You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The carbon removal company has a pitch to solve the industry’s biggest “moral hazard.”
The carbon removal industry has exploded over the past few years, with billions of dollars in government funding and venture capital flowing to startups, nonprofits, and university research centers working on different ways to pull carbon out of the atmosphere. But all the attention has also stirred up a long running controversy about whether this solution is a dangerous distraction.
Critics worry that governments and corporations will not work as hard to cut greenhouse gas emissions if they believe they’ll eventually be able to reverse them. Some have warned this is already happening. On Thursday, Climeworks, one of the leading companies developing machines that suck carbon dioxide from the air, published a manifesto of sorts to fend off the risk that its technology is used to delay climate action.
The Swiss company’s statement calls for “a clear distinction between emissions reductions and carbon removals” in corporate and national climate plans and in the carbon market. It can be read as a pitch to improve the ever-popular but dangerously vague net-zero pledge. In theory, a plan to achieve net-zero emissions should involve both reducing emissions and then reaching a sort of equilibrium where any remaining releases are canceled out by removing carbon from the atmosphere.
The problem with net zero is it puts a lot more emphasis on the second part, and doesn’t require much transparency about the first. For example, a clothing brand pledging to achieve net zero by 2050 might buy renewable energy to power its stores, but avoid making more difficult changes to its production process or supply chain to reduce emissions, with the vague intention to balance them out later.
Climeworks is urging companies and governments to instead set two separate targets: One for how much they plan to reduce their carbon output, and a second for the level of remaining emissions they plan to balance out with carbon removal. It’s an idea with roots in academia; a 2019 paper argued that unpacking net-zero goals this way would help ensure that investments in carbon removal are truly additional to essential investments in emissions reductions.
“What we are saying is that removals should not stand as an excuse to not reduce your emissions,” said Louis Uzor, the climate policy manager at Climeworks.
The prospect of removing carbon from the atmosphere is undeniably seductive. “Depending on how you look at things, the technology represents either the ultimate insurance policy or the ultimate moral hazard,” New Yorker writer Elizabeth Kolbert wrote in a 2017 story about the kinds of machines that Climeworks is building.
It’s not hard to see how the fantasy version could turn into a nightmare. Our future ability to remove carbon will be limited by all kinds of constraints, like clean energy availability, land use, finance, and community support. If we operate under the assumption that we’ll be able to remove huge amounts of carbon from the atmosphere in a few decades, and that capacity doesn’t materialize, we could end up with more catastrophic warming — and still be far off from stabilizing the climate.
“Carbon removal capacity is going to be finite,” said Holly Buck, an assistant professor of environment and sustainability at the University of Buffalo. “Its in our interest to really constrain the residual emissions to the smallest amount possible to make sure that we can, in fact, compensate for them.”
At first glance, it may seem like Climeworks’ manifesto undermines its entire business model. Carbon removal "has a different role to play and should not be substituting emission reductions,” the statement reads. But today, companies like H&M and Square pay Climeworks for carbon removal to compensate for some of their emissions. Even the band Coldplay has bought credits to offset emissions from its tour.
Uzor argues its clients are not purchasing removals in place of cutting emissions. Paying Climeworks to remove carbon is still really expensive — upwards of $600 per metric ton of carbon. “It’s quite obvious that if you can reduce [emissions] for even up to $200 per ton, you’re still better off reducing than going with Climeworks,” he said. Rather, customers are lining up because they have emissions that are considered “hard to abate,” meaning there may not be any way to eliminate them for a long time. Uzor said their clients understand that if they want to achieve net zero in the next few decades, “they better start working with us now, because we have a whole industry that needs to scale up.”
Buck, of the University of Buffalo, pointed out that making it the norm to set a carbon removal goal could actually be great for Climeworks’ business. She’s optimistic that the company’s message comes from a place of genuine concern, but she thinks governments should be the ones leading the way by setting stronger requirements to cut emissions. “If people in the private sector are going to try to basically create policy in the absence of governments doing it, this seems good, but I don't think it’ll solve all the problems.”
Gilles Dufrasne, a lead on global carbon markets at the nonprofit Carbon Market Watch, said his organization supports the ideas in the statement, noting that this clear distinction would bring more transparency to climate plans and progress.
