You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Everything you need to know — including one big (potential) drawback.
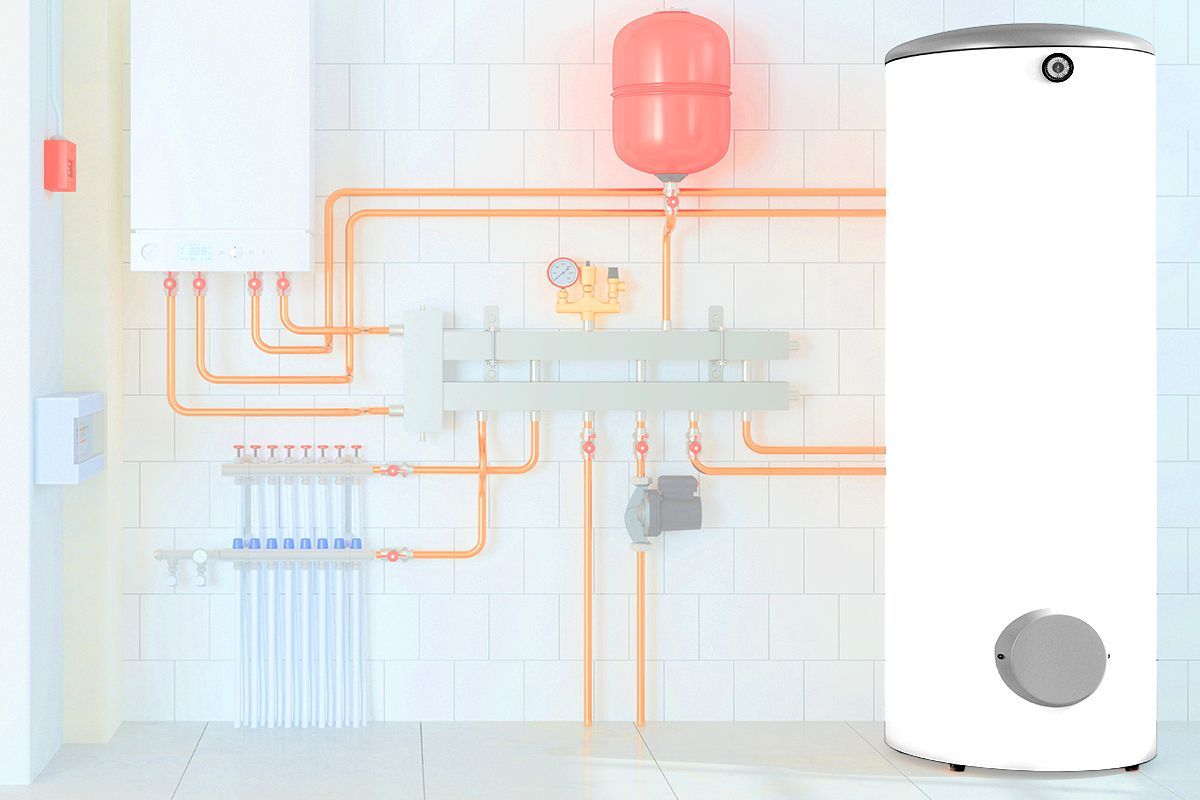
The humble water heater, like your fridge or septic tank, is the type of home technology that you only notice if and when it breaks. For most homeowners, that’s every 13 years. But if you’re on a mission to decarbonize your life, you might want to rethink your current set-up, and perhaps consider a makeover. Per the Department of Energy, water heating accounts for roughly 18% of the average household’s energy use, making it the second largest energy expense in any home.
Back in April, the DOE released new residential water heater standards that it says will save American households approximately $7.6 billion per year on their energy bills “while significantly cutting energy waste and harmful carbon pollution.” The standards will also, in effect, phase out electric resistance water heaters, which currently account for half the U.S. market, in favor of more energy-efficient heat pump water heaters by 2029. If any of that confuses you, read on. We’re breaking down everything you need to know about this oft-forgotten, basement-dwelling home technology, from the taxonomy of water heater types to tax credit and rebate tips to product recommendations.
