You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
An exclusive interview with the Rivian CEO about the future of electric vehicles.

It has been an astonishing year for the electric vehicle industry. In the past 12 months, the world’s three largest car markets — the United States, the European Union, and China — have unveiled aggressive new subsidies or ambitious new targets to accelerate EV adoption. Even automakers that have long sat out the electric revolution, such as Toyota, are now getting in the game.
That might be good news for R.J. Scaringe, the founder and chief executive of Rivian Automotive. Rivian is angling to use the EV revolution to become one of a handful of new American entrants to the automotive space. You can think of its high-end trucks and SUVs, the R1T and R1S, as the Patagonia meets Apple meets Jeep of the vehicle space. But the company, which designs and manufactures its trucks in America, has struggled with scaling issues and delivered only 42,000 electric vehicles since 2021.
I recently had the chance to sit down with Scaringe and chat about what’s next for Rivian and the broader electric vehicle industry. Our conversation has been lightly edited for concision and clarity.
It seems like over the past year — between the Inflation Reduction Act, between things we’ve seen internationally — the entire electric-vehicle market has undergone a number of shifts that the wider world still hasn’t caught up to yet. Could you give us a snapshot of the sector right now, as you see it?
I think we have seen these really large-scale shifts. You could almost look at it across every vantage point.
You have it from the vantage point of policymakers. If you'd told me just a few years ago that Europe would be committing to 100% of new vehicles being electric, you know, within the next 10 years. That California would be making that commitment in the same way. That the United States, through EPA regulations, is going to be 60% EV of new sales by 2030, I don't think I would have believed it. It’s awesome to see that — literally the reason I started the company is to help drive and instigate that change.
But in parallel with that, we see a shift in how consumers are looking at it. The performance envelope and the drivability of an electric vehicle makes it so much more desirable than an alternative. Buying a non-EV just feels very old. Aside from carbon emissions and environmental responsibility, it's just not interesting.
And then I think the third element is the way that the manufacturers have responded. Up until not too long ago, electrification was sort of a thing you had to do to generate some credits and to look responsible as a company, but they weren't really committed to it. Now, most big vehicle manufacturers have begun to really lean into their electrification strategies.
So with all those things happening, then the question becomes like, what does five years from now look like? What does 10 years from now look like?
I think policy is going to ping-pong around a little bit, unfortunately. Electrification and sustainability have become politicized — it makes no sense at all that it has been, but unfortunately it is. So as a result of that, you will see a little bit of variation there.
But I don't think, at a macro level, [the trend] is going to change. The slope of the curve is going to continue to be policy that drives toward electrification, policy that drives toward moving off of fossil fuels. I think consumers have made the switch and it's a diode-like switch — it's one directional.
I don't think we're going to see consumers have any reignited interest in combustion-powered vehicles. You're going to see a lot of entrenched things try to switch that. But the reality is consumers have made it clear that shift is going to come. It’s not as if everyone has reached that decision [today]. But you can see the slope of the curve.
Once you drive an electric vehicle, again, you can't go back. So for example, for us, more than 75% of our vehicles are sold to first-time EV customers, which is really cool, which means our brand is creating new EV customers. We're helping to drive that change. But once you're in a vehicle, you just can't imagine, like, going back to the pump or dealing with the sound of an engine.
And manufacturers now are all working towards both creating supply of vehicles, but also making sure that the products that they offer are interesting enough to generate demand.
The big question is: There's new brands like us, and then there's existing brands, and which of those brands emerge as the sort of stronger pools of demand — that because of their product attributes, the way those attributes are combined together, the way those are put in under a brand position, which of those offerings, create sort of breakaway interests from consumers?
Do you see consumers deciding my next vehicle will be electric? Or at this point, are consumers still being like, I'd like to go electric, but I want these different attributes. And I'm looking around.
Yeah, both. I think the vast majority of customers are now at least asking themselves the question, "Should I be thinking about electric?"
That doesn't mean they're going to decide on electric, either because of concerns around charging infrastructure or price, or the vehicle that they're looking for doesn't exist — "I want a minivan, but there's no electric minivan that's out there.” There may not be a form factor that fits your desire to see convertible electric vehicles today. So like you may end up in a non-EV choice, because it doesn't exist yet on the supply side. But everyone is asking the question. Or a lot of people are.
