You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The founder of Galvanize Climate Solutions and a 2020 presidential candidate does some math on how smart climate policy could help the U.S. in a trade war.

We’re now four months into a worldwide trade war, and the economic data confirms it’s Americans who are paying the price. A growing body of surveys and forecasts indicate that inflation will be a persistent, wallet-draining reality for U.S. households. Voters now expect inflation to hit 7.3% next year, and as of March, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development projects that tariffs and trade tensions could help drive U.S. inflation up by 0.3 percentage points in 2025.
But there are solutions for whipping inflation. One is unleashing an abundance of clean energy.
Clean energy can have a powerful deflationary ripple effect, lowering prices across the economy. Solar has for years been the cheapest form of new energy around the world, and recent research from Goldman Sachs shows that prices of clean technologies like large-scale solar power and battery storage are falling. These lower costs are helping to keep electricity prices more stable, even as demand rises due to the growing number of data centers, the return of U.S. manufacturing, and the electrification of transport and heating.
As a thought experiment, my team gathered data on the U.S. energy market to estimate the potential deflationary effect that accelerating clean energy development could have on the American economy. At the end of our analysis, we found that accelerating renewable energy development nationwide could reduce inflation by 0.58 percentage points — meaning that if inflation were running at 4%, widespread clean energy would bring it down to 3.42%. This would save the average American family approximately $441 each year, or nearly three months’ worth of electricity bills.
While our model doesn’t completely capture all of America’s regional complexities regarding energy policy or resource availability, it shows what’s possible. Call it the “Clean Energy Dividend” — a measurable financial return Americans receive when renewable deployment expands.
These numbers are based on something that’s already happening in Texas, where building new clean energy projects is relatively easy. Since 2019, Texas has expanded its solar capacity by 729% and wind power by 49%, faster than any other state in the nation. These developments have added approximately 39,000 gigawatt-hours of solar, 41,000 gigawatt-hours of wind to the Texas grid. In that same time, Texas has also added 9,300 megawatts of battery capacity — a 8,941% increase.
To match Texas’ success, the rest of America would need to significantly ramp up its clean energy production. According to our analysis, the other 49 states combined would need to produce nearly 73% more renewable electricity than currently planned for 2025. That means that instead of adding 66,300 gigawatt-hours of clean power to the grid this year as projected, they’d need to add 114,700 gigawatt-hours. It’s an ambitious target, but one that would help keep costs down for consumers and businesses.
The deflationary impact would hit in two ways: from direct reductions in electricity bills and from lower costs for goods and services.
First, on direct reductions: The Electric Reliability Council of Texas market, otherwise known as ERCOT, is projected to experience a 12% decrease in wholesale electricity prices from 2024 to 2025; the rest of the United States, meanwhile, is expected to see a 3% increase in retail electricity prices during the same period. This creates a 15% gap between Texas and the national average.
The average American household uses about 10,791 kilowatt-hours of electricity annually, which currently costs approximately $1,779 per year. With a projected 3% national increase, this would rise to $1,828 in 2025. If prices fell by 12% as in Texas, however, the cost would decrease to $1,571, resulting in a direct savings of about $258 per household.
Second, beyond direct savings: Our analysis found that electricity costs constitute about 2.4% of all business expenses in the economy. When businesses pay less for electricity, they typically pass about 70% of those savings to consumers through lower prices. This translates to an additional $183 in annual savings per household on everyday goods and services.
Combining these figures, the total benefit per household would be $441 annually. In terms of inflation, the direct effect on electricity bills contributes 0.34%, and the indirect effect through price decreases on other goods contributes 0.24%. Together, they account for a 0.58% reduction in inflation.
Far more than the U.S. would like to admit, its economy remains highly susceptible to oil shocks. Nearly every economic recession in the U.S. since the 1940s has been preceded by a large increase in the price of fossil fuels. Similarly, all but three oil shocks have been followed by a recession. And while the price of oil is low now, this doesn’t guarantee it will be in the future. When energy costs rise sharply — whether from conflicts, production cuts, or supply chain disruptions — the effects cascade through every sector of our economy.
Renewable energy serves as a powerful buffer against these inflationary pressures. That said, expanding renewable energy faces challenges. Some communities oppose projects such as wind and solar farms due to concerns about land use, aesthetics, and environmental impacts, leading to delays or cancellations. At the national level, the Trump administration is doing everything it can to hinder investment and slow the growth of renewable energy infrastructure. These obstacles can impede progress toward a more stable and affordable energy future — even in Texas.