Andy Meyer is a senior program manager at Efficiency Maine, an independent agency that implements energy efficiency programs in the state. His team is responsible for providing resources on heat pump water heaters to Maine residents, who buy one out of every 10 purchased in the U.S.
Ben Foster is vice president of operations at Barnett Plumbing & Water Heaters, a leading heat pump water heater contractor in California. He’s also developed loaner water heater programs supported by TECH Clean California, and notes that most contractors don’t have access to loaner programs:
Joseph Wachunas is a senior project manager at the New Buildings Institute, a nonprofit working to reduce emissions and deliver climate solutions through the built environment. At NBI, he heads up the Advanced Water Heating Initiative, which aims to decarbonize water heating through heat pump water heaters.
“Heat pump water heaters are simple to install — any plumber or handy person can do it — but plumbers may not be familiar with them. So if you talk with a plumber who has concerns, consider calling another plumber,” Meyer told me. “Again, Mainers have installed over 70,000 in the last 12 years. They are no longer new.”
A heat pump water heater is made up of a compressor, storage tank, condenser, evaporator coil, fan, backup heating elements, and refrigerant. The compressor, located in the upper compartment of the water heater, uses refrigerant to heat the water in the storage tank (via the condenser, which acts as a heat exchanger). The evaporator coil and fan work to change refrigerant from liquid back to gas after the water has been heated. The backup electric heating elements kick in only in periods of high demand to ensure consistent hot water supply.
A common misconception about heat pumps in general is that they don’t work in colder climates. This is not at all the case — half of electric water heaters in Maine, for instance, are now heat pumps. As long as they are installed indoors and in an area where pipes won’t freeze (typically, a basement), heat pump water heaters work throughout the year in all climates, according to Meyer and Wachunas. The rule of thumb, per the DOE, is to install your heat pump water heater in locations that remain in the 40 degree to 90 degree Fahrenheit range year-round.
Per the DOE, replacing your standard electric water heater with a heat pump water heater can save you up to 10% on your electricity bill, reducing your water heating energy consumption and costs by up to 70%.
The number one mistake homeowners make when it comes to their water heaters is waiting until they’re broken to replace them. This severely limits your options for new water heaters — as Foster notes, no one “wants to go days without hot water, let alone weeks,” and it can take weeks or even months to fit your home for a heat pump water heater. (We’ll get into why a bit later.)
“A lot of contractors, if you want a heat pump and you have a leaking water heater that needs to be replaced today, they're just going to convince you to go with gas,” Foster said.
Some contractors have loaner water heater programs, so you can temporarily use a gas heater in an emergency situation, but these programs are few and far between. If you’ve had your water heater for 10 years or more — even if it’s working just fine — it might be time to think about replacing it. If you do, you’ll need to consider a few things about your home and lifestyle, especially if you’re considering a heat pump water heater:
Heat pump water heaters require a significant amount of space. Per Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, heat pump water heaters can require more than 6 feet of height clearance to account for their air filters, as well as a 3-foot diameter space to provide clearance for the drain pan and other connections. Additionally, the heat pump water heater should be positioned so the exhaust outlet is at least 8 inches away from a wall, door, or ceiling.
Also, since heat pump water heaters work by drawing heat from the surrounding air, they require 700 cubic feet of unenclosed space surrounding the water heater location. While it is possible to install a heat pump water heater in a location with insufficient air volume (for instance, by installing the water heater with a door equipped with top and bottom grills), this would require extra work from your contractor. Taking all these measurements into account, this basically means that a heat pump water heater requires a 10-foot by 9-foot room with an 8-foot-tall ceiling.
