You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
All of the awesome earth-moving and none of the planet- or lung-harming emissions.

Construction is a dirty business, literally and figuratively. Mud and gunk and tar come with the territory for those who erect buildings and pave roads for a living. And the industrial machines that provide the muscle for the task run on hulking diesel engines that spew carbon and soot as they work.
Heavy equipment feels like an unlikely place to use all-electric power in order to ditch fossil fuels. The sheer size and intense workload of a loader or excavator means it has enormous energy needs. Yet the era of electric construction equipment has begun, with companies such as Volvo, Komatsu, and Bobcat all now marketing electric dirt movers and diggers. One big reason why: Full-size machines create the opportunity to make construction projects quieter and cleaner — a potentially huge benefit for those that happen in dense areas around lots of people.
Volvo, for example, appeared at last week’s Advanced Clean Transportation Expo in Anaheim, California, primarily to tout its efforts to reduce emissions in the trucking industry via hydrogen-powered semis, electric trucks, and technological refinements to reduce pollution such as nitrous oxide from traditional diesel. But the Swedish brand also trotted out its clean power dirt movers.
The L120 electric loader that is now taking reservations has a lifting capacity of 6 metric tons on pure electric power, making it useful for job sites such as recycling centers and ports. To see such a beast in person — and displayed on pristine convention-center carpet as if it were this year’s Ford Mustang, no less — is an odd and humbling experience that elicits a little-boy level of glee at beholding a big machine. Its bucket, large enough to carry a basketball team, seems to exist on a scale that is too big for battery power, yet Volvo claims the L120 can match the performance of its diesel brethren.
Volvo also brought an electric excavator, the machine used for shoveling out huge bucketfuls of earth. The EC230 Electric is based on the diesel-powered machine of the same name, but with a stack of batteries adding up to 450 kilowatt-hours of capacity and 650 volts of power give the excavator seven to eight hours of runtime on clean electric power.
“Going to the 600-volt battery packs with similar power density that we’re using in [semi] trucks allowed us to take that into the larger construction equipment,” Keith Brandis, VP of policy and regulatory affairs for Volvo North America, told me. “A big breakthrough for us was making sure that the duty cycle — the vibration, the harshness, the temperature extremes — was proven. We have coolant that runs throughout that battery pack, so we precondition the temperatures for very cold starts as well as during very hot temperatures.”
Indeed, the two big boys on display in Anaheim expand Volvo’s lineup of electric construction machines up to seven. The new full-size offerings also take battery power up to a scale needed for serious projects, where it could cut the noise and pollution that emanate from a site. Volvo says its e-machines are already at work on the restoration project in New York City’s Battery Park, at the southern end of Manhattan, where the local government made quiet and clean construction equipment a priority.
Volvo is not alone in this space. Komatsu builds a slate of electric excavators in a variety of sizes leading up to the 20-ton PC210LCE, which the Japanese brand introduced in 2023.
At the smaller end, Bobcat now builds battery-powered mini-loaders and compact excavators. Caterpillar made an EV dump truck a couple of years ago, and more heavy-duty electric machines for industries like mining are on the way.
Although electric loaders and excavators have begun to match the capability of their combustion-powered cousins and have reached a battery runtime that spans a full workday, Volvo and other heavy equipment manufacturers face a few hurdles in convincing more construction companies to go electric. Just like with passenger cars, there is the matter of price. Battery-powered equipment costs more up front, so companies must be convinced that the savings they’ll reap via reduced fuel and maintenance costs will make the electric equipment less expensive in the long run.
And just like with passenger cars, incentives play an outsized role in affordability. Brandis noted that municipalities often have fixed budgets for equipment replacement, which is inconvenient when clean, electric equipment costs substantially more. “We typically rely on purchase incentives or infrastructure incentives, grants, or vouchers that are available,” he said, such as California’s HVIP voucher for zero-emission heavy equipment.
Then there is the construction version of range anxiety, simply ensuring there is enough electricity at any job site to recharge a division of electric loaders. At locations where sufficient electrical infrastructure is already in place, Volvo is helping electric buyers install switchgears, meters, and EV chargers built to talk to the big machines. “It eliminates one other problem point for the customer because we’ve already proven that the operability is there with the equipment,” Brandis told me.
