You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On a crucial — and underappreciated — phrase in the Global Stocktake.

Now it is over. Early on Wednesday morning, negotiators in Dubai reached an agreement at the 28th Conference of the Parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, the global meeting otherwise known as COP28.
Their final text for the Global Stocktake — a kind of report card on humanity’s progress on its Paris Agreement goals — is contradictory and half-hearted. Instead of blunt language instructing countries to “phase out fossil fuels,” it instead provides a range of options that could let countries achieve “deep, rapid, and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.” One of these possibilities is the tripling of global renewable capacity; another is a call for “transitioning away from fossil fuels.”
So far, this language — this call for leaving fossil fuels — has attracted the most attention by far. Simon Stiell, the UN’s top climate official, said that it marked “the beginning of the end” of the fossil-fuel era, while the climate journalist and activist Bill McKibben has argued that the phrase can become a useful tool for activists, who can now beat it across the head of the Biden administration.
But a separate phrase in the agreement caught my attention. Immediately after calling for transitioning away from fossil fuels, the text makes a different point: that the world must accelerate the development of “zero- and low-emission technologies, including, inter alia, renewables, nuclear, abatement and removal technologies such as carbon capture and utilization and storage, particularly in hard-to-abate sectors, and low-carbon hydrogen production.”
This language may rankle some readers because it seems to give pride of place to carbon capture and storage technology, or CCS, which would allow fossil fuel-burning plants to catch emissions before they enter the atmosphere. (It also seems to conflate CCS with carbon removal technology, even though they are different.) But I believe that the overarching demand — the call for accelerating climate-friendly technologies — represents a crucial insight, one that I could not stop thinking about at the COP itself, and one that is linked to any realistic demand to phase out fossil fuels. Here is that insight: The world will only be able to decarbonize when it develops abundant energy technologies that emit little carbon and that are price-competitive if not cheaper than their fossil-fueled alternatives.
Just as COP28 began, the Rhodium Group, an energy research firm, published a new study looking at how carbon pollution will rise and fall through the end of the century. Unlike other such studies — which ask either how the planet will fare if no new climate policy passes, or what the world must do to avoid 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming — this new study tried to look at what was likely to happen. Given what we know about how countries’ emissions rise and fall with their economies, and when and how they tend to pass climate policy, how much warming can we expect by the end of the century?
As the report’s authors put it, the study was aimed not at policymakers, but at policy takers — the officials, executives, engineers, and local leaders who are starting to plan for the world of 2100.
Here’s the good news: Global greenhouse gas emissions are likely to peak this decade, the report found. Sometime during the 2020s, humanity’s emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other climate pollution will reach an all-time high and begin to fall. (Right now, we emit the equivalent of 50.6 billion tons of the stuff every year.) This will represent a world-historic turning point in our species’ effort to govern the global climate system, and it will probably happen before Morocco, Portugal, and Spain host the 2030 World Cup.
And that is roughly where the good news ends. Because unlike in rosy net-zero studies where humanity’s carbon emissions peak and then rapidly fall to zero, the report does not project any near-term pollution plunge. Instead, global emissions waver and plateau through the 2030s and 2040s, falling in some years, rising slightly in others, cutting an unmistakably downward trend while failing to get anywhere close to zero. By 2060, annual emissions will have fallen to 39 gigatons, only 22% below today’s levels.
And — worse news, now — that is as low as emissions will ever get this century, the report projects. Driven by explosive economic growth in Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, global emissions begin to rise — slowly but inexorably — starting in the 2060s. They keep rising in the 2070s, 2080s, and 2090s. By the year 2090, emissions will have reached 44 gigatons, only 13% below today’s levels and roughly where emissions stood in 2003.
