the loss of experienced people who would typically have helped communicate with local authorities in the hours after flash flood warnings were issued overnight.”
President Trump announced this weekend that his administration plans to send up to 15 letters on Monday to important trade partners detailing their tariff rates. Though Trump didn’t specify which countries would receive such letters or what the rates could be, he said the tariffs would go into effect on August 1 — an extension from the administration’s 90-day pause through July 9 — and range “from maybe 60% or 70% tariffs to 10% and 20% tariffs.” Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent added on CNN on Sunday that the administration would subsequently send an additional round of letters to 100 less significant trade partners, warning them that “if you don’t move things along” with trade negotiations, “then on August 1, you will boomerang back to your April 2 tariff level.” Trump’s proposed tariffs have already rattled industries as diverse as steel and aluminum, oil, plastics, agriculture, and bicycles, as we’ve covered extensively here at Heatmap. Trump’s weekend announcement also sent jitters through global markets on Monday morning.
President Trump’s gutting of the Inflation Reduction Act with the signing of the budget reconciliation bill last week will add an extra 7 billion tons of emissions to the atmosphere by 2030, a new analysis by Climate Brief has found. The rollback on renewable energy credits and policy means that “U.S. emissions are now set to drop to just 3% below current levels by 2030 — effectively flatlining — rather than falling 40% as required to hit the now-defunct [Paris Agreement] target,” Carbon Brief notes. As a result, the U.S. will be about 2 billion tons short of its emissions goal by 2030, adding an emissions equivalent of “roughly the annual output of Indonesia, the world’s sixth-largest emitter.”
To reach its conclusions, Carbon Brief utilized modeling by Princeton University’s REPEAT Project, which examined how the current obstacles facing U.S. wind and solar energy will impact U.S. emissions targets, as well as the likely slowdown in electric vehicle sales and energy efficiency upgrades due to the removal of subsidies. “Under this new set of U.S. policies, emissions are only expected to be 20% lower than 2005 levels by 2030,” Carbon Brief writes.
Engineering giant SKF announced late last week that it had set a new world record for tidal turbine reliability, with its systems in northern Scotland having operated continuously for over six years at 1.5 megawatts “without the need for unplanned or disruptive maintenance.” The news represents a significant milestone for the technology since “harsh conditions, high maintenance, and technical challenges” have traditionally made tidal systems difficult to implement in the real world, Interesting Engineering notes. The pilot program, MayGen, is operated by SAE Renewables and aims, as its next step, to begin deploying 3-megawatt powertrains for 30 turbines across Scotland, France, and Japan starting next year.
Satellites monitoring the Southern Ocean have detected for the first time a collapse and reversal of a major current in the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. “This is an unprecedented observation and a potential game-changer,” said physicist Marilena Oltmanns, the lead author of a paper on the finding, adding that the changes could “alter the Southern Ocean’s capacity to sequester heat and carbon.”
A breakthrough in satellite ocean observation technology enabled scientists to recognize that, since 2016, the Southern Ocean has become saltier, even as Antarctic sea ice has melted at a rate comparable to the loss of Greenland’s ice. The two factors have altered the Southern Ocean’s properties like “we’ve never seen before,” Antonio Turiel, a co-author of the study, explained. “While the world is debating the potential collapse of the AMOC in the North Atlantic, we’re seeing that the Southern Ocean is drastically changing, as sea ice coverage declines and the upper ocean is becoming saltier,” he went on. “This could have unprecedented global climate impacts.” Read more about the oceanic feedback loop and its potential global consequences at Science Daily, here.
The French public research university Sciences Po will open the Paris Climate School in September 2026, making it the first school in Europe to offer a “degree in humanities and social sciences dedicated to ecological transition.” The first cohort will comprise 100 master’s students in an English-language program. “Faced with the ecological emergency, it is essential to train a new generation of leaders who can think and act differently,” said Laurence Tubiana, the dean of the Paris Climate School.
A fifth of U.S. counties now restrict renewables development, according to exclusive data gathered by Heatmap Pro.
A solar farm 40 minutes south of Columbus, Ohio.
A grid-scale battery near the coast of Nassau County, Long Island.
A sprawling wind farm — capable of generating enough electricity to power 100,000 homes — at the northern edge of Nebraska.