Heat pump water heaters also require monthly and yearly service, Meyer told me. You should change the water filter every two to six months, and clear the condensate lines to ensure your unit doesn’t get clogged with mold or bacteria. Additionally, if your unit is a hybrid, you’ll have to keep an eye on its anode rod, which can become corroded over time and lead to heating issues. You’ll have to flush your heat pump water heater annually to avoid corrosion.
If you’re going to DIY it, understanding your household’s water needs is key to sizing and installing a new heat pump water heater. First, determine your house’s peak hour demand (the maximum amount of water your house uses in one hour per day) using this worksheet from the DOE. You can then use that number (measured in gallons) to determine what size heat water heater to buy — look at the heater’s first hour rating, a.k.a. the amount of hot water the heater can supply per hour, starting with a tank full of hot water. You’ll want your heater’s first hour rating to be equal to (or ideally, higher than) your peak hour demand.
Though you should use the worksheet to determine your unique peak hour demand, a general rule is that households of one to two people should use a 50-gallon water heater, while households of three or more people should use a 65- to 80-gallon tank. The average family uses 50 gallons of hot water per day, Wachunas explained. “So even if you have lots of showers in the morning, your heat pump in two to four hours will heat that water back up and you have plenty of extra supply.”
If you’re between two sizes of heat pump water heaters, always upsize, Foster said. This ensures that the heat pump is the primary source of heat, as opposed to the much less efficient backup electric mechanisms. In other words, it’s far more efficient (and less expensive!) for a larger heat pump water heater to heat a few extra gallons of water using the heat pump than it is for a smaller heat pump water heater to have to use its electric elements to keep up with excess demand.
Since many heat pump water heaters have certain voltage requirements, you may have to upgrade your electrical panel for 240-volt hardwired service. The cost and time involved in having your service upgraded can vary and depends on whether the power lines coming into your house are above ground. If they’re underground, Foster explained, a contractor will have to excavate and run new cables, which can take over a year. The best way to determine if you’ll need to upgrade your service is to have a trusted contractor do an assessment on your home. (This is also why it’s essential to plan in advance.)
Basements are always the best places for heat pump water heaters, regardless of climate. Other common locations for installation include garages, interior rooms, and rooms outside the thermal envelope, like attached sheds and utility rooms. The garage does not have to be insulated if outdoor temperatures are usually above 50°F, but if temperatures dip below freezing and the garage is uninsulated, it’d be best to consider another location. Interior rooms, like laundry or IT rooms, are a great choice because a heat pump water heater can utilize any waste heat generated by the equipment in the room. Finally, rooms outside the thermal envelope, like attached sheds, can be even more efficient than interior spaces in hot or warm climates because of the excess hot air.
Feeling ready to go shopping? Here’s everything you need to know about the buying and installation process.
This plug-in model caused quite a stir when it came out two years ago, and for good reason. Its low voltage allows it to be plugged into a standard outlet, making it a great fit for smaller homes with fewer residents, or anyone in need of a quick fix. (This is also a relatively foolproof choice for DIYers because of the quick and easy installation process.) For those wanting a model with a bit more flexibility but still an easy install, there’s the A.O. Smith Signature 900 Plug-in Hybrid, which is more expensive but has the added benefit of back-up electric resistance elements that help with higher hot water demand. Alternatively, you can go for the 120-Volt Rheem ProTerra Plug-in Water Heater with HydroBoost, which utilizes a mixing valve for maximum hot water output.
If app functionality is especially important to you, Rheem’s ProTerra line might be particularly appealing. The EcoNet app allows users to monitor the hot water heater from their phone, with status updates on potential leaks as well as compressor health, hot water availability and the unit’s set water temperature.
Another solid choice for larger families, for roughly the same price, is A.O. Smith’s Signature 900 80-Gal. For further durability, consider Bradford White’s Aerotherm Series water heaters, which can only be purchased through a qualified contractor, but are frequently praised for their resilience and anti-microbial technology.
