You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
It’s been just over a week since one of the 350-foot-long blades of a wind turbine off the Massachusetts coast unexpectedly broke off, sending hunks of fiberglass and foam into the waters below. As of Wednesday morning, cleanup crews were still actively removing debris from the water and beaches and working to locate additional pieces of the blade.
The blade failure quickly became a crisis for residents of Nantucket, where debris soon began washing up on the island’s busy beaches. It is also a PR nightmare for the nascent U.S. offshore wind industry, which is already on the defensive against community opposition and rampant misinformation about its environmental risks and benefits.
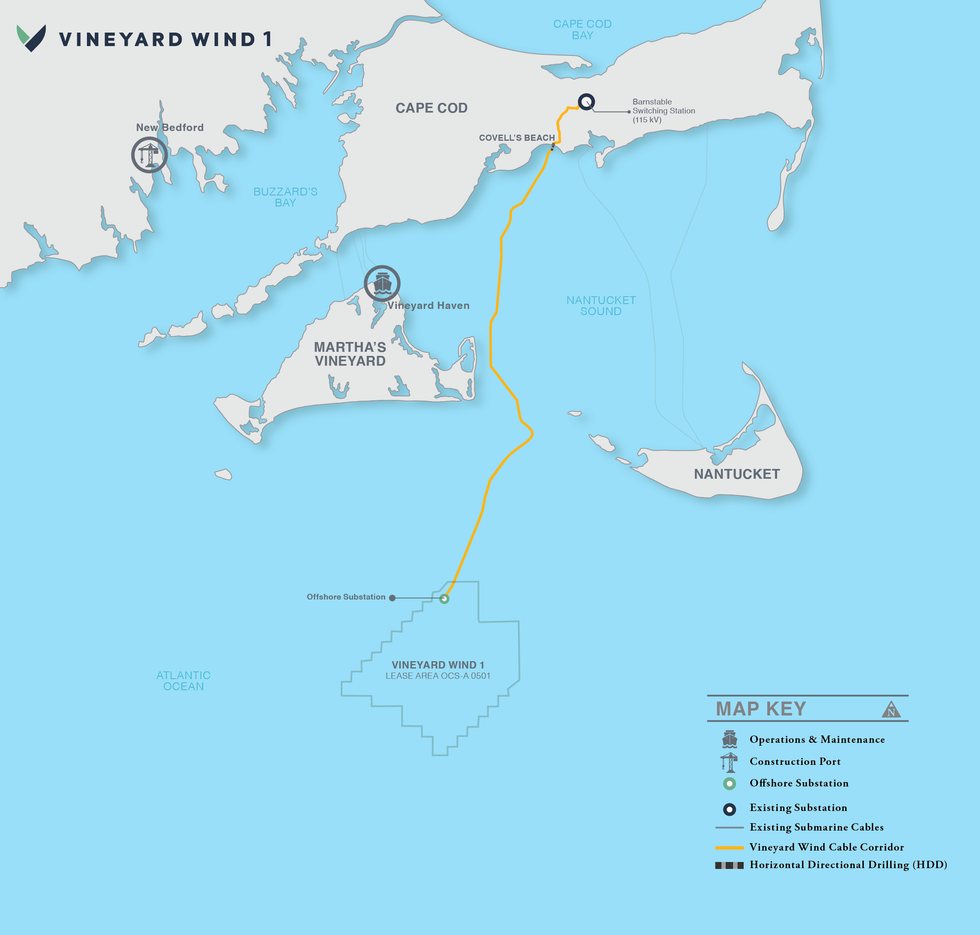
The broken turbine is part of Vineyard Wind 1, which is being developed by Avangrid and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners. The project was still under construction when the breakage occurred, but it was already the largest operating offshore wind farm in the US, with ten turbines sending power to the New England Grid as of June. The plan is to bring another 52 online, which will produce enough electricity to power more than 400,000 homes. Now both installation and power generation have been paused while federal investigators look into the incident.
There’s still a lot we don’t know about why this happened, what the health and safety risks are, and what it means for this promising clean energy solution going forward. But here’s everything we’ve learned so far.