And I think what will happen over the next 10 years is those questions today that may not get answered with something that leads to an electric vehicle purchase, that will change. The vehicle that I want, that form factor will be available in an electric offering. And the infrastructure is getting solved too.
Then I think the reality of buying a combustion powered vehicle, in light of the policy that's coming, is sort of like building a horse barn in 1910. Like, imagine buying a Chevy Suburban in 2030. Like, what are you going to do with that, right? In 10 years? Yeah, like gas stations will be slowly disappearing. It's just weird.
It's also, like, your second largest asset.
You're buying this thing that absolutely has no future in our society. And will just increasingly become more and more of a relic of the past. But I think the anticipation of that is leading people to say I don't want to be buying a relic of the past.
I think we're one product cycle away from that really driving consumer demand.
What year do you see?
I think towards the end of this decade. This swing is nonlinear because once you get to that point, whether you're thinking about residual value, or just thinking about standing out as, like, the weird person who still drives a combustion powered vehicle, it's just gonna swing really fast.
What’s the biggest obstacle to electrification right now — to consumers making that decision? Is it just acceptance? Is it charging? Additional policy that needs to happen?
There's a number of them. But I think the biggest is customer choice.
Until recently, there were very, very few choices. Even today, I'd say there are very few good choices, especially across all price bands. So if you want to spend $20,000, you just don't have a good choice to make. You want to spend $35,000 or $40,000, there's a couple of choices. But there's still not a lot of choices. And we've seen that manifest in the extreme market share that Tesla has, because of the lack of choice from other manufacturers.
It's funny, because there aren't that many sub $25,000 new vehicles, period. Do you think we'll get back to that place in a few years in EVs? Or that we might have, you know, a Model 3 that gets there with local incentives, but everything will be nominally above $25,000.
$25,000 starts to get pretty low. I mean, the average selling price, or ASP — like, across the industry now — the average selling price of a new vehicle in the States is about double that, right? It’s like $50,000.
Also, I remember when I could buy a new car for less, but, like, inflation is happening.I bought a new car back in the day for less than $10,000. You can't do that anymore.
What does Rivian need to do to be ready for that moment, five years from now, when consumers are ready to make that leap?
This is the really exciting part for us.
The objective of our R1 program was to serve as our handshake to the world. I often say, it's like it opened the brand umbrella for us as a company and it communicated from a brand point of view and values point of view.
We have vehicles that, we say, enable adventure. They can take your kids to the beach, they can take you to the theme park, they can go to your folks' house for the weekend, you can go mountain biking — just these vehicles that enable life.
And we did that at a premium price with a flagship set of products, the R1T and R1s, that have led to the R1 vehicles being the best-selling electric vehicles over a $70,000 price point. Within that range there, they are the best selling vehicles in the premium segment today, the best-selling electric vehicles.
So as we now look at R2, we need to take that same brand excitement that we've generated, and apply it to a smaller form factor and a much lower price point, and therefore a much bigger addressable market, and carry with it the essence of what was embodied in R1, but make it accessible to so many more people.
So the timing of that program fits beautifully with what we see as this big shift, as a lot of people ask themselves, Am I gonna get an electric car? Well maybe the next one.
So we hope that the R2 platform helps pull a lot of customers across that jump where I want to spend $45,000 or $40,000 in a vehicle. It needs to fit my life. So it's my kids, my pets, my gear — it needs to be able to go places and get dirty and go down a rough road. Our brand fits that so well, but today, a lot of customers just can't afford it, or don't want to spend $70,000-plus, so that's where R2 comes in. I couldn't be more excited about what's coming with that program. Because it just fits so nicely into the market.
What’s the timing on R2?
Beginning of '26. So that vehicle will be produced in our second plant and in Atlanta.
I want to talk about factories for a second. I think Rivian was early to what we would now call reshoring — although, of course, for Rivian, it wasn't really "re," it was just locating manufacturing in the United States with engineering talent located here as well. Lots of other companies are now joining that for various policy and political risk reasons. I think for Rivian, the ramp up has been challenging. What advice would you have to other firms looking to, you know, stand up a manufacturing line and a new factory in the United States?
