You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
“We grew quickly and made some mistakes,” Generate executive Jonah Goldman told Heatmap.

In a tumultuous time for clean energy financing, leading infrastructure investment firm Generate Capital is seeking to realign its approach. Last month the firm trumpeted its appointment of a new CEO, the first in its 11-year history. Less publicly, it also implemented firm-wide layoffs, representatives confirmed to Heatmap.
“Like many others in our space, we grew quickly and made some mistakes,” Jonah Goldman, Generate’s head of external affairs, told me. He was responding to a report from infrastructure and energy intelligence platform IJ Global, which last week reported that Generate had “shut down its equity investing arm” and laid off 50 people. While Goldman confirmed that there were indeed layoffs earlier this summer, he would not specify how many employees were let go, and disputed the claim that any particular team was dissolved. “We have not ‘shut down’ any strategies,” he told me. “Our investment team continues to find opportunities across the capital stack.”
Goldman’s comments echoed those of the firm’s new CEO, David Crane, a former undersecretary for infrastructure at the Department of Energy. In an article published to Generate’s website a few weeks ago, Crane admitted that the firm had “deviated from our operational roots,” a reference to the firm’s unconventional investment strategy.
Generate is unique as a sustainability-focused investor, in that it often acts as an owner and operator for the projects it finances rather than taking a passive equity stake The firm also provides tailored project financing options for its partners to help manage risk.
But over the past few years, Generate made a number of large equity investments in companies whose projects it did not directly oversee. These included utility-scale solar and energy storage developer Pine Gate Renewables, which is on the verge of bankruptcy, and green hydrogen developer Ambient Fuels, which was recently acquired by Electric Hydrogen amidst tumult in the industry.
“While other investors had no choice but to act as pure investors, we were distracted from who we are and what we were good at,” Crane wrote, noting that this distraction led to “poor performance in one component of our investment portfolio.” That would appear to be its equity division.
Generate’s model is designed to bridge a critical gap in the climate tech ecosystem known as the “missing middle,” the phase at which a company with some proven tech has outgrown early-stage venture capital but is still considered too risky for most traditional infrastructure investors. Historically, the firm has generated high returns by backing “leading-edge technologies,” Jigar Shah, the firm’s co-founder and former director of the DOE’s Loan Programs Office, said on the Open Circuit podcast he co-hosts. These include investments in projects involving fuel cells, anaerobic digesters, and battery storage.
Shah hasn’t worked at Generate since he joined the Biden administration in 2021. But from the outside, he says, the firm appears to have moved away from taking these riskier but potentially more lucrative bets. “They ended up with 38 people in their capital markets team, and their capital markets team went out to the marketplace and said, Hey, we have all this stuff to sell. And the people that they went to said, Well, that’s interesting, but what we really would love is boring community solar,“ Shah said on the podcast. As he saw it, Generate began making equity investments into lower-risk projects such as community solar, which naturally generated stable but lower returns. Then once interest rates went up post-Covid, that put downward pressure on equity returns.
Shah said it’s these slipping returns that have made it harder for Generate to raise capital over the past two years. Axios Pro recently reported that the firm is now exploring an IPO to bring in additional funding, following hesitation from some of its existing backers to reinvest.
While Goldman acknowledged that “there is some skepticism in the capital markets about our space now,” he disagreed with the idea that Generate has abandoned its focus on leading-edge technologies. “We have invested over the last number of years in a lot of assets that are predictable assets with predictable cash flows that have performed very strongly for our investors. And we continue to have the creativity of the team that’s focused on trying to bring newer technologies to the market to bridge the bankability gap,” he told me.
By way of example, he highlighted two of the firm’s most recent investments, a $200 million loan to Pacific Steel Group for the first green steel mill in California and a $100 million scalable credit facility for green data center developer Soluna, which allows the company to increase its borrowing capacity as new projects come online.
The latter deal was announced just weeks after Crane stepped into his new role. Having served as the CEO of five publicly traded energy companies before joining Generate, Crane is now promising to turn around the firm’s fortunes. With the Trump administration rolling back federal support for clean energy infrastructure and investors remaining cautious, Crane has said that now is the time to jump on undervalued opportunities.
“Right now, there’s a lot of noise telling people to stop writing checks. But this is precisely the time to invest in the infrastructure that will power the next twenty years,” he wrote. Goldman backed this up, telling me, “We believe managers who understand the space and who can take advantage of the opportunities that are underpriced in this tougher market environment are set up to succeed.”