Vineyard Wind
On the evening of Saturday, July 13, Vineyard Wind received an alert that there was a problem with one of its turbines. The equipment contains a “delicate sensoring system,” CEO Klaus Moeller told the Nantucket Select Board during a public meeting last week. Though he did not describe what the alert said, he added that “one of the blades was broken and folded over.” Later at the meeting, a spokesperson for GE Vernova, which manufactured and installed the turbines, said that “blade vibrations” had been detected. About a third of the blade, or roughly 120 feet, fell into the water.
Two days later, Vineyard Wind contacted the town manager in Nantucket to explain that modeling showed the potential for debris from the blade to travel toward the island. Sure enough, fiberglass shards and other scraps began washing up on shore the next day, and all beaches on the island’s south shore were quickly closed to the public.
On Thursday morning, another large portion of the damaged blade detached and fell into the ocean. Monitoring and recovery crews continued to find debris throughout the area over the weekend. The beaches have since reopened, but visitors have been advised to wear shoes and leave their pets at home as cleanup continues.
During GE’s second quarter earnings call on July 24, GE Vernova CEO Scott Strazik and Vice President of Investor Relations Michael Lapides said the company had identified a “material deviation” as the cause of the accident, and that the company is continuing to work on a "root cause analysis" to get to the bottom of how said deviation happened in the first place.
The turbine was one of GE’s Haliade-X 13-megawatt turbines, which are manufactured in Gaspé, Canada, and it was still undergoing post-installation testing by GE when the failure occurred — that is, it was not among those sending power to the New England grid. This was actually the second issue the company has had at this particular turbine site. One of the original blades destined for the site was damaged during the installation process, and the one that broke last week was a replacement, Craig Gilvard, Vineyard Wind’s communications director, told the New Bedford Light.
By Vineyard Wind’s account at the meeting last week, the accident triggered an automatic shut down of the system and activated the company’s emergency response plan, which included immediately notifying the U.S. Coast Guard, the federal Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement, and regional emergency response committees.
Moeller, the CEO, said during the meeting that the company worked with the Coast Guard to immediately establish a 500 meter “safety zone” around the turbine and to send out notices to mariners. According to the Coast Guard’s notice log, however, the safety zone went into effect three days later. In response to my questions, the Coast Guard confirmed that the zone was established around 8pm that night and announced to mariners over radio broadcast.
Two days after the turbine broke, on Monday, Vineyard Wind contacted the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for aid in modeling where the turbine debris would travel in the water. The agency estimated pieces would likely make landfall in Nantucket that day. Vineyard Wind put out a press release about the accident and subsequently contacted the Nantucket town manager. At the Nantucket Select Board meeting last week, Moeller said the company followed regulatory protocols but that there was “really no excuse” for how long it took to inform the public, and said, “we want to move much quicker and make sure that we learn from this.”
The Interior Department’s Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement has ordered the company to cease all power production and installation activities until it can determine whether this was an isolated incident or affects other turbines.
By Tuesday, Vineyard Wind said it had deployed two small teams to Nantucket in addition to hiring a local contractor to remove debris on the island. The company later said it would “increase its local team to more than 50 employees and contractors dedicated to beach clean-up and debris recovery efforts.”
GE Vernova is responsible for recovering offshore debris and has not published any public statements about the effort. In response to a list of questions, a GE Vernova spokesperson said, “We continue to work around the clock to enhance mitigation efforts in collaboration with Vineyard Wind and all relevant state, local and federal authorities. We are working with urgency to complete our root cause analysis of this event.”
There have been no reported injuries as a result of the accident.
Vineyard Wind and GE Vernova have stressed that the debris are “not toxic.” At the Select Board meeting, GE’s executive fleet engineering director Renjith Viripullan said that the blade is made of fiberglass, foam, and balsa wood. It is bonded together using a “bond paste,” he said, and likened the blade construction to that of a boat. “That's the correlation we need to think about,” he said.
One of the board members asked if there was any risk of PFAS contamination as a result of the accident. Viripullan said he would need to “take that question back” and follow up with the answer later. (This was one of the questions I asked GE, but the company did not respond to it.)
That being said, the debris poses some dangers. Photos of cleanup crews posted to the Harbormaster’s Facebook page show workers wearing white hazmat suits. Vineyard Wind said “members of the public should avoid handling debris as the fiber-glass pieces can be sharp and lead to cuts if handled without proper gloves.”