There, Republican lawmakers have introduced a wave of legislation aimed at imposing new fees and regulatory hurdles on renewable energy projects, restricting further development, and mandating costly backup power requirements. These measures could raise wholesale electricity prices by 14%, according to an analysis by Aurora Energy Research. Just as the rest of America should be emulating Texas’ success, Texas is busy unraveling it to resemble the rest of America.
Still, there are several factors that can speed renewable deployment nationwide: streamlining permitting processes, developing competitive electricity markets, ensuring sufficient transmission infrastructure, and passing supportive regulatory frameworks. While geography will always affect which resources are viable, every region has significant untapped potential — from geothermal in the West to solar in the South.
No matter where you stand on decarbonization and the fight against climate change, we should pay attention to any idea that can fight inflation, put money back in Americans pockets, create jobs, make our energy more secure, and help the environment all at once. The Clean Energy Dividend may not solve everything—but it’s about as close to a win-win-win as we’re going to find.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On power plant emissions, Fervo, and a UK nuclear plant
Current conditions: A week into Atlantic hurricane season, development in the basin looks “unfavorable through June” • Canadian wildfires have already burned more land than the annual average, at over 3.1 million hectares so far• Rescue efforts resumed Wednesday in the search for a school bus swept away by flash floods in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa.
The Environmental Protection Agency plans to announce on Wednesday the rollback of two major Biden-era power plant regulations, administration insiders told Bloomberg and Politico. The EPA will reportedly argue that the prior administration’s rules curbing carbon dioxide emissions at coal and gas plants were misplaced because the emissions “do not contribute significantly to dangerous pollution,” per The Guardian, despite research showing that the U.S. power sector has contributed 5% of all planet-warming pollution since 1990. The government will also reportedly argue that the carbon capture technology proposed by the prior administration to curb CO2 emissions at power plants is unproven and costly.
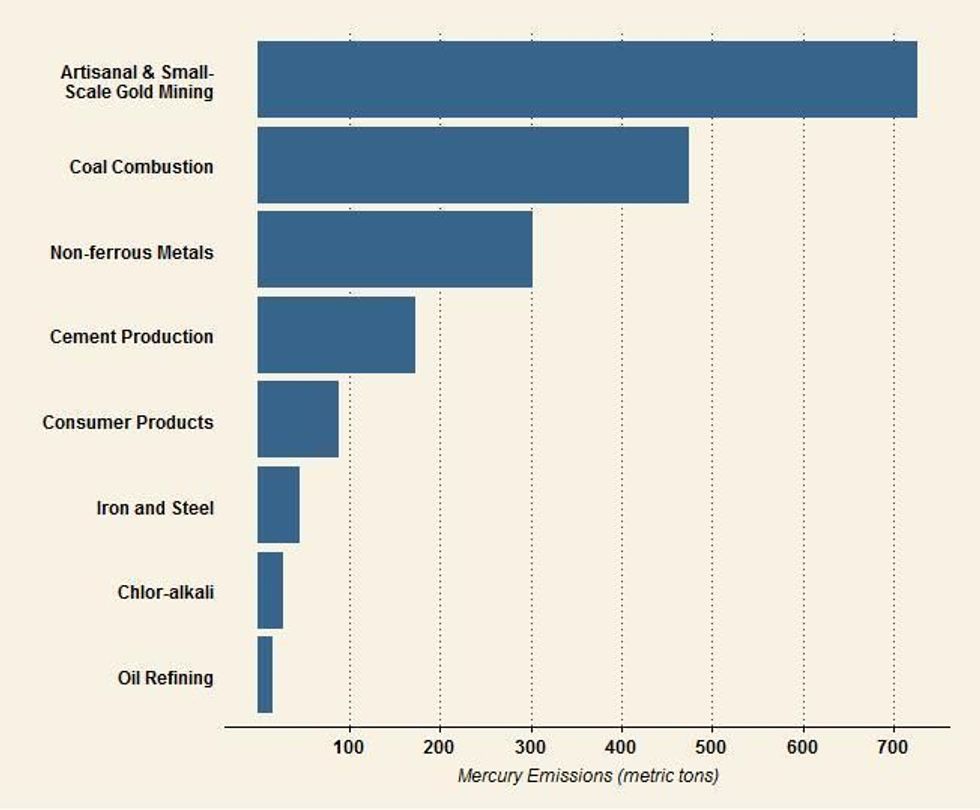
Similarly, the administration plans to soften limits on mercury emissions, which are released by burning coal, arguing that the Biden administration “improperly targeted coal-fire power plants” when it strengthened existing regulations in 2024. Per a document reviewed by The New York Times, the EPA’s proposal will “loosen emissions limits for toxic substances such as lead, nickel, and arsenic by 67%,” and for mercury at some coal power plants by as much as 70%. “Reversing these protections will take lives, drive up costs, and worsen the climate crisis,” Climate Action Campaign Director Margie Alt said in a statement. “Instead of protecting American families, [President] Trump and [EPA Administrator Lee] Zeldin are turning their backs on science and the public to side with big polluters.”
