You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On Toyota’s recalls, America’s per-capita emissions, and Sierra Club drama

Current conditions: Drought is worsening in the U.S. Northeast, where cities such as Pittsburgh and Bangor, Maine have recorded 30% less rainfall than average • Temperatures in the Mississippi Valley are soaring into the triple digits, with cities such as Omaha, Nebraska and St. Louis breaking daily temperature records with highs of up to 20 degrees Fahrenheit above average • A heat wave in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, has sent temperatures as high as 114 degrees.
Orsted is offering investors a nearly 70% discount on the new shares issued to raise money to save its American offshore wind projects amid the Trump administration’s aggressive crackdown on the industry. The Danish energy giant won nearly unanimous approval from its shareholders earlier this month for a rights issue aimed at raising $9.4 billion. Shares in the company, which is half owned by the government in Copenhagen, closed around $32 each on Friday. But the offering of 901 million new shares came at a subscription rate of about $10.50 each. Orsted’s projects in the northeastern U.S. already “struggled” with what The Wall Street Journal listed as “supply-chain bottlenecks, higher interest rates, and trouble getting tax credits,” which culminated in the restructuring last year that saw the company “pull out of two high-profile wind projects off the coast of New Jersey.”
The offshore wind industry, as I noted in yesterday’s newsletter, is just starting to fight back. The owners of the Rhode Island offshore project Revolution Wind, which Trump halted unilaterally, filed a lawsuit claiming the administration illegally withdrew its already-finalized permits. After the administration filed a lawsuit to revoke the permits of US Wind’s big project off Maryland’s coast, the company said it intends “to vigorously defend those permits in federal court, and we are confident that the court will uphold their validity and prevent any adverse action against them.” But the multi-agency assault on offshore turbine projects has only escalated in recent months, as the timeline Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo produced shows. And Orsted is facing other headwinds. The company just warned investors of lower profits this year after weaker-than-forecast wind speeds reduced the output of its turbines.
Toyota issued a voluntary recall for some 591,000 Toyota and Lexus cars over a slight glitch in the display screen. The 12.3-inch screen could fail to turn on after the car started, or go black while driving. Toyota said it will begin notifying owners if affected vehicles by mid-November. The move came just days after the Japanese auto giant — which owns both its eponymous passenger car brand and the associated luxury line, Lexus — recalled 62,000 electric vehicles, including the Toyota bZ4X SUV and the Lexus RZ300e sedan and its luxury SUV, the RZ450. Subaru, in which Toyota owns a minority stake, is also recalling its electric SUV, the Solterra. With all four EVs, the issue revolved around a faulty windshield defroster that “may not remove frost, ice and/or fog from the windshield glass due to a software issue in the electrical control unit,” the company said in a press release..
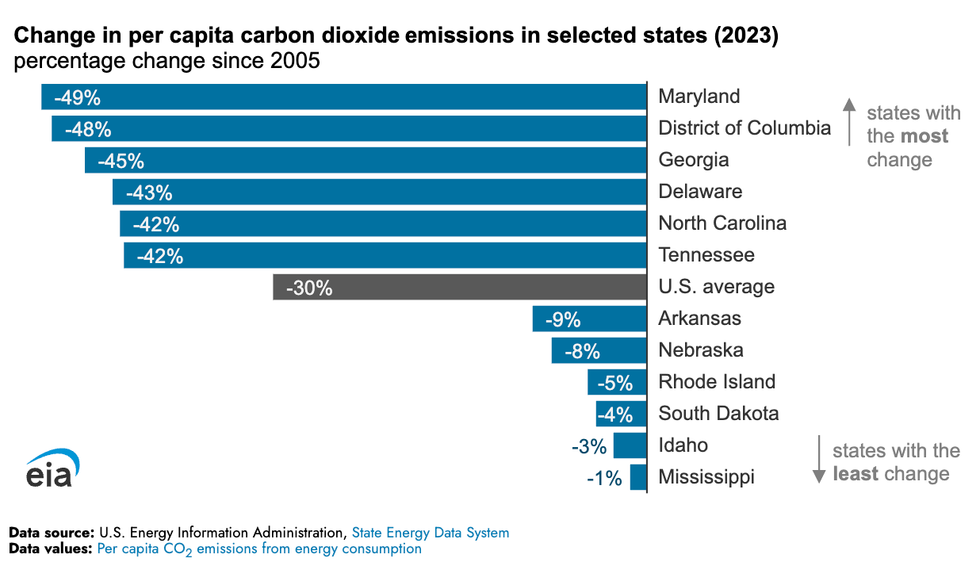
Americans who complain that the U.S. should bear less responsibility for mitigating climate change like to point out that China produces far more planet-heating emissions per year, and that India is not far behind. The cumulative nature of carbon in the atmosphere makes for an easy rebuke, since the U.S. and Western Europe are overwhelmingly responsible for the emissions of the past two centuries. But a less historically abstract response could be that Americans still have by far the highest per capita emissions of any large country. That doesn’t mean the U.S. isn’t making progress on a per capita level, though. Between 2005 and 2023, per capita emissions from primary energy consumption decreased in every U.S. state, with an average drop of 30%, even as the American population grew by 14%, according to a new analysis by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. The dip is largely thanks to the electric power sector burning less coal. Increased electricity generation from natural gas, which releases about half as much carbon per unit of energy when burned as coal, and the growth of renewables such as wind and solar have reduced the need for the dirtier fuel. But the EIA forecasts that overall U.S. emissions are set to climb by 1% as electricity demand increases.
