You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The West loves its wide open spaces. Utah, though, is something else.
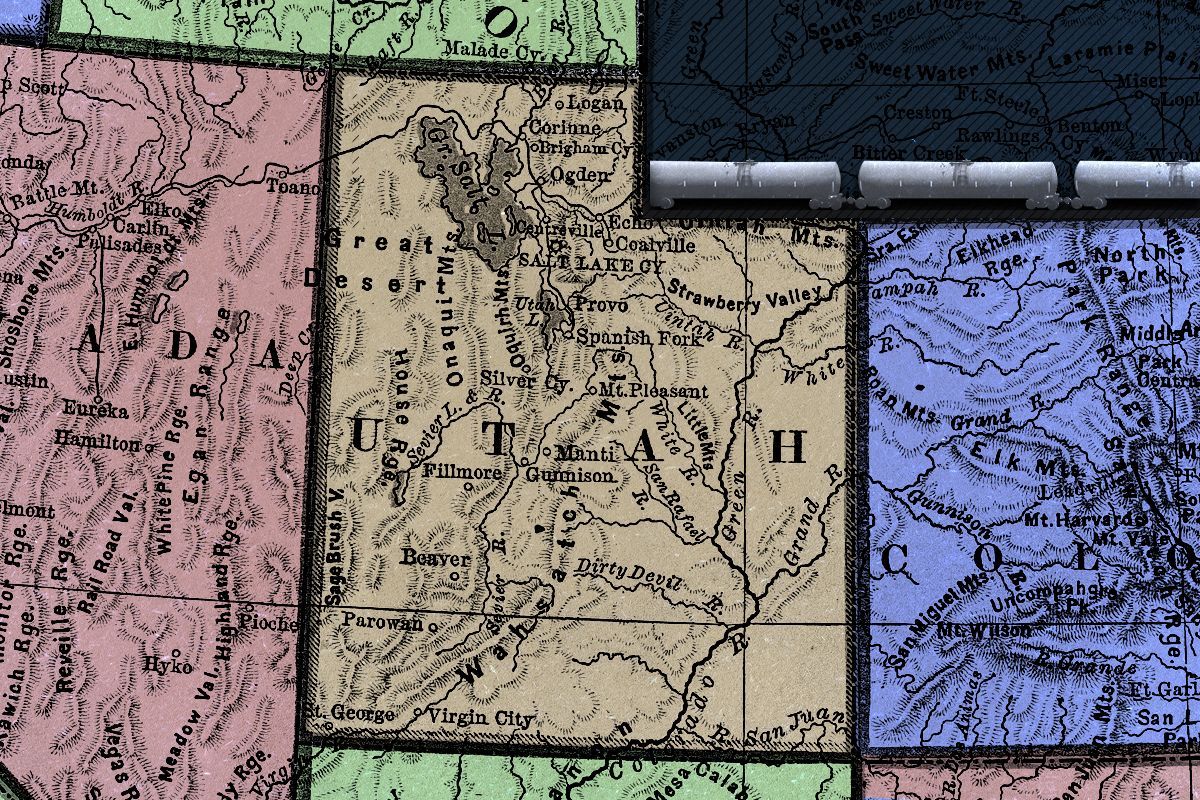
Every state would like to think itself singular but, truly, there is no place like Utah. The Beehive State has long fascinated outsiders; today, that attention is largely trained on Netflix exposés about the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, ballerina farmers, and Crumbl cookies, but historically, the obsession has been with its land. Utah has the nation’s highest density of National Parks; its rivers, canyons, mountains, and deserts have stirred Mark Twain, John Wesley Powell, John Muir, and Edward Abbey. To quote a more contemporary literary conduit, Post Malone: “It’s a free country out there. You can buy suppressors in Utah. You can … walk into the grocery store with a handgun on your hip. Cowboy shit.”
More recently, Utah has sought out a different source of outsider attention — that of the United States Supreme Court. Two lawsuits that originated in the state are currently under consideration by the justices. The first, Seven County Infrastructure Coalition v. Eagle County, Colorado, concerns the scope of the National Environmental Policy Act with regard to the construction of a railroad spur that would link Utah’s oil fields to the national rail lines. (Though the tracks would be in Utah, the connection would ultimately increase hazardous waxy crude oil shipments through the Colorado county in the case citation.) The second lawsuit, Utah v. the United States — which the court has yet to decide whether or not it will hear — involves the state suing the federal government over its allegedly unconstitutional control of “unused” lands by the Bureau of Land Management. If Utah prevails in the case, it could mean the vast reshaping of the American West, about 47% of which is federal land.