Though members of the public raised concerns at the meeting and to the press that fiberglass fragments in the ocean threaten marine life and public health, it is not yet clear how serious the risks are, and several efforts are underway to further assess them. Vineyard Wind is developing a water quality testing plan for the island and setting up a process for people to file claims. GE hired a design and engineering firm to conduct an environmental assessment, which it will present at a Nantucket Select Board meeting later this week. The Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection has requested information from the companies about the makeup of the debris to evaluate risks, and the Department of Fish and Game is monitoring for impacts to the local ecosystem.
As of last Wednesday morning, Vineyard Wind had collected “approximately 17 cubic yards of debris, enough to fill more than six truckloads, and several larger pieces that washed ashore.” It is not yet known what fraction of the turbine that fell off has been recovered. Vineyard Wind did not respond to a request for the latest numbers in time for publication, but I’ll update this piece if I get a response.
Yes. In May, a blade on the same model of turbine, the GE Haliade-X, sustained damage at a wind farm being installed off the coast of England called Dogger Bank. At the Nantucket Select Board meeting, a spokesperson for GE said the Dogger Bank incident was “an installation issue specific to the installation of that blade” and that “we don’t think there’s a connection between that installation issue and what we saw here.” Executives emphasized this point during the earnings call and chalked up the Dogger Bank incident to “an installation error out at sea.”
Several blades have also broken off another GE turbine model dubbed the Cypress at wind farms in Germany and Sweden. After the most recent incident in Germany last October, the company used similar language, telling reporters that it was working to “determine the root cause.”
A “company source with knowledge of the investigations” into the various incidents recently told CNN that “there were different root causes for the damage, including transportation, handling, and manufacturing deviations.”
GE Vernova’s stock price fell nearly 10% last Wednesday.
The backlash was swift. Nantucket residents immediately wrote to Nantucket’s Select Board to ask the town to stop the construction of any additional offshore wind turbines. “I know it's not oil, but it's sharp and maybe toxic in other ways,” Select Board member Dawn Holgate told company executives at the meeting last week. “We're also facing an exponential risk if this were to continue because many more windmills are planned to be built out there and there's been a lot of concern about that throughout the community.”
The Select Board plans to meet in private on Tuesday night to discuss “potential litigation by the town against Vineyard Wind relative to recovery costs.”
“We expect Vineyard Wind will be responsible for all costs and associated remediation efforts incurred by the town in response to the incident,” Elizabeth Gibson, the Nantucket town manager said during the meeting last week.
The Aquinnah Wampanoag tribe is also calling for a moratorium on offshore wind development and raised concerns about the presence of fiberglass fragments in the water.
On social media, anti-wind groups throughout the northeast took up the story as evidence that offshore wind is “not green, not clean.” Republican state representatives in Massachusetts cited the incident as a reason for opposing legislation to expedite clean energy permitting last week. Fox News sought comment from internet personality and founder of Barstool Sports David Portnoy, who owns a home on Nantucket and said the island had been “ruined by negligence.” The Texas Public Policy Foundation, a nonprofit funded by oil companies and which is backing a lawsuit against Vineyard Wind, cited the incident as evidence that the project is harming local fishermen. The First Circuit Court of Appeals is set to hear oral arguments on the case this Thursday.
Meanwhile, environmental groups supportive of offshore wind tried to do damage control for the industry. “Now we must all work to ensure that the failure of a single turbine blade does not adversely impact the emergence of offshore wind as a critical solution for reducing dependence on fossil fuels and addressing the climate crisis,” the Sierra Club’s senior advisor for offshore wind, Nancy Pyne, wrote in a statement. “Wind power is one of the safest forms of energy generation.”
This story was last updated July 24 at 3:15 p.m. The current version contains new information and corrects the location where the turbine blades are produced. With assistance from Jael Holzman.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Current conditions: A bomb cyclone is headed up the East Coast, bringing more cold air and possible blizzard conditions to the Northeast, especially New England • Even Tampa Bay, where so-called snowbirds from the Northeast go to winter, could see snow by the end of this week • A storm system named Kristin is on track to bring thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail to Greece.

