You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The Department of Energy announced Wednesday that it was scrapping the loan guarantee.
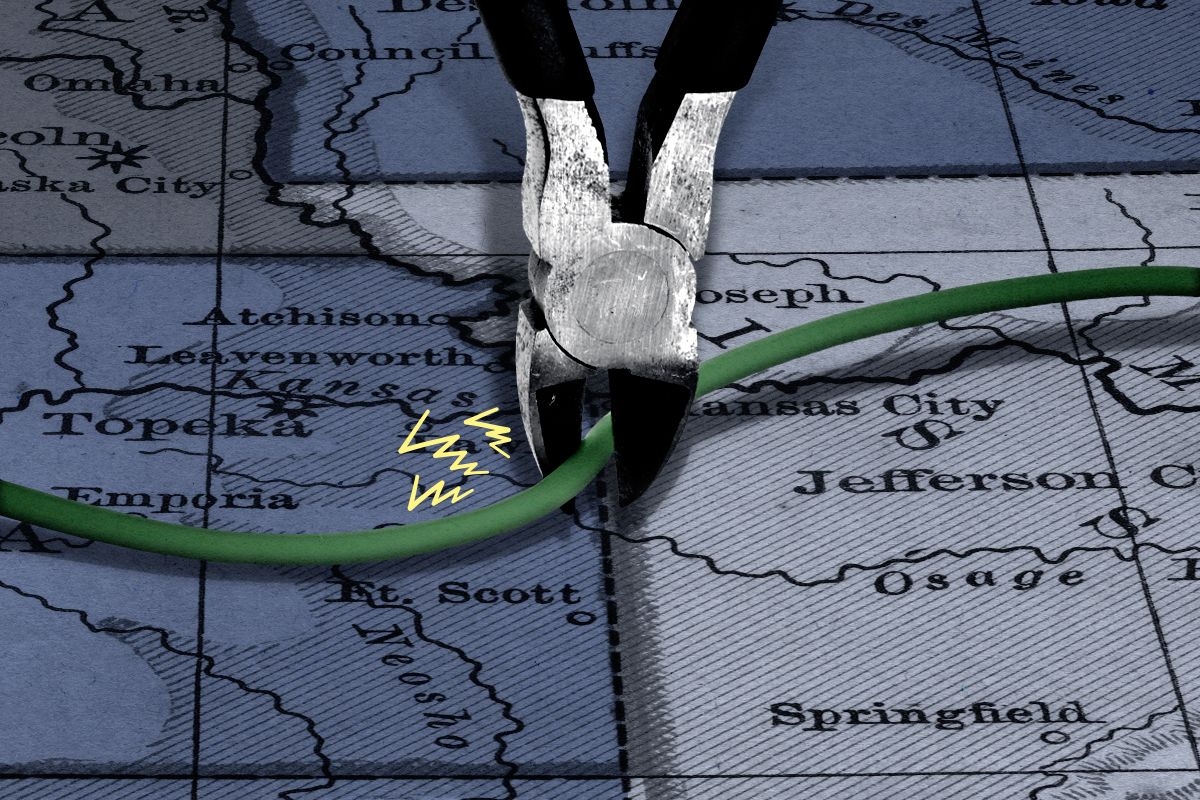
The Department of Energy canceled a nearly $5 billion loan guarantee for the Grain Belt Express, a transmission project intended to connect wind power in Kansas with demand in Illinois that would eventually stretch all the way to Indiana.
“After a thorough review of the project’s financials, DOE found that the conditions necessary to issue the guarantee are unlikely to be met and it is not critical for the federal government to have a role in supporting this project. To ensure more responsible stewardship of taxpayer resources, DOE has terminated its conditional commitment,” the Department of Energy said in a statement Wednesday.
The $11 billion project had been in the works for more than a decade and had won bipartisan approval from state governments and regulators across the Midwest. The conditional loan guarantee announced in November 2024 would have secured up to $4.9 billion in financing to fund phase one of the project, which would run from Ford County in Kansas to Callaway County in Missouri.
In response to a request for comment, an Invenergy spokesperson said, “While we are disappointed about the LPO loan guarantee, a privately financed Grain Belt Express transmission superhighway will advance President Trump’s agenda of American energy and technology dominance while delivering billions of dollars in energy cost savings, strengthening grid reliability and resiliency, and creating thousands of American jobs.”