The problem with construction, however, is that sometimes it takes place in remote locations far from easy connections. At ACT, Ray Gallant of Volvo construction equipment said this is the point at which the power has to come to the customer. Volvo recently acquired the battery production business of Proterra, which, among other things, would help the corporation develop battery electric storage solutions that it could deploy remotely — at a far-flung job site, say.
“When we’re in remote sites, we have to take the electrons to the electric machines,” he said.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The Fish and Wildlife Service has lifted its ban on issuing permits for incidental harm to protected eagles while also pursuing enforcement actions — including against operators that reported bird deaths voluntarily.
When Trump first entered office, he banned wind projects from receiving permits that would allow operators to unintentionally hurt or kill a certain number of federally protected eagles, transforming one of his favorite attacks on the industry into a dangerous weapon against clean energy.
One year later, his administration is publicly distancing itself from the ban while quietly issuing some permits to wind companies and removing references to the policy from government websites. At the same time, however, the federal government is going after wind farm operators for eagle deaths, going so far as to use the permitting backlog it manufactured to intimidate companies trying in good faith to follow the law, with companies murmuring about the risk of potential criminal charges.
Two days before Christmas, a coalition of renewable energy trade groups whose members include some of the world’s largest clean energy companies sued the Trump administration, arguing that several of its policies delaying permits for their projects violated the Administrative Procedures Act. One of those policies was the ban on granting new bald and golden eagle “incidental take permits.” These serve as the government’s way of acknowledging that hurting or killing protected bird species in small numbers is unavoidable no matter how many design protections are put in place.
After that lawsuit was filed, the Trump administration began wiping references to the ban from government websites discussing the permitting program. Some of these changes were recent: Wind companies discovered references to the ban were deleted from these webpages sometime between the case being filed and mid-January, according to screenshots and sworn statements submitted as exhibits in the case. The now-deleted language describing the ban said it was premised on Trump’s Day 1 anti-wind executive order, which a federal judge ruled in December violated the Administrative Procedures Act.
I am also starting to hear that the Fish and Wildlife Service is sending wind farm operators eagle permits again, though I do not know how many have gone out or to whom.
When it comes to bald eagles, at least, the Fish and Wildlife Service is supposed to “automatically” issue general permits for incidental take through an electronic self-certification system. A spokesperson for the advocacy groups behind the lawsuit confirmed in a statement to me that the Fish and Wildlife Service is “now processing” these general permits “because they cannot halt them given their self-certification structure.”
The spokespoerson added that to their knowledge, the agency still isn’t issuing permits requiring more thorough levels of government analysis because of other Trump administration policies. Complex permits are likely still impeded by an order requiring sign-off from Interior Secretary Doug Burgum on environmental permits for solar and wind projects.
Garrett Peterson, acting chief of public affairs for the Fish and Wildlife Service, confirmed in a statement Friday afternoon that the office is currently allowing general permits for wind farms “that meet eligibility and issuance criteria.”
This change in practice also comes after a string of losses — many, many losses — in court over Trump’s stop work orders blocking offshore wind construction. The Trump administration may be trying to avoid yet another embarrassing defeat.
Still, the wind industry isn’t out of the woods entirely. Team Trump seems to be pivoting to enforcing the law protecting bald and golden eagles — the aptly titled Bald and Golden Eagle Protection Act.
On January 12, the trade groups filed a motion asking the judge in the case for a preliminary injunction lifting all of the anti-renewable permitting policies addressed in the case, including the eagle permit ban, until the court could make a final ruling. Attached to the motion was a voluminous, candid, and fearful statement from executive directors for the trade groups, making a lot of information about Trump’s war on renewable energy public for the first time. One of those confessions was the existence of a memo banning water permits for projects that defied the Trump administration’s preferred “aesthetics,” news of which I scooped on Thursday in my newsletter The Fight.
Another disclosure by the trade groups made my jaw drop. The eagle permit ban appeared to have become a cudgel for the administration to use against companies reporting bird deaths in good faith, departing from what the coalition said was a “longstanding policy” of “enforcement discretion so long as wind farm operators can demonstrate that they are implementing best practices.” This situation was significant and dire, according to the statement — so much so the trade groups were “unwilling to disclose specific projects” that were harmed by the eagle permit ban “due to ongoing concerns about potential persecution or retaliation in direct response to their participation in this lawsuit.”
These enforcement actions do happen, but are not usually a public affair unless the charges are particularly serious. Those instances have been rare, reserved for companies demonstrating what the Bald and Golden Eagle Protection Act describes as a “wanton disregard” for the lives of the birds.
