You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On a new report from the Energy Institute, high-stakes legislating, and accelerating nuclear development

Current conditions: Monsoon rains hit the southwestern U.S., with flash floods in Roswell, New Mexico, and flooding in El Paso, Texas • The Forsyth Fire in Utah has spread to 9,000 acres and is only 5% contained • While temperatures are falling into the low 80s in much of the Northeast, a high of 96 degrees Fahrenheit is forecast for Washington, D.C., where Republicans in the Senate seek to finish their work on the “One Big, Beautiful Bill.”
The world used more of just about every kind of energy source in 2024, including coal, oil, gas, renewables, hydro, and nuclear, according to the annual Statistical Review of World Energy, released by the Energy Institute. Here are some of the key numbers from the report:
You can read the full report here.
Virginia Republican Jen Kiggans is a vice chair of the Conservative Climate Caucus and a signatory of several letters supporting the preservation of clean energy tax credits in the Inflation Reduction Act, including one letter she co-authored with Pennsylvania’s Brian Fitzpatrick criticizing the House reconciliation bill’s rough approach to slashing the credits. On Wednesday, however, she said on X that the Senate language “responsibly phases out certain tax credits while preserving American investment and innovation in our energy sector.”
The Senate is still pushing to have the reconciliation bill on President Trump’s desk by July 4, and is expected to work through the weekend to get it done. But as Sahil Kapur of NBC News reported Wednesday, House and Senate leaders have been attempting to hash out yet another version of the bill that could pass both chambers quickly, meaning the legislation is still very much in flux.
Shell is in early talks to acquire fellow multinational oil giant BP, the Wall Street Journal reported. While BP declined to comment to the Journal, Shell called the story “market speculation” and said that “no talks are taking place.”
BP is currently valued at $80 billion, which would make a potential tie-up the largest corporate oil deal since the Exxon Mobil merger, according to the Journal.
Both Shell and BP have walked back from commitments to and investments in decarbonization and green energy in recent months. BP said in September of last year that it would divest from its U.S. wind business, while Shell said in January that it would “pause” its investment in the U.S. offshore wind industry and took an accompanying charge of $1 billion.
The combined company would be better positioned to compete with supermajors like Exxon, which is now worth over $450 billion, while Shell and BP have a combined valuation around $285 billion.

Three Mile Island Unit 1 will restart a year early, its owner Constellation said Wednesday. When Constellation and Microsoft announced the plan to restart the nuclear facility last fall they gave a target date of 2028. More recently, however, PJM Interconnection, the interstate electricity market that includes Pennsylvania, approved a request made from the state’s governor, Josh Shapiro, to fast-track the plant’s interconnection, the company said, meaning it could open as soon as 2027.
Constellation reported “significant progress” on hiring and training new workers, with around 400 workers either hired or due to start new jobs soon. “We’re on track to make history ahead of schedule, helping America achieve energy independence, supercharge economic growth, and win the global AI race,” Constellation’s chief executive Joe Dominguez said.
The Chinese electric carmarker BYD is addressing rising inventory and lower prices by cutting back its production plans. The company “has slowed its production and expansion pace in recent months by reducing shifts at some factories in China and delaying plans to add new production lines,” Reuters reported.
The slowdown comes “as it grapples with rising inventory even after offering deep price cuts in China's cutthroat auto market,” according to the Reuters report.
In 2024, BYD beat out Tesla in annual sales, with over 4 million cars sold, for a total annual revenue over $100 billion. Tesla’s revenue was just short of $100 billion last year.
While BYD’s factories may be slowing down, it is still looking to expand, especially overseas. In April, more than 7,000 BYD battery electric cars were registered in Europe, according to Bloomberg. This more-than-doubling since last year slingshotted BYD past Tesla on the continent, where its sales have fallen by almost 50%.
“Where does the power sector go from here?” an audience member asked at our exclusive Heatmap subscriber event in New York on Wednesday, referring to a potential future without the Inflation Reduction Act. “Higher costs,” Emily Pontecorvo answered. There is one potential bright spot, however, as Robinson Meyer explained: “If I were a Democrat considering running an affordability campaign or a cost-of-living campaign in ’26 or ’28, there’s lots of openings to talk about clean energy — the policy that’s happening right now — utility rates, and energy affordability.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
How will America’s largest grid deal with the influx of electricity demand? It has until the end of the year to figure things out.
