You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:

Current conditions: Cyclone Dana, currently over the Bay of Bengal, is set to touch down in eastern India tomorrow • Parts of Texas will see record-breaking or near record-breaking temperatures today and tomorrow • The state of Connecticut is under a red flag warning, with dry conditions leading to brush fires.
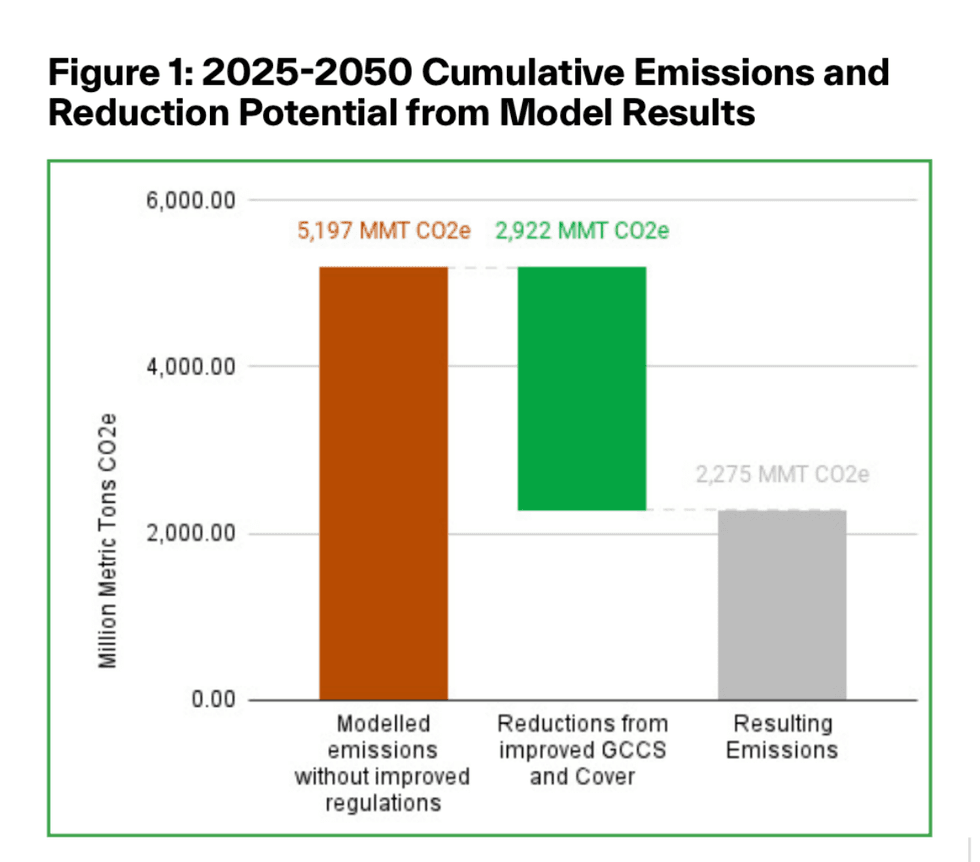
A new report by the environmental nonprofit Industrious Labs finds that landfill methane emissions could be reduced 56% by 2050 if the Environmental Protection Agency makes a few key changes to the existing Clean Air Act. While landfills are the third largest-source of methane emissions in the U.S., only those with a certain waste capacity are required to implement gas collections systems, which extract greenhouse gasses from the decomposing waste. The report recommends expanding the number of landfills that must install collection systems, as well as requiring landfills to install or expand these systems within one year after waste is placed in a new area. The EPA has committed to updating these rules in 2025.
Cuba’s president, Miguel Díaz-Canel, confirmed that Hurricane Oscar has left at least seven dead in Cuba, all in the Guantánamo region. The municipalities of San Antonio and Imias have been hardest hit, with unprecedented flooding. The storm made landfall on Cuba in Sunday, and has since been downgraded to a tropical storm as it heads toward Bermuda. Díaz-Canel said that rescue operations are ongoing, and that there are still areas that remain completely inaccessible.