“Utah is all crazy, all the time right now,” Stephen Bloch, the legal director of the Southern Utah Wilderness Alliance, a conservation nonprofit opposing Utah v. the U.S., told me.
While not immediately apparent, there is nevertheless a strange logic to the two lawsuits that otherwise appear to have little to do with one another beyond the fact of their geography. At their core, both cases are ultimately about who gets to decide to do what with Utah’s land.
To anyone familiar with land use issues in the Mountain West, all of this is fairly routine. A strain of libertarianism and anti-government individualism runs through the more conservative inland Western states, coloring everything from the gun ownership policies so colorfully observed by Post Malone to whom the states back for president. Yet in the extent to which it is willing to pursue this common ideal, Utah is still an outlier.
“Westerners revere their public lands,” Betsy Gaines Quammen, a historian and author of American Zion: Cliven Bundy, God & Public Lands in the West, told me. “This is what makes the West the West — that you can come out and just go hiking, and you’re not trespassing.” Take the recent Montana Senate race, in which incumbent Democrat Jon Tester wielded his opponent Tim Sheehy’s comparatively mild comments about privatizing public lands as a cudgel in a deep red state. (Tester, it must be added, lost his reelection bid.) But in Utah, instead of celebrating federal land as the embodiment of this Western inheritance, its politicians are trying to eliminate them.
In the case of Utah, this goal is immediate and obvious. State officials claim that the 18.5 million acres of “unappropriated” BLM land in the state — that is, public lands not already designated as national parks, monuments, wilderness areas, national forests and conservation areas, or Tribal lands — are held in violation of the U.S. Constitution, which doesn’t explicitly authorize the federal government to hold land indefinitely. “Utah deserves priority when it comes to managing this land,” the state’s Republican Governor Spencer Cox said at a news conference in August, adding, “Utah is in the best position to understand and respond to the unique needs of our environment and communities.”
While Utah’s crown jewel, its “Mighty Five” National Parks, would remain under federal management, the state of Wyoming — which has backed Utah’s lawsuit in an amicus brief along with Idaho, Alaska, and the Arizona legislature — wants even more. “In Wyoming’s filing, they’re like, ‘Oh no, we’re in for everything,” Bloch said. “‘There shouldn’t be any federal land in Wyoming’ — including national parks.” More than 95% of Yellowstone National Park — the nation’s first national park, designated in 1872 — sits within Wyoming’s borders.
It seems doubtful that the Supreme Court will take up this case. For one thing, Utah is attempting to leapfrog the lower courts by taking its complaints directly to SCOTUS, a shortcut it says is justified by its concerns being “of profound importance not just to Utah, but to all the States in the Nation.” For another, President Biden’s Department of Justice has pointed out that what Utah seeks is outside the powers vested in the judicial branch; only Congress has decision-making authority over public lands. On the other hand, “Anyone right now, I think, would hesitate to say definitively, ‘Here’s what the Supreme Court will do,’” Aaron Weiss, the deputy director of the Center for Western Priorities, a nonpartisan conservation advocacy group, told me.
Seven County Infrastructure Coalition is a different story. Opponents of the railway claim that the government’s environmental review took into account the remote economic benefits of the railway — including induced employment, a notoriously inexact projection — while not equally weighing the indirect health impacts of the rail line, such as the pollution of additional fracking wells in the Uinta Basin or frontline communities near the refineries on the Gulf, where the crude oil is ultimately headed. The Supreme Court (minus Neil Gorsuch, who recused himself at the 11th hour) heard oral arguments in the case this week, however, and appears on track to rule that the government’s NEPA review for the railroad was sufficient. That would ultimately be a win for the Uinta Basin Railway and the business coalition that brought the suit after the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit ruled there were flaws in the upstream and downstream analyses.
“I’m really worried that the court could end up inadvertently blessing this fundamentally arbitrary, imbalanced result, where an agency is allowed to talk about all the indirect benefits that they want — to go as far down the line, as far upstream, to the ends of the Earth chasing these indirect benefits — but not bother talking about the corresponding costs,” Jason Schwartz, the legal director at the Institute for Policy Integrity at New York University’s School of Law, told me. “That undermines the very purpose of NEPA, which was to present the public and decision-makers with a full and balanced view of both the economic and environmental perspectives.” (Schwartz authored an amicus brief for the Institute of Policy Integrity against the government’s NEPA review.)
A ruling that reaffirms the current scope of NEPA wouldn’t be a shock — the court has always sided with the government in such cases, E&E News notes. What’s different this time is that the plaintiffs presented the court with a third option, an avenue that would severely limit the scope of the NEPA’s environmental review process going forward by restraining agency considerations only to what falls under their immediate purview. Chief Justice John Roberts has sounded skeptical of this pitch so far; it’s this third path, however, that the oil and gas producer Anschutz submitted an amicus brief to the court to support, drawing attention to the fact that “far more is at stake … than the 88-mile rail line in rural Utah.” (The company’s owner, Philip Anchutz, has close ties to Gorsuch.)