As America’s largest electricity market was deliberating over how to reform the interconnection of data centers, its independent market monitor threw a regulatory grenade into the mix. Just before the Thanksgiving holiday, the monitor filed a complaint with federal regulators saying that PJM Interconnection, which spans from Washington, D.C. to Ohio, should simply stop connecting new large data centers that it doesn’t have the capacity to serve reliably.
The complaint is just the latest development in a months-long debate involving the electricity market, power producers, utilities, elected officials, environmental activists, and consumer advocates over how to connect the deluge data centers in PJM’s 13-state territory without further increasing consumer electricity prices.
The system has been pushed into crisis by skyrocketing capacity auction prices, in which generators get paid to ensure they’re available when demand spikes. Those capacity auction prices have been fueled by high-octane demand projections, with PJM’s summer peak forecasted to jump from 154 gigawatts to 210 gigawatts in a decade. The 2034-35 forecast jumped 17% in just a year.
Over the past two two capacity auctions, actual and forecast data center growth has been responsible for over $16.6 billion in new costs, according to PJM’s independent market monitor; by contrast, the previous year’s auction generated a mere $2.2 billion. This has translated directly to higher retail electricity prices, including 20% increases in some parts of PJM’s territory, like New Jersey. It has also generated concerns about reliability of the whole system.
PJM wants to reform how data centers interconnect before the next capacity auction in June, but its members committee was unable to come to an agreement on a recommendation to PJM’s board during a November meeting. There were a dozen proposals, including one from the monitor; like all the others, it failed to garner the necessary two-thirds majority vote to be adopted formally.
So the monitor took its ideas straight to the top.
The market monitor’s complaint to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission tracks closely with its plan at the November meeting. “PJM is currently proposing to allow the interconnection of large new data center loads that it cannot serve reliably and that will require load curtailments (black outs) of the data centers or of other customers at times. That result is not consistent with the basic responsibility of PJM to maintain a reliable grid and is therefore not just and reasonable,” the filing said. “Interconnecting large new data center loads when adequate capacity is not available is not providing reliable service.”
A PJM spokesperson told me, “We are still reviewing the complaint and will reserve comment at this time.”
But can its board still get a plan to FERC and avoid another blowout capacity auction?
“PJM is going to make a filing in December, no matter what. They have to get these rules in place to get to that next capacity auction in June,” Jon Gordon, policy director at Advanced Energy United, told me. “That’s what this has been about from the get-go. Nothing is going to stop PJM from filling something.”
The PJM spokesperson confirmed to me that “the board intends to act on large load additions to the system and is expected to provide an indication of its next steps over the next few weeks.” But especially after the membership’s failure to make a unified recommendation, what that proposal will be remains unclear. That has been a source of agita for the organizations’ many stakeholders.
“The absence of an affirmative advisory recommendation from the Members Committee creates uncertainty as to what reforms PJM’s Board of Managers may submit to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), and when stakeholders can expect that submission,” analysts at ClearView Energy Partners wrote in a note to clients. In spite of PJM’s commitments, they warned that the process could “slip into January,” which would give FERC just enough time to process the submission before the next capacity auction.
One idea did attract a majority vote from PJM’s membership: Southern Maryland Electric Cooperative’s, which largely echoed the PJM board’s own plan with some amendments. That suggestion called for a “Price Responsive Demand” system, in which electricity customers would agree to reduce their usage when wholesale prices spike. The system would be voluntary, unlike an earlier PJM proposal, which foresaw forcing large customers to curtail their power. “The load elects to not take on a capacity obligation, therefore does not pay for capacity, and is required to reduce demand during stressed system conditions,” PJM explained in an update. The Southern Maryland plan tweaks the PRD system to adjust its pricing mechanism. but largely aligns with what PJM’s staff put forward.
“There’s almost no real difference between the PJM proposal and that Southern Maryland proposal,” Gordon told me.
