In his State of the Union address Tuesday night, President Donald Trump unveiled what he called the new “ratepayer protection pledge.” Under the effort, the White House will tell “major tech companies that they have the obligation to provide for their own power needs.” By mandating the bring-your-own-generation approach, the Trump administration is endorsing a push that’s been ongoing for months. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation, the U.S. grid watchdog, called for data centers to build their own generators. An industry-backed proposal in the nation’s largest power grid would do something similar. “This is a unique strategy,” Trump said. “We have an old grid that could never handle the [amount] of electricity that’s needed.” With tech companies constructing new power plants, Trump said, towns should welcome data center projects that could end up lowering electricity rates by inviting more power onto the local grid.
The political blowback to data centers is gaining strength. It is, as my colleague Jael Holzman wrote recently, “swallowing American politics.” On the right, Senator Josh Hawley, the populist Republican from Missouri, introduced legislation this month to restrict data center construction. On the left, Senator Bernie Sanders, the democratic socialist from Vermont, reiterated his proposal this week to halt all data center projects. In the center, Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro, a Democrat with unusually strong support among his state’s GOP voters, recently outlined plans for a more “selective” approach to data centers, as I reported in this newsletter.
2. Mississippi’s governor gives a full-throated defense of data centers
Trump isn’t the only Republican pushing back against the data center blowback. On Tuesday, Mississippi Governor Tate Reeves delivered an impassioned defense of his state’s data center buildout. “I understand individuals who would rather not have any industrial project in their backyard. We all choose where to live, whether it’s urban, suburban, agrarian, or industrial. I do not understand the impulse to prevent our country from advancing technologically — except as civilizational suicide,” Reeves wrote in a post on X. “I don’t want to go gently. I love this country, and want her to rise. That’s why Mississippi has become the home of the world’s most impressive supercomputers. We are committed to America and American power. We know that being the hub of the world’s most awesome technology will inevitably bring prosperity and authority to our state. There is nobody better than Mississippians to wield it.”
Replying to Sanders’ proposal, Reeves said he’s “tempted to sit back and let other states fritter away the generational chance to build. To laugh at their short-sightedness. But the best path for all of us would be to see America dominate.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
3. Tesla’s Cybertruck may be more explosive than the infamous Ford Pinto
The subcompact Ford Pinto gained infamy in the 1970s for its tendency to explode when the gas tank ruptured in a crash. The Ford Motor Company sold just under 3.2 million Pintos. By the official death toll, 27 people died as a result of fires from the vehicles exploding. Tesla has sold more than 34,000 Cybertrucks; already, five people have died in fire fatalities.
That, according to a calculation by the automotive blog Fuel Arc, means the Tesla Cybertruck has 14.52 deaths per 100,000 units, compared to the Ford Pinto’s 0.85 deaths. “The Cybertruck is far more dangerous (by volume) than the historic poster child for corporate greed and grossly antagonistic design,” Fuel Arc’s Kay Leadfoot wrote. “I look forward to the Cybertruck being governmentally crash-tested by the NHTSA, which it has not been thus far. Until then, I can’t recommend sitting in one.” That is, however, based on the lower death toll figure for the Pinto. Back in 1977, Mother Jones published a blockbuster cover story under the headline “Pinto Madness” claiming that the number of deaths could be as high as 900.
4. Texas sues a wind turbine recycling company
Texas accused the recycling company Global Fiberglass Solutions of illegally dumping thousands of wind turbine blades near the central town of Sweetgrass. The company allegedly hired several subcontractors to break down, transport and recycle the blades, but failed to properly dispose of the waste and instead created what Windpower Monthly called a “stockpile” of more than 3,000 blades across two sites in the town. Attorney General Ken Paxton, a Republican candidate for U.S. Senate, seized on a Trumpian critique of the energy source, saying the dumps damage “beautiful Texas land and threaten surrounding communities.”
Off the Atlantic Coast, meanwhile, Orsted is at a transitional moment for two of its offshore wind projects. The Danish developer just brought the vessel Wind Scylla to port after completing the installation of turbines at its Revolution Wind project in New England. The boat is headed to New York next to start installing the first wind turbine at Sunrise Wind, according to OffshoreWIND.biz.
5. The first new U.S. aluminum smelter in 50 years is getting a processing plant
Last month, I told you that Century Aluminum inked a deal with Emirates Global Aluminum to build the first smelter in the U.S. in half a century in Oklahoma. On Tuesday, the U.S. Aluminum Company, a local firm in the state, joined the project, signing an agreement to “explore the development of an aluminum fabrication plant near the new smelter.” If completed, the project — already dubbed Oklahoma Primary Aluminum — would roughly double U.S. primary production of the metal.
The Biden administration had placed what Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin called “a big bet on aluminum” back in 2024. By spring of last year, our colleague Katie Brigham was chronicling the confusion over how Trump’s tariffs on aluminum would work. With the recent Supreme Court ruling upending Trump’s trade policies, that one may remain a headscratcher for a little while longer.