The Biden administration announced that it’s providing $428 million in funding for 14 clean energy manufacturing projects across 15 communities with decommissioned coal facilities. This infusion of cash is intended to address critical supply chain vulnerabilities, and is expected to attract over $500 million in private capital while creating over 1,900 jobs. The selected projects focus on five areas: grid components, batteries, low-carbon materials, clean power generation, and energy efficient products. “By leveraging the know-how and skillset of the former coal workforce, we are strengthening our national security while helping advance forward-facing technologies and revitalize communities across the nation,” Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm said.
Climate activists have quite the history of taking extreme action to make a point —
blocking roads, throwing soup at works of art, and chaining themselves to oil tankers to name a few. While it always causes a stir, a new study released in Nature finds that these actions could actually be an effective means of increasing support for more moderate climate organizations.
The study’s authors conducted a survey of over 1,400 UK residents before and after the activist group Just Stop Oil shut down traffic on a major highway, which ultimately led to a 3.3% increase in support for the supposedly more moderate environmental group Friends of the Earth. This is likely due to the “radical flank effect,” in which a movement’s fringe boosts support for more mainstream activists by making them seem more reasonable in comparison. One of the study’s authors, Markus Ostarek, said that though the boost in support was modest, the study indicates that moderate groups could “use these moments of high momentum to directly negotiate with policymakers.”

Kern County, located in California’s Central Valley, has approved a major carbon capture and storage project spearheaded by California Resources Corp, the largest oil and gas producer in the state. The project aims to capture up to 48 million metric tons of carbon dioxide from the company’s gas field operations, and inject it underground ino the Elk Hills oil field. While the state’s governor, Gavin Newsom, is supportive of this tech, it faces opposition from community members and activists who are worried about leaks and prolonging reliance on fossil fuels. There are 13 other carbon storage projects pending approval in the state.
Climate activists will stage a “noise demonstration” outside the office of the International Monetary Fund in Washington, D.C. today, during its annual meeting with the World Bank. They’ll use bullhorns and other noisemakers to ensure that finance ministers “cannot ignore calls for climate action.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Alternative proteins have floundered in the U.S., but investors are leaning in elsewhere.
Vegans and vegetarians rejoiced throughout the 2010s as food scientists got better and better at engineering plant and fungi-based proteins to mimic the texture, taste, and look of meat. Tests showed that even some meat enthusiasts couldn’t tell the difference. By the end of the decade, “fake meat” was booming. Burger King added it to the menu. Investment in the sector topped out at $5.6 billion in 2021.
Those heady days are now over — at least in the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. champions a “carnivore diet,” price-conscious Americans are prioritizing affordable calories, and many consumers insist the real thing still simply tastes better. Investment in alternative proteins has fallen each year since 2021, with the industry raising a comparably meager $881 million in 2025.
In China, however, the industry is just starting to pick up steam. Early-stage startups have been popping up ever since the country’s Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs included “future foods” such as lab-grown meat and plant-based eggs in its 2021 – 2025 five-year plan, indicating that these modern proteins will play a role in helping to secure the country’s domestic food supply chain.
“26% of the world’s meat is consumed by China, and about 50% of the world’s seafood,” Albert Tseng, co-founder of the venture firm Dao Foods, which backs Chinese companies developing climate-friendly proteins, told me. And yet the average Chinese consumer still only eats about half as much meat as the typical American, meaning that as the country gets richer, those numbers are only poised to grow. “The history of the world is essentially that as incomes rise, demand for protein also rises,” Tseng said.
But letting the protein patterns of the past dictate the future will have serious implications for the climate. Livestock production accounts for roughly 14% to 18% of global greenhouse gas emissions from things like methane releases and land-use changes. Yet it can seem unthinkable for many consumers to cut back on the foods they love, which is why some of the alternate protein sector’s most well-known companies are aiming to replicate the taste, look, and feel of meat.