Climeworks’ statement also included a second, related plea. The company wants carbon credit certifiers to distinguish between projects that reduce or avoid emissions, like a wind farm or protection of a forest that might otherwise be chopped down, and those that remove carbon from the atmosphere, like Climeworks’ direct air capture plants. Thus far, Uzor said, Climeworks has refrained from working with large carbon registries like Verra or the American Carbon Registry, where many companies go to buy carbon offsets, because it couldn’t compete in that environment as long as its projects were lumped together with those that reduce emissions, which sell offsets for a fraction of the price.
This is another delicate subject. The growth of carbon removal projects is colliding with major tumult in the carbon market. Traditional carbon offset projects that purport to reduce emissions have been raked over the coals by researchers and journalists who have found time and again that those projects exaggerated their benefits. Derik Broekhoff, a senior scientist at the Stockholm Environment Institute, said that the Science Based Targets Initiative, a nonprofit that creates voluntary standards for corporate climate action, has also begun discouraging companies from buying these kinds of offsets while encouraging investments in carbon removal. “It’s led to this kind of perverse outcome where everyone’s chasing removals,” said Derik Broekhoff, a senior scientist at the Stockholm Environment Institute. “Yet if you look at a global level, what we really need to do is reduce emissions rapidly and significantly. So it ends up being a bit of a distraction.”
Uzor said some have opposed the idea to clearly separate removals because it could make them seem like a superior product. But he insisted that wasn’t Climework’s intent. “Currently, global emissions are still on the rise, so any avoided emission that is timely and properly done, based on robust assessment, is massively needed.”
It doesn’t seem like this will end up being such a big ask. Verra, the largest carbon offset registry in the world, plans to introduce a “removals” label in the middle of this year, said Anne Thiel, Verra’s senior manager of communications in an email.
But shoring up the integrity of the market is another question altogether — and one where Climeworks does have a clear advantage. The benefits of a direct air capture project are pretty easy to measure, but other types of carbon removal projects, like those that involve storing carbon in soil or sinking it to the bottom of the ocean, will be a lot harder to verify.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The surge in electricity demand from data centers is making innovation a necessity.
Electric utilities aren’t exactly known as innovators. Until recently, that caution seemed perfectly logical — arguably even preferable. If the entity responsible for keeping the lights on and critical services running decides to try out some shiny new tech that fails, heating, cooling, medical equipment, and emergency systems will all trip offline. People could die.
“It’s a very conservative culture for all the right reasons,” Pradeep Tagare, a vice president at the utility National Grid and the head of its corporate venture fund, National Grid Partners, told me. “You really can’t follow the Silicon Valley mantra of move fast, break things. You are not allowed to break things, period.”
But with artificial intelligence-driven load growth booming, customer bills climbing, and the interconnection queue stubbornly backlogged, utilities now face little choice but to do things differently. The West Coast’s Pacific Gas and Electric Company now has a dedicated grid-innovation team of about 60 people; North Carolina-based utility Duke Energy operates an emerging technologies office; and National Grid, which serves U.S. customers in the Northeast, has invested in about 50 startups to date. Some 64% of utilities have expanded their innovation budgets in the past year, according to research by NGP, while 42% reported working with startups in some capacity.
The innovators on these teams are well aware that their reputation precedes them when it comes to bringing novel tech to market — and not in a flattering way. “I think historically we’ve done a poor job partnering with too many companies and spreading ourselves thin,” Quinn Nakayama, the senior director of grid research, innovation, and development at PG&E, told me. That’s led to a pattern known as “death by pilot,” in which utilities trial many promising solutions but are too risk-averse, cost-conscious, and slow-moving to deploy them, leaving the companies with no natural customers.
It doesn’t help that regulators such as public utilities commissions understandably require new investments to meet a strict “prudency” standard, proving that they can achieve the desired result at the lowest reasonable cost consistent with good practices. Yet this can be a high bar for tech that’s yet untested at scale. And because investor-owned utilities earn a guaranteed rate of return on approved infrastructure investments, they’re incentivized to pursue capital-intensive projects over smaller efficiency improvements. Freedom from the pressure of a competitive market has also traditionally meant freedom from the pressure to innovate.