Sales of electric vehicles in Europe surged 30% to a record high last year, with battery-powered models outselling gas-burning cars for the first time last month, the Financial Times reported. The increase came despite a 38% drop in Tesla’s annual sales on the continent as Chinese rival BYD zoomed past Elon Musk’s automaker. Electric vehicles now account for 17% of EU car sales, up from 14% in 2024.
Tesla, meanwhile, is shifting gears. During a quarterly earnings call Wednesday evening, Musk announced plans to end production of the Model S sedan, its first fully original car design, and Model X SUV. “It’s time to basically bring the Model S and X programs to an end with an honorable discharge, because we’re really moving into a future that is based on autonomy,” he said. “So if you’re interested in buying a Model S and X, now would be the time to order it.” He said he would continue offering support for the existing models “for as long as people have the vehicles.” The big seller in the quarter, however, wasn’t any car at all. The company sold a record number of its utility-scale Megapack batteries. In a shareholder deck, the company told investors it had “achieved our highest quarterly energy storage deployments, driven by record Megapack deployments.” That brought revenue from the energy sector up 27% from 2024 to $12.8 billion.
The Department of Energy has overhauled a set of nuclear safety rules and shared them with companies it’s regulating without making the changes public. Citing leaked documents, NPR reported Wednesday that the agency had cut more than 750 pages from earlier versions of the rules, “leaving only about one-third of the number of pages in the original documents.” The changes include loosening rules on monitoring radiation leaks in groundwater and raising the threshold for an accident investigation. When I asked Emmet Penney, a nuclear historian and a senior fellow at the right-leaning Foundation for American Innovation, what he made of the report, he said the cuts eliminated a number of dubiously useful rules, including reducing how much security is required at nuclear stations, and praised Secretary of Energy Chris Wright. “Reducing costs burdens like unnecessary security for test reactors is a smart move from the DOE, as is clarifying vague radiation standards,” he told me. “These changes demonstrate Secretary Wright’s seriousness when it comes to catalyzing the nuclear renaissance.”
Also on Wednesday, the Energy Department announced a new initiative asking states to express interest in hosting “Nuclear Lifecycle Innovation Campuses,” where companies across the nuclear fuel cycle could set up shop, including recycling used fuel.
Electric and gas utilities requested almost $31 billion worth of rate increases last year, according to a new analysis by the energy policy nonprofit PowerLines. That compares to $15 billion in 2024. “In case you haven’t already done the math: That’s more than double what utilities asked for just a year earlier,” Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote. Electricity prices went up by 6.7% in the past year, outpacing the 2.7% increase for prices overall. That makes power prices 37% more expensive than just five years ago. “These increases, a lot of them have not actually hit people's wallets yet,” PowerLines executive director Charles Hua told a group of reporters Wednesday afternoon. “So that shows that in 2026, the utility bills are likely to continue to rise, barring some major, sweeping action.” Those could affect some 81 million consumers, he said.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Drax built its business off a loophole in carbon accounting. Under the international rules on how to quantify emissions, the carbon from losing a tree is counted in the country where it’s felled. That meant chopping down old-growth trees in forests in the American South and shipping the vitamin-sized wood pellets to England to burn in a power plant counted as low-carbon energy in the United Kingdom — even if the power plant had to burn twice as much wood to equal the energy from coal. At long last, European and American policymakers are waking up to the realities of the wood pellet energy industry. Enviva, a major wood pellet producer, went bankrupt in 2024. Drax, meanwhile, has been losing green-energy subsidies in its native U.K. Now the company is facing the potential loss of the new biggest market for its wood pellets. Japan, compensating for the nuclear reactors still sitting idle 15 years after the Fukushima disaster, is set to soon surpass the U.K. as the world’s largest pellet importer market. But Japanese policymakers are now considering pulling support for all projects over 10 megawatts. “The real intention is quite simple: no new government support, phasing out. We don’t see any clear path of bringing down costs in the foreseeable future,” one government official told the Financial Times. “Existing projects might survive but no new projects are coming.”
