You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On corporate climate resilience, the freezing Iowa caucus, and EV tipping points

Current conditions: New York City’s Central Park has officially broken its 701-day snow-free streak • Extreme flooding from Cyclone Belal submerged cars in the ocean island nation of Mauritius • It’s 24 degrees Fahrenheit and cloudy in Davos, where the 54th annual World Economic Forum gathering begins this week.
Former President Donald Trump handily won the Republican Iowa caucus on Monday night, and his speeches at the event were sprinkled with anti-climate lines we’re likely to hear more of in his 2024 presidential campaign, writes Heatmap’s Jeva Lange. In his victory speech, Trump made a jab about electric vehicle range anxiety, and promised to do more “drilling” if he gets the White House back. Earlier in the evening he told would-be voters that “I stood up for ethanol like nobody has ever stood up for it” – a dig at Biden’s climate agenda, which has aimed to limit liquid fuel in vehicles, a sensitive issue for Iowa voters during their primary season. On Sunday a group of young climate protesters disrupted one of Trump’s rallies, calling him a “climate criminal.” Trump told them to “go home to mommy.”
This was the coldest caucus in Iowa’s history thanks to a weather system that dragged temperatures below freezing for most of the country. As Lange notes: “Scientists say the arctic blast is exactly the kind of extreme event we can expect more of in a climate-changed world.”
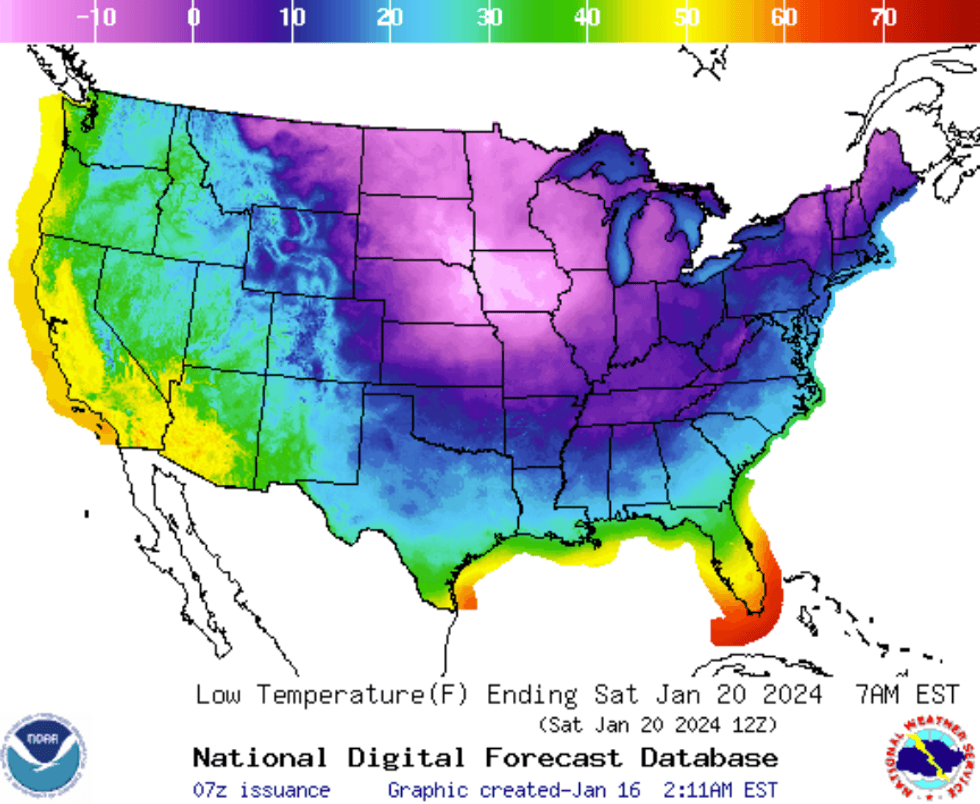
Half a million students in southern states have the day off as a dangerous cold snap forces school closures across Alabama, Arkansas, Tennessee, and Texas. ERCOT, which manages most of Texas’ electric load, has asked residents to conserve energy as the state faces wind chill advisories and hard freeze warnings. At least five deaths have so far been attributed to the severe winter weather. More than 70 million people across the country remain under winter weather alerts of some kind, and something like 250 daily cold temperature records are expected to be shattered today. Temperatures could warm slightly Wednesday but the National Weather Service expects another arctic blast to descend Thursday. Here's a look at the temperature lows currently forecast for Friday night:
Oil and gas giant Shell is facing its “most significant shareholder push on climate policy,” reports the Financial Times. A group of 27 investors – including Europe’s largest asset manager Amundi – are backing an independent resolution filed by activist group Follow This demanding the company do more to slash its greenhouse gas emissions. The resolution calls on Shell to better align its pollution targets with the Paris Agreement and focuses specifically on the emissions customers generate when they use Shell’s products, known as Scope 3 emissions. The company called the resolution “unrealistic and simplistic” and insisted its targets already align with the Paris Agreement. This isn’t Follow This’ first resolution aimed at Shell, but this one appears to have the most momentum: Its investor-backers own about 5% of Shell’s shares. Support for the resolution is expected to grow ahead of a vote at the company’s annual general meeting in May, The Guardian reports.