Just as tech giants such as Google, Salesforce, and Amazon were able to expand rapidly in the wake of the dot-com bubble and consolidate their positions in the market, Generate’s leadership say they’re now well positioned to help select clean energy companies do the same.
It will certainly be a boon for the sector if they can, given the abundance of undercapitalized climate tech opportunities, from clean cement to thermal energy storage, next-generation geothermal, and carbon capture, all looking to build first-of-a-kind projects. And there’s not nearly enough infrastructure funding to go around.
So if Generate has indeed lost the confidence of its investors, it’s critical that Crane, Goldman, and company regain it swiftly. Their ability to do so could shape not only which technologies drive the energy transition, but how quickly they do so.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Talking with Climate Power senior advisor Jesse Lee.
For this week's Q&A I hopped on the phone with Jesse Lee, a senior advisor at the strategic communications organization Climate Power. Last week, his team released new polling showing that while voters oppose the construction of data centers powered by fossil fuels by a 16-point margin, that flips to a 25-point margin of support when the hypothetical data centers are powered by renewable energy sources instead.
I was eager to speak with Lee because of Heatmap’s own polling on this issue, as well as President Trump’s State of the Union this week, in which he pitched Americans on his negotiations with tech companies to provide their own power for data centers. Our conversation has been lightly edited for length and clarity.
What does your research and polling show when it comes to the tension between data centers, renewable energy development, and affordability?
The huge spike in utility bills under Trump has shaken up how people perceive clean energy and data centers. But it’s gone in two separate directions. They see data centers as a cause of high utility prices, one that’s either already taken effect or is coming to town when a new data center is being built. At the same time, we’ve seen rising support for clean energy.
As we’ve seen in our own polling, nobody is coming out looking golden with the public amidst these utility bill hikes — not Republicans, not Democrats, and certainly not oil and gas executives or data center developers. But clean energy comes out positive; it’s viewed as part of the solution here. And we’ve seen that even in recent MAGA polls — Kellyanne Conway had one; Fabrizio, Lee & Associates had one; and both showed positive support for large-scale solar even among Republicans and MAGA voters. And it’s way high once it’s established that they’d be built here in America.
A year or two ago, if you went to a town hall about a new potential solar project along the highway, it was fertile ground for astroturf folks to come in and spread flies around. There wasn’t much on the other side — maybe there was some talk about local jobs, but unemployment was really low, so it didn’t feel super salient. Now there’s an energy affordability crisis; utility bills had been stable for 20 years, but suddenly they’re not. And I think if you go to the town hall and there’s one person spewing political talking points that they've been fed, and then there’s somebody who says, “Hey, man, my utility bills are out of control, and we have to do something about it,” that’s the person who’s going to win out.
The polling you’ve released shows that 52% of people oppose data center construction altogether, but that there’s more limited local awareness: Only 45% have heard about data center construction in their own communities. What’s happening here?
There’s been a fair amount of coverage of [data center construction] in the press, but it’s definitely been playing catch-up with the electric energy the story has on social media. I think many in the press are not even aware of the fiasco in Memphis over Elon Musk’s natural gas plant. But people have seen the visuals. I mean, imagine a little farmhouse that somebody bought, and there’s a giant, 5-mile-long building full of computers next to it. It’s got an almost dystopian feel to it. And then you hear that the building is using more electricity than New York City. This is very intimidating
The big takeaway of the poll for me is that coal and natural gas are an anchor on any data center project, and reinforce the worst fears about it. What you see is that when you attach clean energy [to a data center project], it actually brings them above the majority of support. It’s not just paranoia: We are seeing the effects on utility rates and on air pollution — there was a big study just two days ago on the effects of air pollution from data centers. This is something that people in rural, urban, or suburban communities are hearing about.
Do you see a difference in your polling between natural gas-powered and coal-powered data centers? In our own research, coal is incredibly unpopular, but voters seem more positive about natural gas. I wonder if that narrows the gap.
I think if you polled them individually, you would see some distinction there. But again, things like the Elon Musk fiasco in Memphis have circulated, and people are aware of the sheer volume of power being demanded. Coal is about the dirtiest possible way you can do it. But if it’s natural gas, and it’s next door all the time just to power these computers — that’s not going to be welcome to people.
I'm sure if you disentangle it, you’d see some distinction, but I also think it might not be that much. I’ll put it this way: If you look at the default opposition to data centers coming to town, it’s not actually that different from just the coal and gas numbers. Coal and gas reinforce the default opposition. The big difference is when you have clean energy — that bumps it up a lot. But if you say, “It’s a data center, but what if it were powered by natural gas?” I don’t think that would get anybody excited or change their opinion in a positive way.
