You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Here’s how much you should worry about the coming solar storm.
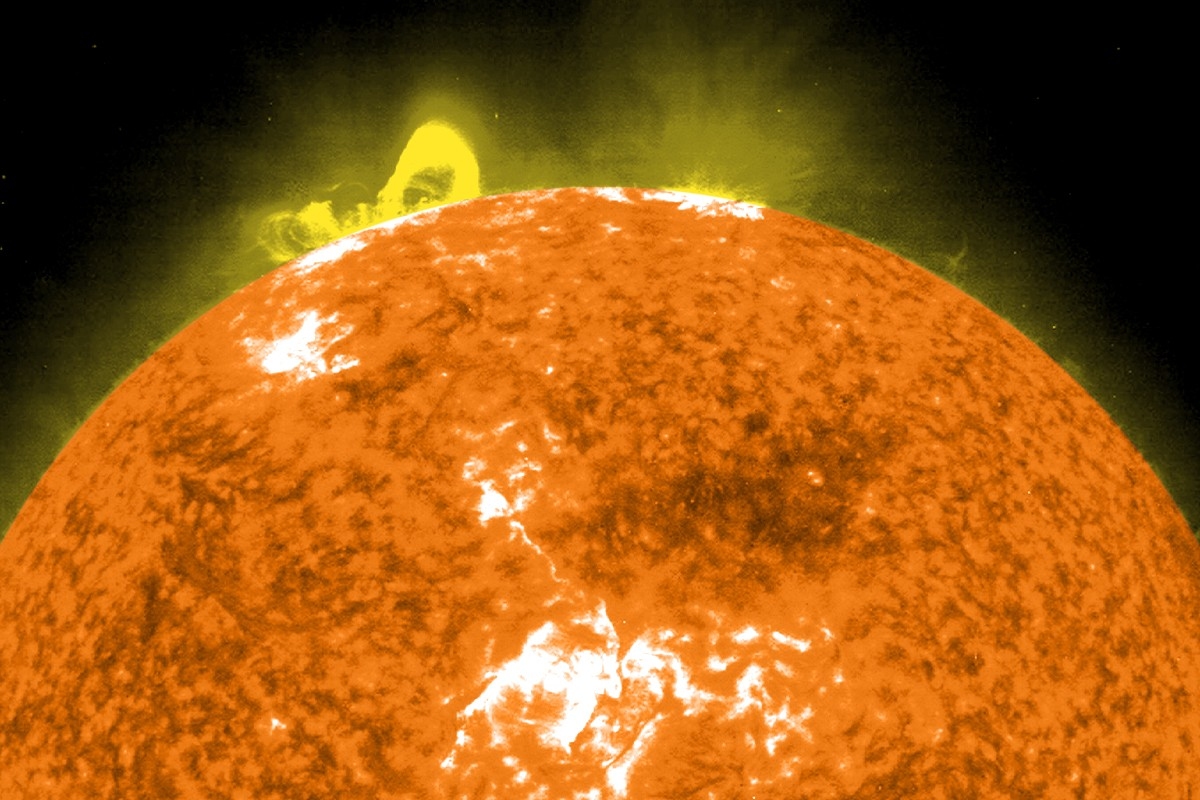
You have probably heard by now that there’s a big solar storm on its way toward us. (If not, sign up for Heatmap AM, our daily roundup of climate and energy news.) On Wednesday, the sun started ejecting massive columns of geomagnetic activity out into space in Earth’s direction. That geomagnetism is due to arrive around 11p.m. ET on Friday, triggering huge fluctuations in the Earth’s geomagnetic field.
Those fluctuations can actually generate their own electric current. And too much of that current can wreak havoc on the electrical grid.
The last time we got a heads up like this about a geomagnetic surge of this magnitude was in 2005, when coal generation was close to its peak in the U.S. and renewables were providing less than half the energy they do now. So how does that changing energy mix affect the risk to the grid this time around?
Not too much, said representatives from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Organization on Friday morning. The other thing that’s happened since 2005 is that we've started paying a lot more attention to space weather — which, despite its name, bears little resemblance to Earth weather — which means grid operators are a lot better prepared to deal with it.
“We’ve been working with the power distribution community over the past decade to help them better understand space weather,” Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist with NOAA, said in a press briefing. “And their engineers have taken that information and used it to build systems that can protect the power lines more rapidly than they could before. So we’ve seen improvements in technology on the grid that get triggered by these events, and then work to protect the different assets.”