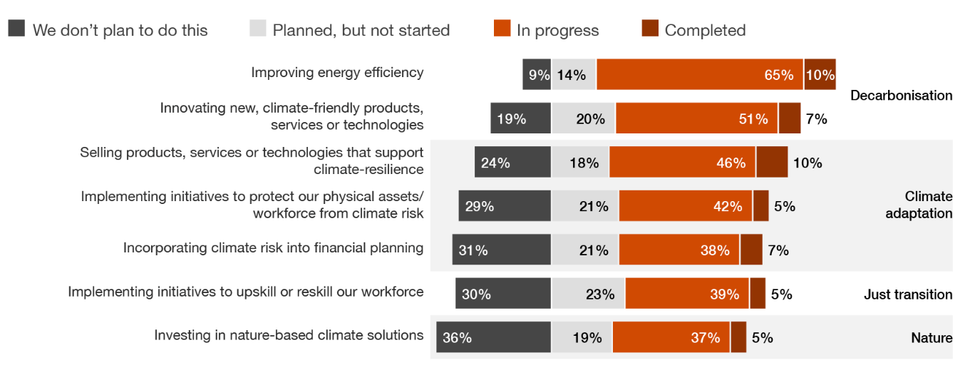
A growing number of company executives across the globe are worried their firms won’t survive the next 10 years unless they undergo a major overhaul, according to a survey of 4,700 CEOs conducted by consulting firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC). About 45% of the respondents are concerned about their current business models, up from 39% on last year’s survey. Among their top anxieties are artificial intelligence and – you guessed it – climate change. Nearly one-third of CEOs say they expect climate change to “alter the way they create, deliver, and capture value over the next three years.” About two-thirds of respondents say their firms are improving their energy efficiency, but support is lacking for other climate-related company initiatives:
The electric vehicle tipping point has come and gone for carmaker BMW, according to the company’s chief financial officer. Most of BMW’s sales growth now comes from EVs, not combustion vehicles, CFO Walter Mertl said at a media event yesterday. He added that “the current sales plateau of combustion cars will continue and then fall off slightly.” After the company’s EV sales nearly doubled in 2023 to more than 375,000, EVs now make up 15% of total sales, and the company expects to sell more than 500,000 EVs in 2024, Reuters reports.
FEMA has partnered with the Red Cross to create a printable emergency preparedness children’s game featuring a cartoon penguin named Pedro as its main character:
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Whether any of them will hold up in court is now the big question.
Environmental lawyers are in for years of déjà vu as the Trump administration relitigates questions that many believed were settled by the Supreme Court nearly 20 years ago.
On Thursday, Trump rescinded the “endangerment finding,” the Environmental Protection Agency’s 2009 determination that greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles threaten Americans’ public health and welfare and should be regulated. In the short term, the move repeals existing vehicle emissions standards and prevents future administrations from replacing them. In the longer term, what matters is whether any of the administration’s justifications hold up in court.
In its final rule, the EPA abandoned its attempt to back the move using a bespoke climate science report published by the Department of Energy last year. The report was created by a working group assembled in secret by the department and made up of five scientists who have a track record of pushing back on mainstream climate science. Not only was the report widely refuted by scientists, but the assembly of the working group itself broke federal law, a judge ruled in late January.
“The science is clear that climate change is creating a risk for the public and public health, and so I think it’s significant that they realized that it creates a legal risk if they were to try to assert otherwise,” Carrie Jenks, the executive director of Harvard’s Environmental and Energy Law Program, told me.
Instead, the EPA came up with three arguments to justify its decision, each of which will no doubt have to be defended in court. The agency claims that each of them can stand alone, but that they also reinforce each other. Whether that proves to be true, of course, has yet to be determined.
Here’s what they are:
Congress never specifically told the EPA to regulate greenhouse gas emissions. If it did, maybe we would have accomplished more on climate change by now.
What happened instead was that in 1999, a coalition of environmental and solar energy groups asked the EPA to regulate emissions from cars, arguing that greenhouse gases should be considered pollutants under the federal Clean Air Act. In 2007, in a case called Massachusetts v. EPA, the Supreme Court agreed with the second part. That led the EPA to consider whether these gases posed enough of a danger to public health to warrant regulation. In 2009, it concluded they did — that’s what’s known as the endangerment finding. After reaching that finding, the EPA went ahead and developed standards to limit emissions from vehicles. It later followed that up with rules for power plants and oil and gas operations.