For those keen to shrink their individual carbon output at a much faster pace than American society at large, Heatmap’s award-winning Decarbonize Your Life series walks through the benefits and drawbacks to driving less, eating less steak, installing solar panels, and renovating homes to be more energy efficient.
Following rebellions from various state chapters, the Sierra Club terminated its executive director, Ben Jealous, last month, as I reported here in this newsletter at the time. Now the group has named its new leader: Loren Blackford. The Sierra Club veteran, who served in various senior roles before taking on the interim executive director job last month, won unanimous support from the group’s board of directors on Saturday.
Jealous had previously served as a chief executive of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People and the 2018 Democratic nominee for Maryland governor before becoming the first non-white leader of the 133-year-old Sierra Club. His appointment marked a symbolic turning of the page from the group’s early chapters under its founder, John Muir, who made numerous derogatory remarks about Black and Native Americans. Jealous was accused of sexual harassment earlier this year.
Thermal battery company Fourth Power just announced $20 million in follow-on funding, building on its $19 million Series A round from 2023. While other thermal storage companies such as Rondo and Antora are targeting the decarbonization of high-temperature industrial processes such as smelting or chemical manufacturing, Fourth Power aims to manufacture long-duration energy storage systems for utilities and power producers.
“In our view, electricity is the biggest problem that needs to be solved,” Fourth Power’s CEO Arvin Ganesan told Heatmap’s Katie Brigham. “There is certainly a future application for heat, but we don’t think that’s where to start.” The company’s tech works by taking in excess renewable electricity from the grid, which is used to heat up liquid tin to 2,400 degrees Celsius, nearly half the temperature of the sun’s surface. That heat is then stored in carbon blocks and later converted back into electricity using thermophotovoltaic cells. This latest funding will accelerate the deployment of the startup’s first one megawatt hour demonstration plant.
The tropical storm that later became Hurricane María formed exactly eight years ago today and went on to lay waste to Puerto Rico’s aging electrical system. The grid remains fragile and expensive, with frequent outages and some of the highest rates in the U.S. on the hours when the power is accessible. That has spurred a boom in rooftop solar panels. Now more than 10% of the island’s electricity consumption comes from rooftop solar power. Data released by the grid operator LUMA Energy showed approximately 1.2 gigawatts of residential and commercial rooftop solar had been installed under Puerto Rico’s net-metering regulations as of June 2025. New analysis by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis found that is equal to about 10.3% of Puerto Rico’s total power consumption — and that’s not counting any off-grid systems.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Current conditions: Springlike weather is bringing rain from Texas to Michigan • A Saharan dust storm known as a calima is headed for Europe, threatening “blood rain” as far north as Luxembourg • The Greenlandic capital of Nuuk is poised for days of snow, but with limited accumulation.