Yeah, well, we launched our R1T, the R1s, and then our two different variants of our commercial van. In any vehicle, a launch is tough, you’ve got thousands of components coming from hundreds of suppliers that have to ramp in unison and be beautifully synchronized. Any one of those parts can throw it off — there's a whole host of things that can go wrong from a quality or production process point of view. And so we were doing that for the first time. New workforce, new supply chain, new plant, new product, new technology.
And we weren't only doing the first time, we were doing it the first time times three, so it's just really challenging.
And then the operational backdrop was far worse than what we could have ever imagined. So the supply chain catastrophe that was 2022 was our launching ramp here. And then managing the build out of a large 5,000-plus person workforce to produce vehicles in our first plant, in the middle of a pandemic, was also really hard.
It was a hard launch and hard ramp. I don't think you could have designed a more complex environment to do that in. And the strategy we had of those three vehicles happening at the same time, in hindsight, knowing what we know now about what the environment was, we would have created more separation.
In 2017, someone should have come to you and been like, there's going to be a global pandemic.
If somebody only told us that.
So as we think about R2, we're simplifying the launch, we have one product that we're launching, it's a new product, leveraging a lot of the existing technology topology that we have in R1. So there's less technical risk, obviously. There’s also dramatic focus on part simplification, joint simplification and manufacturability. So it’s a very, very different vehicle architecture than what we did in R1. All the scars from ramping R1 are informing and driving this deep focus on manufacture building as we go into R2.
Would that have happened anyway or because of the needs of the R2 platform?
I think it's sometimes the pains of the present that enable the skills of the future. I look at like all the pain we've gone through on R1, created this proximity and an appreciation for manufacturing simplicity that, one, everyone would have agreed that that's necessary for R2, but two, embody that in such a deep way because you've lived through it is really powerful. And it's not like a whole different team is doing R2, it's the team that had to go through the R1 launch.
We’re coming off that — there's still people that are involved with the ramp, but a lot of the people that were on that are now moving to our or have moved, I should say, to R2, and so they're directly talking about stuff like, Hey, that was a real big challenge when we had to attach the C pillar trim on this part because the clips do this, this and this. Let's rethink that. Heck, let's get rid of all the clips. Those types of big questions are now coming up.
How do you see and how you think about vehicle weight right now?
Weight or wait? We get asked about both.
Ha, that’s true. Weight — W E I G H T. Rivian has obviously made two very big vehicles right now, and that increases the material needed for them — the bigger the vehicle, the bigger the battery, the bigger the mineral needs. At the same time, consumers seem to prefer larger motor vehicles. So I'm curious, like, do you think we're gonna find a sweet spot on vehicle weight? Do you think there's a trade-off between consumer demand, consumer tastes, and vehicle size? And if so, what does that mean for profitability? Because if vehicles are getting bigger, and it also means less safe for other people, not vehicles?
Yeah. There's a lot of questions.
First of all, our R1 vehicles are and will be our biggest consumer vehicles. They’re the flagship vehicles, as you'd expect — we have a three row SUV and, like, call it a large truck. And as a result of their physical size, their weight is also high, as a result of batteries, and drive train, chassis architecture, all this stuff. R2 will be a much lighter product, inherently.
And that's, I think, where you start to see where the vast majority of demand is going to be — that mid-size or smallish crossover and SUV space, where the vehicles are themselves smaller and therefore require less materials. This goes back to before the start of the company.
We also have to recognize that in order to drive electrification and to drive this transition, we have to be building products that are both just deeply desirable, but also respond to what customers want. So I talked before about what are the things that would block EV adoption? If we told customers the only way you can get an EV is if it's a small sedan, we're not going to sell a lot of EVs, you're going to see low penetration because customers want a vehicle that can fit all their kids, the gear, their stuff, they want larger SUVs —
And for energy density reasons, actually, the smaller the vehicle, the more likely it is to be fossil.
There's a lot of challenges. So I think what we're seeing is customers do want things that fit a form factor that applies what they've grown accustomed to. And we started with the large truck and largest SUV to do that.
The other thing just to note, and I think this is often missed, but if you're to pick the vehicles on the road, that from a carbon emissions point of view, you wanted to reduce carbon emissions by the largest percentage, you wouldn't pick the smallest vehicles in the road to replace, you'd go to the biggest, the least efficient. A 17 mile-per-gallon, 3-row SUV being replaced with a 80 to 90 mile-per-gallon equivalent R1S is a far better trade than a 45 mile-per-gallon ICE Vehicle being replaced with a 100 mile per gallon equivalent EV. Those deltas are really important.
