You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:

Current conditions: Breezy weather in Sarasota, Florida, is increasing today’s fire danger • Turin, Italy, is bracing for an April’s worth of rain in a single day • The aurora borealis may be visible over the northern U.S. tonight and tomorrow thanks to a geomagnetic storm.
The International Energy Agency released its monthly analysis of the global oil market on Tuesday, writing “buckle up.” The group cut its forecast by almost a third, estimating world oil demand will rise by 730,000 barrels per day in 2025, down from its estimate of just over 1 million barrels per day last month. The group further predicted the slowdown will extend into 2026 due to a “fragile macroeconomic environment” and the continued growth of EVs. Though “imports of oil, gas, and refined products were given exemptions from the tariffs announced by the United States,” IEA wrote that its analysis took into consideration “concerns that the measures could stoke inflation, slow economic growth, and intensify trade disputes.” The group noted that the new tariffs also make it more expensive to buy steel and the equipment required for drilling, and that “the situation is still fluid and substantial risks remain.”
On Monday, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries also cut its 2025 global oil demand forecast. Likewise citing the Trump tariffs, OPEC sees world oil demand rising 1.3 million barrels per day in 2025 and 1.28 million barrels per day in 2026, each down about 150,000 barrels per day from March’s forecast.
On Monday, energy executives and trade groups formally warned the Trump administration that its cuts to the Department of Energy would sabotage the president’s stated goal of “energy dominance.” As Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer previously reported, the agency stands to lose nearly one-fifth of its employees to buyouts and layoffs, with The New York Times reporting Monday that some of the deepest cuts are anticipated at the Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations and the Loan Program Office, which also provides support for clean energy development. “LPO continues to play a critical role in financing infrastructure that enables new nuclear power development, revitalizes domestic mineral production, and modernizes both grid and gas systems — all central to the administration’s goals of lowering energy costs, reshoring manufacturing, and achieving energy dominance,” the 30 signatories wrote in the letter, which was addressed to Energy Secretary Chris Wright.
President Trump’s executive order meant to boost “beautiful clean coal” could cost “tens of billions” of solar grid interconnection investments, according to comments made by Grid Strategies president Rob Gramlich in a webinar reported on by PV Magazine. (Gramlich is also a Heatmap contributor.)
As my colleague Matthew Zeitlin pointed out last week, many of coal’s uses can be “easily substituted with other sources, such as natural gas,” which is part of why coal production has fallen in the U.S. since 2008. Trump’s order could extend about 50 gigawatts of coal that would otherwise likely have been retired, thereby limiting the amount of wind and solar that can come online. Gramlich’s co-host for the webinar, Roth Capital Partners Managing Director Phil Shen, added that he was “incrementally more pessimistic” about utility-scale solar given the administration’s bolstering of coal.
Wisconsin has seen a record number of wildfires in 2025, with local experts citing the warming climate and extended droughts as part of what is fueling the blazes. “We’ve never had this many fires in January and February ever in the state of Wisconsin,” Jim Bernier, the forest fire section manager of the state Department of National Resources, said in comments reported by Wisconsin Public Radio. Wisconsin averages around 864 wildfires annually; there have already been 470 wildfires in 2025, double what would be expected by this time of year. Making matters worse, researchers say that areas where urban development borders wildlands account for nearly 10% of the fire-prone land in the state. “We have to mentally prepare ourselves that … we’re in it for a long haul,” Bernier said.