“There are so many ways to make NEPA more efficient without arbitrarily decreasing the sometimes crucial information related to indirect effects that NEPA currently provides,” Schwartz told me. Sam Sankar, the senior vice president for programs at Earthjustice, which is supporting the defense, added to me that his read on Seven County Infrastructure Coalition case is that it proves how this Supreme Court has “a pretty aggressive deregulatory, anti-environmental agenda.” The Seven County Infrastructure Coalition told Heatmap in a statement that with regards to the railroad, “we remain committed to advancing this critical infrastructure, which aims to unlock economic opportunities and support the region’s long-term development,” but that it could not comment further as the case remains under deliberation.
A threat to NEPA is also a challenge to who gets a say in what Utah does with its land, of course. Like Utah v. the U.S., the filing for Seven County Infrastructure Coalition bristles with indignation over the government’s determinations about how things should be done or what impacts should be considered, even if the Surface Transportation Board ultimately gave the railroad the green light. Utah, meanwhile, originated as a reaction to the BLM’s Public Lands Rule, in which the agency considers conservation as a land use on equal footing with those of energy development, mining, or grazing. (Specifically, Utah lawmakers were furious about the BLM closing some roads to motorized vehicles. “That’s something that Utah gets very worked up about,” Bloch, the legal director at SUWA, told me.)
There is always a risk of overascribing the state of Utah’s otherwise seemingly inexplicable actions to Mormonism — a religion that is far from monolithic and is often the subject of derision from outsiders. But Quammen, the historian, told me that you can’t separate today’s public land policies from the cultural and theological inheritances and beliefs reinforced over generations of Mormon tradition. “A lot of the people taking these stands [over public lands] come from families that have been in that area for generations, so they have stories and ideologies that have been passed down — as has their relationship with the land,” Quammen explained.
Weiss, of Western Priorities, concurred. “There are some folks in Utah who truly believe that this land belongs to them,” he said.
Quammen noted by way of example that Cliven Bundy, who led a standoff at the Malheur National Wildlife Refuge in Oregon in 2016 over the demand that the BLM cede its land to the states, told her his legal right to the public lands where he grazes his cattle in Nevada started when his ancestor’s horse drank from its Virgin River — although in fact it was a Southern Paiute river before that. (That’s not the only historically inaccurate ownership claim that might be at play in Utah; Bloch of SUWA noted that the lands within the exterior boundaries of the state were ceded to the federal government in 1848 through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo at the end of the U.S.-Mexico War, and in that sense, “they’ve never been ‘Utah lands’ so there’s nothing to ‘give back’ to Utah.”)
Preservationists and conservationists during the settlement era saw Utah’s landscape as untrammeled (“also not true, because it was Indigenous land,” Quammen added) and in need of protection, but early church belief viewed it differently. “They thought that the land being utilized, built, and made productive was pleasing to the eye of God,” Quammen said. Finally, Joseph Smith, the founder of LDS, emphasized the importance of his adherents understanding the U.S. Constitution inside and out. In the case of public lands disputes, this resurfaces in the claim that the federal government can’t own land indefinitely, Quammen told me. “That’s the piece about understanding the Constitution better than constitutional scholars.” Ironically, it disregards the state’s constitution, in which Utah explicitly agreed in 1894 to “forever disclaim[s] all right and title to the unappropriated public lands” in order to be granted statehood.
There is, of course, a significant small-government push in the Republican Party, too; privatizing land was part of the party’s presidential platform this year. It can be hard to tell, however, where one influence ends and another begins: William Perry Pendley, a key figure in the Reagan administration during the Sagebrush Rebellion fight over public lands in the 1970s and 1980s, authored the Project 2025 chapter on the Department of the Interior. Doug Burgum, Trump’s nominee for the head of the department, recently met with Utah’s Republican Senator Mike Lee, a devout Latter-Day Saint, who afterward posted, “Great meeting with @dougburgum and planning the return of American lands to the American people.” And if Trump attempts to walk back protections of Bears Ears and Grand Staircase Escalante National Monuments again, that land would be added to the pot of what Utah is seeking to acquire.
Utah’s organizers seem prepared to make an appeal to Congress or the Trump administration if the Supreme Court doesn’t make a move in their favor; funding for the messaging for Stand for Our Land, the publicity arm of the lawsuit, has reportedly outpaced the spending on lawyers. (A request for comment to the Utah Attorney General’s Office and Gov. Spencer J. Cox went unanswered.)