How Greenhouse Gas Emissions Could Fall — Then Rise — in the 21st Century
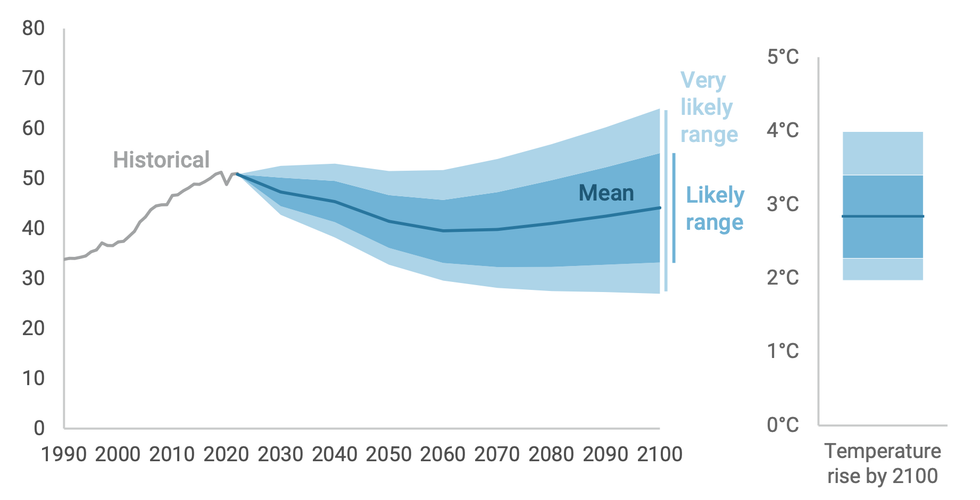
In other words, after a century of work to fight climate change, humanity will find itself roughly where it began. But now, with several thousand additional gigatons of emissions in the atmosphere, the planet will be about 2.8 degrees Celsius warmer (or about 5 degrees Fahrenheit). At its high end estimate, temperatures could rise as much as 4 degrees Celsius, or more than 7 degrees Fahrenheit.
This temperature rise will be caused by legacy emissions from polluters like the United States and China, but as the century goes on, it will increasingly come from Asian and African countries such as Vietnam, Indonesia, Nigeria, Kenya, and others. Why? It’s not like these countries, say, reject renewables or electric vehicles: In fact, Rhodium anticipates that renewables will have grown up to 22-fold by the end of the century.
Instead, emissions rise because fossil fuels are cheap and globally abundant — they remain one of the easiest ways to power an explosively growing society — and because of the growth of the so-called hard-to-abate sectors in these countries are slated to grow just as quickly as the economies themselves. Indonesia, Nigeria, and Vietnam will demand many megatons of new steel, cement, and chemicals to furnish their growing societies; right now, the only economical way to make those materials requires releasing immense amounts of carbon pollution into the atmosphere.
Let’s be clear: Rhodium’s report is a projection, not a prophecy. It should not provoke despair, I think, but determination. Many of the so-called hard-to-abate activities, such as steel or petrochemical making, should more aptly be called activities-that-we-haven’t-tried-very-hard-to-abate yet; people will likely find a way to do them by the middle of the century. (When I asked Bill Gates what he thought about the Rhodium Group’s findings, he replied that predicting the carbon intensity of certain activities in 2060 was all but impossible: We might have safe, cheap, and abundant nuclear fission by then, or even nuclear fusion.)
Yet it heralds a shift in climate geopolitics that, while it has not yet happened, is not so far away. Since the modern era of global climate politics began in 1990, most carbon emissions have come from just a handful of countries: China, the United States, and the 37 other rich, developed democracies that make up the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, or OECD. These countries have emitted 55% of climate pollution since 1990, while the rest of the world — the remaining low- and middle-income countries — have emitted only 45%.
But from now to 2100, that relationship is set to reverse. Through the end of the century, China and the OECD countries emit only 40% of total global emissions, according to Rhodium’s projections. The rest of the world, meanwhile, will emit 60% of global emissions.
In other words, decarbonization will soon become a challenge for middle-income countries. These countries will not be able to spend extra to buy climate-friendly technologies, but they are simply too populous for rich countries to subsidize. At the same time, these countries lack an existing fleet of fossil-fuel-consuming equipment, so they will not need to transition away from fossil fuels in the first place. Unlike in the United States, where we will have to shut down our oil-and-gas economy as we build a new one to replace it, Kenya or Indonesia can more or less build a climate-friendly middle-class economy de novo, much in the same way that in the 2000s countries “leapfrogged” landline telephones and adopted cell phones. Yet countries will only be able to leapfrog the fossil-fuel era if the climate equivalent of cell phones exist: if climate-friendly technologies are plentiful, useful, and price-competitive.
That’s not all it will take, of course. The world will have to phase down the production and consumption of fossil fuels, because the existence of climate-friendly technologies will not guarantee their use. Humanity may also have to create and enforce a strong moral taboo around burning fossil fuels, much in the same way that it has created a taboo around, say, child labor. But none of that can happen unless climate-friendly alternatives exist: Otherwise countries will ensure that they gain access to the energy that their development requires.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Removing the subsidies would be bad enough, but the chaos it would cause in the market is way worse.
In their efforts to persuade Republicans in Congress not to throw wind and solar off a tax credit cliff, clean energy advocates have sometimes made what would appear to be a counterproductive argument: They’ve emphasized that renewables are cheap and easily obtainable.