And then I think the last part is — and this is something that I sort of lightly referenced — but there's so much amplified noise around the imperfections of electrification today that is creating a bunch of misinformation around the sustainability of an electric vehicle. No one, including ourselves, is saying an electric vehicle has zero footprint. Everything we do in our industrialized society has a footprint. If you use a light switch in your house, you have footprint. If you buy anything, or eat anything, for that matter, it has a footprint.
So the question is how do we approach a world that can be sustainable for generations upon generations, which means it needs to be a world that's powered by the sun. So that's either direct with photovoltaics or indirect with wind but either way it's sun powered. And that relies on us shifting off of an overall industrial economy that's running on fossil fuels.
And core to that is the things that need to move through stored energy. I think the vast majority [of that stored energy] will likely be in the form of batteries. There are hard problems like planes, but by the end of my lifetime, very few things on the planet will move with propulsion coming from fossil fuels.
And so the world is going to have a diverse set of needs. You're going to see everything from large trucks to buses, to large SUVs, to minivans to station wagons to hatchbacks to sports cars to — everything needs to be electrified.
And that means our vehicles are going to be a little heavier across the board because you know, the average vehicle weight is going to go up because everything's carrying a battery as opposed to a plastic fuel tank.
But you also get into a world where this becomes very circular. So we could talk about raw material extraction and some of the challenges with that. But in my lifetime, we'll also see a world where the source of our lithium is old lithium-ion batteries. And so you get this closed loop and it's why every lithium manufacturer, lithium processor in the world is focused, very focused on access to recycled content, and recycling becomes a really key feedstock as this system starts to reach scale.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Deep Fission says that building small reactors underground is both safer and cheaper. Others have their doubts.
In 1981, two years after the accident at Three Mile Island sent fears over the potential risks of atomic energy skyrocketing, Westinghouse looked into what it would take to build a reactor 2,100 feet underground, insulating its radioactive material in an envelope of dirt. The United States’ leading reactor developer wasn’t responsible for the plant that partially melted down in Pennsylvania, but the company was grappling with new regulations that came as a result of the incident. The concept went nowhere.
More than a decade later, the esteemed nuclear physicist Edward Teller resurfaced the idea in a 1995 paper that once again attracted little actual interest from the industry — that is, until 2006, when Lowell Wood, a physicist at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, proposed building an underground reactor to Bill Gates, who considered but ultimately abandoned the design at his nuclear startup, TerraPower.
Now, at last, one company is working to make buried reactors a reality.
Deep Fission proposes digging boreholes 30 inches in diameter and about a mile deep to house each of its 15-megawatt reactors. And it’s making progress. In August, the Department of Energy selected Deep Fission as one of the 10 companies enrolled in the agency’s new reactor pilot program, meant to help next-generation startups split their first atoms by July. In September, the company announced a $30 million reverse merger deal with a blank check firm to make its stock market debut on the lesser-known exchange OTCQB. Last month, Deep Fission chose an industrial park in a rural stretch of southeastern Kansas as the site of its first power plant.
Based in Berkeley, California, the one-time hub of the West Coast’s fading anti-nuclear movement, the company says its design is meant to save money on above-ground infrastructure by letting geology do the work to add “layers of natural containment” to “enhance safety.” By eliminating much of that expensive concrete and steel dome that encases the reactor on the surface, the startup estimates “that our approach removes up to 80% of the construction cost, one of the biggest barriers for nuclear, and enables operation within six months of breaking ground.”
“The primary benefit of placing a reactor a mile deep is cost and speed,” Chloe Frader, Deep Fission’s vice president of strategic affairs, told me. “By using the natural pressure and containment of the Earth, we eliminate the need for the massive, above-ground structures that make traditional nuclear expensive and slow to build.”
“Nuclear power is already the safest energy source in the world. Period,” she said. “Our underground design doesn’t exist because nuclear is unsafe, it exists because we can make something that is already extremely safe even safer, simpler, and more affordable.”