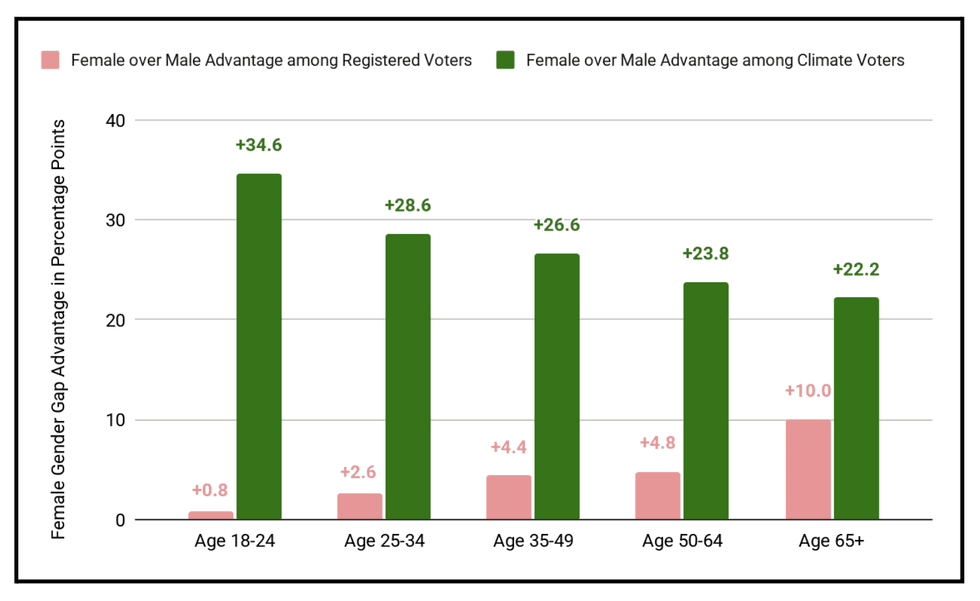
A new report released Monday found that women are “significantly more likely than men to name climate change or environmental issues as their top political priority.” The research, conducted by the Environmental Voter Project, revealed that 62% of climate voters are women, compared to just 37% being men. The divide is most pronounced among young voters, with women aged 18-24 twice as likely as men of the same age to list climate as a top priority. “This report confirms what so many of us have known for years: women are leading the charge against the climate crisis,” Jane Fonda said in a statement shared with the study’s release. “Mothers, grandmothers, and daughters are showing up, organizing, and voting like our lives — and the lives of our children — depend on it.”
Making buses free in New York City would wipe out $600 million a year in net fare revenues for the Metropolitan Transportation Authority — but create $1.5 billion a year in benefits for riders, boost ridership by 23%, and save riders 36 million hours a year, according to a new study by the transportation economist Charles Komanoff.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Even releasing hundreds of millions of barrels from the world’s strategic reserves will only cover about a month of missing supply.
Every day the Strait of Hormuz remains closed, the global oil supply deficit increases by millions of barrels. So far, even the biggest responses to the crisis are at best short-term and partial.
Today the International Energy Agency announced a coordinated deployment of 400 million barrels from its member states’ strategic reserves. The United States, which has a 414 million-barrel Strategic Petroleum Reserve, has yet to detail its plans to deploy reserves. President Trump appeared to confirm, however, that the U.S. would release some oil from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. “Right now, we’ll reduce it a little bit, and that brings the prices down,” he told a Cincinnati television station Wednesday.
Four-hundred-million barrels may sound like a lot, but even the back-of-the-envelope math about how far that will go is unforgiving.
Around 20 million barrels per day of oil were going through the Strait of Hormuz last year, according to the IEA, representing about a quarter of the world’s seaborne oil trade. Since its effective closure starting February 28 in response to the U.S. and Israeli strikes on Iran, some oil that would otherwise transit the strait is still getting out: The Saudi pipeline to the Red Sea can handle up to 7 million barrels per day; an Emirati pipeline can transit up to 2 million barrels per day; and Iran itself is still managing to export oil. That leaves some 10 million barrels not making it to the market, according to Greg Brew, an analyst at the Eurasia Group.
The IEA’s 400 million barrels therefore add up to just about 40 more days of missing supply — and that doesn’t take into account the matter of actually getting those barrels to market.
That will still take some time, Ben Cahill, a senior associate at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, explained to me.
“The question is how much of that volume can be offset by a stock release, and when. The timing really matters,” he said. “The U.S. SPR, for example, takes 13 days to hit the market from the time of a presidential order, according to the DOE. So we still have a period of big potential supply shortfalls.”
Then there are the shut-ins, oil wells that are no longer being pumped across the Gulf region due to the conflict, which add up to around 6 million to 7 million barrels per day across Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, and Iraq.