Take this statement published by Advanced Energy United over the weekend: “By effectively removing tax credits for some of the most affordable and easy-to-build energy resources, Congress is all but guaranteeing that consumers will be burdened with paying more for a less reliable electric grid.”
If I were a fiscal hawk, a fossil fuel lobbyist, or even an average non-climate specialist, I’d take this as further evidence that renewables don’t need tax credits. The problem is that there’s a lot more nuance to the “cheapness” of renewables than snappy statements like this convey.
“Renewables are cheap and they’ve gotten cheaper, but that doesn’t mean they are always the cheapest thing, unsubsidized,” Robbie Orvis, the senior director of modeling and analysis at Energy Innovation, told me back in May at the start of the reconciliation process. Natural gas is still competitive with renewables in a lot of markets — either where it’s less windy or sunny, where natural gas is particularly cheap, or where there are transmission constraints, for example.
Just because natural gas plants might be cheaper to build in those places, however, doesn’t mean they will save customers money in the long run. Utilities pass fuel costs through to customers, and fuel costs can swing dramatically. That’s what happened in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine, Europe swore off Russian gas, and the U.S. rushed to fill the supply gap, spiking U.S. natural gas prices and contributing to the largest annual increase in residential electricity spending in decades. Winter storms can also reduce natural gas production, causing prices to shoot up. Wind and solar, of course, do not use conventional fuels. The biggest factor influencing the price of power from renewables is the up-front cost of building them.
That’s not the only benefit that’s not reflected in the price tags of these resources. The Biden administration and previous Congress supported tax credits for wind and solar to achieve the policy goal of reducing planet-warming emissions and pollution that endangers human health. But Orvis argued you don’t even need to talk about climate change or the environment to justify the tax credits.
“We’re not saying let’s go tomorrow to wind, water, and solar,” Orvis said. “We’re saying these bring a lot of benefitsonto the system, and so more of them delivers more of those benefits, and incentives are a good way to do that.” Another benefit Orvis mentioned is energy security — because again, wind and solar don’t rely on globally-traded fuels, which means they’re not subject to the actions of potentially adversarial governments.
Orvis’ colleague, Mike O’Boyle, also raised the point that fossil fuels receive subsidies, too, both inside and outside the tax code. There’s the “intangible drilling costs” deduction, allowing companies to deduct most costs associated with drilling, like labor and site preparation. Smaller producers can also take a “depletion deduction” as they draw down their oil or gas resources. Oil and gas developers also benefit from low royalty rates for drilling on public lands, and frequently evade responsibility to clean up abandoned wells. “I think in many ways, these incentives level the playing field,” O’Boyle said.
When I reached out to some of the clean energy trade groups trying to negotiate a better deal in Trump’s tax bill, many stressed that they were most worried about upending existing deals and were not, in fact, calling for wind and solar to be subsidized indefinitely. “The primary issue here is about the chaos this bill will cause by ripping away current policy overnight,” Abigail Ross Hopper, the CEO of the Solar Energy Industries Association, told me by text message.
The latest version of the bill, introduced late Friday night, would require projects to start construction by 2027 and come online by 2028 to get any credit at all. Projects would also be subject to convoluted foreign sourcing rules that will make them more difficult, if not impossible, to finance. Those that fail the foreign sourcing test would also be taxed.
Harry Godfrey, managing director for Advanced Energy United, emphasized the need for “an orderly phase-out on which businesses can follow through on sound investments that they’ve already made.” The group supports an amendment introduced by Senators Joni Ernst, Lisa Murkowski, and Chuck Grassley on Monday that would phase down the tax credit over the next two years and safe harbor any project that starts construction during that period to enable them to claim the credit regardless of when they begin operating.
“Without these changes, the bill as drafted will retroactively change tax policy on projects in active development and construction, stranding billions in private investment, killing tens of thousands of jobs, and shrinking the supply of new generation precisely when we need it the most,” Advanced Energy United posted on social media.
In the near term, wind and solar may not need tax credits to win over natural gas. Energy demand is rising rapidly, and natural gas turbines are in short supply. Wind and solar may get built simply because they can be deployed more quickly. But without the tax credits, whatever does get built is going to be more expensive, experts say. Trade groups and clean energy experts have also warned that upending the clean energy pipeline will mean ceding the race for AI and advanced manufacturing to China.
Godfrey compared the reconciliation bill’s rapid termination of tax credits to puncturing the hull of a ship making a cross-ocean voyage. You’ll either need a big fix, or a new ship, but “the delay will mean we’re not getting electrons on to the grid as quickly as we need, and the company that was counting on that first ship is left in dire straits, or worse.”
A new subsidy for metallurgical coal won’t help Trump’s energy dominance agenda, but it would help India and China.