That strategy isn’t going to fly in China though, Tseng told me. His goal is to slowly woo Chinese consumers away from meat and dairy with alluring plant-based, fungi-based, and lab-grown alternatives — ideally without customers even realizing what’s happening. For example, one of Dao’s portfolio companies, ZhongGu Mycelium, embeds the “superfood” mycelium — the root-like structure of fungi — into flour, boosting the protein-content and nutritional value of everyday products like dumplings and buns.
“We’re trying to actually crowd out demand for other proteins by infusing staple foods with the superfood ingredients that are more familiar, but also satiate people and provide the nutrition they need,” Tseng explained.
Tseng, a Canadian of Chinese descent, founded Dao Foods in 2018, with the idea that a regionally focused platform would allow him and his portfolio companies to develop deeper insights into the Chinese consumer. One lesson so far: In China, highlighting the health benefits and novelty of new proteins in their own right tends to resonate more than replicating the experience of eating meat or dairy. Dao Foods’ portfolio companies are making everything from coconut milk tea to rice proteins and plant-based hot pot broth — products designed to fit seamlessly into the country’s existing culinary culture without necessarily taking the place of meat.
“Direct replacement is probably not a sound commercial pathway,” Tseng said. Designer proteins command a higher price and are thus largely enjoyed by people explicitly trying to reduce their meat intake, whether for climate, health, or animal welfare reasons. But that conscious consumer segment concerned about the environment or animal rights is essentially nonexistent in China, Tseng told me. Rather, meat is viewed as a sign of status for the country’s growing upper and middle classes.
That cultural mismatch may be part of the reason Beyond Meat floundered when it entered China amidst the COVID lockdowns of 2020, a year after going public with a nearly $4 billion valuation. It finally exited the market early last year, and today its market capitalization is less than $400 million — a roughly 90% decline. Impossible Foods has long planned to launch in China too — the founder told Bloomberg in 2019 that it was “the most important country for our mission” — but that has yet to happen. Impossible CEO Peter McGuinness said last summer that the company was still years away from profitability.
China definitely hasn’t given up on the sector yet — it’s barely even gotten started. The country is now in the process of finalizing its five-year plan for 2026 – 2030, and “future foods” are expected to remain a part of the roadmap. Tseng noted that local mayors who implement the national government’s dictates are already competing to attract alternative protein companies to their regions, betting they’ll become drivers of regional GDP just as solar panel and electric vehicle manufacturers have been. “We’ve moved two or three companies now from one region of China to another because they’ve been interested in developing an area of expertise in sustainable food or future foods,” he told me.
So far, these regional enticements have largely come in the form of non-cash incentives. For example, ZhongGu Mycelium, is moving from Mongolia to the Western China municipality of Chengdu, where it will establish a new mycelium research and development facility and production hub. The move was a no-brainer given that “they were being offered a new factory space predominantly rent free for the first three years,” Tseng told me. Not only that, but the local government is “connecting them with the local business environment and food companies in that area. They’re providing some tax incentives, and they’re providing connections to the local university for research support.”
The U.S. can’t offer this level of state support even in the best of times. And with the current meat-loving administration in office, the likelihood of the alternative proteins market receiving any degree of federal backing is essentially nil. We simply aren’t hearing much these days from some names that were making waves just five years ago.
“A lot of these companies were ahead of consumer demand,” Kim Odhner, the co-founder of the sustainable food venture firm Unovis Asset Management, told me. When he started Unovis in 2018, companies such as Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat — an early Unovis investment — were gaining serious momentum. The firm has thus far weathered the downturn with its broad portfolio of meat and dairy alternatives — which includes an investment in Dao Foods, where it serves as a founding partner and shareholder. But as Odhner told me, “One of the most important lessons is that the whole build it and they will come mentality is very dangerous.” Many of the sector’s anticipated customers — in the U.S. and Europe at least — have yet to show up.