Now Trump’s EPA is arguing that this three-step progression — categorizing greenhouse gases as pollutants under the Clean Air Act, making a scientific finding that they endanger public health, and setting regulations — was all wrong. Instead, the agency now believes, it’s necessary to consider all three at once.
Using the EPA’s logic, the argument comes out something like this: If we consider that U.S. cars are a small sliver of global emissions, and that limiting those emissions will not materially change the trajectory of global warming or the impacts of climate change on Americans, then we must conclude that Congress did not intend for greenhouse gases to be regulated when it enacted the Clean Air Act.
“They are trying to merge it all together and say, because we can’t do that last thing in a way that we think is reasonable, we can’t do the first thing,” Jenks said.
The agency is not explicitly asking for Massachusetts v. EPA to be overturned, Jenks said. But if its current argument wins in court, that would be the effective outcome, preventing future administrations from issuing greenhouse gas standards unless Congress passed a law explicitly telling it to do so. While it's rare for the Supreme Court to reverse course, none of the five justices who were in the majority on that case remain, and the makeup of the court is now far more conservative than in 2007.
The EPA also asserted that the “major questions doctrine,” a legal principle that says federal agencies cannot set policies of major economic and political significance without explicit direction from Congress, means the EPA cannot “decide the Nation’s policy response to global climate change concerns.”
The Supreme Court has used the major questions doctrine to overturn EPA’s regulations in the past, most notably in West Virginia v. EPA, which ruled that President Obama’s Clean Power Plan failed this constitutional test. But that case was not about EPA’s authority to regulate greenhouse gases, the court solely struck down the particular approach the EPA took to those regulations. Nevertheless, the EPA now argues that any climate regulation at all would be a violation.
The EPA’s final argument is about the “futility” of vehicle emissions standards. It echoes a portion of the first justification, arguing that the point alone is enough of a reason to revoke the endangerment finding absent any other reason.
The endangerment finding had “severed the consideration of endangerment from the consideration of contribution” of emissions, the agency wrote. The Clean Air Act “instructs the EPA to regulate in furtherance of public health and welfare, not to reduce emissions regardless [of] whether such reductions have any material health and welfare impact.”
Funnily enough, to reach this conclusion, the agency had to use climate models developed by past administrations, including the EPA’s Optimization Model for reducing Emissions of GHGs from Automobiles, as well as some developed by outside scientists, such as the Finite amplitude Impulse Response climate emulator model — though it did so begrudgingly.
The agency “recognizes that there is still significant dispute regarding climate science and modeling,” it wrote. “However, the EPA is utilizing the climate modeling provided within this section to help illustrate” that zero-ing out emissions from vehicles “would not materially address the health and welfare dangers attributed to global climate change concerns in the Endangerment Finding.”
I have yet to hear back from outside experts about the EPA’s modeling here, so I can’t say what assumptions the agency made to reach this conclusion or estimate how well it will hold up to scrutiny. We’ll be talking to more legal scholars and scientists in the coming days as they digest the rule and dig into which of these arguments — if any — has a chance to prevail.
The state is poised to join a chorus of states with BYO energy policies.
With the backlash to data center development growing around the country, some states are launching a preemptive strike to shield residents from higher energy costs and environmental impacts.
A bill wending through the Washington State legislature would require data centers to pick up the tab for all of the costs associated with connecting them to the grid. It echoes laws passed in Oregon and Minnesota last year, and others currently under consideration in Florida, Georgia, Illinois, and Delaware.
Several of these bills, including Washington’s, also seek to protect state climate goals by ensuring that new or expanded data centers are powered by newly built, zero-emissions power plants. It’s a strategy that energy wonks have started referring to as BYONCE — bring your own new clean energy. Almost all of the bills also demand more transparency from data center companies about their energy and water use.
This list of state bills is by no means exhaustive. Governors in New York and Pennsylvania have declared their intent to enact similar policies this year. At least six states, including New York and Georgia, are also considering total moratoria on new data centers while regulators study the potential impacts of a computing boom.
“Potential” is a key word here. One of the main risks lawmakers are trying to circumvent is that utilities might pour money into new infrastructure to power data centers that are never built, built somewhere else, or don’t need as much energy as they initially thought.
“There’s a risk that there’s a lot of speculation driving the AI data center boom,” Emily Moore, the senior director of the climate and energy program at the nonprofit Sightline Institute, told me. “If the load growth projections — which really are projections at this point — don’t materialize, ratepayers could be stuck holding the bag for grid investments that utilities have made to serve data centers.”