Crammed into the Senate’s reconciliation bill alongside more attention-grabbing measures that could cripple the renewables industry in the U.S. is a new provision to amend the Inflation Reduction Act to support metallurgical coal, allowing producers to claim the advanced manufacturing tax credit through 2029. That extension alone could be worth up to $150 million a year for the “beautiful clean coal” industry (as President Trump likes to call it), according to one lobbyist following the bill.
Putting aside the perversity of using a tax credit from a climate change bill to support coal, the provision is a strange one. The Trump administration has made support for coal one of the centerpieces of its “energy dominance” strategy, ordering coal-fired power plants to stay open and issuing a raft of executive orders to bolster the industry. President Trump at one point even suggested that the elite law firms that have signed settlements with the White House over alleged political favoritism could take on coal clients pro bono.
But metallurgical coal is not used for electricity generation, it’s used for steel-making. Moreover, most of the metallurgical coal the U.S. produces gets exported overseas. In other words, cheaper metallurgical coal would do nothing for American energy dominance, but it would help other countries pump up their production of steel, which would then compete with American producers.
The new provision “has American taxpayers pay to send metallurgical coal to China so they can make more dirty steel and dump it on the global market,” Jane Flegal, the former senior director for industrial emissions in the Biden White House, told me.
The U.S. produced 67 million short tons of metallurgical coal in 2023, according to data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, more than three-quarters of which was shipped abroad. Looking at more recent EIA data, the U.S. exported 57 million tons of metallurgical coal through the first nine months of 2024. The largest recipient was India, the final destination for over 10 million short tons of U.S. metallurgical coal, with almost 9 million going to China. Almost 7 million short tons were exported to Brazil, and over 5 million to the Netherlands.
“Metallurgical coal accounts for approximately 10% of U.S. coal output, and nearly all of it is exported. Thermal coal produced in the United States, by contrast, mostly is consumed domestically,”according to the EIA.
The tax credit comes at a trying time for the metallurgical coal sector. After export prices spiked at $344 per short ton in the second quarter of 2022 following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine (much of Ukraine’s metallurgical coal production occurs in one of its most hotly contested regions), prices fell to $145 at the end of 2024, according to EIA data.
In their most recent quarterly reports, a number of major metallurgical coal producers told investors they wanted to reduce costs “as the industry awaits a reversal of the currently weak metallurgical coal market,” according to S&P Global Commodities Insights, citing low global demand for steel and economic uncertainty.
There was “not a whisper” of the provision before the Senate’s bill was released, according to the lobbyist, who was not authorized to speak publicly. “No one had any inkling this was coming,” they told me.
But it’s been a pleasant surprise to the metallurgical coal industry and its investors.
Alabama-based Warrior Met Coal, which exports nearly all the coal it produces, reported a loss in the first quarter of 2025,blaming “the combination of broad economic uncertainty around global trade, seasonal demand weakness, and ample spot supply is expected to result in continued pressure on steelmaking coal prices.” Its shares were up almost 6% in afternoon trading Monday.
Tennessee-based Alpha Metallurgical Resources reported a $34 million first quarter loss in May, citing “poor market conditions and economic uncertainty caused by shifting tariff and trade policies,” and said it planned to reduce capital expenditures from its previous forecast. Its shares were up almost 7%.
While environmentalists have kept a hawk’s eye on the hefty donations from the oil and gas industry to Trump and other Republicans’ campaign coffers, it appears that the coal industry is the fossil fuel sector getting specific special treatment, despite being far, far smaller. The largest coal companies are worth a few billion dollars; the largest oil and gas companies are worth a few hundred billion.
But coal is very important to a few states — and very important to Donald Trump.
The bituminous coal that has metallurgical properties tends to be mined in Appalachia, with some of the major producers and exporters based in Tennessee and Alabama, or larger companies with mining operations in West Virginia.
One of those, Alliance Resource Partners, shipped almost 6 million tons of coal overseas. Its chief executive, Joseph Craft, andhis wife, Kelly, the former ambassador to the United Nations, are generous Republican donors. Craft was a guest at the White House during the signing ceremony for the coal executive orders.
Representatives of Warrior, Alpha Metallurgical, and Alliance Resources did not respond to a requests for comment.
While coal companies and their employees tend to be loyal Republican donors, the relative small size of the industry puts its financial clout well south of the oil and gas industry, where a single donor like Continental Resources’s Harold Hamm can give over $4 million and the sector as a whole can donate $75 million. This suggests that Trump and the Senate’s attachment to coal has more to do with coal’s specific regional clout, or even the aesthetics of coal mining and burning compared to solar panels and wind turbines.