But that’s changing.
To help bridge at least some of these divides, NGP set up a business development unit specifically for startups. “Their sole job is to work with our portfolio companies, work with our business units, and make sure that these things get deployed,” Tagare told me. Over 80% of the firm’s portfolio companies, he said, now have tie-ups of some sort with National Grid — be that a pilot or a long-term deployment — while “many” have secured multi-million dollar contracts with the utility.
While Tagare said that NGP is already reaping the benefits from investments in AI to streamline internal operations and improve critical services, hardware is slower to get to market. The startups in this category run the gamut from immediately deployable technologies to those still five or more years from commercialization. LineVision, a startup operating across parts of National Grid’s service territories in upstate New York and the U.K., is a prime example of the former. Its systems monitor the capacity of transmission lines in real-time via sensors and environmental data analytics, thus allowing utilities to safely push 20% to 30% more power through the wires as conditions permit.
There’s also TS Conductor, a materials science startup that’s developed a novel conductor wire with a lightweight carbon core and aluminum coating that can double or triple a line’s capacity without building new towers and poles. It’s a few years from achieving the technical and safety validation necessary to become an approved supplier for National Grid. Then five or more years down the line, NGP hopes to be able to deploy the startup Veir’s superconductors, which promise to boost transmission capacity five- to tenfold with materials that carry electricity with virtually zero resistance. But because this requires cooling the lines to cryogenic temperatures — and the bulky insulation and cooling systems need to do so — it necessitates a major infrastructure overhaul.
PG&E, for its part, is pursuing similar efficiency goals as it trials tech from startups including Heimdell Power and Smart Wires, which aim to squeeze more power out of the utility’s existing assets. But because the utility operates in California — the U.S. leader in EV adoption, with strong incentives for all types of home electrification — it’s also focused on solutions at the grid edge, where the distribution network meets customer-side assets like smart meters and EV charging infrastructure.
For example, the utility has a partnership with smart electric panel maker Span, which allows customers to adopt electric appliances such as heat pumps and EV chargers without the need for expensive electrical upgrades. Span’s device connects directly to a home’s existing electric panel, enabling PG&E to monitor and adjust electricity use in real time to prevent the panel from overloading while letting customers determine what devices to prioritize powering. Another partnership with smart infrastructure company Itron has similar aims — allowing customers to get EV fast chargers without a panel upgrade, with the company’s smart meters automatically adjusting charging speed based on panel limits and local grid conditions.
Of course, it’s natural to question how motivated investor-owned utilities really are to deploy this type of efficiency tech — after all, the likes of PG&E and National Grid make money by undertaking large infrastructure projects, not by finding clever means of avoiding them. And while both Nakayama and Tagare can’t deny what appears to be a fundamental misalignment of incentives, they both argue that there’s so much infrastructure investment needed — more than they can handle — that the friction is a non-issue.
“We have capital coming out of our ears,” Nakayama told me. Given that, he said, PG&E’s job is to accelerate interconnection for all types of loads, which will bring in revenue to offset the cost of the upgrades and thus lower customer rates. Tagare agreed.
“At least for the next — pick a number, five, seven, 10 years — I don’t see any of this slowing down,” he said.
And yet despite all that capital flow, PG&E still carries billions of dollars in wildfire-related financial obligations after its faulty equipment was found liable for sparking a number of blazes in Northern California in 2017 and 2018. The resulting legal claims drove the utility into bankruptcy in 2019, before it restructured and reemerged the following year. But the threat of wildfires in its service territory still looms large, which Nakayama said limits the company’s ability to allocate funds toward the basic poles and wires upgrades that are so crucial for easing the congested interconnection queue and bringing new load online.
Nakayama wants California’s legislature and courts to revise rules that make utilities strictly liable for wildfires caused by their equipment, even when all safety and mitigation procedures were followed. “In order for me to feel comfortable moving some of my investments out of wildfire into other areas of our business in a more accelerated fashion, I have to know that if I make the prudent investments for wildfire risk mitigation, I’m not going to be held liable for everything in my system,” he told me.