New York City’s Department of Consumer and Worker Protection filed a lawsuit late last week against Radiant Solar and its owner, William James Bushell, demanding $18 million in restitution and about $1.7 million in penalties for damaging New Yorkers’ homes and leaving the customers across the city in debt. It’s the largest sum the city has ever sought from a home improvement contractor. The city argued that Radiant, as The New York Times put it, “engaged in a dizzying array of mechanical and monetary malfeasance for years.” That included padding loans with undisclosed “dealer fees,” signing customers up for large loans they didn't ask for, failing to file paperwork for customers to receive tax credits, and neglecting city approval processes. The company even allegedly ran a bogus sweepstakes for a new Tesla.
Redwood Materials’ big transformation is bringing in the money. Amid a two-year slump in lithium prices, the battery recycling startup announced the launch of a new venture last summer to provide grid-scale storage from restored battery packs. Yesterday, as Heatmap’s Katie Brigham wrote, “it’s clear just how much that bet has paid off.” The company raised a $425 million round of Series E funding for the new venture, called Redwood Energy. The money came from such investors as Google and Nvidia’s venture capital arms
A new PowerLines report puts the total requested increases at $31 billion — more than double the number from 2024.
Utilities asked regulators for permission to extract a lot more money from ratepayers last year.
Electric and gas utilities requested almost $31 billion worth of rate increases in 2025, according to an analysis by the energy policy nonprofit PowerLines released Thursday morning, compared to $15 billion worth of rate increases in 2024. In case you haven’t already done the math: That’s more than double what utilities asked for just a year earlier.
Utilities go to state regulators with its spending and investment plans, and those regulators decide how much of a return the utility is allowed to glean from its ratepayers on those investments. (Costs for fuel — like natural gas for a power plant — are typically passed through to customers without utilities earning a profit.) Just because a utility requests a certain level of spending does not mean that regulators will approve it. But the volume and magnitude of the increases likely means that many ratepayers will see higher bills in the coming year.
“These increases, a lot of them have not actually hit people's wallets yet,” PowerLines executive director Charles Hua told a group of reporters Wednesday afternoon. “So that shows that in 2026, the utility bills are likely to continue to rise, barring some major, sweeping action.” Those could affect some 81 million consumers, he said.
Electricity prices have gone up 6.7% in the past year, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, outpacing overall prices, which have risen 2.7%. Electricity is 37% more expensive today than it was just five years ago, a trend researchers have attributed to geographically specific factors such as costs arising from wildfires attributed to faulty utility equipment, as well as rising costs for maintaining and building out the grid itself.
These rising costs have become increasingly politically contentious, with state and local politicians using electricity markets and utilities as punching bags. Newly elected New Jersey Governor Mikie Sherrill’s first two actions in office, for instance, were both aimed at effecting a rate freeze proposal that was at the center of her campaign.
But some of the biggest rate increase requests from last year were not in the markets best known for high and rising prices: the Northeast and California. The Florida utility Florida Power and Light received permission from state regulators for $7 billion worth of rate increases, the largest such increase among the group PowerLines tracked. That figure was negotiated down from about $10 billion.
The PowerLines data is telling many consumers something they already know. Electricity is getting more expensive, and they’re not happy about it.
“In a moment where affordability concerns and pocketbook concerns remain top of mind for American consumers, electricity and gas are the two fastest drivers,” Hua said. “That is creating this sense of public and consumer frustration that we're seeing.”
The battery recycling company announced a $425 million Series E round after pivoting to power data centers.
Amidst a two year-long slump in lithium prices, the Nevada-based battery recycling company Redwood Materials announced last summer that it had begun a new venture focused on grid-scale energy storage. Today, it’s clear just how much that bet has paid off.
The company announced a $425 million round of Series E funding for the new venture, known as Redwood Energy. That came from some big names in artificial intelligence, including Google and Nvidia’s venture capital arm, NVentures. This marks the final close of the funding round, increasing the total from $350 million announced in October.
Redwood Energy adapts the company’s original mission — breaking down spent batteries to recover, refine, and resell critical minerals — to suit the data center revolution. Instead of merely extracting battery materials, the company can now also repurpose electric vehicle batteries that still have some life left in them as energy storage solutions for AI data centers, allowing Redwood to get value from the battery throughout its lifecycle.
“Regardless of where lithium prices are, if we can put [a lithium-ion battery] in a large-scale energy storage system, it can have a lot more value before we break it down into critical materials,” Claire McConnell, Redwood’s new VP of business development for energy storage, told me.