These projects — and hundreds of others — will never get built in the United States. They were blocked and ultimately killed by a regulatory sea-change that has reshaped how local governments consider and approve energy projects. One by one, counties and municipalities across the country are passing laws that heavily curtail the construction of new renewable power plants.
These laws are slowing the energy transition and raising costs for utility ratepayers. And the problem is getting worse.
The development of new wind and solar power plants is now heavily restricted or outright banned in about one in five counties across the country, according to a new and extensive survey of public records and local ordinances conducted by Heatmap News.
“That’s a lot,” Nicholas Bagley, a professor at the University of Michigan Law School, told us. Bagley said the “rash of new land use restrictions” owes partly to the increasing politicization of renewable energy.
Across the country, separate rules restrict renewables construction in 605 counties. In some cases, the rules greatly constrain where renewables can be built, such as by requiring that wind turbines must be placed miles from homes, or that solar farms may not take up more than 1% of a county’s agricultural land. In hundreds of other cases, the rules simply forbid new wind or solar construction at all.
Even in the liberal Northeast, where climate concern is high and municipalities broadly control the land use process, the number of restrictions is rising. At least 59 townships and municipalities have curtailed or outright banned new wind and solar farms across the Northeast, according to Heatmap’s survey.
Even though America has built new wind and solar projects for decades, the number of counties restricting renewable development has nearly doubled since 2022.
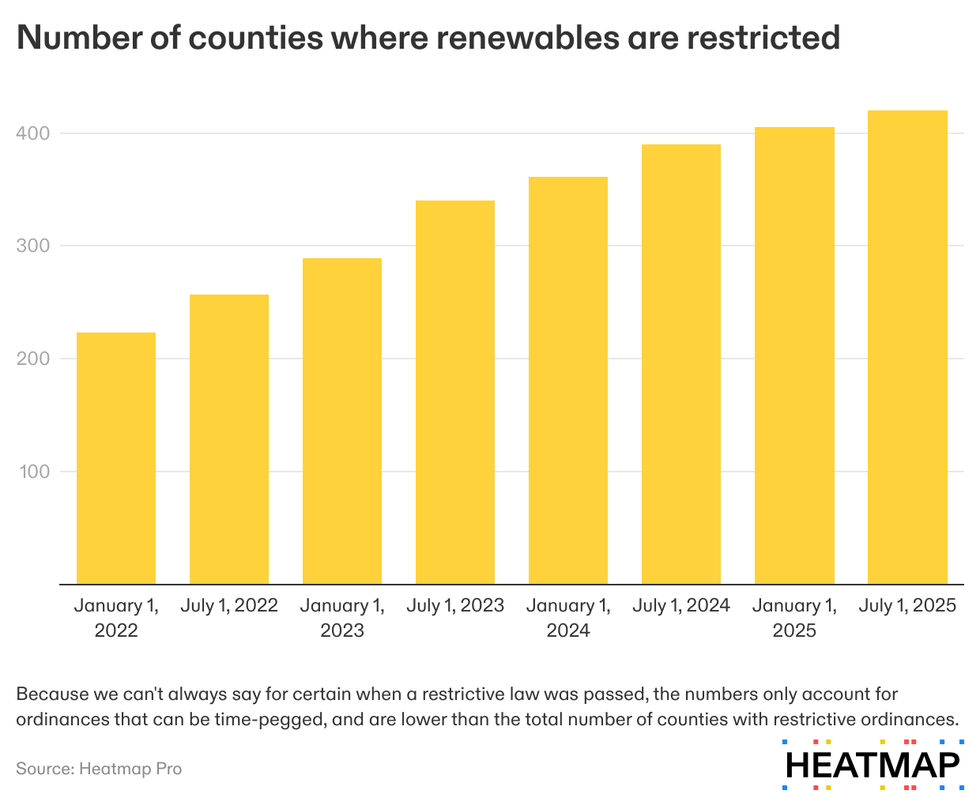
When the various state, county, and municipality-level ordinances are combined, roughly 17% of the total land mass of the continental United States has been marked as off limits to renewables construction.
These figures have not been previously reported. Over the past 12 months, our energy intelligence platform Heatmap Pro has conducted what it believes to be the most comprehensive survey of county and municipality-level renewables restrictions in the United States. In part, that research included surveys of existing databases of local news and county laws, including those prepared by the Sabin Center for Climate Change Law at Columbia University.