Split-system heat pump water heaters are the answer for truly huge houses, where the heat pump itself is outside while the storage tank remains inside. “You can chain together as many heat pump units as you want with as many storage tanks as you want,” Foster said. “So you can create as big a system as you want.” While split-system heat pump water heaters are much less widely-available in the U.S. than they are in Asia and Europe, you can purchase this one online. SANCO is also shipping a new fifth generation unit soon, Quit Carbon advises, which may prove more cost-effective and will qualify for more rebates in California.
The quietest HPWH on the market, at 45 decibels, is made by A.O. Smith, according to Foster. It’s available in 50, 65, and 80 gallon sizes, so it can accommodate a variety of household types. Another quiet option is LG’s Inverter Heat Pump Water Heater, though LG is much newer to the heat pump water heater game than Rheem and A.O. Smith, so it may be more difficult to find qualified contractors.
Three more expert contractors I spoke with — Nate Adams, a longtime HVAC insulation and sealing contractor in West Virginia who specializes in electrification retrofits for homeowners; John Semmelhack, an HVAC consultant and the owner of Think Little, a building science consulting firm specializing in mechanical system design for passive house and net-zero energy homes; and Tim Portman, the owner of Portman Mechanical, specializing in electrification, heating and cooling, and home performance — had concerns about heat pump water heater installations.
Adams said heaters he’s installed have had a 50% failure rate, while Portman and Semmelhack cite a 60% failure rate. These issues have seemingly cropped up after 2018 and are almost entirely occurring with A.O. Smith and Rheem’s fifth generation of water heater models; older generations performed and continue to perform much better. “All my installs from 2014-2018 are still running to my knowledge,” says Adams. “Which is a big part of my frustration— we had this figured out already.”
The specific causes of these failures vary, spanning from tanks bursting to heat pumps losing charge, according to Adams. Semmelhack and Portman, meanwhile, pointed mainly to refrigerant leaks and compressor issues. (A.O. Smith and Rheem did not respond to requests for comment.) “All of the failures are happening inside the first year of operation,” noted Semmelhack. “So it's happening pretty quick, which makes us think that it's a factory problem and not an environmental problem inside the household.”
Semmelhack and Portman are hopeful about Cala’s new heat pump water heaters, which use an AI-powered control system to forecast hot water demand and heat the water in the tank accordingly with a heat pump. They’re aiming to start shipping those units in 2025, and you can preorder and learn more here.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
A chat with CleanCapital founder Jon Powers.
This week’s conversation is with Jon Powers, founder of the investment firm CleanCapital. I reached out to Powers because I wanted to get a better understanding of how renewable energy investments were shifting one year into the Trump administration. What followed was a candid, detailed look inside the thinking of how the big money in cleantech actually views Trump’s war on renewable energy permitting.
The following conversation was lightly edited for clarity.
Alright, so let’s start off with a big question: How do investors in clean energy view Trump’s permitting freeze?
So, let’s take a step back. Look at the trend over the last decade. The industry’s boomed, manufacturing jobs are happening, the labor force has grown, investments are coming.
We [Clean Capital] are backed by infrastructure life insurance money. It’s money that wasn’t in this market 10 years ago. It’s there because these are long-term infrastructure assets. They see the opportunity. What are they looking for? Certainty. If somebody takes your life insurance money, and they invest it, they want to know it’s going to be there in 20 years in case they need to pay it out. These are really great assets – they’re paying for electricity, the panels hold up, etcetera.
With investors, the more you can manage that risk, the more capital there is out there and the better cost of capital there is for the project. If I was taking high cost private equity money to fund a project, you have to pay for the equipment and the cost of the financing. The more you can bring down the cost of financing – which has happened over the last decade – the cheaper the power can be on the back-end. You can use cheaper money to build.
Once you get that type of capital, you need certainty. That certainty had developed. The election of President Trump threw that into a little bit of disarray. We’re seeing that being implemented today, and they’re doing everything they can to throw wrenches into the growth of what we’ve been doing. They passed the bill affecting the tax credits, and the work they’re doing on permitting to slow roll projects, all of that uncertainty is damaging the projects and more importantly costs everyone down the road by raising the cost of electricity, in turn making projects more expensive in the first place. It’s not a nice recipe for people buying electricity.