Grid operators can also respond in lower tech ways, such as by deferring maintenance or taking systems offline. And to be clear, if there are any grid effects, those will happen just to long-distance transmission lines. Transformers and any wires connecting to your house should be totally fine.
Will the solar storm affect solar panels? According to NOAA, any panels here on Earth should be totally fine since they’re protected by the planet’s atmosphere. Solar panels in space, e.g. those powering satellites, are at more risk depending on the height of their orbit, particularly if they’re outside the reach of the Earth’s magnet field.
The magnetic field will also determine how bad the storm gets here. Earth’s magnetic field points northward. (That’s why compasses work.) If the the solar storm’s magnetic field is oriented in the same direction, its effects will be dampened. “Think of a magnet,” said Shawn Dahl, another of NOAA’s space weather forecasters. “If you take two negative magnets and you try to put them together, they don’t connect, right? Same thing here.” That magnetic orientation can change in the course of a single storm, however, and if suddenly those two poles start drawing together, the effects can intensify.
As of now, NOAA has classified the situation as a severe geomagnetic storm — G4, on a scale that goes up to G5 — of which several have hit Earth since 2005, including one in late March. Those were weaker than the one barreling toward us at the moment, however, although we won’t know how severe this one will be until it passes satellites stationed about a million miles out in space — that is, at most 45 minutes before it hits.
So, is NOAA concerned? “Yeah, we’re a little concerned,” Dahl said, adding that in addition to coordinating with utilities and other operators of critical infrastructure, NOAA is also briefing the Federal Emergency Management Agency. GPS and other satellite-dependent technologies could experience disruptions. Will those be debilitating to society? Probably not.
There’s also one big upside: “The biggest manifestation of space weather is the aurora,” Steenburgh said, a.k.a. the Northern Lights, which could be visible as far south as Alabama. Even if you can’t see anything with the naked eye, it’s worth pointing your cell phone at the sky and snapping a pic, said Brent Gordon, another NOAA space scientist.
“Cell phones are much better than our eyes and capturing light,” Gordon explained. “Just just go out your back door and take a picture with a newer cellphone and you'd be amazed at what is what you see in that picture versus what you see with your eyes.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Clean energy stocks were up after the court ruled that the president lacked legal authority to impose the trade barriers.
The Supreme Court struck down several of Donald Trump’s tariffs — the “fentanyl” tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China and the worldwide “reciprocal” tariffs ostensibly designed to cure the trade deficit — on Friday morning, ruling that they are illegal under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act.
The actual details of refunding tariffs will have to be addressed by lower courts. Meanwhile, the White House has previewed plans to quickly reimpose tariffs under other, better-established authorities.
The tariffs have weighed heavily on clean energy manufacturers, with several companies’ share prices falling dramatically in the wake of the initial announcements in April and tariff discussion dominating subsequent earnings calls. Now there’s been a sigh of relief, although many analysts expected the Court to be extremely skeptical of the Trump administration’s legal arguments for the tariffs.
The iShares Global Clean Energy ETF was up almost 1%, and shares in the solar manufacturer First Solar and the inverter company Enphase were up over 5% and 3%, respectively.
First Solar initially seemed like a winner of the trade barriers, however the company said during its first quarter earnings call last year that the high tariff rate and uncertainty about future policy negatively affected investments it had made in Asia for the U.S. market. Enphase, the inverter and battery company, reported that its gross margins included five percentage points of negative impact from reciprocal tariffs.
Trump unveiled the reciprocal tariffs on April 2, a.k.a. “liberation day,” and they have dominated decisionmaking and investor sentiment for clean energy companies. Despite extensive efforts to build an American supply chain, many U.S. clean energy companies — especially if they deal with batteries or solar — are still often dependent on imports, especially from Asia and specifically China.
In an April earnings call, Tesla’s chief financial officer said that the impact of tariffs on the company’s energy business would be “outsized.” The turbine manufacturer GE Vernova predicted hundreds of millions of dollars of new costs.
Companies scrambled and accelerated their efforts to source products and supplies from the United States, or at least anywhere other than China.