The aerial assault the United States and Israel launched on Iran this past weekend is already sending oil prices upward. By Sunday evening, the price for West Texas Intermediate crude, the benchmark for the oil drilled in the U.S., had risen 2.78% to just over $67 per barrel. Brent crude, the benchmark typically used to measure Europe’s production, 2.87% to nearly $73 per barrel. Murban crude, the benchmark set out of Abu Dhabi, surged by more than 4% to north of $74. By rendering the Strait of Hormuz — the waterway between the United Arab Emirates and Iran through which 15% of global oil flows and which tapers to just 20 miles wide at its narrowest point — impassable, the conflict could send prices per barrel as high as $100 or more, the consultancy Wood Mackenzie warned Sunday night. “The key question is when do vessels re-establish export flows,” Alan Gelder, Wood Mackenzie’s senior vice president of refining, chemicals and oil markets, said in a statement. “No doubt, tanker rates and insurance will increase dramatically, but these costs would only be a small part of the oil price impact associated with a curtailment of oil flows if they last for more than a few days.”
The rise in prices began weeks ago as the biggest U.S. troop buildup in the Middle East since 2003 seemed to presage war. The market isn’t just reflecting a fear of an unpredictable and prolonged halt to tanker traffic through the Strait. Insurers are threatening to cancel policies on vessels that dare to pass the waterway right now, the Financial Times reported. Iranian attacks on buildings and infrastructure belonging to America’s Arab allies across the Persian Gulf suggests the rest of the region’s oil production could face damage. “Right next door, you’ve got Iraq, you’ve got Saudi Arabia, and you’ve got the Emirates and others who collectively are more like 20 million barrels per day. And that is obviously a much bigger deal,” Rory Johnston, petroleum analyst and author of Commodity Context, told Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin.
A North Dakota judge finalized a $345 million judgement against Greenpeace USA on Friday, ordering the American chapter of the famed activist group to pay out the damages from its protests against the construction of the Dakota Access Pipeline. The ruling came after judge James Gion decided in October to slash almost half the $667 million that a jury awarded developer Energy Transfer Partners a year ago. The Dallas-based company called the ruling an “important step in this legal process of holding Greenpeace accountable for its unlawful and damaging actions against us.” In its own statement, Greenpeace said, “this is not the end of the case — or Greenpeace USA.” Rather, the group said it will request a new trial and, if necessary, “appeal the decision to the North Dakota Supreme Court.” The organization, which has since its founding in 1971 embarked on audacious acts of protest to raise awareness about environmental destruction, cast its fight against the ruling as a battle to protect Americans’ First Amendment rights. “In the years since the Standing Rock protests, anti-protest laws have spread across the U.S. and the world. Two of the most important components of change and progress throughout human history — free speech and peaceful protest – have never been more endangered,” Greenpeace said in the statement. “We must defend those rights. Our future depends on it.”
Last year, the International Seabed Authority, a little known United Nations agency based in Jamaica, debated how to establish rules for giving private companies permits to collect mineral-rich nodules off the deep ocean floor in waters far from any country’s maritime borders. Under outside pressure from the U.S., which is not a signatory to the ISA and has vowed under the Trump administration to go it alone on deep-sea mining, countries failed to reach an agreement. When the body reconvenes this week in the capital city of Kingston, the head of the ISA is determined to finalize a plan. In an interview with The New York Times, ISA chief Leticia Caravalho promised to broker a deal this year, lest an area in international waters become what she called the Wild West. “The world agreed 30 years ago that this is an area that belongs to all of us, and we should go there collectively,” she said. Banning mining outright, as some countries (and groups such as Greenpeace) have called for, would only take money away from scientific research and delay setting strict environmental protections, she said. “Being able to make the rules before activity starts is unique in human history,” she said.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
The 220-megawatt ACES Delta green hydrogen project in Utah is by far the largest in the U.S. Now it’s ready to launch. As of last week, all 40 of the electrolyzers at the facility were installed and fully operational, supplier HydrogenPro told the trade publication Hydrogen Insight. It’s a critical milestone for a sector facing mounting challenges as the federal tax credit known as 45V begins its earlier phase out next year and the Trump administration yanks funding for the two regional hubs meant to hasten deployment of green hydrogen technology. Not every project is panning out as well. In New York, the developer Plug Power announced plans to abandon a 120-megawatt plant and sell the land to a data center company.