But in September, I went to the RE+ conference in California – I thought that was going to be a funeral march but it wasn’t. People were saying, Now we have to shift and adjust. This is a huge industry. How do we get those adjustments and move forward?
Investors looked at it the same way. Yes, how will things like permitting affect the timeline of getting to build? But the fundamentals of supply and demand haven’t changed and in fact are working more in favor of us than before, so we’re figuring out where to invest on that potential. Also, yes federal is key, but state permitting is crucial. When you’re talking about distributed generation going out of a facility next to a data center, or a Wal-Mart, or an Amazon warehouse, that demand very much still exists and projects are being built in that middle market today.
What you’re seeing is a recalibration of risk among investors to understand where we put our money today. And we’re seeing some international money pulling back, and it all comes back to that concept of certainty.
To what extent does the international money moving out of the U.S. have to do with what Trump has done to offshore wind? Is that trade policy? Help us understand why that is happening.
I think it’s not trade policy, per se. Maybe that’s happening on the technology side. But what I’m talking about is money going into infrastructure and assets – for a couple of years, we were one of the hottest places to invest.
Think about a European pension fund who is taking money from a country in Europe and wanting to invest it somewhere they’ll get their money back. That type of capital has definitely been re-evaluating where they’ll put their money, and parallel, some of the larger utility players are starting to re-evaluate or even back out of projects because they’re concerned about questions around large-scale utility solar development, specifically.
Taking a step back to something else you said about federal permitting not being as crucial as state permitting–
That’s about the size of the project. Huge utility projects may still need federal approvals for transmission.
Okay. But when it comes to the trendline on community relations and social conflict, are we seeing renewable energy permitting risk increase in the U.S.? Decrease? Stay the same?
That has less to do with the administration but more of a well-structured fossil fuel campaign. Anti-climate, very dark money. I am not an expert on where the money comes from, but folks have tried to map that out. Now you’re even seeing local communities pass stuff like no energy storage [ordinances].
What’s interesting is that in those communities, we as an industry are not really present providing facts to counter this. That’s very frustrating for folks. We’re seeing these pass and honestly asking, Who was there?
Is the federal permitting freeze impacting investment too?
Definitely.
It’s not like you put money into a project all at once, right? It happens in these chunks. Let’s say there’s 10 steps for investing in a project. A little bit of money at step one, more money at step two, and it gradually gets more until you build the project. The middle area – permitting, getting approval from utilities – is really critical to the investments. So you’re seeing a little bit of a pause in when and how we make investments, because we sometimes don’t know if we’ll make it to, say, step six.
I actually think we’ll see the most impact from this in data center costs.
Can you explain that a bit more for me?
Look at northern Virginia for a second. There wasn’t a lot of new electricity added to that market but you all of the sudden upped demand for electricity by 20 percent. We’re literally seeing today all these utilities putting in rate hikes for consumers because it is literally a supply-demand question. If you can’t build new supply, it's going to be consumers paying for it, and even if you could build a new natural gas plant – at minimum that will happen four-to-six years from now. So over the next four years, we’ll see costs go up.
We’re building projects today that we invested in two years ago. That policy landscape we invested in two years ago hasn’t changed from what we invested into. But the policy landscape then changed dramatically.
If you wipe out half of what was coming in, there’s nothing backfilling that.
Plus more on the week’s biggest renewables fights.
Shelby County, Indiana – A large data center was rejected late Wednesday southeast of Indianapolis, as the takedown of a major Google campus last year continues to reverberate in the area.
Dane County, Wisconsin – Heading northwest, the QTS data center in DeForest we’ve been tracking is broiling into a major conflict, after activists uncovered controversial emails between the village’s president and the company.