Fervo Energy announced Wednesday morning that it has secured $206 million in financing for its 400-megawatt Cape Station geothermal project in southwest Utah. The bulk of the new funding, $100 million, comes from the Breakthrough Energy Catalyst program.
Fervo’s announcement follows on the heels of the company’s Tuesday announcement that it had drilled its hottest and deepest well yet — at 15,000 feet and 500 degrees Fahrenheit — in just 16 days. As my colleague Katie Brigham reports, Fervo’s progress represents “an all too rare phenomenon: A first-of-a-kind clean energy project that has remained on track to hit its deadlines while securing the trust of institutional investors, who are often wary of betting on novel infrastructure projects.” Read her full report on the clean energy startup’s news here.
The United Kingdom said Tuesday that it will move forward with plans to construct a $19 billion nuclear power station in southwest England. Sizewell C, planned for coastal Suffolk, is expected to create 10,000 jobs and power 6 million homes, The New York Times reports. Sizewell would be only the second nuclear power plant to be built in the UK in over two decades; the country generates approximately 14% of its total electricity supply through nuclear energy. Critics, however, have pointed unfavorably to the other nuclear plant under construction in the UK, Hinkley Point C, which has experienced multiple delays and escalating costs throughout its development. “For those who have followed Sizewell’s progress over the years, there was a glaring omission in the announcement,” one columnist wrote for The Guardian. “What will consumers pay for Sizewell’s electricity? Will it still be substantially cheaper in real terms than the juice that will be generated at Hinkley Point C in Somerset?” The UK additionally announced this week that it has chosen Rolls-Royce as the “preferred bidder” to build the country’s first three small modular nuclear reactors.
The European Union on Tuesday proposed a ban on transactions with Nord Stream 1 and 2 as part of a new package of sanctions aimed at Russia, Bloomberg reports. “We want peace for Ukraine,” the president of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, said at a news conference in Brussels. “Therefore, we are ramping up pressure on Russia, because strength is the only language that Russia will understand.” The package would also lower the price cap on Russian oil to $45 a barrel, down from $60 a barrel, von der Leyen said, as well as crack down on Moscow’s “shadow fleet” of vessels used to transport sanctioned products like crude oil. The EU’s 27 member states need to unanimously agree to the package for it to be adopted; their next meeting is on June 23.
The world’s oceans hit their second-highest temperature ever in May, according to the European Union’s Earth observation program Copernicus. The average sea surface temperature for the month was 20.79 degrees Celsius, just 0.14 degrees below May 2024’s record. Last year’s marine heat had been partly driven by El Niño in the Pacific, so the fact that the oceans remain warm in 2025 is alarming, Copernicus senior scientist Julien Nicolas told the Financial Times. “As sea surface temperatures rise, the ocean’s capacity to absorb carbon diminishes, potentially accelerating the build-up of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and intensifying future climate warming,” he said. In some areas around the UK and Ireland, the sea surface temperature is as high as 4 degrees Celsius above average.

The Pacific Island nation of Tonga is poised to become the first country to recognize whales as legal persons — including by appointing them (human) representatives in court. “The time has come to recognize whales not merely as resources but as sentient beings with inherent rights,” Tongan Princess Angelika Lātūfuipeka Tukuʻaho said in comments delivered ahead of the U.N. Ocean Conference in Nice, France.
Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and the rest only have so much political capital to spend.
When Donald Trump first became a serious Presidential candidate in 2015, many big tech leaders sounded the alarm. When the U.S. threatened to exit the Paris Agreement for the first time, companies including Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Facebook (now Meta) took out full page ads in The New York Times and The Wall Street Journal urging Trump to stay in. He didn’t — and Elon Musk, in particular, was incensed.
But by the time specific climate legislation — namely the Inflation Reduction Act — was up for debate in 2022, these companies had largely clammed up. When Trump exited Paris once more, the response was markedly muted.
Now that the IRA’s tax credits face clear and present threats, this same story is playing out again. As the Senate makes its changes to the House’s proposed budget bill, tech giants such as Microsoft, Google, Meta, and Amazon are keeping quiet, at least publicly, about their lobbying efforts. Most did not respond to my request for an interview or a statement clarifying their position, except to say they had “nothing to share on this topic,” as Microsoft did.