Transparency with local communities is key when it comes to questions of renewable buildout, affordability, and powering data centers. What is the message you want to leave people with about Climate Power’s research in this area?
Contrary to this dystopian vision of power, people do have control over their own destinies here. If people speak out and demand that data centers be powered by clean energy, they can get those data centers to commit to it. In the end, there’s going to be a squeeze, and something is going to have to give in terms of Trump having his foot on the back of clean energy — I think something will give.
Demand transparency in terms of what kind of pollution to expect. Demand transparency in terms of what kind of power there’s going to be, and if it’s not going to be clean energy, people are understandably going to oppose it and make their voices heard.
This week is light on the funding, heavy on the deals.
This week’s Funding Friday is light on the funding but heavy on the deals. In the past few days, electric carmaker Rivian and virtual power plant platform EnergyHub teamed up to integrate EV charging into EnergyHub’s distributed energy management platform; the power company AES signed 20-year power purchase agreements with Google to bring a Texas data center online; and microgrid company Scale acquired Reload, a startup that helps get data centers — and the energy infrastructure they require — up and running as quickly as possible. Even with venture funding taking a backseat this week, there’s never a dull moment.
Ahead of the Rivian R2’s launch later this year, the EV-maker has partnered with EnergyHub, a company that aggregates distributed energy resources into virtual power plants, to give drivers the opportunity to participate in utility-managed charging programs. These programs coordinate the timing and rate of EV charging to match local grid conditions, enabling drivers to charge when prices are low and clean energy is abundant while avoiding periods of peak demand that would stress the distribution grid.
As Seth Frader-Thompson, EnergyHub’s president, said in a statement, “Every new EV on the road is a win for drivers and the environment, and by managing charging effectively, we ensure this growth remains a benefit for the grid as well.”
The partnership will fold Rivian into EnergyHub’s VPP ecosystem, giving the more than 150 utilities on its platform the ability to control when and how participating Rivian drivers charge. This managed approach helps alleviate grid stress, thus deferring the need for costly upgrades to grid infrastructure such as substations or transformers. Extending the lifespan of existing grid assets means lower electricity costs for ratepayers and more capacity to interconnect new large loads — such as data centers.
Google seems to be leaning hard into the “bring-your-own-power” model of data center development as it looks to gain an edge in the AI race.
The latest evidence came on Tuesday, when the power company and utility operator AES announced a partnership with the hyperscaler to provide on-site power for a new data center in Texas. signing 20-year power purchase agreements. AES will develop, own, and operate the generation assets, as well as all necessary electricity infrastructure, having already secured the land and interconnection agreements to bring this new power online. The data center is set to begin operations in 2027.
As of yet, neither company has disclosed the exact type of energy infrastructure that AES will be building, although Amanda Peterson Corio, Google’s head of data center energy, said in a press release that it will be “clean.”
“In partnership with AES, we are bringing new clean generation online directly alongside the data center to minimize local grid impact and protect energy affordability,” she said.
This announcement came the same day the hyperscaler touted a separate agreement with the utility Xcel Energy to power another data center in Minnesota with 1.6 gigawatts of solar and wind generation and 300 megawatts of long-duration energy storage from the iron-air battery startup Form Energy.
The microgrid developer Scale has acquired Reload, a “powered land” startup founded in 2024, for an undisclosed sum. What is “powered land”? Essentially, it’s land that Reload has secured and prepared for large data centers customers, obtaining permits and planning for onsite energy infrastructure such that sites can be energized immediately. This approach helps developers circumvent the years-long utility interconnection queue and builds on Scale’s growing focus on off-grid data center projects, as the company aims to deliver gigawatts of power for hyperscalers in the coming years powered by a diverse mix of sources, from solar and battery storage to natural gas and fuel cells.
Early last year, the Swedish infrastructure investor EQT acquired Scale. The goal, EQT said, was to enable the company “to own and operate billions of dollars in distributed generation assets.” At the time of the acquisition, Scale had 2.5 gigawatts of projects in its pipeline. In its latest press release the company announced it has secured a multi-hundred-megawatt contract with a leading hyperscaler, though it did not name names.
As Jan Vesely, a partner at EQT said in a statement, “By bringing together Reload’s campus development capabilities, Scale’s proven islanded power operating platform, and EQT’s deep expertise across energy, digital infrastructure and technology, we are supporting a more integrated approach to delivering power for next-generation digital infrastructure today.”