There’s a lot going on in hydrogen, including entirely new colors added to the rainbow scheme that describes how the fuel is made. If you want a quick 101 guide, this episode of Heatmap's Shift Key podcast is a good place to start.
At this stage in the new nuclear race, the company that looks likely to deploy the first small modular reactor in North America is GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy, the U.S.-Japanese joint venture building its debut BWRX-300 at the Darlington nuclear plant in Ontario, Canada. The developer is set to build another one of the third-generation, 300-megawatt reactors at the Tennessee Valley Authority soon after, and, as I reported for Heatmap, received major funding from the Department of Energy last year to pull it off. Until now, five European countries have been considering buying their own BWRX-300s: Czechia, Estonia, Finland, Poland, and Sweden. Now add a sixth. Lithuania just signed onto a memorandum of understanding in Washington promising to assess the potential to deploy the reactor, according to World Nuclear News.
There is a bright spot for clean energy in the Middle East. In Iraq, the first 250-megawatt section of what’s designed to be a 1-gigawatt solar farm is expected to enter operation in the next few days after the facility’s transmission connection powered on for the first time. Located in the Basra region, site of some of the bloodiest battles of the Iraq war, the project is a joint venture between the French giant TotalEnergies, which has a 45% stake; the Basrah Oil Company, which commands 30% of the solar farm; and QatarEnergy, with 25%, according to Renewables Now.
It starts — but doesn’t end — with the Strait of Hormuz.
For the second time in a year, the United States and Israel have launched a major aerial assault on Iran. Strikes were reported across the country early Saturday, targeting Iranian leadership and military infrastructure. In retaliation, Iran has launched attacks on Israel and Gulf nations allied with the U.S., with several of the targets appearing to be American military installations. “The United States military is undertaking a massive and ongoing operation,” President Trump said in a video posted to Truth Social explaining his rationale for launching the war.
While the conflict has quickly metastasized across the region, it has the potential to affect the entire world by disrupting the production and shipment of oil and natural gas.
Iran and its neighbors on the Persian Gulf are some of the largest oil and gas producers in the world and the country has long threatened to disrupt oil exports as an act of self-defense or retaliation from attack.
That may be already happening. According to data from Bloomberg, some oil tankers are pausing or turning around outside the vital Strait of Hormuz, a narrow, deep channel between Iran and Oman that connects the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea and thus to global markets in and bordering the Indian Ocean.
The strait has been “effectively closed,” according to a report from Tasnim, a semi-official news agency linked to the Iran Revolutionary Guard Corps. British naval officials also said they had “received multiple reports” of broadcasts that “have claimed that the Strait of Hormuz (SoH) has been closed.” And a European Union naval official told Reuters that the Iranian Revolutionary Guard had been broadcasting “no ship is allowed to pass the Strait of Hormuz” to ships in the area. Some tankers are still navigating the strait, according to marine tracking data from Kpler.
But it’s questionable whether Iran can actually maintain any attempted closure of the strait, whether by laying mines or directly threatening and attacking ships.
So far, U.S. attacks are “targeting, fairly heavily, naval assets and assets that are close to the Gulf,” Greg Brew, an analyst at the Eurasia Group, told me, which “suggests that they are trying to degrade Iran’s ability to disrupt energy traffic through the Strait of Hormuz.”
The U.S. is “trying to reduce the risks of Iranian effort to close the strait as part of this operation, rather than waiting to see if the Iranians escalate in that direction. The Iranians have responded by claiming that the strait has been closed. The problem for them now, though, is that they’ll have to enforce that threat.”
Closing the strait was a “tail risk” that had been roiling the oil market in the lead-up to Trump’s decision to launch the attack, Rory Johnston, petroleum analyst and author of Commodity Context, told me.
Global oil prices had gotten skittish over the past weeks, with the Brent crude benchmark getting as low at $66.30 per barrel in early February and getting near $73 per barrel on Friday. Brent prices approached $80 per barrel last June during the 12 Day War between Iran and Israel.