That’s not to say they have no opinion about the fate of clean energy tax credits. Microsoft, Google, Meta, and Amazon have all voluntarily set ambitious net-zero emissions targets that they’re struggling to meet, largely due to booming data center electricity demand. They’re some of the biggest buyers of solar and wind energy, and are investing heavily in nuclear and geothermal. (On Wednesday morning, Pennsylvania’s Talen Energy announced an expanded power purchase agreement with Amazon, for nearly 2 gigawatts of power through 2042.) All of these energy sources are a whole lot more accessible with tax credits than without.
There’s little doubt the tech companies would prefer an abundant supply of cheap, clean energy. Exactly how much they’re willing to fight for it is the real question.
The answer may come down to priorities. “It’s hard to overstate how much this race for AI has just completely changed the business models and the way that these big tech companies are thinking about investment,” Jeff Navin, co-founder of the climate-focused government affairs firm Boundary Stone Partners, told me. “While they’re obviously going to be impacted by the price of energy, I think they’re even more interested and concerned about how quickly they can get energy built so that they can build these data centers.”
The tech industry has shown much more reluctance to stand up to Trump, period, this time around. As the president has moved from a political outsider to the central figure in the Republican party, hyperscalers have increasingly curried his favor as they advocate against actions that could pose an existential risk to their business — think tighter regulations on the tech sector or AI, or tariffs on key supplies made in Asia.
As Navin put it to me, “When you have a president who has very strong opinions on wind turbines and randomly throws companies’ names in tweets in the middle of the night, do you really want to stick your neck out and take on something that the president views as unpopular if you’ve got other business in front of him that could be more impactful for your bottom line?”
It is undeniably true that the AI-driven data center boom is pushing these companies to look for new sources of clean power. Last week Meta signed a major nuclear deal with Constellation Energy. Microsoft is also partnering with Constellation to reopen Three Mile Island, while Google and Amazon have both announced investments in companies developing small modular reactors. Meta, Google, and Microsoft are also investing in next-generation geothermal energy startups.
But while the companies are eager to tout these partnerships, Navin suspects most of their energy lobbying is now being directed towards efforts such as permitting reform and building out transmission infrastructure. Publicly available lobbying records confirm that these are indeed focus areas, as they’re critical to bringing data centers online quickly, regardless of how they’re powered and whether that power is subsidized. “They’re not going to stop construction on an energy project that has access to electricity just because that electricity is marginally more expensive,” Navin told me. “There’s just too much at stake.”
Tech companies have lobbied on numerous budget, tax, sustainability, and clean energy issues thus far this year. Amazon’s lobbying report is the only one to specifically call out efforts on “renewable energy tax credits,” while Meta cites “renewable energy policy” and Microsoft name-drops the IRA. But there’s no hard and fast standard for how companies describe the issues they’re lobbying on or what they’re looking to achieve. And perhaps most importantly, the reports don’t disclose how much money they allot to each issue, which would illuminate their priorities.
Lobbying can also happen indirectly, via industry groups such as the Clean Energy Buyers Association and the Data Center Coalition. Both have been vocal advocates for preserving the tax credits. The Wall Street Journal recently detailed a lobbying push by the latter — which counts Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, and Google among its most prominent members — that involved meetings with about 30 Republican senators and a letter to Senate Majority Leader John Thune.
DCC didn’t respond to my request for an interview. But CEBA CEO Rich Powell told me, “If we take away these incentives right now, just as we’re getting the rust off the gears and getting back into growth mode for the electricity economy, we’re really concerned about price spikes.”
The leader of another industry group, Advanced Energy United, shared Powell’s concern that passing the bill would mean higher electricity prices. Taking away clean energy incentives would ”fundamentally undercut the financing structure for — let’s be frank — the vast majority of projects in the interconnection queue today,” Harry Godfrey, the managing director of AEU, told me.
Being part of an industry association is by no means a guarantee of political alignment on every issue. Microsoft, Google, Meta, and Amazon are also members of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce — by far the largest lobbying group in the U.S. — which has a long history of opposing climate action and the IRA itself. Apple even left the Chamber in 2009 due to its climate policy stances.
But Powell and Godfrey implied that the tech giants' views are — or at least ought to be — in alignment with theirs. “Many of our members are lobbying independently. Many of them are lobbying alongside us. And then many of them are supporting CEBA to go and lobby on this,” Powell told me, though he wouldn’t reveal what actions any specific hyperscalers were taking.
Godfrey said that AEU’s positions are “certainly reflective of what large energy consumers, notably tech companies, have been working to pursue across a variety of technologies and with applicability to a couple of different types of credits.”