But our research team has also called thousands of counties, many of whose laws were not in existing public databases, and we have updated our data in real time as counties passed ordinances and opposed projects progress (or not) through the zoning process. This data is normally available to companies and individuals who subscribe to Heatmap Pro. In this story, we are making a high-level summary of this data available to the public for the first time.
Restrictions have proliferated in all regions of the country.
Forty counties in Virginia alone now have an anti-renewable law on the books, effectively halting solar development in large portions of the state, even as the region experiences blistering electricity load growth.
These anti-solar laws have even begun to slow down energy development across the sunny Southwest. Counties in Nevada and Arizona have rejected new solar development in the same parts of the state that have already seen a high number of solar projects, our data show. Since President Trump took office in January, the effect of these local rules have become more acute — while solar developers could previously avoid the rules by proposing projects on federal land, a permitting slowdown at the Bureau of Land Management is now styming solar projects of all types in the region, as our colleague Jael Holzman has reported.
In the Northeast and on the West Coast, where Democrats control most state governments, towns and counties are still successfully fighting and cancelling dozens of new energy projects. Battery electricity storage systems, or BESS projects, now draw particular ire. The high-profile case of the battery fire in Moss Landing, California, in January has led to a surge of local opposition to BESS projects, our data shows. So far in 2025, residents have cited the Moss Landing case when fighting at least six different BESS projects nationwide.
That’s what happened with Jupiter Power, the battery project proposed in Nassau County, Long Island. The 275-megawatt project was first proposed in 2022 for the Town of Oyster Bay, New York. It would have replaced a petroleum terminal and improved the resilience of the local power grid.
But opposed residents began attending public meetings to agitate about perceived fire and environmental risks, and in spring 2024 successfully lobbied the town to pass a six-month moratorium on battery storage systems. The developer of the battery storage system, Jupiter Power, announced it would withdraw after the town passed two consecutive extensions to the moratorium and residents continued agitating for tighter restrictions.
That pattern — a town passes a temporary moratorium that it repeatedly extends — is how many projects now die in the United States.
The Nebraska wind project, North Fork Wind, was effectively shuttered when Knox County passed a permanent wind-energy ban. And the solar project south of Columbus, Ohio? It died when the Ohio Power Siting Board ruled that “that any benefits to the local community are outweighed by public opposition” to the project, which would have generated 70 megawatts, enough to power about 9,000 homes.
The developers of both of these projects are now waging lengthy and expensive legal appeals to save them; neither has won yet. Even in cases where the developer ultimately prevails against a local law, opposition can waste years and raise the final cost of a project by millions of dollars.
Our Heatmap Pro platform models opposition history alongside demographic, employment, voting, and exclusive polling data to quantify the risk a project will face in every county in the country, allowing developers to avoid places where they are likely to be unsuccessful and strategize for those where they have a chance.
Access to the full project- and county-level data and associated risk assessments is available via Heatmap Pro.
And more on the week’s biggest conflicts around renewable energy projects.
1. Jackson County, Kansas – A judge has rejected a Hail Mary lawsuit to kill a single solar farm over it benefiting from the Inflation Reduction Act, siding with arguments from a somewhat unexpected source — the Trump administration’s Justice Department — which argued that projects qualifying for tax credits do not require federal environmental reviews.
2. Portage County, Wisconsin – The largest solar project in the Badger State is now one step closer to construction after settling with environmentalists concerned about impacts to the Greater Prairie Chicken, an imperiled bird species beloved in wildlife conservation circles.
3. Imperial County, California – The board of directors for the agriculture-saturated Imperial Irrigation District in southern California has approved a resolution opposing solar projects on farmland.
4. New England – Offshore wind opponents are starting to win big in state negotiations with developers, as officials once committed to the energy sources delay final decisions on maintaining contracts.
5. Barren County, Kentucky – Remember the National Park fighting the solar farm? We may see a resolution to that conflict later this month.
6. Washington County, Arkansas – It seems that RES’ efforts to build a wind farm here are leading the county to face calls for a blanket moratorium.
7. Westchester County, New York – Yet another resort town in New York may be saying “no” to battery storage over fire risks.