That might please restive stakeholders, or at least be something PJM’s board could go forward with knowing that the balance of its voting membership agreed with something similar.
“We maintain our view that a final proposal could resemble the proposed solution package from PJM staff,” the ClearView note said. “We also think the Board could propose reforms to PJM’s PRD program. Indeed, as noted above, SMECO’s revisions to the service gained majority support.”
The PJM plan also included relatively uncontroversial reforms to load forecasting to cut down on duplicated requests and better share information, and an “expedited interconnection track” on which new, large-scale generation could be fast-tracked if it were signed off on by a state government “to expedite consideration of permitting and siting.”
Gordon said that the market monitor’s complaint could be read as the organization “desperately trying to get FERC to weigh in” on its side, even if PJM is more likely to go with something like its own staff-authored submission.
“The key aspect of the market monitor’s proposal was that PJM should not allow a data center to interconnect until there was enough generation to supply them,” Gordon explained. During the meeting preceding the vote, “PJM said they didn’t think they had the authority to deny someone interconnection.”
This dispute over whether the electricity system has an obligation to serve all customers has been the existential question making the debate about how to serve data centers extra angsty.
But PJM looks to be trying to sidestep that big question and nibble around the edges of reform.
“Everybody is really conflicted here,” Gordon told me. “They’re all about protecting consumers. They don’t want to see any more increases, obviously, and they want to keep the lights on. Of course, they also want data center developers in their states. It’s really hard to have all three.”
Atomic Canyon is set to announce the deal with the International Atomic Energy Agency.
Two years ago, Trey Lauderdale asked not what nuclear power could do for artificial intelligence, but what artificial intelligence could do for nuclear power.
The value of atomic power stations to provide the constant, zero-carbon electricity many data centers demand was well understood. What large language models could do to make building and operating reactors easier was less obvious. His startup, Atomic Canyon, made a first attempt at answering that by creating a program that could make the mountains of paper documents at the Diablo Canyon nuclear plant, California’s only remaining station, searchable. But Lauderdale was thinking bigger.
In September, Atomic Canyon inked a deal with the Idaho National Laboratory to start devising industry standards to test the capacity of AI software for nuclear projects, in much the same way each update to ChatGPT or Perplexity is benchmarked by the program’s ability to complete bar exams or medical tests. Now, the company’s effort is going global.
On Wednesday, Atomic Canyon is set to announce a partnership with the United Nations International Atomic Energy Agency to begin cataloging the United Nations nuclear watchdog’s data and laying the groundwork for global standards of how AI software can be used in the industry.
“We’re going to start building proof of concepts and models together, and we’re going to build a framework of what the opportunities and use cases are for AI,” Lauderdale, Atomic Canyon’s chief executive, told me on a call from his hotel room in Vienna, Austria, where the IAEA is headquartered.
The memorandum of understanding between the company and the UN agency is at an early stage, so it’s as yet unclear what international standards or guidelines could look like.
In the U.S., Atomic Canyon began making inroads earlier this year with a project backed by the Institute of Nuclear Power Operators, the Nuclear Energy Institute, and the Electric Power Research Institute to create a virtual assistant for nuclear workers.
Atomic Canyon isn’t the only company applying AI to nuclear power. Last month, nuclear giant Westinghouse unveiled new software it’s designing with Google to calculate ways to bring down the cost of key components in reactors by millions of dollars. The Nuclear Company, a startup developer that’s aiming to build fleets of reactors based on existing designs, announced a deal with the software behemoth Palantir to craft the software equivalent of what the companies described as an “Iron Man suit,” able to swiftly pull up regulatory and blueprint details for the engineers tasked with building new atomic power stations.
Lauderdale doesn’t see that as competition.
“All of that, I view as complementary,” he said.
“There is so much wood to chop in the nuclear power space, the amount of work from an administrative perspective regarding every inch of the nuclear supply chain, from how we design reactors to how we license reactors, how we regulate to how we do environmental reviews, how we construct them to how we maintain,” he added. “Every aspect of the nuclear power life cycle is going to be transformed. There’s no way one company alone could come in and say, we have a magical approach. We’re going to need multiple players.”