After all, anyone can donate money, but in Trump’s Washington, only one resource can be beautiful and clean.
Two former Department of Energy staffers argue from experience that severe foreign entity restrictions aren’t the way to reshore America’s clean energy supply chain.
The latest version of Congress’s “One Big, Beautiful Bill” claims to be tough on China. Instead, it penalizes American energy developers and hands China the keys to dominate 21st century energy supply chains and energy-intensive industries like AI.
Republicans are on the verge of enacting a convoluted maze of “foreign entity” restrictions and penalties on U.S. manufacturers and energy companies in the name of excising China from U.S. energy supply chains. We share this goal to end U.S. reliance on Chinese minerals and manufacturing. While at the U.S. Department of Energy and the White House, we worked on numerous efforts to combat China’s grip on energy supply chains. That included developing tough, nuanced and, importantly, workable rules to restrict tax credit eligibility for electric vehicles made using materials from China or Chinese entities — rules that quickly began to shift supply chains away from China and toward the U.S. and our allies.
That experience tells us that the rules in the Republican bill will have the opposite effect. In reality, they will make it much more difficult for U.S. companies to move supply chains away from Chinese control. The GOP’s proposed restrictions require every developer of a critical minerals project, advanced manufacturing facility, or clean energy power plant to sift through their supply chains and contracts for any relationship with a Chinese (or Russian, Iranian, or North Korean) entity. Using a Chinese technology license, or too many subcomponents, or materials produced in China — even if there are few or no alternatives — would be enough to render a company ineligible for the very incentives they need to finance and build new U.S. energy production or manufacturing facilities.
This would put companies in the position of having to prove the absence of Chinese entanglements (and guarantee that there will be none in the future) to qualify for tax credits, an all but impossible task, particularly given the untested set of new rules. Huge portions of the supply chain have flowed through China for decades, including 65% of global lithium processing and 97% of solar wafer manufacturing. American companies are already working to distance themselves from Chinese expertise and components, but the complex, commingled nature of global supply chains and corporate business structures make it infeasible to flip the switch overnight.
On top of that, the latest version of the bill would impose a brand new tax on any new solar and wind projects that have too much foreign entity “assistance,” while providing the Treasury Secretary carte blanche for determining what that might be. The result: An impossible bind, whereby the very sectors that need the most support to disentangle from China are now the ones most penalized by the new Republican “foreign entity” restrictions.
The fact is that China is ahead, not behind, in many energy sectors, and America desperately needs help playing catch-up. Ford’s CEO has called Chinese battery and electric vehicle technologies “an existential threat” to U.S. automaking. In energy supply chains for nuclear, solar, batteries, and critical minerals, China is not merely producing cheap knockoffs of American inventions, it is churning outcutting-edge battery chemistries, advancedmanufacturing processes, and high-speedcharging systems, all at lower cost. And at least until the Inflation Reduction Act enacted incentives for U.S. manufacturing and deployment, the gap between the U.S. and China waswidening.
These untested foreign entity rules will widen that gap once more. Since the start of the year, developers have abandoned more than $14 billion in domestic clean energy deployment and manufacturing projects, citing the uncertain tariff and tax policy environment, and that was before the new tax on solar and wind. New analysis from Energy Innovation finds that the latest version of the bill would reduce U.S. generation capacity by 300 gigawatts over the next decade — multiple times what we will need to power new data centers for artificial intelligence. Stopping clean energy projects in their tracks is also likely to trigger an energy price shock by constraining the very energy technologies that can be built most quickly. In the end we will cede not only our supply chains to China, but also our competitive edge in the race for AI and manufacturing dominance.
Fortunately, we have all the ingredients in this country already to achieve energy leadership. The U.S. boasts deep capital markets, a highly skilled manufacturing and construction workforce, a strong consumer economy driving demand, and, in spite of recent attacks, the world’s greatest universities and national labs. We simply need policy to provide a workable path for companies to invest with certainty, bring factories back to the United States, hire American workers, and learn to produce these technologies at scale.
With the Inflation Reduction Act’s domestic production incentives and supply chain restrictions, hundreds of companies stepped up over the past few years and made that bet, pouring billions of dollars into American supply chains. Should they be enacted, the reconciliation bill’s foreign entity rules would slam the brakes on all that activity, playing right into China’s hands.
There is a way to apply a set of carefully crafted restrictions to wean us off Chinese supply chains, but we cannot afford to saddle American energy with new taxes and red tape. If we scatter rakes across the floor for companies to step on, they will just throw up their hands and send their investments overseas, leaving us more reliant on China than before.