Even though the tariffs were quickly dialed back following a brutal market reaction, costs that were still being felt through the end of last year. Tesla said during its January earnings call that it expected margins to shrink in its energy business due to “policy uncertainty” and the “cost of tariffs.”
Alphabet and Amazon each plan to spend a small-country-GDP’s worth of money this year.
Big tech is spending big on data centers — which means it’s also spending big on power.
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, announced Wednesday that it expects to spend $175 billion to $185 billion on capital expenditures this year. That estimate is about double what it spent in 2025, far north of Wall Street’s expected $121 billion, and somewhere between the gross domestic products of Ecuador and Morocco.
This is a “a massive investment in absolute terms,” Jefferies analyst Brent Thill wrote in a note to clients Thursday. “Jarringly large,” Guggenheim analyst Michael Morris wrote. With this announcement, total expected capital expenditures by Alphabet, Microsoft and Meta for 2026 are at $459 billion, according to Jefferies calculations — roughly the GDP of South Africa. If Alphabet’s spending comes in at the top end of its projected range, that would be a third larger than the “total data center spend across the 6 largest players only 3 years ago,” according to Brian Nowak, an analyst at Morgan Stanley.
And that was before Thursday, when Amazon told investors that it expects to spend “about $200 billion” on capital expenditures this year.
For Alphabet, this growth in capital expenditure will fund data center development to serve AI demand, just as it did last year. In 2025, “the vast majority of our capex was invested in technical infrastructure, approximately 60% of that investment in servers, and 40% in data centers and networking equipment,” chief financial officer Anat Ashkenazi said on the company’s earnings call.
The ramp up in data center capacity planned by the tech giants necessarily means more power demand. Google previewed its immense power needs late last year when it acquired the renewable developer Intersect for almost $5 billion.
When asked by an analyst during the company’s Wednesday earnings call “what keeps you up at night,” Alphabet chief executive Sundar Pichai said, “I think specifically at this moment, maybe the top question is definitely around capacity — all constraints, be it power, land, supply chain constraints. How do you ramp up to meet this extraordinary demand for this moment?”
One answer is to contract with utilities to build. The utility and renewable developer NextEra said during the company’s earnings call last week that it plans to bring on 15 gigawatts worth of power to serve datacenters over the next decade, “but I'll be disappointed if we don't double our goal and deliver at least 30 gigawatts through this channel by 2035,” NextEra chief executive John Ketchum said. (A single gigawatt can power about 800,000 homes).
The largest and most well-established technology companies — the Microsofts, the Alphabets, the Metas, and the Amazons — have various sustainability and clean energy commitments, meaning that all sorts of clean power (as well as a fair amount of natural gas) are likely to get even more investment as data center investment ramps up.
Jefferies analyst Julien Dumoulin-Smith described the Alphabet capex figure as “a utility tailwind,” specifically calling out NextEra, renewable developer Clearway Energy (which struck a $2.4 billion deal with Google for 1.2 gigawatts worth of projects earlier this year), utility Entergy (which is Google’s partner for $4 billion worth of projects in Arkansas), Kansas-based utility Evergy (which is working on a data center project in Kansas City with Google), and Wisconsin-based utility Alliant (which is working on data center projects with Google in Iowa).
If getting power for its data centers keeps Pichai up at night, there’s no lack of utility executives willing to answer his calls.
The offshore wind industry is now five-for-five against Trump’s orders to halt construction.
District Judge Royce Lamberth ruled Monday morning that Orsted could resume construction of the Sunrise Wind project off the coast of New England. This wasn’t a surprise considering Lamberth has previously ruled not once but twice in favor of Orsted continuing work on a separate offshore energy project, Revolution Wind, and the legal arguments were the same. It also comes after the Trump administration lost three other cases over these stop work orders, which were issued without warning shortly before Christmas on questionable national security grounds.
The stakes in this case couldn’t be more clear. If the government were to somehow prevail in one or more of these cases, it would potentially allow agencies to shut down any construction project underway using even the vaguest of national security claims. But as I have previously explained, that behavior is often a textbook violation of federal administrative procedure law.
Whether the Trump administration will appeal any of these rulings is now the most urgent question. There have been no indications that the administration intends to do so, and a review of the federal dockets indicates nothing has been filed yet.
The Department of Justice declined to comment on whether it would seek to appeal any or all of the rulings.
Editor’s note: This story has been updated to reflect that the administration declined to comment.