This article is exclusively
for Heatmap Plus subscribers.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.

Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Here come Chip Roy and Lee Zeldin.

National Republican political leaders are beginning to intervene in local battles over battery storage, taking the side of activists against developers. It’s a worrisome trend for an industry that, until recently, was escaping the culture clashes once reserved only for solar and wind energy.
In late July, Texas Congressman Chip Roy sent a letter to energy storage developer Peregrine Energy voicing concerns about a 145 megawatt battery project proposed in rural Gillespie County, an area one hour north of San Antonio that sits in his district. Roy, an influential conservative firebrand running to be state attorney general, asked the company more than a dozen questions about the project, from its fire preparation plans to whether it may have ties to Chinese material suppliers, and stated that his office heard “frustrations and concerns” about the project from “hundreds of constituents – including state and local elected officials.”
“Gillespie County is subject to extreme drought, wildfires, and flash flooding events,” Roy wrote. “Naturally, residents are concerned about the environmental risks a battery storage facility poses to one of [the] most vulnerable areas in Texas, among other things.”
Peregrine told me in an email that the company then sought to assuage the congressman’s concerns, speaking with his staff over the phone. But Roy remained unmoved, now fully backing the local opposition to the project. “My office has met with representatives from Peregrine Energy, and while we appreciate the dialogue, we believe that this project warrants scrutiny,” Roy said in a statement provided by his staff when reached for comment. “We look forward to remaining engaged with Peregrine Energy and continuing to represent the people of Harper who feel strongly that this battery facility poses more harm than good.”
Republican interventions like these may feel out of the ordinary to many in the energy sector. Historically, conservative politicians like Roy often vote against writing new regulations governing the environment and public safety, and Texas has often been a bastion for that kind of policymaking. Not to mention Texas is a major hub for battery storage development, second only to California in total capacity installed onto the grid. The Lone Star state’s strained grid means there is no shortage of demand for excess back-up power.
Unfortunately for battery storage developers, national Republicans are now increasingly open to attacking individual battery storage projects in the same way they’ve sometimes fought solar and wind farms, especially when activists on the ground feel they’ve lost the fight with municipal and state regulators.
Last year, we launched The Fight with a story about the unincorporated town of Acton, California, where a battery project was approved by county officials in an area with high risk of experiencing wildfire. Local opponents of the facility, feeling that county and state courts would not fairly adjudicate their concerns, lobbied their elected representative in Congress – then-Rep. Mike Garcia – to do something, anything in response to the situation. And while Garcia was stymied from halting that individual battery project, he then tried to block the Energy Department from streamlining federal permits for the entire battery storage system sector. (The rulemaking was completed before the start of the Trump 2.0 administration. Garcia lost re-election last year.)
At the time, this was the first full-fledged example I could find of a Republican in Congress really picking up the mantle of the “BESS bomb” panic around large-scale battery facilities potentially posing an unacceptable risk to surrounding host communities. Sure, there’d been scares around lithium-ion batteries in e-bikes, for example. But battery storage in general? The sector has enjoyed bipartisan support at the national level, and definitely still does to some extent given that GOP lawmakers declined to pare back the industry’s Inflation Reduction Act credits in their recently-passed tax megabill.
But now there’s a very clear battery fire “butterfly effect” occurring in which local rage fails to get the attention of government officials focused on energy capacity so activists will just go to whatever ears are most sympathetic to them. This is resulting in percolating Republican ire against battery storage, point blank.
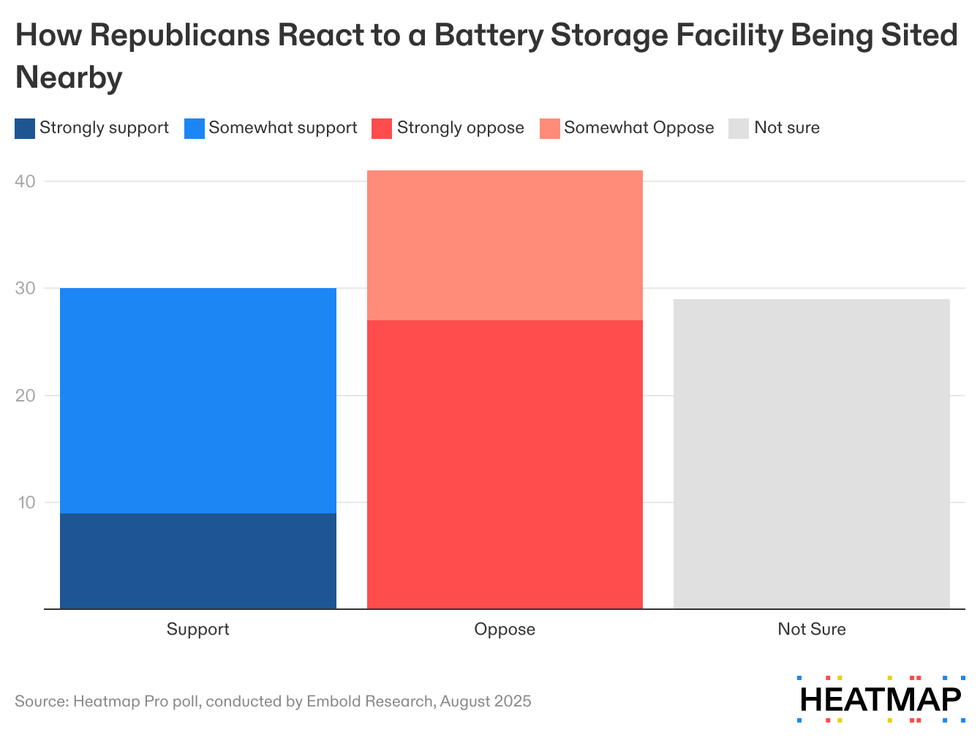
Indeed, Heatmap Pro’s August poll of 3,741 registered voters found that there are now three times as many strong opponents of battery storage facilities among Republicans than strong supporters.