But gaining government recognition, going public, and picking a location for a first power plant may prove the easy part. Convincing others in the industry that its concept is a radical plan to cut construction costs rather than allay the public’s often-outsize fear of a meltdown has turned out to be difficult, to say nothing of what actually building its reactors will entail.
Despite the company’s recent progress, I struggled to find anyone who didn’t have a financial stake in Deep Fission willing to make the case for its buried reactors.
Deep Fission is “solving a problem that doesn't actually exist,” Seth Grae, the chief executive of the nuclear fuel company Lightbridge, told me. In the nearly seven decades since fission started producing commercial electrons on the U.S. grid, no confirmed death has ever come from radiation at a nuclear power station.
“You’re trying to solve a political problem that has literally never hurt anyone in the entire history of our country since this industry started,” he said. “You’re also making your reactors more expensive. In nuclear, as in a lot of other projects, when you build tall or dig deep or lift big and heavy, those steps make the projects much more expensive.”
Frader told me that subterranean rock structures would serve “as natural containment, which also enhances safety.” That’s true to some extent. Making use of existing formations “could simplify surface infrastructure and streamline construction,” Leslie Dewan, a nuclear engineer who previously led a next-generation small modular reactor startup, told IEEE Spectrum.
If everything pans out, that could justify Deep Fission’s estimate that its levelized cost of electricity — not the most dependable metric, but one frequently used by solar and wind advocates — would be between $50 and $70 per megawatt-hour, lower than other SMR developers’ projections. But that’s only if a lot of things go right.
“A design that relies on the surrounding geology for safety and containment needs to demonstrate a deep understanding of subsurface behavior, including the stability of the rock formations, groundwater movement, heat transfer, and long-term site stability,” Dewan said. “There are also operational considerations around monitoring, access, and decommissioning. But none of these are necessarily showstoppers: They’re all areas that can be addressed through rigorous engineering and thoughtful planning.”
As anyone in the geothermal industry can tell you, digging a borehole costs a lot of money. Drilling equipment comes at a high price. Underground geology complicates a route going down one mile straight. And not every hole that’s started ends up panning out, meaning the process must be repeated over and over again.
For Deep Fission, drilling lots of holes is part of the process. Given the size of its reactor, to reach a gigawatt — the output of one of Westinghouse’s flagship AP1000s, the only new type of commercial reactor successfully built from scratch in the U.S. this century — Deep Fission would need to build 67 of its own microreactors. That’s a lot of digging, considering that the diameters of the company’s boreholes are on average nearly three times wider than those drilled for harvesting natural gas or geothermal.
The company isn’t just distinguished by its unique approach. Deep Fission has a sister company, Deep Isolation, that proposes burying spent nuclear fuel in boreholes. In April, the two startups officially partnered in a deal that “enables Deep Fission to offer an end-to-end solution that includes both energy generation and long-term waste management.”
In theory, that combination could offer the company a greater social license among environmental skeptics who take issue with the waste generated from a nuclear plant.
In 1982, Congress passed a landmark law making the federal government responsible for the disposal of all spent fuel and high-level radioactive waste in the country. The plan centered on building a giant repository to permanently entomb the material where it could remain undisturbed for thousands of years. The law designated Yucca Mountain, a rural site in southwestern Nevada near the California border, as the exclusive location for the debut repository.
Construction took years to start. After initial work got underway during the Bush administration, Obama took office and promptly slashed all funding for the effort, which was opposed by then-Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid of Nevada; the nonpartisan Government Accountability Office clocked the move as a purely political decision. Regardless of the motivation, the cancellation threw the U.S. waste disposal strategy into limbo because the law requires the federal government to complete Yucca Mountain before moving on to other potential storage sites. Until that law changes, the U.S. effort to find a permanent solution to nuclear waste remains in limbo, with virtually all the spent fuel accumulated over the years kept in intermediate storage vessels on site at power plants.
Finland finished work on the world’s first such repository in 2024. Sweden and Canada are considering similar facilities. But in the U.S., the industry is moving beyond seeing its spent fuel as waste, as more companies look to start up a recycling industry akin to those in Russia, Japan, and France to reprocess old uranium into new pellets for new reactors. President Donald Trump has backed the effort. The energy still stored in nuclear waste just in this country is sufficient to power the U.S. for more than a century.