The implications of the Supreme Court’s decisions on limiting the scope of NEPA or hearing the public lands lawsuit are vast in both cases. The former could ease the way for expansive oil and gas development in Utah, which would be “a bona fide public health nightmare,” according to Brian Moench, an anesthesiologist on the board of Utah Physicians for a Healthy Environment, which is opposing the railroad, due to all the additional pollution. “If they’re allowed to do this and increase the oil and gas drilling production by 500% — I don't know what you would call the end result. Unlivable, as far as I’m concerned.”
In the case of the public lands, meanwhile, “I think [Utah is] trying to give the impression that these are scrubby lands that nobody cares about when, in fact, it concerns landscapes like Labyrinth Canyon or the Dirty Devil or the Fisher Towers — these very iconic red rock landscapes that Americans think about when they think about visiting the state,” Bloch told me. “Those are the types of places in the crosshairs with this lawsuit.”
Ironically, it’s doubtful that a transfer of public lands would even benefit most Utahns. Because states can’t run deficits, a disaster like a bad wildfire would drain the Utah budget. Additionally, ranchers would pay far more for grazing their cattle on state lands (as high as $19.50 per animal unit per month, per the BLM) than on federal lands, where the fee is a dirt-cheap $1.35. Ultimately, the state likely wouldn’t even possess much of the land it claims to want so badly.
Utah’s politicians “would much prefer to be able to sell off any lands that they want — whether it’s for oil and gas leasing, whether it’s for mansions near national parks. This is very valuable land and a very valuable resource that belongs to all Americans,” Weiss of Western Priorities said. “And Utah would prefer if it belonged to them.”
Public lands and pride in the natural environment are fundamental to many Westerners’ beliefs and identities. By that token, it would seem Utah has made a miscalculation that only an insider could truly appreciate the cost of; by taking over control of portions of its territory from the federal government, it would be, in effect, boxing Utahns out of their own lands —a craven, modern twist if ever there was one.
But to be able to hike or hunt, to pitch a tent, to fish, to stargaze, to graze one’s cattle on nearly 70% of the land in Utah, because it belongs to us, the public?
Now that’s cowboy shit.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On a new report from the Energy Institute, high-stakes legislating, and accelerating nuclear development
Current conditions: Monsoon rains hit the southwestern U.S., with flash floods in Roswell, New Mexico, and flooding in El Paso, Texas • The Forsyth Fire in Utah has spread to 9,000 acres and is only 5% contained • While temperatures are falling into the low 80s in much of the Northeast, a high of 96 degrees Fahrenheit is forecast for Washington, D.C., where Republicans in the Senate seek to finish their work on the “One Big, Beautiful Bill.”
The world used more of just about every kind of energy source in 2024, including coal, oil, gas, renewables, hydro, and nuclear, according to the annual Statistical Review of World Energy, released by the Energy Institute. Here are some of the key numbers from the report:
You can read the full report here.
Virginia Republican Jen Kiggans is a vice chair of the Conservative Climate Caucus and a signatory of several letters supporting the preservation of clean energy tax credits in the Inflation Reduction Act, including one letter she co-authored with Pennsylvania’s Brian Fitzpatrick criticizing the House reconciliation bill’s rough approach to slashing the credits. On Wednesday, however, she said on X that the Senate language “responsibly phases out certain tax credits while preserving American investment and innovation in our energy sector.”
The Senate is still pushing to have the reconciliation bill on President Trump’s desk by July 4, and is expected to work through the weekend to get it done. But as Sahil Kapur of NBC News reported Wednesday, House and Senate leaders have been attempting to hash out yet another version of the bill that could pass both chambers quickly, meaning the legislation is still very much in flux.
Shell is in early talks to acquire fellow multinational oil giant BP, the Wall Street Journal reported. While BP declined to comment to the Journal, Shell called the story “market speculation” and said that “no talks are taking place.”
BP is currently valued at $80 billion, which would make a potential tie-up the largest corporate oil deal since the Exxon Mobil merger, according to the Journal.
Both Shell and BP have walked back from commitments to and investments in decarbonization and green energy in recent months. BP said in September of last year that it would divest from its U.S. wind business, while Shell said in January that it would “pause” its investment in the U.S. offshore wind industry and took an accompanying charge of $1 billion.
The combined company would be better positioned to compete with supermajors like Exxon, which is now worth over $450 billion, while Shell and BP have a combined valuation around $285 billion.