Not to say there’s been no funding news to speak of!
As my colleague Alexander C. Kaufman reported in an exclusive on Thursday, fusion company Shine Technologies raised $240 million in a Series E round, the majority of which came from biotech billionaire Patrick Soon-Shiong. Unlike most of its peers, Shine isn’t gunning to build electricity-generating reactors anytime soon. Instead, its initial focus is producing valuable medical isotopes — currently made at high cost via fission — which it can sell to customers such as hospitals, healthcare organizations, or biopharmaceutical companies. The next step, Shine says, is to scale into recycling radioactive waste from spent fission fuel.
“The basic premise of our business is fusion is expensive today, so we’re starting by selling it to the highest-paying customers first,” the company’s CEO, Greg Piefer told Kaufman, calling electricity customers the “lowest-paying customer of significance for fusion today.”
On the solar siege, New York’s climate law, and radioactive data center
Current conditions: A rain storm set to dump 2 inches of rain across Alabama, Tennessee, Georgia, and the Carolinas will quench drought-parched woodlands, tempering mounting wildfire risk • The soil on New Zealand’s North Island is facing what the national forecast called a “significant moisture deficit” after a prolonged drought • Temperatures in Odessa, Texas, are as much as 20 degrees Fahrenheit hotter than average.
For all its willingness to share in the hype around as-yet-unbuilt small modular reactors and microreactors, the Trump administration has long endorsed what I like to call reactor realism. By that, I mean it embraces the need to keep building more of the same kind of large-scale pressurized water reactors we know how to construct and operate while supporting the development and deployment of new technologies. In his flurry of executive orders on nuclear power last May, President Donald Trump directed the Department of Energy to “prioritize work with the nuclear energy industry to facilitate” 5 gigawatts of power uprates to existing reactors “and have 10 new large reactors with complete designs under construction by 2030.” The record $26 billion loan the agency’s in-house lender — the Loan Programs Office, recently renamed the Office of Energy Dominance Financing — gave to Southern Company this week to cover uprates will fulfill the first part of the order. Now the second part is getting real. In a scoop on Thursday, Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer reported that the Energy Department has started taking meetings with utilities and developers of what he said “would almost certainly be AP1000s, a third-generation reactor produced by Westinghouse capable of producing up to 1.1 gigawatts of electricity per unit.”
Reactor realism includes keeping existing plants running, so notch this as yet more progress: Diablo Canyon, the last nuclear station left in California, just cleared the final state permitting hurdle to staying open until 2030, and possibly longer. The Central Coast Water Board voted unanimously on Thursday to give the state’s last nuclear plant a discharge permit and water quality certification. In a post on LinkedIn, Paris Ortiz-Wines, a pro-nuclear campaigner who helped pass a 2022 law that averted the planned 2025 closure of Diablo Canyon, said “70% of public comments were in full support — from Central Valley agricultural associations, the local Chamber of Commerce, Dignity Health, the IBEW union, district supervisors, marine meteorologists, and local pro-nuclear organizations.” Starting in 2021, she said, she attended every hearing on the bill that saved the plant. “Back then, I knew every single pro-nuclear voice testifying,” she wrote. “Now? I’m meeting new ones every hearing.”
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times. It was a year of record solar deployments, it was a year of canceled solar megaprojects, choked-off permits, and desperate industry pleas to Congress for help. But the solar industry’s political clouds may be parting. The Department of the Interior is reviewing at least 20 commercial-scale projects that E&E News reported had “languished in the permitting pipeline” since Trump returned to office. “That includes a package of six utility-scale projects given the green light Friday by Interior Secretary Doug Burgum to resume active reviews, such as the massive Esmeralda Energy Center in Nevada,” the newswire reported, citing three anonymous career officials at the agency.