The Trump administration first indicated it would pursue some sort of crackdown on eagle deaths from wind farms in early August, when it sent letters to project operators across the country asking for any and all information on the subject. The letters teased the risk of not only civil but criminal liability, stating that certain violators would be forwarded to the Justice Department.
Since then, I’ve heard of just one enforcement action under Trump 2.0 for an eagle death: In early November, Fox News reported that the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service told the Danish energy company Orsted during the government shutdown that it would issue $32,340 in fines over two dead eagles found near wind farms in Nebraska and Illinois. The Fox News story stated that Orsted had come to the Fish and Wildlife Service voluntarily with the dead eagles and would be fined because they died without proper permits; it’s unclear whether the company was pursuing them at the times the birds died. Current rules under the Bald and Golden Eagle Protection Act call for up to $16,590 for every dead bird, so the fine represented nearly the strictest civil penalty FWS could level against Orsted.
The trade group executives’ statement indicates that the enforcement action described in the Fox News article wasn’t a one-off, and that there is a wider wind industry crackdown over dead eagles playing out in the shadows, at least for now. It’s unclear whether this will take the form of a mess of fines, or whether, as the FWS data call suggested, some of this work might lead to allegations of criminality involving the Justice Department.
When I asked for comment on the enforcement efforts, the Fish and Wildlife Service told me to file a public records request under the Freedom of Information Act.
American Clean Power, the largest trade group representing wind companies, did not respond to requests for comment for this story.
Editor’s note: This story has been updated to remove the name of the spokesperson for the litigants.
Plus a pair of venture capital firms close their second funds.
It’s been a big few weeks for both minerals recycling and venture capital fundraising. As I wrote about earlier this week, battery recycling powerhouse Redwood Materials just closed a $475 million Series E round, fueled by its pivot to repurposing used electric vehicle batteries for data center energy storage. But it’s not the only recycling startup making headlines, as Cyclic Materials also announced a Series C and unveiled plans for a new facility. And despite a challenging fundraising environment, two venture firms announced fresh capital this week — some welcome news, hopefully, to help you weather the winter storms.
Toronto-based rare earth elements recycling company Cyclic Materials announced a $75 million Series C funding round last Friday, which it will use to accelerate the commercialization of its rare earth recycling tech in North America and support expansion into Europe and Asia. The round was led by investment management firm T. Rowe Price, with participation from Microsoft, Amazon, and Energy Impact Partners, among others.
Building on this news, today the startup revealed plans for a new $82 million recycling facility in South Carolina — its largest to date. The plant is expected to begin operations in 2028, and Cyclic says its eventual output would be enough to supply the magnets for six million hybrid-electric vehicle motors annually.
The rare earth supply chain is heavily concentrated in China, where these materials have traditionally been extracted through environmentally intensive mining operations. They’re critical components of high-performance permanent magnets, which are used in a wide range of technologies, from electric vehicles and wind turbines to data center electronics and MRI machines. Cyclic’s proprietary recycling system recovers these magnets from end-of-life products and converts them into a powdered mixture of rare earth oxides that can be used to make new magnets. According to the company, its process reduces carbon emissions by 61% while using just 5% of the water required for conventional mining.
The London-based urban sustainability firm 2150 announced on Monday that it had closed its second fund, raising €210 million from 34 limited partners — about $250 million. This brings the firm’s total assets under management to nearly $600 million as it doubles down on its thesis that cities — and the industries behind them — offer the greatest opportunity for sustainability wins. Thus far the firm has invested in companies spanning the gamut from cooling and industrial heat to low-carbon cement and urban mobility.
2150 has already invested in seven companies from its new fund, including the industrial heat pump startup AtmosZero, the refurbished electronics marketplace Getmobil, and the direct air capture company MissionZero. According to TechCrunch, the firm plans to back a total of 20 companies from this fund, typically at the Series A stage. Checks will range from about $6 million to $7 million with roughly half of the fund’s capital reserved for follow-on investments.
It was also a big week for second fund closes. The firm Voyager Ventures raised $275 million for “technologies that modernize the base layer of the economy,” from energy efficiency to AI and carbon removal. According to The Wall Street Journal, the firm is dropping its formerly advertised “climate tech” label to avoid any association with government subsidies or green premiums, focusing instead on advancing the Trump administration’s national security, energy independence, and domestic manufacturing agenda. The strategy appears to be working: Voyager co-founder Sierra Peterson told the Journal that five of its portfolio companies have secured federal contracts during the second Trump administration.
