You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
What happens to the grid when the sun goes away?
Early April is typically a kind of goldilocks moment for solar power. Days are getting longer but the weather is still mild, meaning that higher solar power generation isn’t entirely eaten up by increased demand due to air conditioning.
But that all depends on the sun actually shining.
Monday’s solar eclipse took a big chunk of power off the grid. Since 2017’s eclipse, solar power generation has increased substantially, both locally (think rooftops) and at utility scale (think massive fields of solar panels). In 2017, the U.S. had around 35 gigawatts of utility-scale solar capacity, a figure that had increased to an estimated 95 gigawatts by the end of 2023.
While total solar eclipses are rare (the next one to hit the lower 48 isn’t expected until 2044), the challenges they present to grid operators may be part of the new normal. With vastly expanded renewable energy generation comes a greater degree of unpredictability, as a growing a portion of the generation fleet can drop off the grid due to weather and climate conditions — like, say, clouds of smoke from a wildfire — that cannot be precisely predicted by 17th century science.
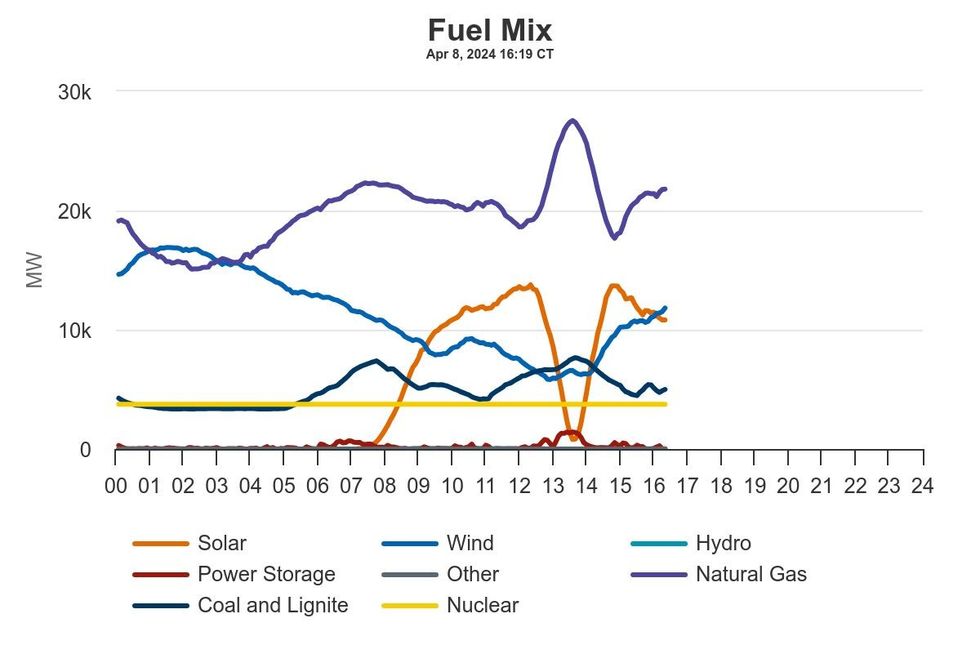
Grid operators were confident they’d be able to manage through the eclipse without any reliability issues, and what actually transpired mostly confirmed their forecasts. In Texas, solar power production shrunk from around 13.5 gigawatts at noon, making up 27% of the grid’s electricity supply, to a mere 0.8 gigawatts at 1:30 p.m. Things did not go as well for the Midcontinent Independent System Operator, however, which includes a swath of the middle of the country from Minnesota to Indiana to Louisiana. Solar output was estimated to drop from around 4 gigawatts at 1 p.m. Central time to 2 gigawatts an hour later, according to Grid Status. Instead, output dropped to around 300 megawatts, causing real-time prices for power on the grid to spike.
Overall, the U.S. Energy Information Administration estimated that some 6,500 megawatts of solar generation capacity would be fully obscured during the eclipse, which would “partially block sunlight to facilities with a combined 84.8 GW of capacity in an even larger swath of the United States around peak solar generating time.” Some 40 gigawatts may have come off the grid, enough power for about 28 million homes, according to a release from Solcast, a solar forecasting company.