The project had long been the object of ire from Missouri Senator Josh Hawley, who recently stepped up his attacks in the hopes that a more friendly administration could help scrap the project. Two weeks ago, Hawley posted on X that he’d had “a great conversation today with @realDonaldTrump and Energy Secretary Chris Wright. Wright said he will be putting a stop to the Grain Belt Express green scam. It’s costing taxpayers BILLIONS! Thank you, President Trump.” The New York Times later reported that Trump had made a call to Wright on the issue with Hawley in the Oval Office.
Hawley celebrated the Grain Belt Express decision, writing on X, “It’s done. Thank you, President Trump,” and exulting in a separate post that “Department of Energy officially TERMINATES taxpayer funding for Green New Deal ‘grain belt express.’”
The senator had claimed that the plan would hurt Missouri farmers due to the use of eminent domain to acquire land for the project. In 2023, Hawley wrote a letter to Invenergy chief executive Michael Polsky claiming that “your company’s Grain Belt Express construction campaign has hurt Missouri’s farmers,” and that “they have lost the use of arable land, seen their property values decline, and been forced to operate under a cloud of uncertainty.”
Controversy over eminent domain and the use of agricultural land by transmission lines illustrates the difficulties in building the long-distance energy infrastructure necessary to decarbonize the grid.
Opposition to the project had been gestating for years but picked up steam in recent weeks. Earlier this month, Andrew Bailey, the Republican attorney general of Missouri, announced an investigation into the project. “This is a HUGE win for Missouri landowners and taxpayers who should not have to fund these green energy scams,” he wrote on X Wednesday following the DOE’s announcement.
As the project appeared to be more imminently imperiled, Invenergy scrambled to preserve its future, including making plans to connect gas to the transmission line. In a letter to Secretary of Energy Chris Wright written earlier this month, the Invenergy vice president overseeing the project wrote that the Grain Belt Express “has been the target of egregious politically motivated lawfare,” echoing language President Trump has used to describe his own travails.
If the author’s intent was to generate sympathy from the administration, it didn’t work. The end of the loan guarantee could be a death blow to the project, and will at the very least force Invenergy into a mad dash to try to match the lost capital.
Editor’s note: This story has been updated to include a comment from Invenergy.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Clean energy stocks were up after the court ruled that the president lacked legal authority to impose the trade barriers.
The Supreme Court struck down several of Donald Trump’s tariffs — the “fentanyl” tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China and the worldwide “reciprocal” tariffs ostensibly designed to cure the trade deficit — on Friday morning, ruling that they are illegal under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act.
The actual details of refunding tariffs will have to be addressed by lower courts. Meanwhile, the White House has previewed plans to quickly reimpose tariffs under other, better-established authorities.
The tariffs have weighed heavily on clean energy manufacturers, with several companies’ share prices falling dramatically in the wake of the initial announcements in April and tariff discussion dominating subsequent earnings calls. Now there’s been a sigh of relief, although many analysts expected the Court to be extremely skeptical of the Trump administration’s legal arguments for the tariffs.
The iShares Global Clean Energy ETF was up almost 1%, and shares in the solar manufacturer First Solar and the inverter company Enphase were up over 5% and 3%, respectively.
First Solar initially seemed like a winner of the trade barriers, however the company said during its first quarter earnings call last year that the high tariff rate and uncertainty about future policy negatively affected investments it had made in Asia for the U.S. market. Enphase, the inverter and battery company, reported that its gross margins included five percentage points of negative impact from reciprocal tariffs.
Trump unveiled the reciprocal tariffs on April 2, a.k.a. “liberation day,” and they have dominated decisionmaking and investor sentiment for clean energy companies. Despite extensive efforts to build an American supply chain, many U.S. clean energy companies — especially if they deal with batteries or solar — are still often dependent on imports, especially from Asia and specifically China.
In an April earnings call, Tesla’s chief financial officer said that the impact of tariffs on the company’s energy business would be “outsized.” The turbine manufacturer GE Vernova predicted hundreds of millions of dollars of new costs.
Companies scrambled and accelerated their efforts to source products and supplies from the United States, or at least anywhere other than China.
Even though the tariffs were quickly dialed back following a brutal market reaction, costs that were still being felt through the end of last year. Tesla said during its January earnings call that it expected margins to shrink in its energy business due to “policy uncertainty” and the “cost of tariffs.”