As Odhner prepares to raise a third fund with Unovis, he’s focusing on supporting growth-stage startups with proven technologies and minimal regulatory risk. That mainly includes businesses producing protein-rich ingredients for established food companies to incorporate into their existing product lines. It would be “very difficult,” he told me, for Unovis to raise money for an early-stage alternative protein fund today.
Like Tseng, Odhner thinks the best approach for the industry is to make inroads at the margins. “I don’t see any time in the near future — even in the distant future — where we’re going to be replacing center-of-the-plate steak with a cultivated meat equivalent,” Odhner told me.
Either way, Tseng and Odhner agree that there’s still real potential — and real money — in the sector. In China at least, Tseng thinks alternative proteins could follow in the footsteps of other clean energy industries such as solar panel and EVs that have taken root in the country despite many of their breakthrough innovations originating elsewhere. Drawing a parallel to the rise of Chinese EVs, he said that while outsiders perceived the industry as taking off overnight, its growth was actually a decades-long journey marked by plenty of missteps.
“But then at some point, it hit a tipping point,” Tseng told me. “And then the Chinese government signaled, investors poured in and supported these companies, and then you get BYD.”
Except for those related to the FIFA World Cup.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency has suspended all of its training and education programs for emergency managers across the country — except for those “directly supporting the 2026 FIFA World Cup.”
FEMA’s National Training and Education Division offers nearly 300 courses for local first responders and emergency managers, while FEMA’s National Disaster and Emergency Management University (formerly called the Emergency Management Institute) acts as the central training organization for emergency management in the United States. Since funding for the Department of Homeland Security lapsed on February 14, FEMA has instructed NTED partners to “cease course delivery operations,” according to communication reviewed by Heatmap. The NDEMU website and independent study materials have also been taken down.
The decision to remove NDEMU materials and freeze NTED courses not related to the World Cup has left emergency management students around the country in the lurch, with some just a few credits shy of certifications that would allow them to seek jobs. Mid-career employees have likewise been unable to meet their continuing training requirements, with courses pending “rescheduling” at a later date.
In states like California, where all public employees are sworn in as disaster service workers, jurisdictions have been left without the resources to train their employees. Additionally, certain preparedness grants require proof that emergency departments are compliant with frameworks such as the National Incident Management System and the Incident Command System. “The federal government says we need to be compliant with this, and they give us a way to do that, and then they take it away,” Laura Maskell, the emergency training and exercise coordinator for the city of San Jose, told me.
Depending on how long the DHS shutdown lasts, the training freeze is likely to exacerbate already dire staffing shortages at many municipal offices around the country. Emergency managers often juggle multiple jobs, ranging from local hazard and mitigation planning to public communication and IT. They also serve as the point people for everything from cybersecurity attacks to spectator safety to extreme-weather disaster response, and staying up to date on the latest procedures and technologies is critical enough to require ongoing education to maintain certification.
Training can be extensive. Becoming a certified emergency manager requires 100 hours of general management and 100 hours of emergency management courses — many of which students complete independently, online, while working other jobs — nearly all of which are currently suspended. The courses are utilized by many other first responders and law enforcement groups, too, from firefighters to university campus safety officers.
Emergency management officials and students I spoke with told me they see FEMA’s decision as capricious — “an intentional choice the government has made to further disrupt emergency management,” as a student who wanted to remain anonymous to protect their FEMA-funded employer from backlash told me — given that FEMA materials were not removed or trainings canceled during previous shutdowns. (Materials were unavailable during the most recent full-government shutdown in 2025.) In the past, FEMA has processed certifications once its offices have reopened; the exception for World Cup-related training adds to the feeling that the decision to remove materials is punitive.
“My understanding is these websites are pretty low maintenance,” Maskell said. She added, “Outside of a specific review cycle, I was not aware that there was any active maintenance or upkeep on these websites. So for them to take these down, allegedly because of the DHS shutdown, that doesn’t make sense to me.”