That’s “barrels gone now and barrels gone in the future,” Brew told me. Oil that was loaded on ships or put into storage before the closure could still end up on the market. “But the shut-ins are barrels that have disappeared.”
Prices also spiked after Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022, leading the U.S. to sell around 180 million barrels of oil from the SPR. Then, however, Russia was able to continue selling its oil on the world market, though the United States and its allies implemented a price cap.
This time, explained Employ America’s managing director of policy implementation, Arnab Datta, the price action has been more restrained even as the real supply hit has been far greater.
“It’s important to understand the scale of this supply shortage versus what we had then, which was a speculative supply shortage,” Datta said, comparing the response to the Ukraine invasion with the current conflict in the Persian Gulf. “This one is a physical supply shortage that's not being realized necessarily in prices.”
Exactly how much oil could be drawn out of the U.S. Strategic Petroleum Reserve is unclear. While its legal drawdown limit is 4.4 million barrels per day, it may not be physically able to hit that even if the U.S. wanted to. The four salt caverns where the oil is stored are likely at different levels of operational readiness, Datta explained, with only some of them having completed modernization operations that have been underway for nearly a decade. It’s also possible some are offline entirely. When oil was drawn from the SPR in 2022, outflows were around a million barrels per day.
Datta told me that it’s “unlikely” SPR’s actual drawdown capacity is much higher than that, and that he’d be “surprised if it was higher than two [million barrels per day].”
Other analysts were even more pessimistic. “Realistic U.S. SPR releases today are likely below the 1.0 [million barrels per day] pace averaged in 2022,” J.P. Morgan analyst Natasha Kaneva wrote in a note to clients Tuesday. The combined expected release rate from the IEA countries “would not materially ease” the shortfall, she wrote.
At best, the IEA release can help keep a lid on price increase, Ryan Cummings, a former economist at the White House Council of Economic Advisors and the chief of staff of the Stanford Institute for Economic Policymaking, told me. “But it’s not big enough to fully offset the current supply gap. And as time goes on, this supply gap will only get worse as there’s more shuttered production.”
Datta and his Employ America colleague Skanda Amarnath have called on the administration to at least clarify what the SPR is currently capable of even if they hold off on releases.
“Regardless of when or under what conditions a release occurs, we encourage the administration to take this moment to announce the operational status of the SPR,” Employ America said in a statement Wednesday.
Salt caverns are not the only place there’s oil underground in the United States, however.
While many rich countries have sizable reserves — Japan, which is heavily dependent on oil imports, maintains private and public stockpiles of about 440 million barrels — the United States is unique in its combination of reserves and production capacity, a legacy of the 1970s oil shock and the 2010s shale boom, making it into an exporting powerhouse.
But even if U.S. producers were to respond by ramping up output substantially (which their investors would almost certainly not want them to do) any new supply would not hit the market quickly enough to meet the physical shortage at play now.
“You can’t pull supply forward in a matter of weeks,” Cahill told me. “The only countries that can typically do that are those with spare production capacity.” And the countries with spare capacity that can ramp up production quickly? They’re “almost exclusively in the Gulf,” Cahill said.
While President Trump has trumpeted a new refinery project in Texas, its developers have said they don’t expect it to be operational until next year. That would process some 160,000 barrels per day, not nearly enough to make a dent in the supply shortage currently confronting the world right now.
The solution to the current shortfall therefore lies in the Persian Gulf, not the Gulf of Mexico.
“Policy measures may have limited impact on oil prices unless safe passage through the Strait of Hormuz is assured,” Kaneva wrote.
Absent a ceasefire between the U.S., Israel, and Iran, that day is likely still far off. After all, how can tankers be expected to sail through the strait when, Brew observed, “the U.S. Navy is saying we’re not even sending our ships?”
A new law piles taxes on the state’s last remaining coal plant, making it too expensive to operate.
Trump may have ordered Washington’s last coal-fired power plant to stay open, but it’s unlikely ever to operate ever again thanks to a crafty bit of policy the Evergreen state just passed.