While the market could likely weather disruption to Iran’s own exports, jumpy behavior in the market was due to pricing in an enhanced risk of a region-wide calamity. Options traders especially were “attempting to hedge that enormous tail risk,” Johnston said, and “that was really moving the market.”
And even if the strait is not directly closed off by the Iranian military, ships may find it financially onerous to attempt the passage. “Insurers told ship owners on Saturday they would cancel policies and raise coverage prices for vessels travelling through the Gulf and Strait of Hormuz after the U.S. and Israel attacked Iran,” the Financial Times reported Saturday.
Another risk to the region’s oil sector is that Iran could retaliate by striking oil production and exporting infrastructure in neighboring countries, Johnston told me. “Right next door, you’ve got Iraq, you’ve got Saudi Arabia, and you’ve got the Emirates and others who collectively are more like 20 million barrels per day. And that is obviously a much bigger deal,” Johnston said, comparing their production to Iran’s own oil industry.
Of course, Iran is still a major exporter despite U.S. sanctions; in the days running up to the U.S. attack, it was shipping out around 3 million barrels per day from Kharg Island in the Strait of Hormuz, according to data from Bloomberg, almost triple its exports from equivalent dates in January and nearly its entire daily production.
Iran’s exports “had actually surged immediately ahead of what’s gone down over the past 24 hours,” Johnston told me. “In the past couple days, you’d seen a large surge of tankers departing Kharg Island, and the inventories on Kharg Island being drawn down, which is kind of what you would do if you expected that your exports were about to get disrupted.”
To the extent Iranian oil exports are cut off, that could be a big deal for China, which has become the number one destination for Middle East oil shipments. Beijing has been building up stockpiles of oil, likely preparing for the risk that sanctioned exporters like Iran and Venezuela would go off the market, as well as wider risks to exports from the Middle East.
“China is highly concerned over the military strikes against Iran,” the Chinese foreign ministry wrote on X. “China calls for an immediate stop of the military actions, no further escalation of the tense situation, resumption of dialogue and negotiation, and efforts to uphold peace and stability in the Middle East.”
Last year, China began to substantially increase its stockpiling of oil, going from 84,000 barrels per day to 430,000 barrels per day, some 83% of the growth of its imports, according to data and estimates from Rystad Energy and Erica Downs, a senior research scholar at the Columbia University Center on Global Energy Policy.
While the U.S. is now far less reliant on oil exports from the Middle East, oil and gas is still a global market. If Middle Eastern oil and gas exports are disrupted, that will likely increase the price of energy — whether it’s gasoline, electricity, or even home heating — as American energy producers can sell their barrels and BTUs at higher prices globally.
It’s either reassure investors now or reassure voters later.
Investor-owned utilities are a funny type of company. On the one hand, they answer to their shareholders, who expect growing returns and steady dividends. But those returns are the outcome of an explicitly political process — negotiations with state regulators who approve the utilities’ requests to raise rates and to make investments, on which utilities earn a rate of return that also must be approved by regulators.
Utilities have been requesting a lot of rate increases — some $31 billion in 2025, according to the energy policy group PowerLines, more than double the amount requested the year before. At the same time, those rate increases have helped push electricity prices up over 6% in the last year, while overall prices rose just 2.4%.
Unsurprisingly, people have noticed, and unsurprisingly, politicians have responded. (After all, voters are most likely to blame electric utilities and state governments for rising electricity prices, Heatmap polling has found.) Democrat Mikie Sherrill, for instance, won the New Jersey governorship on the back of her proposal to freeze rates in the state, which has seen some of the country’s largest rate increases.
This puts utilities in an awkward position. They need to boast about earnings growth to their shareholders while also convincing Wall Street that they can avoid becoming punching bags in state capitols.
Make no mistake, the past year has been good for these companies and their shareholders. Utilities in the S&P 500 outperformed the market as a whole, and had largely good news to tell investors in the past few weeks as they reported their fourth quarter and full-year earnings. Still, many utility executives spent quite a bit of time on their most recent earnings calls talking about how committed they are to affordability.