Even if Americans want an answer to the nuclear waste problem, there isn’t much evidence to suggest they want to see the material stored near their homes. New Mexico, for example, passed a law barring construction of an intermediate storage site in 2023. Texas attempted to do the same, but the Supreme Court found the state’s legislation to be in violation of the federal jurisdiction over waste.
While Deep Fission’s reactors would be “so far removed from the biosphere” that the company seems to think the NRC will just “hand out licenses and the public won’t worry,” said Nick Touran, a veteran engineer whose consultancy, What Is Nuclear, catalogs reactor designs and documents from the industry’s history, “the assumption that it’ll be easy and cheap to site and license this kind of facility is going to be found to be mistaken,” he told me.
The problem with nuclear power isn’t the technology, Brett Rampal, a nuclear expert at the consultancy Veriten, told me. “Nuclear has not been suffering from a technological issue. The technology works great. People do amazing things with it, from curing cancer to all kinds of almost magical energy production,” he told me. “What we need is business models and deployment models.”
Digging a 30-inch borehole a mile deep would be expensive enough, but Rampal also pointed out that lining those shafts with nuclear-grade steel and equipping them with cables would likely pencil out to a higher price than building an AP1000 — but with one one-hundredth of the power output.
Deep Fission insists that isn’t the case, and that the natural geology “removes the need for complex, costly pressure vessels and large engineered structures” on the surface.
“We still use steel and engineered components where necessary, but the total material requirements are a fraction of those used in a traditional large-scale plant,” Frader said.
Ultimately, burying reactors is about quieting concerns that should be debunked head on, Emmet Penney, a historian of the industry and a senior fellow at the Foundation for American Innovation, a right-leaning think tank that advocates building more reactors in the U.S., told me.
“Investors need to wake up and realize that nuclear is one of the safest power sources on the planet,” Penney said. “Otherwise, goofy companies will continue to snow them with slick slide decks about solving non-issues.”
On energy efficiency rules, Chinese nuclear, and Japan’s first offshore wind
Current conditions: Warm air headed northward up the East Coast is set to collide with cold air headed southward over the Great Lakes and Northeast, bringing snowfall followed by higher temperatures later in the week • A cold front is stirring up a dense fog in northwest India • Unusually frigid Arctic air in Europe is causing temperatures across northwest Africa to plunge to double-digit degrees below seasonal norms, with Algiers at just over 50 degrees Fahrenheit this week.

Oil prices largely fell throughout 2025, capping off December at their lowest level all year. Spot market prices for Brent crude, the leading global benchmark for oil, dropped to $63 per barrel last month. The reason, according to the latest analysis of the full year by the Energy Information Administration, is oversupply in the market. China’s push to fill its storage tanks kept prices from declining further. Israel’s June 13 strikes on Iran and attacks on oil infrastructure between Russia and Ukraine briefly raised prices throughout the year. But the year-end average price still came in at $69 per barrel, the lowest since 2020, even when adjusted for inflation.
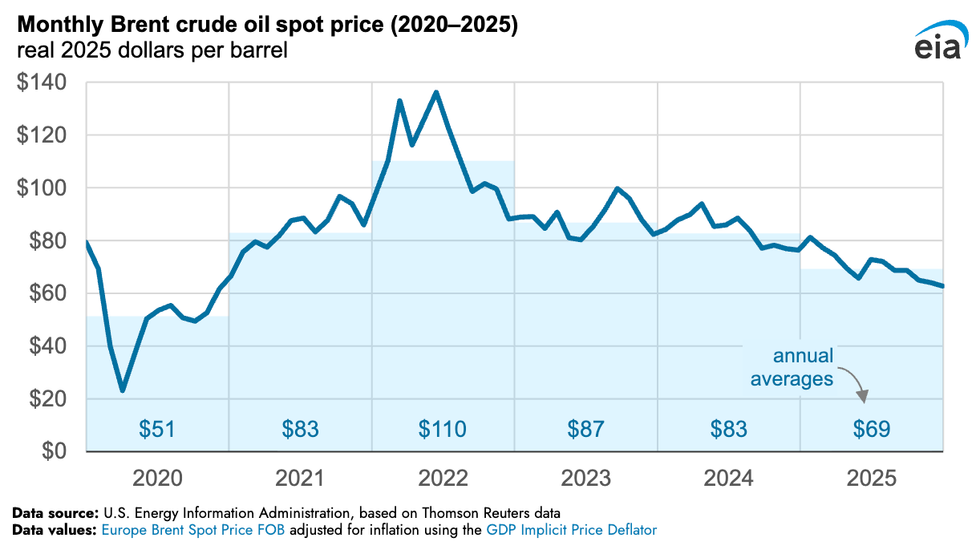
The price drop bodes poorly for reviving Venezuela’s oil industry in the wake of the U.S. raid on Caracas and arrest of the South American country’s President Nicolás Maduro. At such low levels, investments in new infrastructure are difficult to justify. “This is a moment where there’s oversupply,” oil analyst Rory Johnston told my colleague Matthew Zeitlin yesterday. “Prices are down. It’s not the moment that you’re like, I’m going to go on a lark and invest in Venezuela.”