And yet hyperscalers may have already spent a good deal of their political capital fighting for a niche provision in the House’s version of the budget bill, which bans state-level AI regulation for a decade. That would make the AI boom infinitely easier for tech companies, who don’t want to deal with a patchwork of varying regulations, or really most regulations at all.
On top of everything else, big tech in particular is dealing with government-led anti-trust lawsuits, both at home and abroad. Google recently lost two major cases to the Department of Justice, related to its search and advertising business. A final decision is pending regarding the Federal Trade Commission’s antitrust lawsuit against Meta, regarding the company’s acquisition of Instagram and WhatsApp. Not to be outdone, Amazon will also be fighting an antitrust case brought by the FTC next year.
As these companies work to convince the public, politicians, and the courts that they’re not monopolistic rule-breakers, and that AI is a benevolent technology that the U.S. must develop before China, they certainly seem to be relinquishing the clean energy mantle they once sought to carry, at least rhetorically. We’ll know more once all these data centers come online. But if the present is any indication, speed, not green electrons, is the North Star.
Editor’s note: This story has been updated to reflect Amazon’s power purchase agreement with Talen Energy.
The new funding comes as tax credits for geothermal hang in the balance.
The good news is pouring in for the next-generation geothermal developer Fervo Energy. On Tuesday the company reported that it was able to drill its deepest and hottest geothermal well to date in a mere 16 days. Now on Wednesday, the company is announcing an additional $206 million in financing for its Cape Station project in Utah.
With this latest tranche of funding, the firm’s 500-megawatt development in rural Beaver County is on track to deliver 24/7 clean power to the grid beginning in 2026, reaching full operation in 2028. The development is shaping up to be an all-too-rare phenomenon: A first-of-a-kind clean energy project that has remained on track to hit its deadlines while securing the trust of institutional investors, who are often wary of betting on novel infrastructure projects.
The bulk of this latest financing comes from the Bill Gates-backed Breakthrough Energy Catalyst program, which provided $100 million in project-level equity funding. The energy and commodity trading company Mercuria provided $60 million in corporate loans, increasing its existing fixed-term loan from $40 million to $100 million. An additional $45.6 million in short-term debt financing came from XRL-ALC, an affiliate of X-Caliber Rural Capital, which provides loans to infrastructure projects in rural areas. That comes on top of a previous $100 million loan from the firm.
The plan is for Cape Station to deliver 100 megawatts of grid power in 2026, with the additional 400 megawatts by 2028. The facility has the necessary permitting to expand production to two gigawatts — twice the size of a standard nuclear reactor. And on Monday, the company announced that an independent report from the consulting firm DeGolyer & MacNaughton confirms that the project could expand further still — eventually supporting over 5 gigawatts of clean power at depths of up to 13,000 feet. The company’s latest drilling results, which reached 15,765 feet at 520 degrees Fahrenheit, could push the project’s potential power output even higher.
Traditional geothermal wells normally max out at around 10,000 feet, and must be built in locations where a lucky confluence of geological features come together: high temperatures, porous rock, and naturally occurring water or steam. But because Fervo can drill thousands of feet deeper, it’s able to access hot rocks in locations that weren’t previously suitable for geothermal development, pumping high-pressure water down into the wells to fracture rocks and thus create its own geothermal reservoirs.
The primary customer for Fervo’s Cape Station project is Southern California Edison, which signed a 320-megawatt power purchase agreement with the company last year, advertised as the largest geothermal PPA ever. Shell was also announced as a customer this year. Fervo is already providing 3.5 megawatts of power to Google via a pilot project in Nevada, which it’s seeking to expand, entering into a 115 megawatt PPA with NV Energy and the tech giant to further build out production at this location.
Fervo’s latest funding comes on top of last February’s $244 million Series D round led by Devon Energy, as well as an additional $255 million in corporate equity and debt financing that it announced last December. On top of investments from well known climate tech venture firms such as Breakthrough Energy Ventures and Galvanize Climate Solutions, the company has secured institutional investment from Liberty Mutual as well as public pension funds such as the California State Teachers’ Retirement System and the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board.
Fervo, like all clean energy startups, also stands to benefit greatly from the Inflation Reduction Act’s clean energy tax credits, which are now in jeopardy as President Trump’s One Big, Beautiful Bill works its way through the Senate. While Secretary of Energy Chris Wright has traditionally been a booster of geothermal energy and is advocating to keep tax incentives for the technology in place through 2031, the bill as it stands would essentially erase incentives for all geothermal projects that start construction more than 60 days after the bill’s passage.
Fervo broke ground on Cape Station in 2023, so that project will make the cut. For future Fervo developments, it’s much less clear. But for now, the company seems to be flush with cash and potential in a climate tech world awash in ill omens.