When Exelon — which owns several utilities in PJM Interconnection, the country’s largest grid and ground zero for upset over the influx data centers and rising rates — trumpeted its growing rate base, CEO Calvin Butler argued that this “steady performance is a direct result of a continued focus on affordability.”
But, a Wells Fargo analyst cautioned, there is a growing number of “affordability things out there,” as they put it, “whether you are looking at Maryland, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware.” To name just one, Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro said in a speech earlier this month that investor-owned utilities “make billions of dollars every year … with too little public accountability or transparency.” Pennsylvania’s Exelon-owned utility, PECO, won approval at the end of 2024 to hike rates by 10%.
When asked specifically about its regulatory strategy in Pennsylvania and when it intended to file a new rate case, Butler said that, “with affordability front and center in all of our jurisdictions, we lean into that first,” but cautioned that “we also recognize that we have to maintain a reliable and resilient grid.” In other words, Exelon knows that it’s under the microscope from the public.
Butler went on to neatly lay out the dilemma for utilities: “Everything centers on affordability and maintaining a reliable system,” he said. Or to put it slightly differently: Rate increases are justified by bolstering reliability, but they’re often opposed by the public because of how they impact affordability.
Of the large investor-owned utilities, it was probably Duke Energy, which owns electrical utilities in the Carolinas, Florida, Kentucky, Indiana, and Ohio, that had to most carefully navigate the politics of higher rates, assuring Wall Street over and over how committed it was to affordability. “We will never waver on our commitment to value and affordability,” Duke chief executive Harry Sideris said on the company’s February 10 earnings call.
In November, Duke requested a $1.7 billion revenue increase over the course of 2027 and 2028 for two North Carolina utilities, Duke Energy Carolinas and Duke Energy Progress — a 15% hike. The typical residential customer Duke Energy Carolinas customer would see $17.22 added onto their monthly bill in 2027, while Duke Energy Progress ratepayers would be responsible for $23.11 more, with smaller increases in 2028.
These rate cases come “amid acute affordability scrutiny, making regulatory outcomes the decisive variable for the earnings trajectory,” Julien Dumoulin-Smith, an analyst at Jefferies, wrote in a note to clients. In other words, in order to continue to grow earnings, Duke needs to convince regulators and a skeptical public that the rate increases are necessary.
“Our customers remain our top priority, and we will never waver on our commitment to value and affordability,” Sideris told investors. “We continue to challenge ourselves to find new ways to deliver affordable energy for our customers.”
All in all, “affordability” and “affordable” came up 15 times on the call. A year earlier, they came up just three times.
When asked by a Jefferies analyst about how Duke could hit its forecasted earnings growth through 2029, Sideris zeroed in on the regulatory side: “We are very confident in our regulatory outcomes,” he said.
At the same time, Duke told investors that it planned to increase its five-year capital spending plan to $103 billion — “the largest fully regulated capital plan in the industry,” Sideris said.
As far as utilities are concerned, with their multiyear planning and spending cycles, we are only at the beginning of the affordability story.
“The 2026 utility narrative is shifting from ‘capex growth at all costs’ to ‘capex growth with a customer permission slip,’” Dumoulin-Smith wrote in a separate note on Thursday. “We believe it is no longer enough for utilities to say they care about affordability; regulators and investors are demanding proof of proactive behavior.”
If they can’t come up with answers that satisfy their investors, ultimately they’ll have to answer to the voters. Last fall, two Republican utility regulators in Georgia lost their reelection bids by huge margins thanks in part to a backlash over years of rate increases they’d approved.
“Especially as the November 2026 elections approach, utilities that fail to demonstrate concrete mitigants face political and reputational risk and may warrant a credibility discount in valuations, in our view,” Dumoulin wrote.
At the same time, utilities are dealing with increased demand for electricity, which almost necessarily means making more investments to better serve that new load, which can in the short turn translate to higher prices. While large technology companies and the White House are making public commitments to shield existing customers from higher costs, utility rates are determined in rate cases, not in press releases.
“As the issue of rising utility bills has become a greater economic and political concern, investors are paying attention,” Charles Hua, the founder and executive director of PowerLines, told me. “Rising utility bills are impacting the investor landscape just as they have reshaped the political landscape.”