By comparison, during the 2017 eclipse, solar power loss at its peak was between 4 and 6.5 gigawatts and the total loss of power was around 11 gigawatts, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
In states like Texas, the main effect was on utility-scale production of solar, but in the Northeast and parts of the mid-Atlantic and Midwest, there was also a related problem: Behind-the-meter solar fell off, too, thus requiring the homes and businesses that generate power for themselves in the middle of the day to get more power from the grid, increasing demand on the grid at a time of low supply.
New England has seen immense growth in rooftop solar, and solar production was expected to fall by “thousands” of megawatts, according to ISO New England, while the New York Independent System Operators expected to lose 700 megawatts of behind the meter solar.
During the 2017 eclipse, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that “the burden of compensating for the lost energy from solar generators fell to the thermal fleet,” i.e. natural gas, along with some increases in coal and hydropower production.
Since then, the coal fleet has shrunk, thus putting more of the burden of responding to Monday’s eclipse onto gas and hydro, but the basic logic still applies. “Grid operators are expected to rely on natural gas to ensure stability and meet the household demand spike across national grids, as was done during the previous eclipse in 2023 in California and Texas,” according to Solcast. As the sun was dimming in Texas, natural gas generation rose from 18.7 gigawatts to 27.5 gigawatts.
Something else that’s changed since 2017: batteries. By the end of 2023, Texas had installed 5.6 gigawatts of grid storage, most of it providing so-called “ancillary services,” power sources that can respond quickly to immediate needs. ERCOT, the electricity market that covers most of Texas, said in a presentation back in February that it would rely on these ancillary tools to get through the eclipse, and once again, it was right. Power from batteries on the grid got up 1.4 gigawatts during the eclipse.
Editor’s note: This story has been updated to reflect the actual effects of the eclipse on U.S. power generation.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On sparring in the Senate, NEPA rules, and taxing first-class flyers
Current conditions: A hurricane warning is in effect for Mexico as the Category 1 storm Flossie approaches • More than 50,000 people have been forced to flee wildfires raging in Turkey • Heavy rain caused flash floods and landslides near a mountain resort in northern Italy during peak tourist season.
Senate lawmakers’ vote-a-rama on the GOP tax and budget megabill dragged into Monday night and continues Tuesday. Republicans only have three votes to lose if they want to get the bill through the chamber and send it to the House. Already Senators Thom Tillis and Rand Paul are expected to vote against it, and there are a few more holdouts for whom clean energy appears to be one sticking point. Senator Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, for example, has put forward an amendment (together with Iowa Senators Joni Ernst and Chuck Grassley) that would eliminate the new renewables excise tax, and phase out tax credits for solar and wind gradually (by 2028) rather than immediately, as proposed in the original bill. “I don’t want us to backslide on the clean energy credits,” Murkowski told reporters Monday. E&E News reported that the amendment could be considered on a simple majority threshold. (As an aside: If you’re wondering why wind and solar need tax credits if they’re so cheap, as clean energy advocates often emphasize, Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo has a nice explainer worth reading.)
At the same time, Utah’s Senator John Curtis has proposed an amendment that tweaks the new excise tax to make it more “flexible.” The amendments are “setting up a major intra-party fight,” Politicoreported, adding that “fiscal hawks on both sides of the Capitol are warning they will oppose the bill if the phase-outs of Inflation Reduction Act provisions are watered down.” Senators have already defeated amendments proposed by Democrats Jeanne Shaheen of New Hampshire and John Hickenlooper of Colorado to defend clean energy and residential solar tax credits, respectively. The session has broken the previous record for most votes in a vote-a-rama, set in 2008, with no end in sight.
The Department of Energy on Monday rolled back most of its regulations relating to the National Environmental Policy Act, or NEPA, and published a new set of guidance procedures in their place. The longstanding NEPA law requires that the government study the environmental impacts of its actions, and in the case of the DOE, this meant things like permitting and public lands management. In a press release outlining the changes, the agency said it was “fixing the broken permitting process and delivering on President Trump’s pledge to unleash American energy dominance and accelerate critical energy infrastructure.” Secretary of Energy Chris Wright said the agency was cutting red tape to end permitting paralysis. “Build, baby, build!” he said.