Washington’s Governor Bob Ferguson is expected to sign a bill on Wednesday that accomplishes one very narrow goal: It taxes the hell out of any electricity generated by the TransAlta Centralia coal plant, effectively pricing it out of the market.
The Centralia plant was scheduled to close at the end of 2025 and begin undergoing a conversion to run on natural gas. In mid-December, however, Trump’s Secretary of Energy Chris Wright issued an emergency order to keep the plant’s coal unit open through March 16. The forced prolongation was meant “to ensure Americans in the Northwestern region of the United States have access to affordable, reliable and secure electricity heading into the cold winter months,” the DOE said. It was the fourth coal plant with an imminent retirement date Wright had ordered to stay open; a fifth order — for Craig Station in Colorado — followed a few weeks later.
To justify the “emergency,” Wright cited the North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s Winter Reliability Assessment, which found that the region had enough power to meet the expected peak winter demand, but may need additional resources if there were extreme winter events. But utilities in the region had more than a decade to make other plans to meet demand once the plant closed. Even TransAlta’s president and CEO, John Kousinioris, told investors in a February earnings call that he didn’t expect the plant to be needed to meet any emergencies given how much hydropower was available in the region at the time.
In that light — and given the fact that the federal order is going to expire in a few days — the legislature’s quick-footed policy response is somewhat symbolic, a middle finger to Trump’s coal agenda. But Wright recently extended his order keeping Michigan’s J.H. Campbell coal plant open for the third time, through May 18, and it’s possible he could do the same for the Washington plant.
“It would be great if it were symbolic,” Washington State Representative Joe Fitzgibbon, the bill’s lead sponsor, told me. “The bill felt like a layer of security that they would not start operating again, and then if the federal government tried to get more aggressive in their pursuit of the emergency order, that the state would be in a stronger position to ensure that the plant did not restart operations.”
I talked to Fitzgibbon about how the new law works and whether other states may be able to adopt a similar strategy.
I know that this closure had been planned for a very long time. When did the talks start?
There was a big negotiation and agreement in 2011 between the state and TransAlta, as well as environmental advocates and ratepayer advocates, to negotiate a shutdown timeline. The agreement provided that the plant would close by 2025 — that the first boiler would close in 2020 and the second would close in 2025.
There were a lot of elements to that agreement, including TransAlta making some big investments in the Centralia community to help with economic development, workforce development, clean energy investments. They committed $55 million to that community over the lifetime of the agreement. The state’s end of that bargain was that we would not apply any new greenhouse gas requirements to the plant during the lifetime of that memorandum of agreement.
In 2021 when we passed the Climate Commitment Act, our cap and trade program, we exempted the coal plant from coverage, which was controversial, but it felt like the right thing to adhere to the agreement and to keep the plant on track for closure in 2025.
And then Trump’s emergency order in December happened. Do you know how the plant has responded to that order?
They have not been operating since December 19. They were on track to close by the end of 2025 — they ended up closing a few weeks early, right around when the order came down from the Department of Energy. They were all out of coal; they had laid off their employees and had a skeleton crew. The order really didn’t make any sense because TransAlta did not have a customer. There was no utility or industrial customer looking to buy their power because that would have been illegal under another law that we passed, Washington’s clean electricity law, which said no coal could be in Washington rates after 2025.
The state sued the Department of Energy. TransAlta has been very quiet. My sense, reading between the lines, is that they were not eager to get into a legal fight with either the state or the federal government, so they were in this kind of awkward position.
So why did you feel the need to act with this bill?
I felt that the bill was necessary to lock in the closure plan. Even though they don’t have a buyer today, and no utility on the West Coast could really buy their power under Washington, Oregon or California law, that doesn’t mean they couldn’t have found a customer in Idaho or in Nevada or in Utah. Those seem unlikely, but that wasn’t impossible. I felt that the bill would provide the certainty that they would not restart operations.
What does the bill actually do?
The bill did three things. It repealed their exemption from the Climate Commitment Act. It also repeals their exemption from a much older emissions performance standard that they had also been exempt from under the conditions of the memorandum of agreement, and it repeals a long-standing sales tax exemption on the purchase of coal. So with those three elements, it would become extremely expensive for them to generate power at that facility.