THE KICKER
Another day, another landmark energy investment from Google. This time, the tech giant has made a deal with the long-duration energy storage startup Form Energy to deploy what Katie wrote “would be the largest battery in the world by energy capacity: an iron-air system capable of delivering 300 megawatts of power at once while storage 30 gigawatt-hours of energy, enabling continuous discharge for 100 hours straight.” The project will power a data center in Minnesota. “For all of 2025, I believe the installed capacity [added to the grid] in the entire U.S. was 57 gigawatt-hours. And in one project, we’re going to install 30 gigawatt-hours,” Form CEO Mateo Jaramillo told Katie. “What it highlights is, once you get to the 100-hour duration, you can really stop thinking about energy to some extent. “
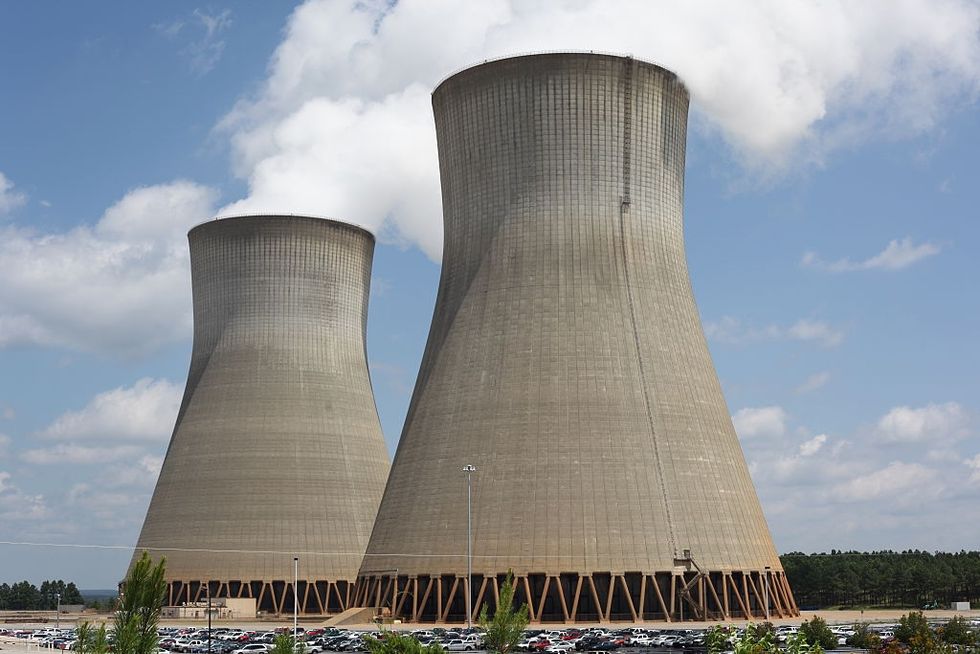




 The cooling towers for the two older reactors at Plant Vogtle.Pallava Bagla/Corbis via Getty Images
The cooling towers for the two older reactors at Plant Vogtle.Pallava Bagla/Corbis via Getty Images
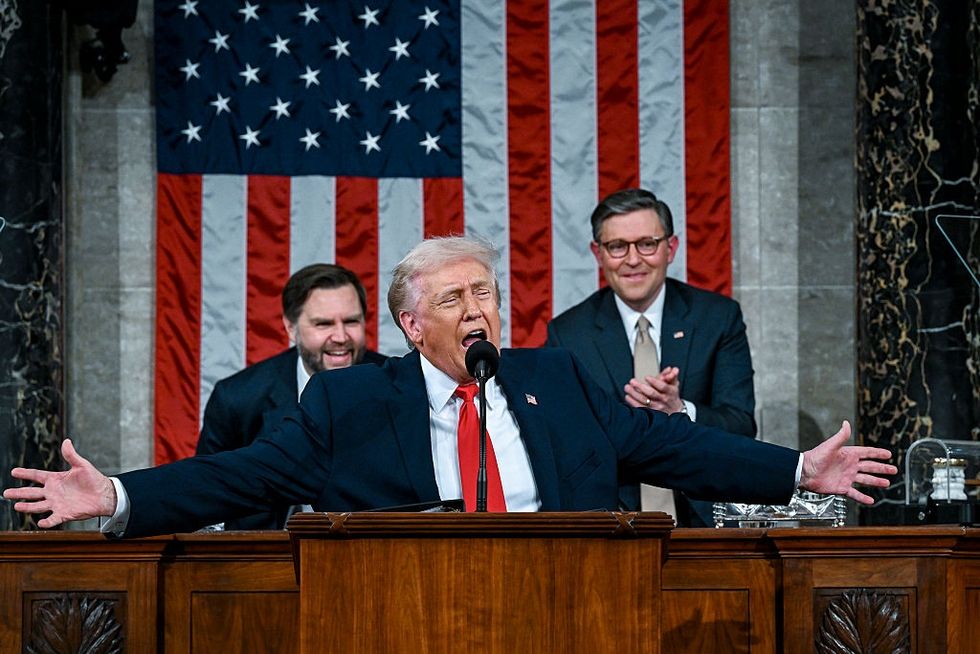 President Trump speaks delivers the State of the Union address. Kenny Holston-Pool/Getty Images
President Trump speaks delivers the State of the Union address. Kenny Holston-Pool/Getty Images