The Energy Department granted a Texas company known for recycling defunct tools from oil and gas drilling an $11.5 million grant to fund an expansion of its existing facility in a rural county between San Antonio and Dallas. The company, Amermin, said the funding will allow it to increase its output of tungsten carbide by 300%, “reducing our reliance on foreign nations like China, which produces 83%” of the world’s supply of the metal used in all kinds of defense, energy, and hardware applications. “Our country cannot afford to rely on our adversaries for the resources that power our energy industry,” Representative August Pfluger, a Texas Republican, said in a statement. “This investment strengthens our district’s role in American energy leadership while providing good paying jobs to Texas families.”
That wasn’t the agency’s only big funding announcement. The Energy Department gave out $2.7 billion in contracts for enriched uranium, with $900 million each to Maryland-based Centrus Energy, the French producer Orano, and the California-headquartered General Matter. “President Trump is catalyzing a resurgence in the nation’s nuclear energy sector to strengthen American security and prosperity,” Secretary of Energy Chris Wright said in a press release. “Today’s awards show that this Administration is committed to restoring a secure domestic nuclear fuel supply chain capable of producing the nuclear fuels needed to power the reactors of today and the advanced reactors of tomorrow.”
Low-income households in the United States pay roughly 30% more for energy per square foot than households who haven’t faced trouble paying for electricity and heat in the past, federal data shows. Part of the problem is that the national efficiency standards for one of the most affordable types of housing in the nation, manufactured homes, haven’t been updated since 1994. Congress finally passed a law in 2007 directing the Department of Energy to raise standards for insulation, and in 2022, the Biden administration proposed new rules to increase insulation and reduce air leaks. But the regulations had yet to take effect when President Donald Trump returned to office last year. Now the House of Representatives is prepared to vote on legislation to nullify the rules outright, preserving the standards set more than three decades ago. The House Committee on Rules is set to vote on advancing the bill as early as Tuesday night, with a full floor vote likely later in the week. “You’re just locking in higher bills for years to come if you give manufacturers this green light to build the homes with minimal insulation,” Mark Kresowik, senior policy director of the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, told me.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
The newest reactor at the Zhangzhou nuclear station in Fujian Province has officially started up commercial operation as China’s buildout of new atomic power infrastructure picks up pace this year. The 1,136-megawatt Hualong One represents China’s leading indigenous reactor design. Where once Beijing preferred the top U.S. technology for large-scale reactors, the Westinghouse AP1000, the Hualong One’s entirely domestic supply chain and design that borrows from the American standard has made China’s own model the new leader.
In a sign of just how many reactors China is building — at least 35 underway nationwide, as I noted in yesterday’s newsletter — the country started construction on two more the same week the latest Hualong One came online. World Nuclear News reported that first concrete has been poured for a pair of CAP1000 reactors, the official Chinese version of the Westinghouse AP1000, at two separate plants in southern China.
Back in October, when Japan elected Sanae Takaichi as its first female prime minister, I told you about how the arch-conservative leader of the Liberal Democratic Party planned to refocus the country’s energy plans on reviving the nuclear industry. But don’t count out offshore wind. Unlike Europe’s North Sea or the American East Coast, the sharp continental drop in Japan’s ocean makes rooting giant turbines to the sea floor impossible along much of its shoreline. But the Goto Floating Wind Farm — employing floating technology under consideration on the U.S. West Coast, too — announced the start of commercial operations this week, pumping nearly 17 megawatts of power onto the Japanese grid. Japanese officials last year raised the country’s goal for installed capacity of offshore wind to 10 gigawatts by 2030 and 45 gigawatts by 2040, Power magazine noted, so the industry still has a long way to go.
