You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The fourth-generation gas-cooled reactor company ZettaJoule is setting up shop at an unnamed university.

The appeal of next-generation nuclear technology is simple. Unlike the vast majority of existing reactors that use water, so-called fourth-generation units use coolants such as molten salt, liquid metal, or gases that can withstand intense heat such as helium. That allows the machines to reach and maintain the high temperatures necessary to decarbonize industrial processes, which currently only fossil fuels are able to reach.
But the execution requirements of these advanced reactors are complex, making skepticism easy to understand. While the U.S., Germany, and other countries experimented with fourth-generation reactors in earlier decades, there is only one commercial unit in operation today. That’s in China, arguably the leader in advanced nuclear, which hooked up a demonstration model of a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor to its grid two years ago, and just approved building another project in September.
Then there’s Japan, which has been operating its own high-temperature gas-cooled reactor for 27 years at a government research site in Ibaraki Prefecture, about 90 minutes north of Tokyo by train. Unlike China’s design, it’s not a commercial power reactor. Also unlike China’s design, it’s coming to America.
Heatmap has learned that ZettaJoule, an American-Japanese startup led by engineers who worked on that reactor, is now coming out of stealth and laying plans to build its first plant in Texas.
For months, the company has quietly staffed up its team of American and Japanese executives, including a former U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission official and a high-ranking ex-administrator from the industrial giant Mitsubishi. It’s now preparing to decamp from its initial home base in Rockville, Maryland, to the Lone Star State as it prepares to announce its debut project at an as-yet-unnamed university in Texas.
“We haven’t built a nuclear reactor in many, many decades, so you have only a handful of people who experienced the full cycle from design to operations,” Mitsuo Shimofuji, ZettaJoule’s chief executive, told me. “We need to complete this before they retire.”
That’s where the company sees its advantage over rivals in the race to build the West’s first commercial high-temperature gas reactor, such as Amazon-backed X-energy or Canada’s StarCore nuclear. ZettaJoule’s chief nuclear office, Kazuhiko Kunitomi, oversaw the construction of Japan’s research reactor in the 1990s. He’s considered Japan’s leading expert in high-temperature gas reactors.
“Our chief nuclear officer and some of our engineers are the only people in the Western world who have experience of the whole cycle from design to construction to operation of a high temperature gas reactor,” Shimofuji said.
Like X-energy’s reactor, ZettaJoule’s design is a small modular reactor. With a capacity of 30 megawatts of thermal output and 12 megawatts of electricity, the ZettaJoule reactor qualifies as a microreactor, a subcategory of SMR that includes anything 20 megawatts of electricity or less. Both companies’ reactors will also run on TRISO, a special kind of enriched uranium with cladding on each pellet that makes the fuel safer and more efficient at higher temperatures.
While X-energy’s debut project that Amazon is financing in Washington State is a nearly 1-gigawatt power station made up of at least a dozen of the American startup’s 80-megawatt reactors, ZettaJoule isn’t looking to generate electricity.
The first new reactor in Texas will be a research reactor, but the company’s focus is on producing heat. The reactor already working in Japan, which produces heat, demonstrates that the design can reach 950 degrees Celsius, roughly 25% higher than the operating temperature of China’s reactor.
The potential for use in industrial applications has begun to attract corporate partners. In a letter sent Monday to Ted Garrish, the U.S. assistant secretary of energy in charge of nuclear power — a copy of which I obtained — the U.S. subsidiary of the Saudi Arabian oil goliath Aramco urged the Trump administration to support ZettaJoule, and said that it would “consider their application to our operations” as the technology matures. ZettaJoule is in talks with at least two other multinational corporations.
The first new reactor ZettaJoule builds won’t be identical to the unit in Japan, Shimofuji said.
“We are going to modernize this reactor together with the Japanese and U.S. engineering partners,” he said. “The research reactor is robust and solid, but it’s over-engineered. What we want to do is use the safety basis but to make it more economic and competitive.”
Once ZettaJoule proves its ability to build and operate a new unit in Texas, the company will start exporting the technology back to Japan. The microreactor will be its first product line.
“But in the future, we can scale up to 20 times bigger,” Shimofuji said. “We can do 600 megawatts thermal and 300 megawatts electric.”
Another benefit ZettaJoule can tap into is the sweeping deal President Donald Trump brokered with Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi in October, which included hundreds of billions of dollars for new reactors of varying sizes, including the large-scale Westinghouse AP1000. That included financing to build GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s 300-megawatt BWRX-300, one of the West’s leading third-generation SMRs, which uses a traditional water-cooled design.
Unlike that unit, however, ZettaJoule’s micro-reactor is not a first-of-a-kind technology, said Chris Gadomski, the lead nuclear analyst at the consultancy BloombergNEF.
“It’s operated in Japan for a long, long time,” he told me. “So that second-of-a-kind is an attractive feature. Some of these companies have never operated a reactor. This one has done that.”