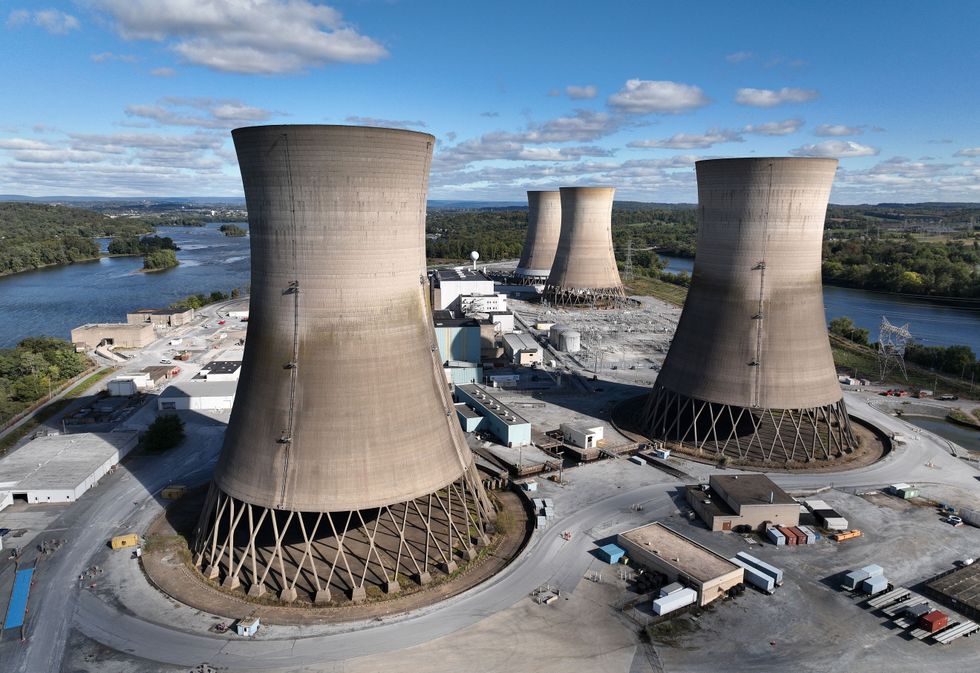

Three Mile Island Unit 1 will restart a year early, its owner Constellation said Wednesday. When Constellation and Microsoft announced the plan to restart the nuclear facility last fall they gave a target date of 2028. More recently, however, PJM Interconnection, the interstate electricity market that includes Pennsylvania, approved a request made from the state’s governor, Josh Shapiro, to fast-track the plant’s interconnection, the company said, meaning it could open as soon as 2027.
Constellation reported “significant progress” on hiring and training new workers, with around 400 workers either hired or due to start new jobs soon. “We’re on track to make history ahead of schedule, helping America achieve energy independence, supercharge economic growth, and win the global AI race,” Constellation’s chief executive Joe Dominguez said.
The Chinese electric carmarker BYD is addressing rising inventory and lower prices by cutting back its production plans. The company “has slowed its production and expansion pace in recent months by reducing shifts at some factories in China and delaying plans to add new production lines,” Reuters reported.
The slowdown comes “as it grapples with rising inventory even after offering deep price cuts in China's cutthroat auto market,” according to the Reuters report.
In 2024, BYD beat out Tesla in annual sales, with over 4 million cars sold, for a total annual revenue over $100 billion. Tesla’s revenue was just short of $100 billion last year.
While BYD’s factories may be slowing down, it is still looking to expand, especially overseas. In April, more than 7,000 BYD battery electric cars were registered in Europe, according to Bloomberg. This more-than-doubling since last year slingshotted BYD past Tesla on the continent, where its sales have fallen by almost 50%.
“Where does the power sector go from here?” an audience member asked at our exclusive Heatmap subscriber event in New York on Wednesday, referring to a potential future without the Inflation Reduction Act. “Higher costs,” Emily Pontecorvo answered. There is one potential bright spot, however, as Robinson Meyer explained: “If I were a Democrat considering running an affordability campaign or a cost-of-living campaign in ’26 or ’28, there’s lots of openings to talk about clean energy — the policy that’s happening right now — utility rates, and energy affordability.”
The science is still out — but some of the industry’s key players are moving ahead regardless.
The ocean is by far the world’s largest carbon sink, capturing about 30% of human-caused CO2 emissions and about 90% of the excess heat energy from said emissions. For about as long as scientists have known these numbers, there’s been intrigue around engineering the ocean to absorb even more. And more recently, a few startups have gotten closer to making this a reality.
Last week, one of them got a vote of confidence from leading carbon removal registry Isometric, which for the first time validated “ocean alkalinity enhancement” credits sold by the startup Planetary — 625.6 to be exact, representing 625.6 metric tons of carbon removed. No other registry has issued credits for this type of carbon removal.