Nearly 300 employees of the Environmental Protection Agency signed a letter addressed to EPA head Lee Zeldin declaring their dissent toward the Trump administration’s policies. The letter accuses the administration of:
“Going forward, you have the opportunity to correct course,” the letter states. “Should you choose to do so, we stand ready to support your efforts to fulfill EPA’s mission.” It’s signed by more than 420 people, 270 being EPA workers. Many of them asked to sign anonymously. In a statement to The New York Times, EPA spokesperson Carolyn Horlan said “the Trump EPA will continue to work with states, tribes and communities to advance the agency’s core mission of protecting human health and the environment and administrator Zeldin’s Powering the Great American Comeback Initiative, which includes providing clean air, land and water for EVERY American.”
At the fourth International Conference on Financing for Development taking place in Spain this week, a group of eight countries including France and Spain announced they’re banding together in an effort to tax first- and business-class flyers as well as private jets to raise money for climate mitigation and sustainable development. “The aim is to help improve green taxation and foster international solidarity by promoting more progressive and harmonised tax systems,” the office of Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sanchez said in a statement. Other countries in the coalition include Kenya, Barbados, Somalia, Benin, Sierra Leone, and Antigua & Barbuda. The group said it will “work towards COP30 on a better contribution of the aviation sector to fair transitions and resilience.” Wopke Hoekstra, who heads up the European Commission for Climate, called for other countries to join the group in the lead-up to COP30 in November.
In case you missed it: Google announced on Monday that it intends to buy fusion energy from nuclear startup Commonwealth Fusion Systems. Of course, CFS will have to crack commercial-scale fusion first (minor detail!), but as The Wall Street Journal noted, the news is significant because it is “the first direct deal between a customer and a fusion energy company.” Google will buy 200 megawatts of energy supplied by CFS’s ARC plant in Virginia. “It’s a pretty big signal to the market that fusion’s coming,” CFS CEO Bob Mumgaard told the Journal. “It’s desirable, and that people are gonna work together to make it happen.” Google’s head of advanced energy Michael Terrell echoed that sentiment, saying the company hopes this move will “prove out and scale a promising pathway toward commercial fusion power.” CFS, which is backed by Bill Gates’ Breakthrough Energy Ventures, aims to produce commercial fusion energy in the 2030s.
All the public property owned by Britain’s King Charles earned a net profit of £1.15 billion ($1.58 billion) last year. The biggest source of income? Offshore wind leases.
It’s the largest facility of its kind of Europe and will immediately make the lithium-sulfur battery startup a major player.
Lyten, the domestic lithium-sulfur battery company, has officially expanded into the European market, announcing that it has acquired yet another shuttered Northvolt facility. Located in Gdansk, Poland, this acquisition represents a new direction for the company: Rather than producing battery cells — as Lyten’s other U.S.-based facilities will do — this 270,000 square foot plant is designed to produce complete battery energy storage systems for the grid. Currently, it’s the largest energy storage manufacturing facility in Europe, with enough equipment to ramp up to 6 gigawatt-hours of capacity. This gives Lyten the ability to become — practically immediately — a major player in energy storage.
“We were very convinced that we needed to be able to build our own battery energy storage systems, so the full system with electronics and switch gear and safety systems and everything for our batteries to go into,” Keith Norman, Lyten’s chief sustainability and marketing officer, told me. “So this opportunity became very, very well aligned with our strategy.”
The well-funded startup has been negotiating this transaction — which is expected to close in the third quarter — since Northvolt’s bankruptcy proceedings got underway at the end of last year. It marks the second time the company has snatched up an old Northvolt asset, the first being a Bay Area-based plant capable of producing 200 megawatt-hours of batteries that’s expected to begin operations late this year.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are an emerging technology yet to be deployed at scale. This chemistry — if perfected — has the potential to be much higher energy-density than lithium-ion, and doesn’t require costly critical minerals prone to supply chain volatility such as nickel, manganese, cobalt, and graphite. These are all key elements of lithium-ion batteries and are primarily refined in China, whereas sulfur — the key material in lithium-sulfur batteries — is cheap and abundant around the world. Right now, the Poland facility is set up to produce lithium-ion energy storage systems, but once it starts switching over production lines, it will become likely the first in the world to manufacture lithium-sulfur systems at scale.
