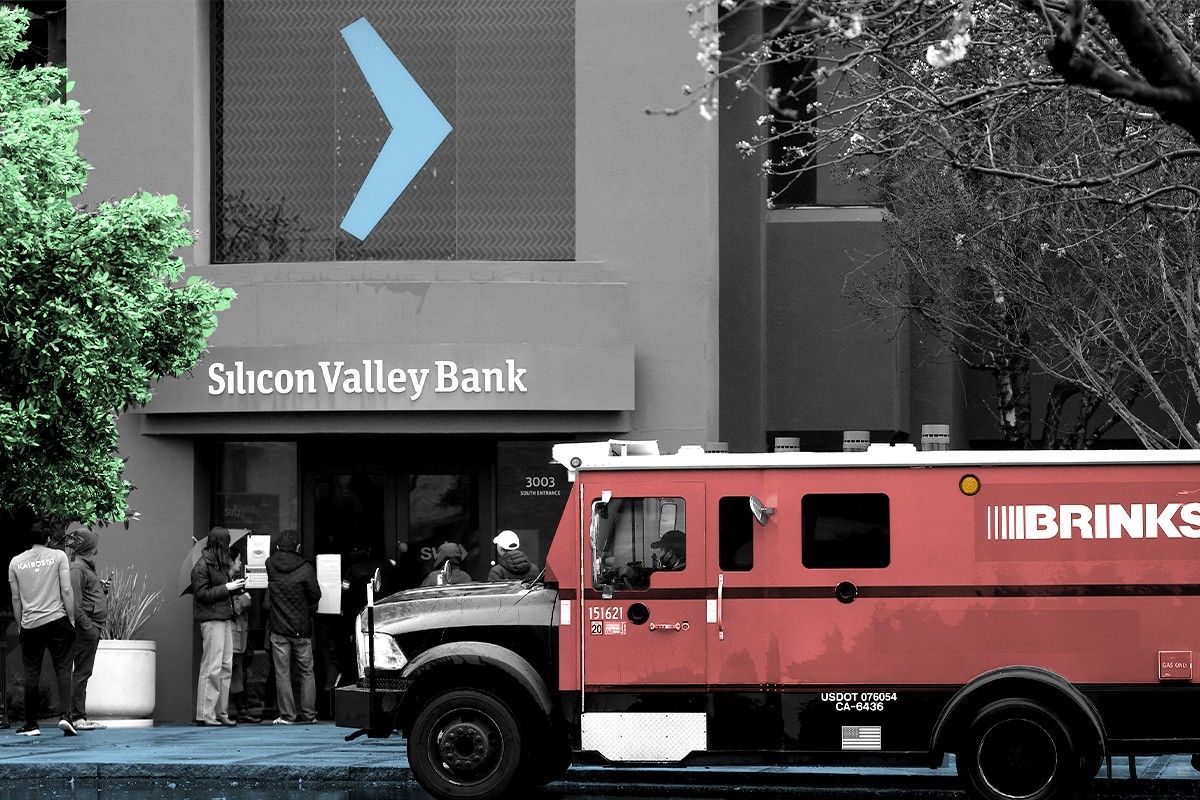
The United States witnessed its largest bank failure since 2008 on Friday, as Silicon Valley Bank ran out of cash and was taken over by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
True to its name, the bank was central to the technology ecosystem and Northern California economy; it claimed half of the country’s venture-backed startups as customers.
But what hasn’t received as much attention is that Silicon Valley Bank was particularly important to the climate-tech sector.
“Silicon Valley Bank was an integral part of the early-stage climate tech community and I hope that they survive in some form to continue that role,” Gabriel Kra, a managing director at Prelude Ventures, told me on Friday.
Silicon Valley Bank served as a banker to dozens of climate and energy-tech companies, holding their cash on a day-to-day basis and issuing billions of dollars in loans in support of the type of large-scale, one-off projects that are essential to the sector.
The bank’s website bragged about its particular support of solar, hydrogen, and energy-storage companies. It provided more than half a billion dollars in revolving credit to Sunrun, the country’s largest residential solar company. (Sunrun did not respond to a request for comment by press time.)
And more than 60 percent of community solar financing nationwide involved SVB in some capacity, the bank claimed on its website.
The bank also published influential annual reports on the climate-tech sector, and it sponsored events for climate VCs and startups — including one at the Lake Tahoe Ritz Carlton as recently as last week.
“They were careful, thoughtful, and willing lenders to early-stage companies,” Kra said. “As a bank, they were focused on that segment of the ecosystem and they understood the risks they were taking more than a bank that wasn’t focused.”
As news of the bank’s downfall spread, at least one venture firm extended emergency support so that companies could still pay their employees.
“The downfall of SVB will launch a thousand tweet threads, but right now our focus is securing payrolls for the Lowercarbon portfolio companies whose cash is tied up so they can keep up their planet-healing work,” Clay Dumas, a founding partner at Lowercarbon Capital, a climate-focused venture fund, told me in an email.
SVB’s collapse “has consumed the time of every founder I know for the last 36 hours,” Tim Latimer, the CEO of Fervo Energy, a geothermal company based in Texas and California, said on Twitter in a response to this story.
The bank’s recent problems weren’t connected to its climate-tech or startup lending, although they did stem from its broad lack of diversification away from the startup sector and Bay Area economy. In 2020 and 2021, the bank’s clients had more cash than they knew what to do with, and the bank chose to buy bonds and other securities to earn a higher yield on deposits. But over the past few months, as startups and the tech sector writ large faced a choppier economy, many of its depositors withdrew their money — and the bank had to sell its assets, which had lost value.
Because of its large number of corporate clients, most of its clients kept balances at the bank in excess of the $250,000 in deposit insurance provided by the federal government. That means many startups are now stuck in a potentially months-long line to get their money back — if they get it at all.
“Startups need cash — they’re not run in the same way that Fortune 500 companies are run,” Kra said. “Losing access to their cash balance for potentially several months can have catastrophic effects. And a small portion of companies in the space are probably looking at that possibility and figuring out how to avoid it.”
This article was updated at 11:35 PM EST on Friday to incorporate new details and quotes.
To receive Robinson Meyer's articles directly in your inbox, sign up for Heatmap Daily:










 Pfluger in the U.S. Capitol. Photo by Andrew Harnik/Getty Images
Pfluger in the U.S. Capitol. Photo by Andrew Harnik/Getty Images