When the ocean absorbs carbon, the CO2 in the air reacts with the water to form carbonic acid, which quickly breaks down into hydrogen ions and bicarbonate. The excess hydrogen increases the acidity of the ocean, changing its chemistry to make it less effective at absorbing CO2, like a sponge that’s already damp. As levels of atmospheric CO2 increase, the ocean is getting more acidic overall, threatening marine ecosystems.
Planetary is working to make the ocean less acidic, so that it can take in more carbon. At its pilot plant in Nova Scotia, the company adds alkalizing magnesium hydroxide to wastewater after it’s been used to cool a coastal power plant and before it’s discharged back into the ocean. When the alkaline substance (which, if you remember your high school chemistry, is also known as a base) dissolves in the water, it releases hydroxide ions, which combine with and neutralize hydrogen ions. This in turn reduces local acidity and raises the ocean’s pH, thus increasing its capacity to absorb more carbon dioxide. That CO2 is then stored as a stable bicarbonate for thousands of years.
“The ocean has just got such a vast amount of capacity to store carbon within it,” Will Burt, Planetary’s vice president of science and product, told me. Because ocean alkalinity enhancement mimics a natural process, there are fewer ecosystem concerns than with some other means of ocean-based carbon removal, such as stimulating algae blooms. And unlike biomass or soil-related carbon removal methods, it has a very minimal land footprint. For this reason, Burt told me “the massiveness of the ocean is going to be the key to climate relevance” for the carbon dioxide removal industry as a whole.
But that’s no guarantee. As with any open system where carbon can flow in and out, how much carbon the ocean actually absorbs is tricky to measure and verify. The best oceanography models we have still don’t always align with observational data.
Given this, is it too soon for Planetary to issue credits? It’s just not possible right now for the startup — or anyone in the field — to quantify the exact amount of carbon that this process is removing. And while the company incorporates error bars into its calculations and crediting mechanisms, scientists simply aren’t certain about the degree of uncertainty that remains.
“I think we still have a lot of work to do to actually characterize the uncertainty bars and make ourselves confident that there aren’t unknown unknowns that we are not thinking about,” Freya Chay, a program lead at CarbonPlan, told me. The nonprofit aims to analyze the efficacy of various carbon removal pathways, and has worked with Planetary to evaluate and inform its approach to ocean alkalinity enhancement.
Planetary’s process for measurement and verification employs a combination of near field observational data and extensive ocean modeling to estimate the rate, efficiency, and permanence of carbon uptake. Close to the point where it releases the magnesium hydroxide, the company uses autonomous sensors at and below the ocean’s surface to measure pH and other variables. This real-time data then feeds into ocean models intended to simulate large-scale processes such as how alkalinity disperses and dissolves, the dynamics of CO2 absorption, and ultimately how much carbon is locked away for the long-term.
But though Planetary’s models are peer-reviewed and best in class, they have their limits. One of the largest remaining unknowns is how natural changes in ocean alkalinity feed into the whole equation — that is, it’s possible that artificially alkalizing the ocean could prevent the uptake of naturally occurring bases. If this is happening at scale, it would call into question the “enhancement” part of alkalinity enhancement.
There’s also the issue of regional and seasonal variability in the efficiency of CO2 uptake, which makes it difficult to put any hard numbers to the efficacy of this solution overall. To this end, CarbonPlan has worked with the marine carbon removal research organization [C]Worthy to develop an interactive tool that allows companies to explore how alkalinity moves through the ocean and removes carbon in various regions over time.
As Chay explained, though, not all the models agree on just how much carbon is removed by a given base in a given location at a given time. “You can characterize how different the models are from each other, but then you also have to figure out which ones best represent the real world,” she told me. “And I think we have a lot of work to do on that front.”
From Chay’s perspective, whether or not Planetary is “ready” to start selling carbon removal credits largely depends on the claims that its buyers are trying to make. One way to think about it, she told me, is to imagine how these credits would stand up in a hypothetical compliance carbon market, in which a polluter could buy a certain amount of ocean alkalinity credits that would then allow them to release an equivalent amount of emissions under a legally mandated cap.
“When I think about that, I have a very clear instinctual reaction, which is, No, we are far from ready,”Chay told me.
Of course, we don’t live in a world with a compliance carbon market, and most of Planetary’s customers thus far — Stripe, Shopify, and the larger carbon removal coalition, Frontier, that they’re members of — have refrained from making concrete claims about how their voluntary carbon removal purchases impact broader emissions goals. But another customer, British Airways, does appear to tout its purchases from Planetary and others as one of many pathways it’s pursuing to reach net zero. Much like the carbon market itself, such claims are not formally regulated.