Heatmap’s Jael Holzman broke the news that the project, also known as Esmeralda 7, had been canceled in October. At the time, NextEra, one of the project’s developers, told her that it was “committed to pursuing our project’s comprehensive environmental analysis by working closely with the Bureau of Land Management.” That persistence has apparently paid off. In a post on X linking to the article, Morgan Lyons, the senior spokesperson at the Solar Energy Industries Association, called the change “quite a tone shift” with the eyes emoji. GOP voters overwhelmingly support solar power, a recent poll commissioned by the panel manufacturer First Solar found. The MAGA coalition has some increasingly prominent fans. As I have covered in the newsletter, Katie Miller, the right-wing influencer and wife of Trump consigliere Stephen Miller, has become a vocal proponent of competing with China on solar and batteries.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
MP Materials operates the only active rare earths mine in the United States at California’s Mountain Pass. Now the company, of which the federal government became the largest shareholder in a landmark deal Trump brokered earlier this year, is planning a move downstream in the rare earths pipeline. As part of its partnership with the Department of Defense, MP Materials plans to invest more than $1 billion into a manufacturing campus in Northlake, Texas, dedicated to making the rare earth magnets needed for modern military hardware and electric vehicles. Dubbed 10X, the campus is expected to come online in 2028, according to The Wall Street Journal.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
New York’s rural-urban divide already maps onto energy politics as tensions mount between the places with enough land to build solar and wind farms and the metropolis with rising demand for power from those panels and turbines. Keeping the state’s landmark climate law in place and requiring New York to generate the vast majority of its power from renewables by 2040 may only widen the split. That’s the obvious takeaway from data from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. In a memo sent Thursday to Governor Kathy Hochul on the “likely costs of” complying with the law as it stands, NYSERDA warned that the statute will increase the cost of heating oil and natural gas. Upstate households that depend on fossil fuels could face hikes “in excess of $4,000 a year,” while New York City residents would see annual costs spike by $2,300. “Only a portion of these costs could be offset by current policy design,” read the memo, a copy of which City & State reporter Rebecca C. Lewis posted on X.
Last fall, this publication’s energy intelligence unit Heatmap Pro commissioned a nationwide survey asking thousands of American voters: “Would you support or oppose a data center being built near where you live?” Net support came out to +2%, with 44% in support and 42% opposed. Earlier this month, the pollster Embold Research ran the exact same question by another 2,091 registered voters across the country. The shift in the results, which I wrote about here, is staggering. This time just 28% said they would support or strongly support a data center that houses “servers that power the internet, apps, and artificial intelligence” in their neighborhood, while 52% said they would oppose or strongly oppose it. That’s a net support of -24% — a 26-point drop in just a few months.
Among the more interesting results was the fact that the biggest partisan gap was between rural and urban Republicans, with the latter showing greater support than any other faction. When I asked Emmet Penney at the right-leaning Foundation for American Innovation to make sense of that for me, he said data centers stoke a “fear of bigness” in a way that compares to past public attitudes on nuclear power.
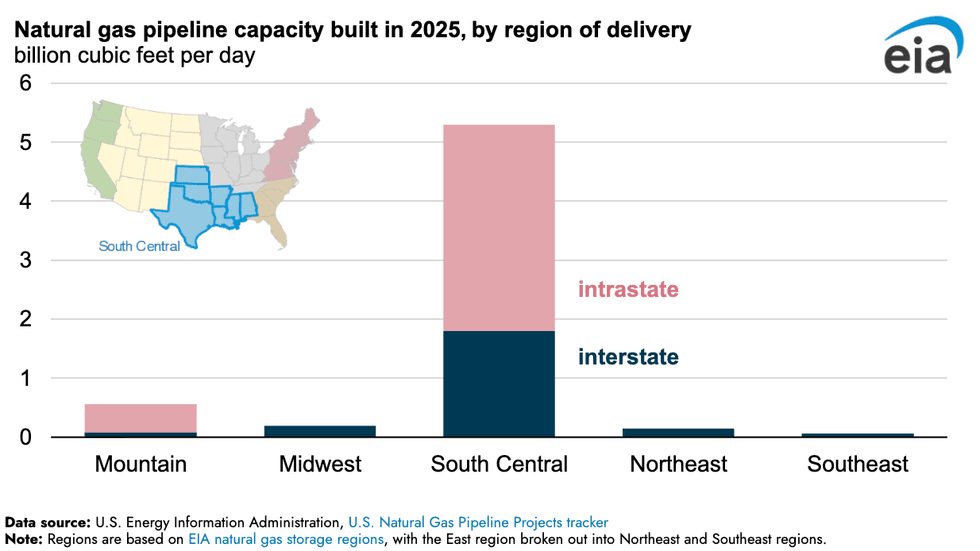
Gas pipeline construction absolutely boomed last year in one specific region of the U.S. Spanning Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama, the so-called South Central bloc saw a dramatic spike in intrastate natural gas pipelines, more than all other regions combined, per new Energy Information Administration data. It’s no mystery as to why. The buildout of liquified natural gas export terminals along the Gulf coast needs conduits to carry fuel from the fracking fields as far west as the Texas Permian.