That Atomic Canyon is making inroads at the IAEA has the potential to significantly broaden the company’s reach. Unlike other energy sources, nuclear power is uniquely subject to international oversight as part of global efforts to prevent civilian atomic energy from bleeding over into weapons production.
The IAEA’s bylaws award particular agenda-setting powers to whatever country has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors. In the nearly seven decades since the agency’s founding, that nation has been the U.S. As such, the 30 other countries with nuclear power have largely aligned their regulations and approaches to the ones standardized in Washington. When the U.S. artificially capped the enrichment levels of traditional reactor fuel at 5%, for example, the rest of the world followed.
That could soon change, however, as China’s breakneck deployment of new reactors looks poised to vault the country ahead of the U.S. sometime in the next decade. It wouldn’t just be a symbolic milestone. China’s emergence as the world’s preeminent nuclear-powered nation would likely come with Beijing’s increased influence over other countries’ atomic energy programs. As it is, China is preparing to start exporting its reactors overseas.
The role electricity demand from the data centers powering the AI boom has played in spurring calls for new reactors is undeniable. But if AI turns out to have as big an impact on nuclear operations as Lauderdale predicts, an American company helping to establish the global guidelines could help cement U.S. influence over a potentially major new factor in how the industry works for years, if not decades to come.
Current conditions: The Northeastern U.S. is bracing for 6 inches of snow, including potential showers in New York City today • A broad swath of the Mountain West, from Montana through Colorado down to New Mexico, is expecting up to six inches of snow • After routinely breaking temperature records for the past three years, Guyana shattered its December high with thermometers crossing 92 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Department of Energy gave a combined $800 million to two projects to build what could be the United States’ first commercial small modular reactors. The first $400 million went to the federally owned Tennessee Valley Authority to finance construction of the country’s first BWRX-300. The project, which Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin called the TVA’s “big swing at small nuclear,” is meant to follow on the debut deployment of GE-Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s 300-megawatt SMR at the Darlington nuclear plant in Ontario. The second $400 million grant backed Holtec International’s plan to expand the Palisades nuclear plant in Michigan where it’s currently working to restart with the company’s own 300-megawatt reactor. The funding came from a pot of money earmarked for third-generation reactors, the type that hew closely to the large light water reactors that make up nearly all the U.S. fleet of 94 commercial nuclear reactors. While their similarities with existing plants offer some benefits, the Trump administration has also heavily invested in incentives to spur construction of fourth-generation reactors that use coolants other than water. “Advanced light-water SMRs will give our nation the reliable, round-the-clock power we need to fuel the President’s manufacturing boom, support data centers and AI growth, and reinforce a stronger, more secure electric grid,” Secretary of Energy Chris Wright said in a statement. “These awards ensure we can deploy these reactors as soon as possible.”
You know who also wants to see more investment in SMRs? Arizona senator and rumored Democratic presidential hopeful Ruben Gallego, who released an energy plan Wednesday calling on the Energy Department to ease the “regulatory, scaling, and supply chain challenges” new reactors still face.
Since he first emerged on the political scene a decade ago, President Donald Trump has made the proverbial forgotten coal miner a central theme of his anti-establishment campaigns, vowing to correct for urbanite elites’ neglect by putting workers’ concerns at the forefront. Yet his administration is now considering overhauling black lung protections that miners lobbied federal agencies to enact and enforce. Secretary of Labor Lori Chavez-DeRemer will “reconsider and seek comments” on parts of the Biden-era silica rule that mining companies and trade groups are challenging in court, the agency told E&E News. It’s unclear how the Trump administration may seek to alter the regulation. But the rule, finalized last year, reduced exposure limits for miners to airborne silica crystals that lodge deep inside lung tissue to 50 micrograms from the previous 100 microgram limit. The rule also required companies to provide expanded medical tests to workers. Dozens of miners and medical advocates protested outside the agency’s headquarters in Washington in October to request that the rule, expected to prevent more than 1,000 deaths and 3,700 cases of black lung per year, be saved.