San Jose’s 6,800 city employees are required to take two to four designated FEMA courses, which Maskell said her team no longer has access to. “We don’t have another way” to train employees “that is readily available to get them that information in a cost-effective, standardized, most importantly up-to-the-federal-requirements way,” she added. Levi’s Stadium in Santa Clara, which falls within San Jose’s jurisdiction, is a World Cup site, and Maskell confirmed that in-person training specific to sports and special events has proceeded uninterrupted.
Depriving emergency managers and first responders of training seems at odds with the safe streets emphasis of the Trump administration. But FEMA has been in crisis since the DOGE cuts of early 2025, which were executed by a series of administrators who believe the agency shouldn’t exist; another 10,000 employees may be cut this spring. (Sure to deepen the chaos at the agency, Trump fired Secretary of Homeland Security Kristi Noem earlier Thursday. FEMA did not respond to a request for comment on this story.) The White House says it wants to shift responsibility for disaster planning and response back to the states — a goal that nevertheless underscores the importance of keeping training and resources accessible, even if the website isn’t being actively updated during the DHS shutdown.
Trainings that remain caught up in the politics of the shutdown include courses at the Center for Homeland Defense and Security, the Rural Domestic Preparedness Consortium, and others. The National Domestic Preparedness Consortium, which is also affected, offers training for extreme weather disasters — education that is especially critical heading into flood and tornado season, with wildfire and hurricane season around the corner. Courses like the National Disaster Preparedness Training Center’s offering of “Evacuation Planning Strategies and Solutions” in San Francisco, one of the World Cup host cities, fall under the exemption and are expected to be held as planned.
Noem had blamed Democrats for holding up $625 million in FEMA grants for FIFA World Cup host cities, funds that would go toward security and planning. Democrats have pushed back on that line, pointing out that World Cup security funding was approved last summer and the agency missed the anticipated January award date for the grant program ahead of the DHS shutdown. Democrats have said they will not fund the department until they reach an agreement on Immigration and Customs Enforcement’s use of deadly force and detention against U.S. citizens and migrant communities. (The House is scheduled to vote Thursday afternoon on a potential DHS funding package; a scheduled Senate vote earlier in the day failed to advance.)
The federal government estimates that as many as 10 million international visitors will travel to the U.S. for the World Cup, which begins in 98 days. “Training and education scheduled for the 11 U.S. World Cup host cities,” the DHS told its partners, “will continue as planned.”
The administration has begun shuffling projects forward as court challenges against the freeze heat up.
The Trump administration really wants you to think it’s thawing the freeze on renewable energy projects. Whether this is a genuine face turn or a play to curry favor with the courts and Congress, however, is less clear.
In the face of pressures such as surging energy demand from artificial intelligence and lobbying from prominent figures on the right, including the wife of Trump’s deputy chief of staff, the Bureau of Land Management has unlocked environmental permitting processes in recent weeks for a substantial number of renewable energy projects. Public documents, media reports, and official agency correspondence with stakeholders on the ground all show projects that had ground to a halt now lurching forward.
What has gone relatively unnoticed in all this is that the Trump administration has used this momentum to argue against a lawsuit filed by renewable energy groups challenging Trump’s permitting freeze. In January, for instance, Heatmap was first to report that the administration had lifted its ban on eagle take permits for wind projects. As we predicted at the time, after easing that restriction, Trump’s Justice Department has argued that the judge in the permitting freeze case should reject calls for an injunction. “Arguments against the so-called Eagle Permit Ban are perhaps the easiest to reject. [The Fish and Wildlife Service] has lifted the temporary pause on the issuance of Eagle take permits,” DOJ lawyers argued in a legal brief in February.