In an announcement letter posted to its website on Tuesday, the firm wrote, “Abundance is not automatic, but it is technologically favored,” going on to explain that it will focus its investments on three areas that it considers the “fundamental drivers of growth” — electrification, critical materials and resources such as AI computing infrastructure and minerals, and advanced manufacturing. “As energy, compute, and production scale in tandem, systems become more durable and scarcity recedes,” the letter went on to state.
The firm has already begun investing out of this second fund, which held its first close in October 2024. Its investments include backing for the EV charging platform ENAPI, a company called Electroflow Technologies that’s pursuing a novel approach to lithium extraction, and the advanced industrial materials startup Leeta Materials.
Axios reported on Wednesday that “a source familiar” with Form Energy’s plans says the long-duration battery storage startup is seeking to raise between $300 million and $500 million, in what’s likely to be its last equity round before targeting an IPO in 2027. The company, which is developing 100-plus-hour grid-scale storage using its iron-air technology, last raised a $405 Series F funding round in October 2024, bringing its total funding to over $1.2 billion.
The company is now deploying its very first commercial batteries in Minnesota. Form has yet to release a public statement about either its fundraising or IPO plans, so watch this space for further developments.
Current conditions: The bomb cyclone barrelling toward the East Coast is set to dump up to 6 inches of snow on North Carolina in one of the state’s heaviest snowfalls in decades • The Arctic cold and heavy snow that came last weekend has already left more than 50 people dead across the United States • Heavy rain in the Central African Republic is worsening flooding and escalating tensions on the country’s border with war-ravaged Sudan.
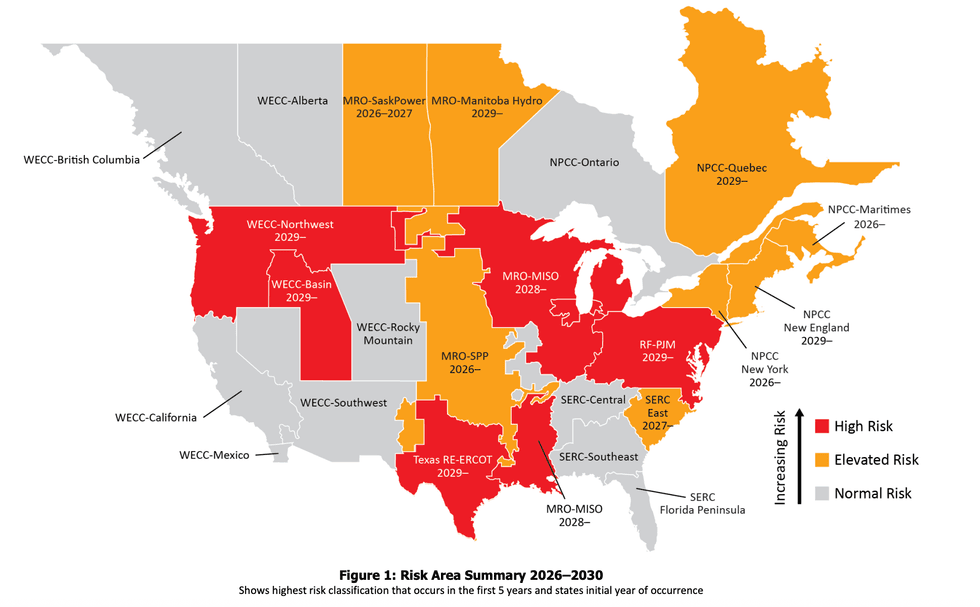
Every year, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation — a quasi-governmental watchdog group that monitors the health of the power grids in the United States and Canada — publishes its analysis of where things are headed. The 2025 report just came out, and America is bathed in a sea of red. The short of it: Electricity demand is on track to outpace supply throughout much of the country. The grids that span the Midwest, Texas, the Northwest, and the Mid-Atlantic face high risks — code red for reliability. The systems in the Northeast, the Carolinas, the Great Plains, and broad swaths of Canada all face elevated risk over the next four years. The failure to build power plants quickly enough to meet surging demand is just one issue. NERC warned that some grids, such as those in the Pacific Northwest, the Mountain West, and Great Basin states, are staring down potential instability from the addition of primarily weather-dependent renewables such as solar panels and wind turbines that, absent batteries and grid-forming technologies, make managing systems built around firm sources such as coal and hydroelectricity harder to balance.