To what do you owe the support behind this bill to?
I would say it was less controversial than most climate bills, but it didn’t get a lot of Republican votes. It got a handful in the House, which is unusual — most of the time, our climate bills don’t get any Republican votes. The fact that TransAlta was not opposing the bill and that nobody was really opposing it — because the only interest that wants to see the plant continue operations is the federal government — helped. I think that the fact that Puget Sound Energy, our state’s largest utility, was planned to be the customer for their transition to natural gas in 2028 meant that there was pretty strong consensus — or as strong of consensus as we ever get on climate legislation in our legislature — that it did not make sense to restart coal generation at that facility.
This legislation draws on some specific Washington policies. Do you think it is replicable in other places?
I think what’s replicable in other places is cap and trade. Washington and California are the only states that have economy-wide cap and trade programs. I think it is a testament to the power and durability of having an emissions cap. Our circumstances are a little bit unique here because we only have one coal plant and we have a lot of hydropower, but I think if we didn’t have cap and trade in place, the likelihood of the plant starting up again would have been higher, as well as the power of our 100% clean electricity law.
It’s a little odd that the Trump administration targeted this plant considering it was going to re-open as a natural gas plant. What do you make of that?
It’s strictly ideological for them. They’re so closely tied with the coal industry that I think that Chris Wright was looking for any coal plant that was scheduled to close around the country that he could stop closing. I think that they don’t understand our region and didn’t understand our laws and didn’t understand our electricity markets. I don’t know if other coal plants that have been proposed for closure are planned for transition to gas. In general I’m not a big fan of new gas generation, but I thought if there was anywhere it made sense, it was in this one location where so much of the infrastructure could be repurposed — where it wasn’t a brand new facility that was going to have a long lifespan. They would still have to stop generating gas power by 2045 under our clean electricity law.
I think the feds overplayed their hand. Our laws and our commitment as a state to getting off fossil fuels were more than they could overcome here, and I would love for other states to learn from Washington’s experience in how successful you can be if you stand your ground against the federal government.
Current conditions: The Central United States is bracing for flooding as soaking storms deluge the region • Arctic air is barreling southward to replace the record warmth in the Midwest and Northeast • Temperatures in the Indian state of Gujarat are hitting 104 degrees Fahrenheit.
If you know anything about America’s flagship nuclear reactor, the Westinghouse AP1000, you know the only two built in the country so far cost around $35 billion total to install, more than double their original cost estimate. While the best projections at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology suggest the next AP1000 will be the cheapest option per megawatt of any reactors currently in development in the U.S., no one really knows exactly how much the project would cost. Westinghouse can now put a number on how much building a bunch of new AP1000s would do for the U.S. economy, however. A study it commissioned by the consultancy PricewaterhouseCoopers found that, assuming an 80-year lifespan, a fleet of 10 new AP1000s would add more than $1 trillion to America’s gross domestic product.
Here are some more numbers from PwC’s report:
The 10-reactor target comes from one of President Donald Trump’s four executive orders on nuclear power last May directing the Department of Energy to build a fleet of new large-scale reactors with an already-certified design. The AP1000 is the obvious frontrunner to fulfill that order, and the agency has already begun meeting with utilities and developers, as Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer reported last month. Dan Sumner, Westinghouse’s interim chief executive, said the report “highlights that work to deploy a 10-unit AP1000 fleet can begin immediately” and called the reactor “the only fully licensed, construction-ready advanced reactor available today.”
In a Tuesday morning post on X, Secretary of Energy Chris Wright announced that the U.S. Navy had “successfully escorted an oil tanker through the Strait of Hormuz to ensure oil remains flowing to global markets,” crediting President Donald Trump with “maintaining stability of global energy during the military operations against Iran.” Newswires promptly blasted out the story. Oil prices went for what The Wall Street Journal called “another wild ride.” Then, abruptly, Wright deleted the tweet. Hours later, White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt corrected the record: “The U.S. Navy has not escorted a tanker or vessel at this time.” The Energy Department ultimately blamed a staffer for incorrectly captioning a video of Wright speaking.