Over the past 12 to 18 months, she explained that the company had started to receive more and more used electric vehicle battery packs “in better condition than we initially anticipated.” Given the substantial electricity load growth underway, McConnell said the company saw it as “perfect moment” to “develop something that could be really unique for that market.”
At the time of Redwood Energy’s launch last June, the company announced that it had stockpiled over a gigawatt-hour of used EV batteries, with an additional 5 gigawatt-hours expected over the following year. Its first microgrid pilot is already live and generating revenue in Sparks, Nevada, operating in partnership with the data center owner and operator Crusoe Energy. That project is off-grid, supplying solar-generated electricity directly to Crusoe’s data center. Future projects could be grid-connected though, storing energy when prices are low and dispatching it when there are spikes in demand.
The company also isn’t limiting itself to used battery packs, McConnell told me. Plenty of manufacturers, she said, are sitting on a surplus of new batteries that they’re willing to offload to Redwood. The potential reasons for that glut are easy to see: already-slower-than-expected EV adoption compounded by Trump’s rollback of incentives has left many automakers with lower than projected EV sales. And even in the best of times, automakers routinely retool their product lines, which could leave them with excess inventory from an older model.
While McConnell wouldn’t reveal what percent of packs are new, she did tell me they make up a “pretty meaningful percentage of our inventory right now,” pointing to a recently announced partnership with General Motors meant to accelerate deployment of both new and used battery packs for energy storage.
While Redwood isn’t abandoning its battery recycling roots, this shift in priorities toward data center energy storage comes after a tough few years for the battery recycling sector overall. By last June, lithium prices had fallen precipitously from their record highs in 2022, making mineral recycling far less competitive. Then came Trump’s cuts to consumer electric vehicle incentives, further weakening demand. On top of that, the rise of lithium-iron phosphate batteries — which now dominate the battery storage sector and are increasingly common in EVs — have reduced the need for nickel and cobalt in particular, as they’re not a part of this cheaper battery chemistry.
All this helped create the conditions for the bankruptcy of one of Redwood’s main competitors, Li-Cycle, in May 2025. The company went public via a SPAC merger in 2021, aiming to commercialize its proprietary technique for shredding whole lithium-ion battery packs at once. But it ultimately couldn’t secure the funds to finish building out its recycling hub in Rochester, New York, and it was acquired by the commodities trading and mining company Glencore last summer.
“We started really early, and in a way we started Redwood almost too early,” JB Straubel, Redwood’s founder and Tesla’s co-founder, told TechCrunch last summer. He was alluding to the fact that in 2017, when Redwood was founded, there just weren’t that many aging EVs on the road — nor are there yet today. So while an influx of used EV batteries is eventually expected, slower than anticipated EV adoption means there just may not be enough supply yet to sustain a company like Redwood on that business model alone.
In the meantime, Redwood has also worked to recycle and refine critical minerals from battery manufacturing scrap and used lithium-ion from consumer electronics. Partnerships with automakers such as Toyota, Volkswagen, and General Motors, as well as global battery manufacturer Panasonic, have helped bolster both its EV battery recycling business and new storage endeavor. The goal of building a domestic supply chain for battery materials such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, and copper also remains as bipartisan as ever, meaning Redwood certainly isn’t dropping the recycling and refining arm of its business, even as it shifts focus toward energy storage.
For instance, it’s also still working on the buildout of a recycling and battery component production facility in Charleston, South Carolina. While three years ago the company announced that this plant would eventually produce over 100 gigawatt-hours of cathode and anode battery components annually, operations on this front appear to be delayed. When Redwood announced that recycling and refining operations had begun in Charleston late last year, it made no mention of when battery component production would start up.
It’s possible that this could be taking a backburner to the company’s big plans to expand its storage business. While the initial Crusoe facility offers 63 megawatt-hours of battery energy storage, McConnell told me that Redwood is now working on projects “in the hundreds of megawatt-hours, looking to gigawatt-hour scale” that it hopes to announce soon.
The market potential is larger than any of us might realize. Over the next five or so years, McConnell said, “We expect that repurposed electric vehicle battery packs could make up 50% of the energy storage market.”