And while wildfire prevention itself is an area rich with technical innovation and a central focus of the utility’s startup ecosystem, Nakayama emphasizes that PG&E has a host of additional priorities to consider. “We need [virtual power plants]. We need new technologies. We need new investments. We need new capital. We need new wildfire-related liability,” he told me.
Utilities — especially his — rarely get seen as the good guys in this story. “I know that PGE gets vilified a lot,” Nakayama acknowledged. But he and his colleagues are “almost desperate to try to figure out how to bring down rates,” he promised.
Current conditions: The Central United States is facing this year’s largest outbreak of severe weather so far, with intense thunderstorms set to hit an area stretching from Texas to the Great Lakes for the next four days • Northern India is sweltering in temperatures as high as 13 degrees Celsius above historical norms • Australia issued evacuation alerts for parts of Queensland as floodwaters inundate dozens of roads.
The price of futures contracts for crude oil fell below $85 per barrel Monday after President Donald Trump called the war against Iran “very complete, pretty much,” declaring that there was “nothing left in a military sense” in the country. “They have no navy, no communications, they’ve got no air force. Their missiles are down to a scatter. Their drones are being blown up all over the place, including their manufacturing of drones,” Trump told CBS News in a phone interview Monday. “If you look, they have nothing left.”
The dip, just a day after prices surged well past $100 per barrel, highlights what Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin described as the challenge of depending too much on fossil fuels for a payday. “Even $85 is substantially higher than the $57 per barrel price from the end of last year. At that point, forecasters from both the public and the private sectors were expecting oil to stick around $60 a barrel through 2026,” he wrote. “Of course, crude oil itself is not something any consumer buys — but those high prices would likely feed through to higher consumer prices throughout the U.S. economy.”
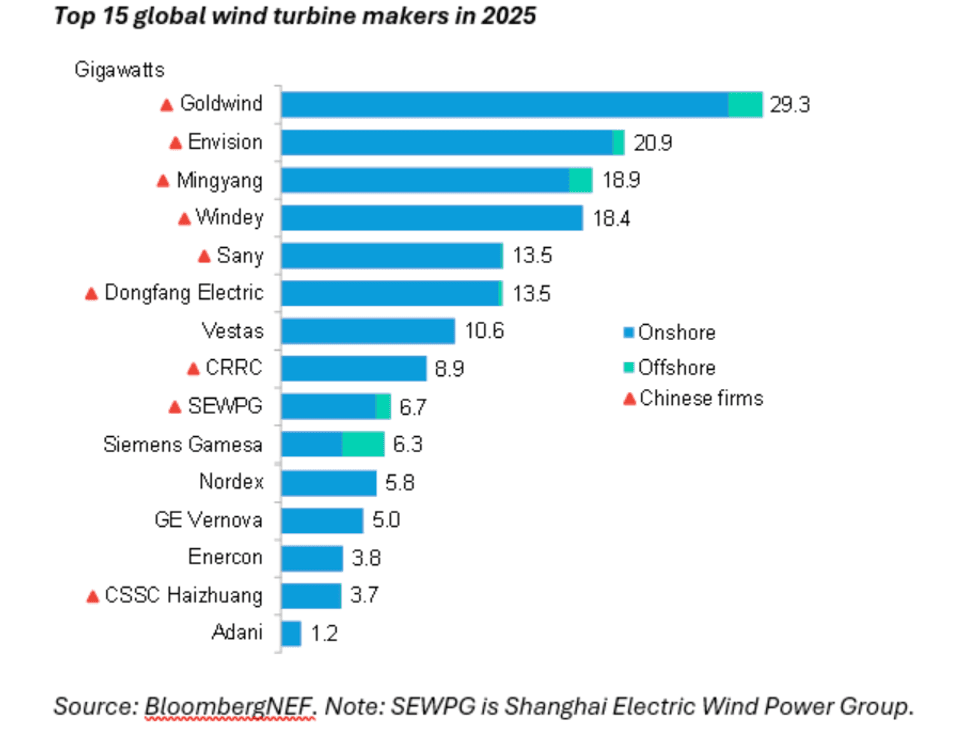
The global wind industry set a record last year, adding 169 gigawatts of turbines throughout 2025, according to the latest analysis from the consultancy BloombergNEF. The 38% surge compared to 2024 came as the momentum in the sector shifted to Asia. Chinese companies made up eight of the top 10 global wind turbine suppliers, the report found, as domestic installations in the People’s Republic reached an all-time high. India, meanwhile, edged out the U.S. and Germany as the world’s second largest market after China. Of all global wind additions, 161 gigawatts, or 95%, were onshore turbines, mostly spurred on by the domestic boom in China. Not only did that same building blitz help Beijing-based Goldwind hold onto its top spot as the world’s leading turbine supplier, it vaulted Chinese manufacturers into the next five slots in the global ranking. “Thanks to stable long-term policy support, wind installations over the past decade have become increasingly concentrated in mainland China,” Cristian Dinca, wind associate at BloombergNEF and lead author of the report, said in a statement. “Chinese manufacturers consistently top the global rankings. They benefitted particularly in 2025, as companies and provinces rushed to commission projects ahead of power market reforms and to meet targets set out in the Five Year Plan.”