Less than a month after Roy’s letter to Peregrine, EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin personally visited his native Long Island, New York, to voice his support for those campaigning against a Key Capture Energy battery project in Hauppauge, a hamlet within the town of Islip. The EPA has no role in whether the project is built or not. But the endorsement – coupled with a New York Post op-ed declaring “battery sites are too risky for New York” – came right before a 12-month battery moratorium Islip had enacted was set to expire.
This week Islip extended the moratorium, indefinitely stopping the battery project. Next week, the New York City Council’s committee on fire and emergency management will be holding a public hearing to specifically address the local fears about storage projects.
As for Roy and Peregrine Energy, it’s unclear how the Texas Republican could stop the facility on his own. It has the permits necessary to build and Texas doesn’t have the kind of stringent environmental regulation that creates opportunities to stall construction.
But the lawmaker’s existing political clout in Washington and motivation to win the Republican primary nomination in a heated statewide contest make him a dangerous enemy for any company to have, especially energy developers linked in some way to the transition. As Garcia showed a year ago and Zeldin demonstrated over the summer, someone with a national platform and a megaphone could do a lot of damage to a single project, or worse. We’ve yet to truly see what will come from the flapping of this butterfly’s wings.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Things in Sulphur Springs are getting weird.
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton is trying to pressure a company into breaking a legal agreement for land conservation so a giant data center can be built on the property.
The Lone Star town of Sulphur Springs really wants to welcome data center developer MSB Global, striking a deal this year to bring several data centers with on-site power to the community. The influx of money to the community would be massive: the town would get at least $100 million in annual tax revenue, nearly three times its annual budget. Except there’s a big problem: The project site is on land gifted by a former coal mining company to Sulphur Springs expressly on the condition that it not be used for future energy generation. Part of the reason for this was that the lands were contaminated as a former mine site, and it was expected this property would turn into something like a housing development or public works project.
The mining company, Luminant, went bankrupt, resurfaced as a diversified energy company, and was acquired by power giant Vistra, which is refusing to budge on the terms of the land agreement. After sitting on Luminant’s land for years expecting it to be used for its intended purposes, the data center project’s sudden arrival appears to have really bothered Vistra, and with construction already underway, the company has gone as far as to send the town and the company a cease and desist.
This led Sulphur Springs to sue Vistra. According to a bevy of legal documents posted online by Jamie Mitchell, an activist fighting the data center, Sulphur Springs alleges that the terms of the agreement are void “for public policy,” claiming that land restrictions interfering with a municipality’s ability to provide “essential services” are invalid under prior court precedent in Texas. The lawsuit also claims that by holding the land for its own use, Vistra is violating state antitrust law by creating an “energy monopoly.” The energy company filed its own counterclaims, explicitly saying in a filing that Sulphur Springs was part of crafting this agreement and that “a deal is a deal.”
That’s where things get weird, because now Texas is investigating Luminant over the “energy monopoly” claim raised by the town. It’s hard not to see this as a pressure tactic to get the data center constructed.
In an amicus brief filed to the state court and posted online, Paxton’s office backs up the town’s claim that the land agreement against energy development violates the state’s antitrust law, the Texas Free Enterprise and Antitrust Act, contesting that the “at-issue restriction appears to be perpetual” and therefore illegally anti-competitive. The brief also urges the court not to dismiss the case before the state completes its investigation, which will undoubtedly lead to the release of numerous internal corporate documents.
“Sulphur Springs has alleged a pattern of restricting land with the potential for energy generation, with the effect of harming competition for energy generation generally, which would necessarily have the impact of increasing costs for both Sulphur Springs and Texas consumers generally,” the filing states. “Evaluating the competitive effects of Luminant’s deed restrictions as well as the harm to Texans generally is a fact-intensive matter that will require extensive discovery.”
The Texas attorney general’s office did not respond to multiple requests for comment on the matter. It’s worth noting that Paxton has officially entered the Republican Senate primary, challenging sitting U.S. Senator John Cornyn. Contrary to his position in this case, Paxton has positioned himself as a Big Tech antagonist and fought the state public utilities commission in pursuit of releasing data on the crypto mining industry’s energy use.