Beavers may be the trick to heal nature’s burn scars after a wildfire. A team of scientists at the U.S. Forest Service and Colorado State University are building fake beaver dams in scorched areas to study how wetlands created by the dams impact the restoration of the ecosystem and water quality after a blaze. “It’s kind of a brave new world for us with this type of work,” Tim Fegel, a doctoral candidate at Colorado State, who led the research, said in a press release.
Rob talks about the removal of Venezuela’s Nicolás Maduro with Commodity Context’s Rory Johnston.
Over the weekend, the U.S. military entered Venezuela and captured its president, Nicolás Maduro, and his wife. Maduro will now face drug and gun charges in New York, and some members of the Trump administration have described the operation as a law enforcement mission.
President Donald Trump has taken a different tack. He has justified the operation by asserting that America is going to “take over” Venezuela’s oil reserves, even suggesting that oil companies might foot the bill for the broader occupation and rebuilding effort. Trump officials have told oil companies that the U.S. might not help them recover lost assets unless they fund the American effort now, according to Politico.
Such a move seems openly imperialistic, ill-advised, and unethical — to say the least. But is it even possible? On this week’s episode of Shift Key, Rob talks to Rory Johnston, a Toronto-based oil markets analyst and the founder of Commodity Context. They discuss the current status of the Venezuelan oil industry, what a rebuilding effort would cost, and whether a reopened Venezuelan oil industry could change U.S. energy politics — or even, as some fear, bring about a new age of cheap fossil fuels.
Shift Key is hosted by Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap, and Jesse Jenkins, a professor of energy systems engineering at Princeton University. Jesse is off this week.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from our conversation:
Robinson Meyer: First of all, does Venezuela have the world’s largest hydrocarbon reserves — like, proven hydrocarbon reserves? And number two, let’s say that Trump has made some backdoor deal with the existing regime, that these existing issues are ironed ou to actually use those reserves. What kind of investment are we talking about on that end?
Rory Johnston: The mucky answer to this largest reserve question is, there’s lots of debate. I will say there’s a reasonable claim that at one point Venezuela — Venezuela has a lot of oil. Let’s just say it that way: Venezuela has a lot of oil, particularly the Orinoco Belt, which, again, similar to the oil sands we’re talking about —
Meyer: This is the Orinoco flow. We’re going to call this the Orinoco flow question.
Johnston: Yeah, exactly, that. Similar to the Canadian oil sands, we’re talking about more than a trillion barrels of oil in place, the actual resource in the ground. But then from there you get to this question of what is technically recoverable. Then from there, what is economically recoverable? The explosion in, again, both Venezuelan and Canadian reserve estimates occurred during that massive boom in oil prices in the mid-2000s. And that created the justification for booking those as reserves rather than just resources.
So I think that there is ample — in the same way, like, Russia and the United States don’t actually have super impressive-looking reserves on paper, but they do a lot with them, and I think in actuality that matters a lot more than the amount of technical reserves you have in the ground. Because as we’ve seen, Venezuela hasn’t been able to do much with those reserves.
So in order to, how to actually get that operating, this is where we get back to the — we’re talking tens, hundreds of billions of dollars, and a lot of time. And these companies are not going to do that without seeing a track record of whatever government replaces the current. The current vice president, his acting president — which I should also note, vice president and oil minister, which I think is particularly relevant here — so I think there’s lots that needs to happen. But companies are not going to trip over themselves to expose themselves to this risk. We still don’t know what the future is going to look like for Venezuela.
Mentioned:
The 4 Things Standing Between the U.S. and Venezuela’s Oil
Trump admin sends tough private message to oil companies on Venezuela
Previously on Shift Key: The Trump Policy That Would Be Really Bad for Oil Companies
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by …
Heatmap Pro brings all of our research, reporting, and insights down to the local level. The software platform tracks all local opposition to clean energy and data centers, forecasts community sentiment, and guides data-driven engagement campaigns. Book a demo today to see the premier intelligence platform for project permitting and community engagement.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.