All of this, Chay told me, makes trying to discern the most responsible way to support nascent solutions all the more “squishy.”
Matt Long, CEO and co-founder of [C]Worthy, told me that he thinks it’s both appropriate and important to start issuing credits for ocean alkalinity enhancement — while also acknowledging that “we have robust reason to believe that we can do a lot better” when it comes to assessing these removals.
For the time being, he calls Planetary’s approach to measurement “largely credible.”
“What we need to adopt is a permissive stance towards uncertainty in the early days, such that the industry can get off the ground and we can leverage commercial pilot deployments, like the one that Planetary has engaged in, as opportunities to advance the science and practice of removal quantification,” Long told me.
Indeed, for these early-stage removal technologies there are virtually no other viable paths to market beyond selling credits on the voluntary market. This, of course, is the very raison d’etre of the Frontier coalition, which was formed to help emerging CO2 removal technologies by pre-purchasing significant quantities of carbon removal. Today’s investors are banking on the hope that one day, the federal government will establish a domestic compliance market that allows companies to offset emissions by purchasing removal credits. But until then, there’s not really a pool of buyers willing to fund no-strings-attached CO2 removal.
Isometric — an early-stage startup itself — says its goal is to restore trust in the voluntary carbon market, which has a history of issuing bogus offset credits. By contrast, Isometric only issues “carbon removal” credits, which — unlike offsets — are intended to represent a permanent drawdown of CO2 from the atmosphere, which the company defines as 1,000 years or longer. Isometric’s credits also must align with the registry’s peer-reviewed carbon removal protocols, though these are often written in collaboration with startups such as Planetary that are looking to get their methodologies approved.
The initial carbon removal methods that Isometric dove into — bio-oil geological storage, biomass geological storage, direct air capture — are very measurable. But Isometric has since branched beyond the easy wins to develop protocols for potentially less permanent and more difficult to quantify carbon removal methods, including enhanced weathering, biochar production, and reforestation.
Thus, the core tension remains. Because while Isometric’s website boasts that corporations can “be confident every credit is a guaranteed tonne of carbon removal,” the way researchers like Chay and Long talk about Planetary makes it sound much more like a promising science project that’s being refined and iterated upon in the public sphere.
For his part, Burt told me he knows that Planetary’s current methodologies have room for improvement, and that being transparent about that is what will ultimately move the company forward. “I am constantly talking to oceanography forums about, Here’s how we’re doing it. We know it’s not perfect. How do we improve it?” he said.
While Planetary wouldn’t reveal its current price per ton of CO2 removed, the company told me in an emailed statement that it expects its approach “to ultimately be the lowest-cost form” of carbon removal. Burt said that today, the majority of a credit’s cost — and its embedded emissions — comes from transporting bases from the company’s current source in Spain to its pilot project in Nova Scotia. In the future, the startup plans to mitigate this by co-locating its projects and alkalinity sources, and by clustering project sites in the same area.
“You could probably have another one of these sites 2 kilometers down the coast,” he told me, referring to the Nova Scotia project. “You could do another 100,000 tonnes there, and that would not be too much for the system, because the ocean is very quickly diluted.”
The company has a long way to go before reaching that type of scale though. From the latter half of last year until now, Planetary has released about 1,100 metric tons of material into the ocean, which it says will lead to about 1,000 metric tons of carbon removal.
But as I was reminded by everyone, we’re still in the first inning of the ocean alkalinity enhancement era. For its part, [C]Worthy is now working to create the data and modeling infrastructure that startups such as Planetary will one day use to more precisely quantify their carbon removal benefits.
“We do not have the system in place that we will have. But as a community, we have to recognize the requirement for carbon removal is very large, and that the implication is that we need to be building this industry now,” Long told me.
In other words: Ready or not, here we come.
On mercury rising, climate finance, and aviation emissions
Current conditions: Tropical Storm Andrea has become the first named Atlantic storm of 2025 • Hundreds of thousands are fleeing their homes in southwest China as heavy rains cause rivers to overflow • It’s hot and humid in New York’s Long Island City neighborhood, where last night New York City mayoral candidate Zohran Mamdani delivered his victory speech after defeating former governor and longtime party power broker Andrew Cuomo in the race’s Democratic primary.
The brutal heat dome baking the eastern half of the United States continues today. Cooler weather is in the forecast for tomorrow, but this heat wave has broken a slew of temperature records across multiple states this week:
In Washington, D.C., rail temperatures reached a blistering 135 degrees, forcing the city’s Metro to slow down train service. Meanwhile, in New Jersey, the heat sickened more than 150 people attending a high school graduation ceremony. As power demand surged, the Department of Energy issued an energy emergency in the Southeast to “help mitigate the risk of blackouts.”
As Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin pointed out on Tuesday, in terms of what is on the grid and what is demanded of it, this may be the easiest summer for a long time. “Demands on the grid are growing at the same time the resources powering it are changing,” Zeitlin writes. “Electricity load growth is forecast to grow several percent a year through at least the end of the decade. At the same time, aging plants reliant on oil, gas, and coal are being retired (although planned retirements are slowing down), while new resources, largely solar and batteries, are often stuck in long interconnection queues — and, when they do come online, offer unique challenges to grid operators when demand is high.”
A group of 21 Democrat-led states including New Jersey, Massachusetts, New York, Arizona, and California, is suing the Trump administration for cutting billions of dollars in federal funding, including grants related to climate change initiatives. The lawsuit says federal agencies have been “unlawfully invoking a single subclause” to cancel grants that the administration deems no longer align with its priorities. The clause in question states that federal agencies can terminate grants “pursuant to the terms and conditions of the federal award, including, to the extent authorized by law, if an award no longer effectuates the program goals or agency priorities.” The states accuse the administration of leaning on this clause for “virtually unfettered authority to withhold federal funding any time they no longer wish to support the programs for which Congress has appropriated funding.”
The rollback has gutted projects across states and nonprofits that support diversity, equity, and inclusion, as well as climate change preparation programs and research. The states say the clause is being used unlawfully, and hope a judge agrees. “These cuts are simply illegal,” said New York Attorney General Letitia James. “Congress has the power of the purse, and the president cannot cut billions of dollars of essential resources simply because he doesn’t like the programs being funded.”
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
A brief update from the Bonn Climate Change Conference in Germany: A group of 44 “Least Developed Countries” have called for rich countries to triple the financing goal for climate change adaptation by 2030 compared to 2022 levels. The current target sits at $40 billion a year by 2025, a number set back in 2021 at COP26. According toClimate Home News, tripling the financing goal on 2022 levels would bring in a little less than $100 billion annually. That’s far short of the $160 billion to $340 billion that the United Nations estimates will be needed by 2030. The Indian Express also reports that developing countries have “managed to force a reopening of discussions on the obligations of developed nations to ‘provide’ finance, and not just make efforts towards ‘mobilising’ financial resources, for climate action.” The issue will also be discussed at COP30 in Brazil later this year. The Bonn conference has been running since June 16 and ends tomorrow.
In the UK, aviation is now a bigger source of greenhouse gas emissions than the power sector, according to a new report from the Climate Change Committee. The independent climate advisors say that demand for leisure travel is boosting demand for international flights, and “continued emissions growth in this sector could put future targets at risk.” Meanwhile, the UK power sector has been rapidly decarbonizing, and is now the sixth largest source of emissions. (In the U.S., electricity production is the second-largest source of emissions, behind transportation.) The report also found that heat pump installations increased by 56% in 2024, and that nearly 20% of new vehicles sold were electric. UK emissions were down 50% last year compared to 1990.
The committee applauded the progress but urged more action from the government to cut electricity prices to help speed up the transition to clean technologies. “Our country is among a leading group of economies demonstrating a commitment to decarbonise society,” said Piers Forster, interim chair of the committee. “This is to be celebrated: delivering deep emissions reduction is the only way to slow global warming.”
Voters in North Carolina want Congress to leave the Inflation Reduction Act well enough alone, a new poll from Data for Progress finds. The survey, which asked North Carolina voters specifically about the clean energy and climate provisions in the bill, presented respondents with a choice between two statements: “The IRA should be repealed by Congress” and “The IRA should be kept in place by Congress.” (“Don’t know” was also an option.) The responses from voters broke down predictably along party lines, with 71% of Democrats preferring to keep the IRA in place compared to just 31% of Republicans, with half of independent voters in favor of keeping the climate law. Overall, half of North Carolina voters surveyed wanted the IRA to stick around, compared to 37% who’d rather see it go — a significant spread for a state that, prior to the passage of the climate law, was home to little in the way of clean energy development.
North Carolina now has a lot to lose with the potential repeal of the Inflation Reduction Act, as Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo has pointed out. The IRA brought more than 17,000 jobs to the state, along with $20 billion in investment spread out over 34 clean energy projects. Electric vehicle and charging manufacturers in particular have flocked to the state, with Toyota investing $13.9 billion in its Liberty EV battery manufacturing facility, which opened this past April.
As a fragile ceasefire between Israel and Iran takes hold, oil prices are now lower than they were before the conflict began on June 13.