Until now, Lyten has only owned assets in the U.S., touting that it sources “well over 80%” of its core battery components domestically. But according to Norman, the startup has always looked to Europe as another key market, as its focus revolves around building local supply chains, not just a U.S.-centric one. “We have a vision to be able to have both battery manufacturing and energy storage manufacturing in the U.S. and in Europe, so that we can localize both supply chains,” he explained to me.
In the short-term, however, the company will continue to build its battery capacity in the U.S., including a a gigafactory in Reno planned for 2027, while it focuses on energy storage in Europe. U.S.-made batteries will supply the Poland facility until Lyten’s hypothetical future Europe-based battery factories can ramp, Norman explained.
Immediately after the deal closes, Lyten will restart manufacturing in order to meet Northvolt’s preexisting contracts for lithium-ion systems. Then throughout this year and next, the startup will work to integrate its own lithium-sulfur production lines, ultimately offering customers both lithium-sulfur and lithium-ion energy storage options. The goal is to produce a gigawatt-hour of system capacity by sometime next year.
Offering two distinct energy storage systems reliant on different battery chemistries will work to Lyten’s advantage, Norman told me via email, giving the company “an incredible amount of flexibility to navigate market uncertainty, supply chain uncertainty, geopolitical uncertainty, and varied customer demands.”
The company’s eagerness to acquire shuttered facilities isn’t driven by turbulence in the current political climate, Norman said, but rather by “opportunistic” market circumstances. Yet I also can’t help but notice that this would be a promising way for Lyten to cost-effectively scale at a time when, Norman said, it’s still taking a “wait and see” approach to tariffs and other fluctuating policies that stand to impact the domestic buildout of energy infrastructure.
When I spoke with Norman back in April, right after Trump’s “Liberation Day” tariffs came into effect, he expressed concern over how they could lead to spiraling construction costs. Levies on steel and aluminum, for example, now stand at 50%, while imports from China are still subject to cumulative tariffs of at least 54%. As Norman told me then, “the energy transition is a manufacturing transition,” and Lyten itself is “a hard tech company that needs to build a lot of infrastructure.”
So while the finances of the Poland factory acquisition aren’t public, it’s probably safe to assume that scooping up prebuilt infrastructure from a defunct business, taking over production of tried-and-true lithium-ion-based technologies, and expanding into international markets are all cheap and prudent options in this economy.
In terms of demand for energy storage, Norman also mentioned that the market is hotter in Europe right now than in the U.S., making it an optimal place to kick off its new product line. The company expects to sell storage systems from the Poland plant into a variety of other international markets, as well. In December of last year, Lyten announced that it had received letters of interest from the U.S. Export-Import Bank totalling $650 million in financing to deploy lithium-sulfur energy storage systems in the Caribbean and other developing economies.
As the company expands, it’s on the hunt for even more facilities to grab. “We continue to see assets becoming available or potential capital investments that have already been made in battery manufacturing assets that are potentially coming on the market,” Norman told me. He’s got his eyes on all of it. “That’s a real big priority for us.”
Removing the subsidies would be bad enough, but the chaos it would cause in the market is way worse.
In their efforts to persuade Republicans in Congress not to throw wind and solar off a tax credit cliff, clean energy advocates have sometimes made what would appear to be a counterproductive argument: They’ve emphasized that renewables are cheap and easily obtainable.
Take this statement published by Advanced Energy United over the weekend: “By effectively removing tax credits for some of the most affordable and easy-to-build energy resources, Congress is all but guaranteeing that consumers will be burdened with paying more for a less reliable electric grid.”
If I were a fiscal hawk, a fossil fuel lobbyist, or even an average non-climate specialist, I’d take this as further evidence that renewables don’t need tax credits. The problem is that there’s a lot more nuance to the “cheapness” of renewables than snappy statements like this convey.