Like in solar and batteries, the domestic boom in China is starting to spill over abroad. As Matthew wrote last year, Chinese manufacturers are making a big push into the European market.
Arizona’s utility regulator has repealed rules requiring electricity providers to generate at least 15% of their energy from renewables. Citing “dramatic” changes to the renewable energy landscape, the Arizona Corporation Commission said the cost to ratepayers of the rules adopted two decades ago was no longer justifiable, Utility Dive reported Monday. Since the rules first took effect in 2006, the utilities Arizona Public Services, Tucson Electric Power, and UniSource Energy Services “have collected more than $2.3 billion” in “surcharges from all customer classes to meet these mandates,” the regulator said in a press release following the March 4 ruling. “The mandates are no longer needed and the costs are no longer justified.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Reflect Orbital wants to launch 50,000 giant mirrors into space to bounce sunlight to the night side of the planet to power solar farms after sunset, provide lighting to rescue workers, and light city streets. Now, The New York Times reported Monday, the Hawthorne, California-based startup is asking the Federal Communications Commission for permission to send its first prototype satellite into space with a 60-foot-wide mirror. The company, which has raised more than $28 million from investors, could launch its test project as early as this summer. The public comment period on the FCC application closed yesterday. “We’re trying to build something that could replace fossil fuels and really power everything,” Ben Nowack, Reflect Orbital’s chief executive, told the newspaper.
It’s emblematic of the kind of audacious climate interventions on which investors are increasingly gambling. Last fall, Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer broke news that Stardust Solutions, a startup promising to artificially cool the planet by spraying aerosols into the atmosphere that reflect the sun’s light back into space, had raised $60 million to commercialize its technology. In December, Heatmap’s Katie Brigham had a scoop on the startup Overview Energy raising $20 million to build panels in space and beam solar power back down to Earth.
Emerald AI is a startup whose software Katie wrote last year “could save the grid” by helping data centers to ramp electricity usage up and down like a smart thermostat to allow more computing power to come online on the existing grid. InfraPartners is a company that designs, manufactures, and deploys prefabricated, modular data centers parts. You don’t need to be an expert in the data center industry’s energy problems to hear the wedding bells ringing. On Tuesday, the two companies announced a deal to partner on what they’re calling “flex-ready data centers,” a version of InfraPartners’ off the shelf computing hardware that comes equipped with Emerald AI’s software. “Building more infrastructure the way we have historically will not be fast enough. We need to make the infrastructure we have more intelligent by leveraging AI,” Bal Aujla, InfraPartners’ director of advanced research and engineering, said in a statement. “This partnership will turn data centers from grid constraints into grid partners and unlock more usable capacity from existing infrastructure. The result will be enhanced AI deployment without compromising reliability or sustainability.” Rather than rush to invest in big new power plants, Emerald AI chief scientist Ayse Coskun said making data centers flexible means “we can prudently expand our grid.”