Alphabet and Amazon each plan to spend a small-country-GDP’s worth of money this year.
Big tech is spending big on data centers — which means it’s also spending big on power.
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, announced Wednesday that it expects to spend $175 billion to $185 billion on capital expenditures this year. That estimate is about double what it spent in 2025, far north of Wall Street’s expected $121 billion, and somewhere between the gross domestic products of Ecuador and Morocco.
This is a “a massive investment in absolute terms,” Jefferies analyst Brent Thill wrote in a note to clients Thursday. “Jarringly large,” Guggenheim analyst Michael Morris wrote. With this announcement, total expected capital expenditures by Alphabet, Microsoft and Meta for 2026 are at $459 billion, according to Jefferies calculations — roughly the GDP of South Africa. If Alphabet’s spending comes in at the top end of its projected range, that would be a third larger than the “total data center spend across the 6 largest players only 3 years ago,” according to Brian Nowak, an analyst at Morgan Stanley.
And that was before Thursday, when Amazon told investors that it expects to spend “about $200 billion” on capital expenditures this year.
For Alphabet, this growth in capital expenditure will fund data center development to serve AI demand, just as it did last year. In 2025, “the vast majority of our capex was invested in technical infrastructure, approximately 60% of that investment in servers, and 40% in data centers and networking equipment,” chief financial officer Anat Ashkenazi said on the company’s earnings call.
The ramp up in data center capacity planned by the tech giants necessarily means more power demand. Google previewed its immense power needs late last year when it acquired the renewable developer Intersect for almost $5 billion.
When asked by an analyst during the company’s Wednesday earnings call “what keeps you up at night,” Alphabet chief executive Sundar Pichai said, “I think specifically at this moment, maybe the top question is definitely around capacity — all constraints, be it power, land, supply chain constraints. How do you ramp up to meet this extraordinary demand for this moment?”
One answer is to contract with utilities to build. The utility and renewable developer NextEra said during the company’s earnings call last week that it plans to bring on 15 gigawatts worth of power to serve datacenters over the next decade, “but I'll be disappointed if we don't double our goal and deliver at least 30 gigawatts through this channel by 2035,” NextEra chief executive John Ketchum said. (A single gigawatt can power about 800,000 homes).
The largest and most well-established technology companies — the Microsofts, the Alphabets, the Metas, and the Amazons — have various sustainability and clean energy commitments, meaning that all sorts of clean power (as well as a fair amount of natural gas) are likely to get even more investment as data center investment ramps up.
Jefferies analyst Julien Dumoulin-Smith described the Alphabet capex figure as “a utility tailwind,” specifically calling out NextEra, renewable developer Clearway Energy (which struck a $2.4 billion deal with Google for 1.2 gigawatts worth of projects earlier this year), utility Entergy (which is Google’s partner for $4 billion worth of projects in Arkansas), Kansas-based utility Evergy (which is working on a data center project in Kansas City with Google), and Wisconsin-based utility Alliant (which is working on data center projects with Google in Iowa).
If getting power for its data centers keeps Pichai up at night, there’s no lack of utility executives willing to answer his calls.
The offshore wind industry is now five-for-five against Trump’s orders to halt construction.
District Judge Royce Lamberth ruled Monday morning that Orsted could resume construction of the Sunrise Wind project off the coast of New England. This wasn’t a surprise considering Lamberth has previously ruled not once but twice in favor of Orsted continuing work on a separate offshore energy project, Revolution Wind, and the legal arguments were the same. It also comes after the Trump administration lost three other cases over these stop work orders, which were issued without warning shortly before Christmas on questionable national security grounds.
The stakes in this case couldn’t be more clear. If the government were to somehow prevail in one or more of these cases, it would potentially allow agencies to shut down any construction project underway using even the vaguest of national security claims. But as I have previously explained, that behavior is often a textbook violation of federal administrative procedure law.
Whether the Trump administration will appeal any of these rulings is now the most urgent question. There have been no indications that the administration intends to do so, and a review of the federal dockets indicates nothing has been filed yet.
The Department of Justice declined to comment on whether it would seek to appeal any or all of the rulings.
Editor’s note: This story has been updated to reflect that the administration declined to comment.