A similar dynamic almost played out with large-scale reactors more than two decades ago. In the late 1990s, Japanese developers built four of GE and Hitachi’s ABWR reactor, a large-scale unit with some of the key safety features that make the AP1000 stand out compared to its first- and second-generation predecessors. In the mid 2000s, the U.S. certified the design and planned to build a pair in South Texas. But the project never materialized, and America instead put its resources into Westinghouse’s design.
But the market is different today. Electricity demand is surging in the near term from data centers and in the long term from electrification of cars and industry. The need to curb fossil fuel consumption in the face of worsening climate change is more widely accepted than ever. And China’s growing dominance over nuclear energy has rattled officials from Tokyo to Washington.
“We need to deploy this as soon as possible to not lose the experienced people in Japan and the U.S.,” Shimofuji said. “In two or three years time, we will get a construction permit ideally. We are targeting the early 2030s.”
If every company publicly holding itself to that timeline is successful, the nuclear industry will be a crowded field. But as history shows, those with the experience to actually take a reactor from paper to concrete may have an advantage.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
1. Marion County, Indiana — State legislators made a U-turn this week in Indiana.
2. Baldwin County, Alabama — Alabamians are fighting a solar project they say was dropped into their laps without adequate warning.
3. Orleans Parish, Louisiana — The Crescent City has closed its doors to data centers, at least until next year.
A conversation with Emily Pritzkow of Wisconsin Building Trades
This week’s conversation is with Emily Pritzkow, executive director for the Wisconsin Building Trades, which represents over 40,000 workers at 15 unions, including the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers, the International Union of Operating Engineers, and the Wisconsin Pipe Trades Association. I wanted to speak with her about the kinds of jobs needed to build and maintain data centers and whether they have a big impact on how communities view a project. Our conversation was edited for length and clarity.
So first of all, how do data centers actually drive employment for your members?
From an infrastructure perspective, these are massive hyperscale projects. They require extensive electrical infrastructure and really sophisticated cooling systems, work that will sustain our building trades workforce for years – and beyond, because as you probably see, these facilities often expand. Within the building trades, we see the most work on these projects. Our electricians and almost every other skilled trade you can think of, they’re on site not only building facilities but maintaining them after the fact.
We also view it through the lens of requiring our skilled trades to be there for ongoing maintenance, system upgrades, and emergency repairs.
What’s the access level for these jobs?
If you have a union signatory employer and you work for them, you will need to complete an apprenticeship to get the skills you need, or it can be through the union directly. It’s folks from all ranges of life, whether they’re just graduating from high school or, well, I was recently talking to an office manager who had a 50-year-old apprentice.
These apprenticeship programs are done at our training centers. They’re funded through contributions from our journey workers and from our signatory contractors. We have programs without taxpayer dollars and use our existing workforce to bring on the next generation.
Where’s the interest in these jobs at the moment? I’m trying to understand the extent to which potential employment benefits are welcomed by communities with data center development.
This is a hot topic right now. And it’s a complicated topic and an issue that’s evolving – technology is evolving. But what we do find is engagement from the trades is a huge benefit to these projects when they come to a community because we are the community. We have operated in Wisconsin for 130 years. Our partnership with our building trades unions is often viewed by local stakeholders as the first step of building trust, frankly; they know that when we’re on a project, it’s their neighbors getting good jobs and their kids being able to perhaps train in their own backyard. And local officials know our track record. We’re accountable to stakeholders.
We are a valuable player when we are engaged and involved in these sting decisions.
When do you get engaged and to what extent?
Everyone operates differently but we often get engaged pretty early on because, obviously, our workforce is necessary to build the project. They need the manpower, they need to talk to us early on about what pipeline we have for the work. We need to talk about build-out expectations and timelines and apprenticeship recruitment, so we’re involved early on. We’ve had notable partnerships, like Microsoft in southeast Wisconsin. They’re now the single largest taxpayer in Racine County. That project is now looking to expand.
When we are involved early on, it really shows what can happen. And there are incredible stories coming out of that job site every day about what that work has meant for our union members.
To what extent are some of these communities taking in the labor piece when it comes to data centers?
I think that’s a challenging question to answer because it varies on the individual person, on what their priority is as a member of a community. What they know, what they prioritize.
Across the board, again, we’re a known entity. We are not an external player; we live in these communities and often have training centers in them. They know the value that comes from our workers and the careers we provide.
I don’t think I’ve seen anyone who says that is a bad thing. But I do think there are other factors people are weighing when they’re considering these projects and they’re incredibly personal.
How do you reckon with the personal nature of this issue, given the employment of your members is also at stake? How do you grapple with that?
Well, look, we respect, over anything else, local decision-making. That’s how this should work.
We’re not here to push through something that is not embraced by communities. We are there to answer questions and good actors and provide information about our workforce, what it can mean. But these are decisions individual communities need to make together.
What sorts of communities are welcoming these projects, from your perspective?
That’s another challenging question because I think we only have a few to go off of here.