White Pine County, Nevada – The Trump administration is finally moving a little bit of renewable energy infrastructure through the permitting process. Or at least, that’s what it looks like.
Mineral County, Nevada – Meanwhile, the BLM actually did approve a solar project on federal lands while we were gone: the Libra energy facility in southwest Nevada.
Hancock County, Ohio – Ohio’s legal system appears friendly for solar development right now, as another utility-scale project’s permits were upheld by the state Supreme Court.
The offshore wind industry is using the law to fight back against the Trump administration.
It’s time for a big renewable energy legal update because Trump’s war on renewable energy projects will soon be decided in the courts.
A flurry of lawsuits were filed around the holidays after the Interior Department issued stop work orders against every offshore wind project under construction, citing a classified military analysis. By my count, at least three developers filed individual suits against these actions: Dominion Energy over the Coastal Virginia offshore wind project, Equinor over Empire Wind in New York, and Orsted over Revolution Wind (for the second time).
Each of these cases are moving on separate tracks before different district courts and the urgency is plain. I expect rulings in a matter of days, as developers have said in legal filings that further delays could jeopardize the completion of these projects due to vessel availability and narrow timelines for meeting power contracts with their respective state customers. In the most dire case, Equinor stated in its initial filing against the government that if the stop work order is implemented as written, it would “likely” result in the project being canceled. Revolution Wind faces similar risks, as I’ve previously detailed for Heatmap.
Meanwhile, around the same time these cases were filed, a separate lawsuit was dropped on the Interior Department from a group of regional renewable energy power associations, including Interwest Energy Alliance, which represents solar developers operating in the American Southwest – ground zero for Trump’s freeze on solar permits.
This lawsuit challenges Interior Secretary Doug Burgum’s secretarial orders requiring his approval for renewable energy decisions, the Army Corps of Engineers’ quiet pause on wetlands approvals, and the Fish and Wildlife Services’ ban on permitting eagle takes, as well as its refusal to let developers know if they require species consultations under the Endangered Species Act. The case argues that the administration is implementing federal land law “contrary to Congress’ intent” by “unlawfully picking winners and losers among energy sources,” and that these moves violate the Administrative Procedures Act.
I expect crucial action in this case imminently, too. On Thursday, these associations filed a motion declaring their intent to seek a preliminary injunction against the administration while the case is adjudicated because, as the filing states, the actions against the renewables sector are “currently costing the wind and solar industry billions of dollars.”
Now, a victory here wouldn’t be complete, since a favorable ruling would likely be appealed and the Trump administration has been reluctant to act on rulings they disagree with. Nevertheless, it would still be a big win for renewables companies frozen by federal bureaucracy and ammo in any future legal or regulatory action around permit activity.
So far, Trump’s war on solar and wind has not really been tested by the courts, sans one positive ruling against his anti-wind Day One executive order. It’s easy in a vacuum to see these challenges and think, Wow, the industry is really fighting back! Maybe they can prevail? However I want to remind my readers that simply having the power of the federal government grants one the capacity to delay commercial construction activity under federal purview, no matter the legality. These matters can become whack-a-mole quite quickly.
Dominion Energy’s Coastal Virginia offshore wind project is one such example. Intrepid readers of The Fight may remember I was first to report the Trump administration might try to mess around with the permits previously issued for construction through litigation brought by anti-renewables activists, arguing the government did not adequately analyse potential impacts to endangered whales. Well, it appears we’re getting closer to an answer: In a Dec. 18 filing submitted in that lawsuit, Justice Department attorneys said they have been “advised” that the Interior Department is now considering whether to revoke permits for the project.
Dominion did not respond to a request for comment about this filing, but it is worth noting that the DOJ’s filing concedes Dominion is aware of this threat and “does not concede the propriety” of any review or revocation of the permits.
I don’t believe this alone would kill Coastal Virginia given the project is so far along in construction. But I expect a death by a thousand cuts strategy from the Trump team against renewable energy projects writ large, regardless of who wins these cases.