A solar developer gets into a forest fight in California, and more of the week’s top conflicts around renewables.
1. Sacramento County, California – A solar project has become a national symbol of the conflicts over large-scale renewables development in forested areas.
2. Sedgwick County, Kansas – I am eyeing this county to see whether a fight over a solar farm turns into a full-blown ban on future projects.
3. Montezuma County, Colorado – One southwest Colorado county is loosening restrictions on solar farms.
4. Putnam County, Indiana – An uproar over solar projects is now leading this county to say no to everything, indefinitely.
5. Kalamazoo County, Michigan – I’m eyeing yet another potential legal challenge against Michigan’s permitting reform efforts.
A conversation with Renee Grabe of Nature Forward
This week’s conversation is with Renee Grabe, a conservation advocate for the environmental group Nature Forward who is focused intently on data center development in Northern Virginia. I reached out to her for a fresh perspective on where data centers and renewable energy development fits in the Commonwealth amidst heightened frustration over land use and agricultural impacts, especially after this past election cycle. I thought her views on policy-making here were refreshingly nuanced.
This transcript was lightly edited for clarity.
Tell me more about how you started focusing on data centers.
So, in Fairfax County, in 2020 or 2021, people were pursuing the construction of an indoor ski facility on a landfill. From a climate perspective, to build something that would need to be cooled 24/7 for indoor skiing seemed like a very bad proposal in terms of energy usage. And for what kind of gain?
Then our friends at the Sierra Club were saying, indoor ski slopes? Bad, yes. But data centers? Way, way worse. Those aren’t cooling to support snow but are cooling much larger areas on a much larger scale, dwarfing the area of that one ski slope. This was around the time the Prince William Digital Gateway was showing up – they were saying all these acres of agricultural lands and single-family housing zones were about to be rezoned. This was a big deal, and Sierra Club led the way in opening our eyes to this. The rezoning ultimately passed. The data centers were sued and the people who filed the lawsuit won, but pre-planning for the centers is still allowed to take place.
The way we think about the impacts of data centers, besides the loss of natural lands and the amount of energy that’s going to be needed to power these things, has been diesel generators. These are the things that are backup generation and the camel’s nose under the tent is trying to get them to be primary power.
Now I want to ask you a provocative question: is there any middle ground between letting these projects be built unfettered and outright bans on their development?
We have no regulation today. From our standpoint, these things are coming, they’re here. We know a lot more now than we did in 2022. As we make decisions about how and where to build these facilities we all need – I mean we’re using one right now. I use a data center all day at work. Teams conferencing. ChatGPT to answer a question. We need these. So if we’re going to build them, let’s not give a pass to some of the world’s largest and richest companies. Let’s ask them to put the guardrails on to protect our residences and our infrastructure to make sure they’re as sustainable as possible.
Okay, so what are the guardrails then?
The costs of what was going to go into a data center need to be more transparent. We need to bring accountability to the forefront right away as they’re being built.
In Ohio, they passed a law requiring data center companies to pay for a high percentage of the power they’re using. That cut a significant number of the projects in Ohio. This industry is so speculative and a land grab and a rush to be first to get the most.
You have this dichotomy of land values for residences being inundated, while land values for developers are skyrocketing. We have an affordability crisis going on and we are all on the hook for paying for the infrastructure to power these things.
So when you think about what regulation might make data center development more reasonable, it’s asking for the costs happening to be borne by the industry making them. Let’s get rid of some of the incentives for power users. We don’t need to be encouraging the loss of state revenue, either – we’re leaving money on the table to bring these facilities here.
Lastly, our readers love to get hyperlocal. I know you’re intently focused on Fairfax County right now which has been a big part of the data center boom in Virginia – what’s happening there?
There are a couple things that have happened over the course of this past year. Fairfax County passed a data center zoning ordinance amendment – minimum requirements a data center will have to adhere to. The big thing with that one is, you have to have a special exception if you build within a mile of a Metro station. When you think about good land use and building a data center within a walkable distance of a Metro, that’s eye-openingly poor land use policy and a missed opportunity for transit-oriented development. It doesn’t mean they can’t be built near one but you have to get a special exception.
Some things can’t be regulated at the local level. Like generators. That’s in the hands of the state.
Last night, we had a public hearing at the Fairfax County board level for our policy plan – our comprehensive plan providing guidance for developers who want to get a special exception or rezoning. It is not law. It is not required. It is a visionary document that helps us get to better. They’ve added a section for data centers in that. In May, staff put forward something pretty good, making sure data centers met a minimum level of efficiency. But our chairman of the county board said it went above and beyond our zoning ordinance and said he didn’t think it was appropriate, so staff rewrote that section and stripped out a lot of the specificity and higher standards that were in that document.
At the hearing, they deferred a decision, listening to the public but not having a discussion at the board level. They’ve left the record open through December 9th.