I would say more information earlier on the better. That’s true in any case, but especially with this. For us, when we go about our day-to-day activities, that is how our most successful projects work. Good communication. Time to think things through. It is very early days, so we have some great success stories we can point to but definitely more to come.
The number of data centers opposed in Republican-voting areas has risen 330% over the past six months.
It’s probably an exaggeration to say that there are more alligators than people in Colleton County, South Carolina, but it’s close. A rural swath of the Lowcountry that went for Trump by almost 20%, the “alligator alley” is nearly 10% coastal marshes and wetlands, and is home to one of the largest undeveloped watersheds in the nation. Only 38,600 people — about the population of New York’s Kew Gardens neighborhood — call the county home.
Colleton County could soon have a new landmark, though: South Carolina’s first gigawatt data center project, proposed by Eagle Rock Partners.
That’s if it overcomes mounting local opposition, however. Although the White House has drummed up data centers as the key to beating China in the race for AI dominance, Heatmap Pro data indicate that a backlash is growing from deep within President Donald Trump’s strongholds in rural America.
According to Heatmap Pro data, there are 129 embattled data centers located in Republican-voting areas. The vast majority of these counties are rural; just six occurred in counties with more than 1,000 people per square mile. That’s compared with 93 projects opposed in Democratic areas, which are much more evenly distributed across rural and more urban areas.
Most of this opposition is fairly recent. Six months ago, only 28 data centers proposed in low-density, Trump-friendly countries faced community opposition. In the past six months, that number has jumped by 95 projects. Heatmap’s data “shows there is a split, especially if you look at where data centers have been opposed over the past six months or so,” says Charlie Clynes, a data analyst with Heatmap Pro. “Most of the data centers facing new fights are in Republican places that are relatively sparsely populated, and so you’re seeing more conflict there than in Democratic areas, especially in Democratic areas that are sparsely populated.”
All in all, the number of data centers that have faced opposition in Republican areas has risen 330% over the past six months.
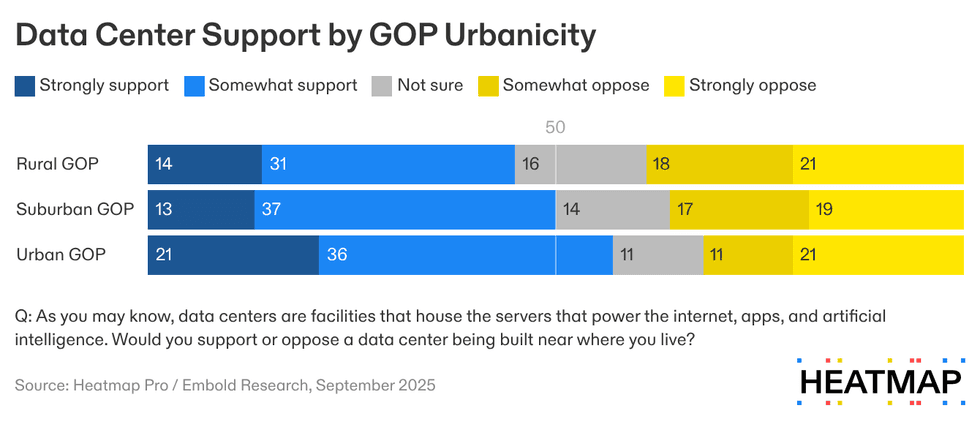
Our polling reflects the breakdown in the GOP: Rural Republicans exhibit greater resistance to hypothetical data center projects in their communities than urban Republicans: only 45% of GOP voters in rural areas support data centers being built nearby, compared with nearly 60% of urban Republicans.
Such a pattern recently played out in Livingston County, Michigan, a farming area that went 61% for President Donald Trump, and “is known for being friendly to businesses.” Like Colleton County, the Michigan county has low population density; last fall, hundreds of the residents of Howell Township attended public meetings to oppose Meta’s proposed 1,000-acre, $1 billion AI training data center in their community. Ultimately, the uprising was successful, and the developer withdrew the Livingston County project.
Across the five case studies I looked at today for The Fight — in addition to Colleton and Livingston Counties, Carson County, Texas; Tucker County, West Virginia; and Columbia County, Georgia, are three other red, rural examples of communities that opposed data centers, albeit without success — opposition tended to be rooted in concerns about water consumption, noise pollution, and environmental degradation. Returning to South Carolina for a moment: One of the two Colleton residents suing the county for its data center-friendly zoning ordinance wrote in a press release that he is doing so because “we cannot allow” a data center “to threaten our star-filled night skies, natural quiet, and enjoyment of landscapes with light, water, and noise pollution.” (In general, our polling has found that people who strongly oppose clean energy are also most likely to oppose data centers.)
Rural Republicans’ recent turn on data centers is significant. Of 222 data centers that have faced or are currently facing opposition, the majority — 55% —are located in red low-population-density areas. Developers take note: Contrary to their sleepy outside appearances, counties like South Carolina’s alligator alley clearly have teeth.