That wasn’t the only thing roiling oil markets. The Financial Times blamed “mixed messages” from U.S., Israeli, and Iranian leadership about the nature of the conflict coming to an end. Then, in a separate scoop from the Journal on Tuesday, the International Energy Agency proposed the largest release of oil reserves in its history, exceeding 182 million barrels of oil. Countries that depend heavily on imported fuels are preparing for shortfalls. Thailand and several oil-poor Asian nations this week ordered government bureaucrats to take the stairs and work from home to save energy. In a Tuesday night post on X, Senator Chris Murphy, the Democrat from Connecticut, said administration officials briefed him on classified intelligence about the war and “on the Strait of Hormuz, they had NO PLAN.” He continued: “I can’t go into more detail about how Iran gums up the Strait, but suffice it say [sic], right now, they don’t know how to get it safely back open. Which is unforgiveable, because this part of the disaster was 100% foreseeable.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
The U.S. solar industry installed just over 43 gigawatts of panels last year, a 14% decrease from 2024, according to the latest report from the consultancy Wood Mackenzie and the Solar Energy Industries Association. The utility-scale sector, which depends heavily on cheap imported panels, shrank nearly 40% quarter-over-quarter in the last three months of 2025. Residential solar declined by just 2%. Still, solar accounted for 54% of all new power-generating capacity in the U.S. In every future scenario the report analyzed, solar made up roughly half of all new capacity every year through 2060.
The solar manufacturing industry, on the other hand, had what the report called “a monumental year.” New cell capacity continued to expand, while the first new wafer capacity since 2016 came online. If you want a primer on how panels work, Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin has a good explainer on what exactly goes on with the different components.
Big companies including Tesla, Google, and the appliance maker Carrier launched a new industry coalition called Utilize on Tuesday “to address the most urgent challenges facing the U.S. energy system: growing electricity demand and rising power bills driven in part by an electrical grid that is built for short periods of peak use but underutilized most of the time.” The companies involved in the group planned to advocate to state governments, utilities, and regulators for “technology-neutral” policies. “For decades, we’ve built the grid to meet peak demand, even though large portions of it sit unused for most hours of the year,” Ian Magruder, the executive director of Utilize, said in a statement. “It’s like building an airplane that only flies with full passengers a few times a year. That excess capacity is hiding in plain sight, and new technologies give us the opportunity to unlock it. Better grid utilization is one of the fastest, most practical levers states can pull to reduce power bills while supporting economic growth.”
The great battle to defend our shores from the invasion of Asian carp has brought together two political foes: President Trump and one of the people widely seen as a candidate for the Democratic nod to replace him in 2028. On Tuesday, Trump posted on Truth Social that he was working with Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer “on trying to save the Great Lakes from the rather violent and destructive” invasive species, which dominate some inland rivers in the U.S. to the point that the fish, first brought over from China in the 1970s, now make up 95% of the total biomass. In the post, Trump said he would ask other governors to join the effort, “including those of Illinois, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, New York,” as well as Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney, whom he called “the future Governor of Canada,” a nod to his often-stated desire of annexing Canada as the U.S.’s 51st state.
Separately, he said, “I am also working to save The Great Salt Lake, in Utah, which, in a short period of time, if nothing is done, will have no water.” He offered no other details. But last week, the federal government reached a deal with Utah to claim 22,311 acres of the Great Salt Lake that had been disputed with the state, the Utah News Dispatch reported.
A conservation ecologist studying macaws in Peru spent his weekends visiting archaeological sites such as 1,000-year-old tombs in the arid north. To his surprise, parrot feathers adorned burial sites on the opposite side of the Andes mountains, in a region nowhere near the birds’ habitat. He spent years trying to find out how the feather got there. The side quest turned into a new study published Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications, in which the scientist, George Olah, concluded that live parrots were traded far and wide across the mountainous region. The feathers pointed to what The New York Times called “a complex trade network that predates the Inca Empire.”