On February 26, E&E News first reported on Interior’s permitting freeze melting, citing three unnamed career agency officials who said that “at least 20 commercial-scale” solar projects would advance forward. Those projects include each of the seven segments of the Esmeralda mega-project that Heatmap was first to report was killed last fall. E&E News also reported that Jove Solar in Arizona, the Redonda and Bajada solar projects in California and three Nevada solar projects – Boulder Solar III, Dry Lake East and Libra Solar – will proceed in some fashion. Libra Solar received its final environmental approval in December but hasn’t gotten its formal right-of-way for construction.
Since then, Heatmap has learned of four other projects on the list, all in Nevada: Mosey Energy Center, Kawich Energy Center, Purple Sage Energy Center and Rock Valley Energy Center.
Things also seem to be moving on the transmission front in ways that will benefit solar. BLM posted the final environmental impact statement for upgrades to NextEra’s GridLance West transmission project in Nevada, which is expected to connect to solar facilities. And NV Energy’s Greenlink North transmission line is now scheduled to receive a final federal decision in June.
On wind, the administration silently advanced the Lucky Star transmission line in Wyoming, which we’ve covered as a bellwether for the state of the permitting process. We were first to report that BLM sent local officials in Wyoming a draft environmental review document a year ago signaling that the transmission line would be approved — then the whole thing inexplicably ground to a halt. Now things are moving forward again. In early February, BLM posted the final environmental review for Lucky Star online without any public notice or press release.
There are certainly reasons why Trump would allow renewables development to move forward at this juncture.
The president is under incredible pressure to get as much energy as possible onto the electric grid to power AI data centers without causing undue harm to consumers’ pocketbooks. According to the Wall Street Journal, the oil industry is urging him to move renewables permitting forward so Democrats come back to the table on a permitting deal.
Then there’s the MAGAverse’s sudden love affair with solar energy. Katie Miller, wife of White House deputy chief of staff Stephen Miller, has suddenly become a pro-solar advocate at the same time as a PR campaign funded by members of American Clean Power claims to be doing paid media partnerships with her. (Miller has denied being paid by ACP or the campaign.) Former Trump senior adviser Kellyanne Conway is now touting polls about solar’s popularity for “energy security” reasons, and Trump pollster Tony Fabrizio just dropped a First Solar-funded survey showing that roughly half of Trump voters support solar farms.
This timing is also conspicuously coincidental. One day before the E&E News story, the Justice Department was granted an extension until March 16 to file updated rebuttals in the freeze case before any oral arguments or rulings on injunctions. In other court filings submitted by the Justice Department, BLM career staff acknowledge they’ve met with people behind multiple solar projects referenced in the lawsuit since it was filed. It wouldn’t be surprising if a big set of solar projects got their permitting process unlocked right around that March 16 deadline.
Kevin Emmerich, co-founder of Western environmental group Basin & Range Watch, told me it’s important to recognize that not all of these projects are getting final approvals; some of this stuff is more piecemeal or procedural. As an advocate who wants more responsible stewardship of public lands and is opposed to lots of this, Emmerich is actually quite troubled by the way Trump is going back on the pause. That is especially true after the Supreme Court’s 2025 ruling in the Seven Counties case, which limited the scope of environmental reviews, not to mention Trump-era changes in regulation and agency leadership.
“They put a lot of scrutiny on these projects, and for a while there we didn’t think they were going to move, period,” Emmerich told me. “We’re actually a little bit bummed out about this because some of these we identified as having really big environmental impacts. We’re seeing this as a perfect storm for those of us worried about public land being taken over by energy because the weakening of NEPA is going to be good for a lot of these people, a lot of these developers.”
BLM would not tell me why this thaw is happening now. When reached for comment, the agency replied with an unsigned statement that the Interior Department “is actively reviewing permitting for large-scale onshore solar projects” through a “comprehensive” process with “consistent standards” – an allusion to the web of review criteria renewable energy developers called a de facto freeze on permits. “This comprehensive review process ensures that projects — whether on federal, state, or private lands — receive appropriate oversight whenever federal resources, permits, or consultations are involved.”