There’s irony there. Solar and wind are among the fastest new generating sources to build. They’re among the cheapest, too, when you consider how expensive turbines for gas plants have grown as manufacturers’ backlogs stretch to the end of the decade. But they’re up against a Trump administration that’s phasing out tax credits and refusing to permit projects — even canceling solar megaprojects that would have matched the capacity of large nuclear stations. The latest tactic, as my colleague Jael Holzman described in a scoop last night, involves challenging the aesthetic value of wind and solar installations.
Copper prices just surged by the most in more than 16 years after what Bloomberg pegged to a “wave of buying from Chinese investors” that “triggered one of the most dramatic moves in the market’s history.” Prices surged as much as 11% to above $14,500 per ton for the first time before falling somewhat. It was enough to earn headlines about “metals mania” and “absolutely bonkers” pricing. The metal is used in virtually every electrical application. Between China commencing its march toward becoming the world’s first “electrostate” and U.S. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell signaling a stronger American economy than previously thought, investors are betting on demand for copper to keep growing. For now, however, the prices on copper futures contracts are already leveling off, and Goldman Sachs forecasts the price to fall before stabilizing at a level still well above the average over the last four years.
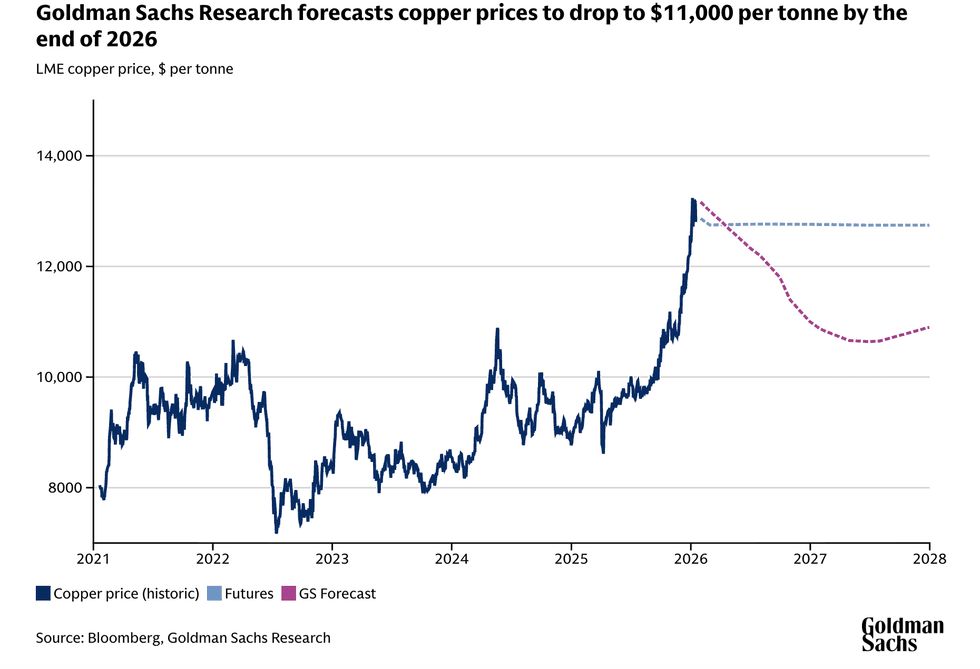
Amid the volatility, the Trump administration may be shying away from a key tool used to make investments in new mines less risky. On Thursday, Reuters reported that two senior Trump officials told U.S. minerals executives that their projects would need to prove financial independence without the federal government guaranteeing a minimum price for what they mine. “We’re not here to prop you guys up,” Audrey Robertson, assistant secretary of the Department of Energy and head of its Office of Critical Minerals and Energy Innovation, reportedly told the executives gathered at a closed-door meeting hosted by a Washington think tank earlier this month. “Don’t come to us expecting that.” The Energy Department said that Reuters’ reporting is “false and relies on unnamed sources that are either misinformed or deliberately misleading.” At least one mining startup, United States Antimony Corporation, and a mining economist have echoed the administration’s criticism. One tool the Trump administration certainly isn’t wavering on is quasi nationalization. Just two days ago I was telling you about the latest company, USA Rare Earth, to give the government an equity stake in exchange for federal financing.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
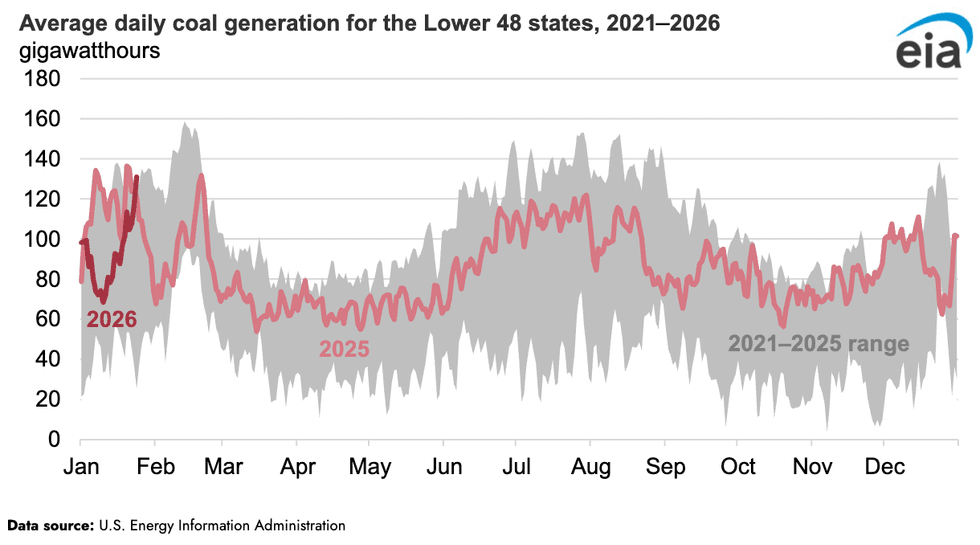