Washington State, despite being in the top 10 states for data center concentration, has not exactly been a hotbed of opposition to the industry. According to Heatmap Pro data, there are no moratoria or restrictive ordinances on data centers in the state. Rural communities in Eastern Washington have also benefited enormously from hosting data centers from the earlier tech boom, using the tax revenue to fund schools, hospitals, municipal buildings, and recreation centers.
Still, concern has started to bubble up. A ProPublica report in 2024 suggested that data centers were slowing the state’s clean energy progress. It also described a contentious 2023 utility commission meeting in Grant County, which has the highest concentration of data centers in the state, where farmers and tech workers fought over rising energy costs.
But as with elsewhere in the country, it’s the eye-popping growth forecasts that are scaring people the most. Last year, the Northwest Power and Conservation Council, a group that oversees electricity planning in the region, estimated that data centers and chip fabricators could add somewhere between 1,400 megawatts and 4,500 megawatts of demand by 2030. That’s similar to saying that between one and four cities the size of Seattle will hook up to the region’s grid in the next four years.
In the face of such intimidating demand growth, Washington Governor Bob Ferguson convened a Data Center Working Group last year — made up of state officials as well as advisors from electric utilities, environmental groups, labor, and industry — to help the state formulate a game plan. After meeting for six months, the group published a report in December finding that among other things, the data center boom will challenge the state’s efforts to decarbonize its energy systems.
A supplemental opinion provided by the Washington Department of Ecology also noted that multiple data center developers had submitted proposals to use fossil fuels as their main source of power. While the state’s clean energy law requires all electricity to be carbon neutral by 2030, “very few data center developers are proposing to use clean energy to meet their energy needs over the next five years,” the department said.
The report’s top three recommendations — to maintain the integrity of Washington’s climate laws, strengthen ratepayer protections, and incentivize load flexibility and best practices for energy efficiency — are all incorporated into the bill now under discussion in the legislature. The full list was not approved by unanimous vote, however, and many of the dissenting voices are now opposing the data center bill in the legislature or asking for significant revisions.
Dan Diorio, the vice president of state policy for the Data Center Coalition, an industry trade group, warned lawmakers during a hearing on the bill that it would “significantly impact the competitiveness and viability of the Washington market,” putting jobs and tax revenue at risk. He argued that the bill inappropriately singles out data centers, when arguably any new facility with significant energy demand poses the same risks and infrastructure challenges. The onshoring of manufacturing facilities, hydrogen production, and the electrification of vehicles, buildings, and industry will have similar impacts. “It does not create a long-term durable policy to protect ratepayers from current and future sources of load growth,” he said.
Another point of contention is whether a top-down mandate from the state is necessary when utility regulators already have the authority to address the risks of growing energy demand through the ratemaking process.
Indeed, regulators all over the country are already working on it. The Smart Electric Power Alliance, a clean energy research and education nonprofit, has been tracking the special rate structures and rules that U.S. utilities have established for data centers, cryptocurrency mining facilities, and other customers with high-density energy needs, many of which are designed to protect other ratepayers from cost shifts. Its database, which was last updated in November, says that 36 such agreements have been approved by state utility regulators, mostly in the past three years, and that another 29 are proposed or pending.
Diario of the Data Center Coalition cited this trend as evidence that the Washington bill was unnecessary. “The data center industry has been an active party in many of those proceedings,” he told me in an email, and “remains committed to paying its full cost of service for the energy it uses.” (The Data Center Coalition opposed a recent utility decision in Ohio that will require data centers to pay for a minimum of 85% of their monthly energy forecast, even if they end up using less.)
One of the data center industry’s favorite counterarguments against the fear of rising electricity is that new large loads actually exert downward pressure on rates by spreading out fixed costs. Jeff Dennis, who is the executive director of the Electricity Customer Alliance and has worked for both the Department of Energy and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, told me this is something he worries about — that these potential benefits could be forfeited if data centers are isolated into their own ratemaking class. But, he said, we’re only in “version 1.5 or 2.0” when it comes to special rate structures for big energy users, known as large load tariffs.
“I think they’re going to continue to evolve as everybody learns more about how to integrate large loads, and as the large load customers themselves evolve in their operations,” he said.
The Washington bill passed the Appropriations Committee on Monday and now heads to the Rules Committee for review. A companion bill is moving through the state senate.
Plus more of the week’s top fights in renewable energy.
1. Kent County, Michigan — Yet another Michigan municipality has banned data centers — for the second time in just a few months.
2. Pima County, Arizona — Opposition groups submitted twice the required number of signatures in a petition to put a rezoning proposal for a $3.6 billion data center project on the ballot in November.
3. Columbus, Ohio — A bill proposed in the Ohio Senate could severely restrict renewables throughout the state.
4. Converse and Niobrara Counties, Wyoming — The Wyoming State Board of Land Commissioners last week rescinded the leases for two wind projects in Wyoming after a district court judge ruled against their approval in December.