War in Iran may be halting shipments of oil and liquified natural gas out of the Persian Gulf. But that isn’t stopping Chinese clean energy manufacturers from preparing to send shipments toward the war-torn region. Despite the conflict, the Jiangsu-based Shuangliang announced last week that it had delivered 80 megawatts of electrolyzers to a Chinese port for shipment to a 300-megawatt green hydrogen and ammonia plant in the special economic zone in Duqm, Oman. I know what you’re going to say: Oman’s status as the region’s Switzerland — a diplomatic powerhouse with a modern history of strategic neutrality in even the most heated geopolitical conflicts — means it isn’t a target for Iranian missiles. And there’s no guarantee the shipment will head there immediately. But it’s a sign of how determined China’s electrolyzer industry is to sell its hardware overseas amid inklings of a domestic slowdown.
Topsy turvy oil prices aren’t great for the U.S.
Oil prices are all over the place as markets reopened this week, climbing as high as $120 a barrel before crashing to around $85 after Donald Trump told CBS News that the war with Iran “is very complete, pretty much,” and that he was “thinking about taking it over,” referring to the Strait of Hormuz, the artery through which about a third of the world’s traded oil flows.
Even $85 is substantially higher than the $57 per barrel price from the end of last year. At that point, forecasters from both the public and the private sectors were expecting oil to stick around $60 a barrel through 2026.
Of course, crude oil itself is not something any consumer buys — but those high prices would likely feed through to higher consumer prices throughout the U.S. economy. That includes the price of gasoline, of course, which has risen by about $0.50 a gallon in the past month, according to AAA, — and jet fuel, which will mean increased travel costs. “Book your airfares now if they haven’t moved already,” Skanda Amarnath, the executive director of the economic policy think tank Employ America, told me.
High oil prices also raise the price of goods and services not directly linked to oil prices — groceries, for instance. “The cost of food, especially at the grocery store, is a function of the cost of diesel,” which fuels the trucks that get food to shelves, Amarnath told me. Diesel prices have risen even more than gasoline in the past week, by over $0.85 a gallon.
“We’ll see how long these prices stay elevated, how they feed their way through the supply chain and the value chain. But it’s clearly the case that it is a pretty adverse situation for both businesses and consumers.”
The oil market is going through one of the largest physical shocks in its modern history. Bloomberg’s Javier Blas estimates that of the 15 million barrels per day that regularly flow through the Strait of Hormuz, only about a third is getting through to the global market, whether through the strait itself or by alternative routes, such as the pipeline from Saudi Arabia’s eastern oil fields to the Red Sea.
Global daily oil production is just above 100 million barrels per day, meaning that around 10% of the oil supply on the market is stuck behind an effective blockade.
“The world is suddenly ‘short’ a volume that, in normal times, would dwarf almost any supply/demand imbalance we debate,” Morgan Stanley oil analyst Martjin Rats wrote in a note to clients on Sunday.
The fact that the U.S. is itself a leading producer and exporter of oil will only provide so much relief. Private sector economists have estimated that every $10 increase in the price of oil reduces economic growth somewhere between 0.1 and 0.2 percentage points.
“Petroleum product prices here in the U.S. tend to reflect global market conditions, so the price at the pump for gasoline and diesel reflect what’s going on with global prices,” Ben Cahill, a senior associate at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, told me. “What happens in the rest of the world still has a deep impact on U.S. energy prices.”
To the extent the U.S. economy benefits from its export capacity, the effects are likely localized to areas where oil production and export takes place, such as Texas and Louisiana. For the economy as a whole, higher oil prices will improve the “terms of trade,” essentially a measure of the value of imports a certain quantity of exports can “buy,” Ryan Cummings, chief of staff at Stanford Institute for Economic Policymaking, told me.
Could the U.S. oil industry ramp up production to capture those high prices and induce some relief?
Oil industry analysts, Heatmap founding executive editor Robinson Meyer, and the TV show Landman have all theorized that there is a “goldilocks” range of oil prices that are high enough to encourage exploration and production but not so high as to take out the economy as a whole. This range starts at around $60 or $70 on the low end and tops out at around $90 or $95. Above that, the economic damage from high prices would likely outweigh any benefit to drillers from expanded production.
And that’s if production were to expand at all.
“Capital discipline” has been the watchword of the U.S. oil and gas industry for years since the shale boom, meaning drillers are unlikely to chase price spikes by ramping up production heedlessly, CSIS’ Ben Cahill told me. “I think they’ll be quite cautious about doing that,” he said.