Coal-fired electricity generation in the Lower 48 states soared 31% last week compared to the previous week amid Winter Storm Fern’s Arctic temperatures, according to a new analysis by the Energy Information Administration. It’s a stark contrast from the start of the month, when milder temperatures led to lower coal-fired power production versus the same period in 2025. Natural gas generation also surged 14% compared to the previous week. Solar, wind, and hydropower all declined. Nuclear generation remained nearly unchanged.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
The specter of an incident known as “whoops” haunts the nuclear industry. Back in the 1980s, the Washington Public Power Supply System attempted to build several different types of reactors all at once, and ended up making history with the biggest municipal bond default in U.S. history at that point. The lesson? Stick to one design, and build it over and over again in fleets so you can benefit from the same supply chain and workforce and bring down costs. That, after all, is how China, Russia, and South Korea successfully build reactors on time and on budget. Now Jeff Bezos’ climate group is backing an effort to get the Americans to adopt that approach. On Thursday, the Bezos Earth Fund gave a $3.5 million grant to the Nuclear Scaling Initiative, a partnership between the Clean Air Task Force, the EFI Foundation, and the Nuclear Threat Initiative. In a statement, the philanthropy’s chief executive, Tom Taylor, called the grant “a targeted bet that smart coordination can unlock much larger public and private investment and turn this first reactor package into a model for many more.” Steve Comello, the executive director at the Nuclear Scaling Initiative, said the “United States needs repeat nuclear energy builds — not one off projects — to bolster energy security, improve grid reliability, and drive economic competitiveness.”
The Netherlands must write stricter emissions-cutting targets into its laws to align with the Paris Agreement in the name of protecting Bonaire, one of its Caribbean island territories, from the effects of climate change. That’s according to a Wednesday ruling by the District Court of The Hague in a case brought by Greenpeace. The decision also found that Amsterdam was discriminating against residents of the island by failing to do enough to help the island adapt to the existing effects of global warming, including sea-level rise, flooding, and extreme weather. Bonaire is the largest and most populous of the trio of islands that form the Dutch Caribbean territory and includes Sint Eustatius and Saba. The lawsuit, the Financial Times noted, was “one of the first to test climate obligations on a national level.”
The least ecologically destructive minerals to harvest for batteries and other technologies come not from the ground but from old batteries and materials that can be recycled. Recyclers can also get supply up and running faster than a mine can open. With the U.S. aggressively seeking supplies of rare earths that don’t come from China, the recycling startup Cyclic Materials sees an opportunity. The company is investing $82 million to build its second and largest plant. At full capacity, the first phase of the new facility in South Carolina will process 2,000 metric tons of magnet material per year. But the firm plans to eventually expand to 6,000 tons.