“Renewables are cheap and they’ve gotten cheaper, but that doesn’t mean they are always the cheapest thing, unsubsidized,” Robbie Orvis, the senior director of modeling and analysis at Energy Innovation, told me back in May at the start of the reconciliation process. Natural gas is still competitive with renewables in a lot of markets — either where it’s less windy or sunny, where natural gas is particularly cheap, or where there are transmission constraints, for example.
Just because natural gas plants might be cheaper to build in those places, however, doesn’t mean they will save customers money in the long run. Utilities pass fuel costs through to customers, and fuel costs can swing dramatically. That’s what happened in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine, Europe swore off Russian gas, and the U.S. rushed to fill the supply gap, spiking U.S. natural gas prices and contributing to the largest annual increase in residential electricity spending in decades. Winter storms can also reduce natural gas production, causing prices to shoot up. Wind and solar, of course, do not use conventional fuels. The biggest factor influencing the price of power from renewables is the up-front cost of building them.
That’s not the only benefit that’s not reflected in the price tags of these resources. The Biden administration and previous Congress supported tax credits for wind and solar to achieve the policy goal of reducing planet-warming emissions and pollution that endangers human health. But Orvis argued you don’t even need to talk about climate change or the environment to justify the tax credits.
“We’re not saying let’s go tomorrow to wind, water, and solar,” Orvis said. “We’re saying these bring a lot of benefitsonto the system, and so more of them delivers more of those benefits, and incentives are a good way to do that.” Another benefit Orvis mentioned is energy security — because again, wind and solar don’t rely on globally-traded fuels, which means they’re not subject to the actions of potentially adversarial governments.
Orvis’ colleague, Mike O’Boyle, also raised the point that fossil fuels receive subsidies, too, both inside and outside the tax code. There’s the “intangible drilling costs” deduction, allowing companies to deduct most costs associated with drilling, like labor and site preparation. Smaller producers can also take a “depletion deduction” as they draw down their oil or gas resources. Oil and gas developers also benefit from low royalty rates for drilling on public lands, and frequently evade responsibility to clean up abandoned wells. “I think in many ways, these incentives level the playing field,” O’Boyle said.
When I reached out to some of the clean energy trade groups trying to negotiate a better deal in Trump’s tax bill, many stressed that they were most worried about upending existing deals and were not, in fact, calling for wind and solar to be subsidized indefinitely. “The primary issue here is about the chaos this bill will cause by ripping away current policy overnight,” Abigail Ross Hopper, the CEO of the Solar Energy Industries Association, told me by text message.
The latest version of the bill, introduced late Friday night, would require projects to start construction by 2027 and come online by 2028 to get any credit at all. Projects would also be subject to convoluted foreign sourcing rules that will make them more difficult, if not impossible, to finance. Those that fail the foreign sourcing test would also be taxed.
Harry Godfrey, managing director for Advanced Energy United, emphasized the need for “an orderly phase-out on which businesses can follow through on sound investments that they’ve already made.” The group supports an amendment introduced by Senators Joni Ernst, Lisa Murkowski, and Chuck Grassley on Monday that would phase down the tax credit over the next two years and safe harbor any project that starts construction during that period to enable them to claim the credit regardless of when they begin operating.
“Without these changes, the bill as drafted will retroactively change tax policy on projects in active development and construction, stranding billions in private investment, killing tens of thousands of jobs, and shrinking the supply of new generation precisely when we need it the most,” Advanced Energy United posted on social media.
In the near term, wind and solar may not need tax credits to win over natural gas. Energy demand is rising rapidly, and natural gas turbines are in short supply. Wind and solar may get built simply because they can be deployed more quickly. But without the tax credits, whatever does get built is going to be more expensive, experts say. Trade groups and clean energy experts have also warned that upending the clean energy pipeline will mean ceding the race for AI and advanced manufacturing to China.
Godfrey compared the reconciliation bill’s rapid termination of tax credits to puncturing the hull of a ship making a cross-ocean voyage. You’ll either need a big fix, or a new ship, but “the delay will mean we’re not getting electrons on to the grid as quickly as we need, and the company that was counting on that first ship is left in dire straits, or worse.”