Rolling back some of the protections would be just the latest effort to gut Biden-era policy. On Wednesday, the White House invited automotive executives to attend what’s expected to be an announcement to shred fuel-efficiency standards for new vehicles, The New York Times reported late on Tuesday.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
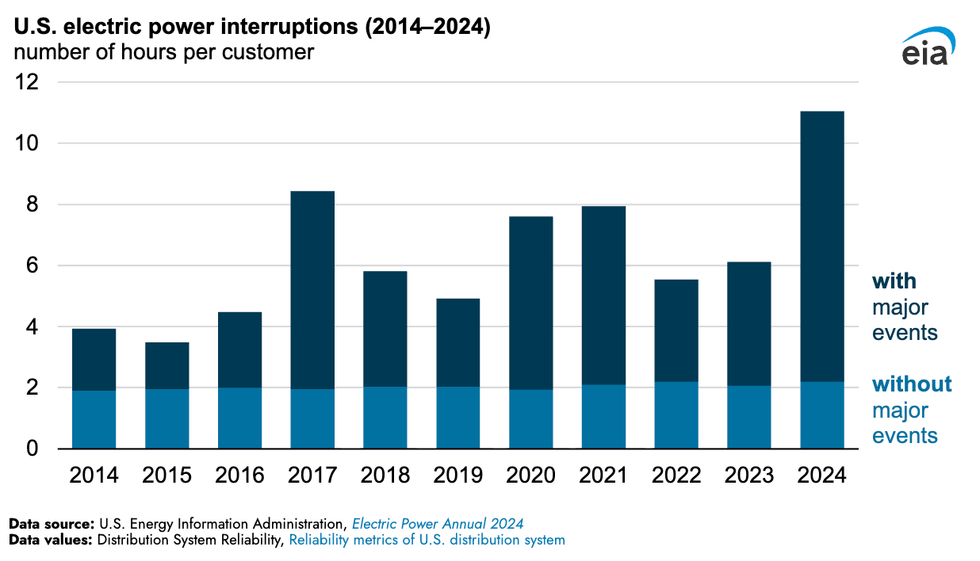
The average American spent a combined 11 hours without electricity last year as a result of extreme weather, worse outages than during any previous year going back a decade. That’s according to the latest analysis by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Blackouts attributed to major events averaged nearly nine hours in 2025, compared to an average of roughly four hours per year in 2014 through 2023. Major hurricanes accounted for 80% of the hours without electricity in 2024.
The latest federal grants may be good news for third-generation SMRs, but one of the leading fourth-generation projects — the Bill Gates-owned TerraPower’s bid to build a molten salt-cooled reactor at a former coal plant in Wyoming — just cleared the final safety hurdle for its construction permit. Calling the approval a “momentous occasion for TerraPower,” CEO Chris Levesque said the “favorable safety evaluation from the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission reflects years of rigorous evaluation, thoughtful collaboration with the NRC, and an unwavering commitment to both safety and innovation.”
TerraPower’s project in Kemmerer, Wyoming, is meant to demonstrate the company’s reactors, which are designed to store power when it’s needed — making them uniquely complementary to grids with large amounts of wind and solar — to avoid the possibility of a meltdown. Still, at a private lunch I attended in October, Gates warned that the U.S. is falling behind China on nuclear power. China is charging ahead on all energy fronts. On Tuesday, Bloomberg reported that the Chinese had started up a domestically-produced gas turbine for the first time as the country seeks to compete with the U.S. on even the fossil fuels American producers dominate.
It’s been a rough year for green hydrogen projects as the high cost of producing the zero-carbon fuel from renewable electricity and water makes finding customers difficult for projects. Blue hydrogen, the version of the fuel made with natural gas equipped with carbon capture equipment, isn’t doing much better. Last month, Exxon Mobil Corp. abandoned plans to build what would have been one of the world’s largest hydrogen production plants in Baytown, Texas. This week, BP withdrew from a blue hydrogen project in England. At issue are strict new standards in the European Union for how much carbon blue hydrogen plants would need to capture to qualify as clean.
You’re not the only one accidentally ingesting loads of microplastics. New research suggests crickets can’t tell the difference between tiny bits of plastics and natural food sources. Evidence shows that crickets can break down microplastics into smaller nanoplastics — which may be even worse in the environment since they’re more easily eaten or absorbed by other lifeforms.