You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
They are even less popular than clean energy projects, an exclusive Heatmap Pro survey found.

Renewables projects aren’t always popular. Heatmap regularly reports on local opposition to solar panels on farmland, wind turbines in the ocean, and grid-scale batteries just about anywhere. But data centers may be even less popular, according to a national poll conducted by our energy intelligence platform Heatmap Pro.
The poll of 3,741 American voters asked, “Would you support or oppose a data center being built near where you live?” and found that 44% of respondents would support or strongly support a data center being built near them while 42% would oppose or strongly oppose it. That’s a net support of only +2%.
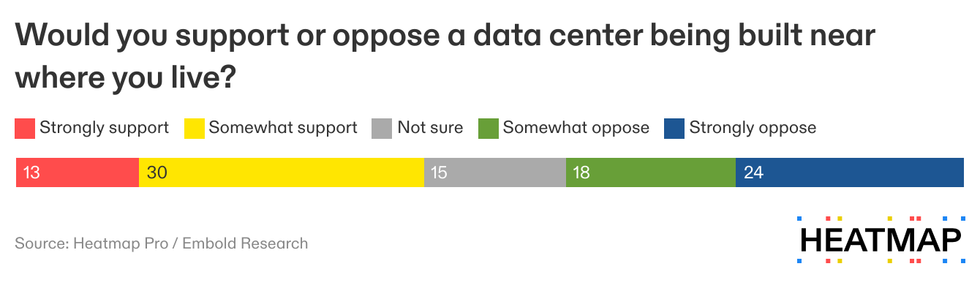
Nearly all energy projects, renewable or not, fared better with the public. When a similar question was asked about natural gas, net support was 34%; for a wind farm it was 19%; for solar it was 34%; for batteries, it was 11%; for geothermal, net support was 36%; for carbon removal, it was 23%; for nuclear power, it was 10%.
It’s worth stepping back and thinking of how remarkable this is. The American public, according to Heatmap’s polling, is more skeptical of data centers which, once built, are essentially warehouses than they are of gas-fired power plants which emit, besides the greenhouse gases, nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide.
They oppose data centers more than they do wind farms with their towering turbines and mechanical hums; more than they do battery storage facilities which can erupt into super-hot fires; or even nuclear power plants, long the go-to reference for “scary energy facility.”
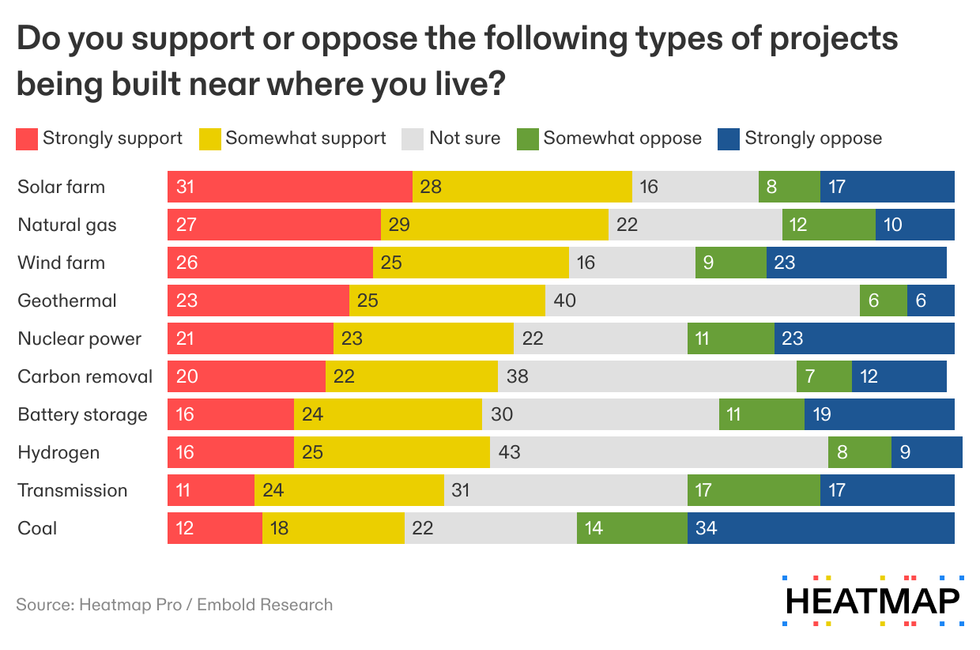
This suggests that political polarization around energy, where Democrats oppose fossil fuels and Republicans oppose renewables, is less potent when it comes to decisions on the ground, although there is a political gradient.
Net support among Democrats was -8%, while among Republicans it was +14%, with independents at -5%. Natural gas projects, by contrast, had positive net support among all groups, while solar projects had overwhelming net support among Democrats (+72%), strong support among independents (+42%), and mild opposition from Republicans at -3%.
The two pieces of energy infrastructure with less net support that data centers are transmission — captured in the survey by the descriptive phrase “large-scale power line” — at net 1% and coal power — by far the most polluting power infrastructure deployed at scale in the United States — at -18%.
Heatmap asked further questions about how Americans understand the benefits and drawbacks of data centers in their communities.
The most convincing was that “data centers create high-paying construction and operations jobs,” which 63% of respondents found very or somewhat convincing — a net convincing of +26%. Just below that was “Data centers can increase local tax revenue that supports schools, emergency services, and infrastructure,” with a net convincing of +24%.
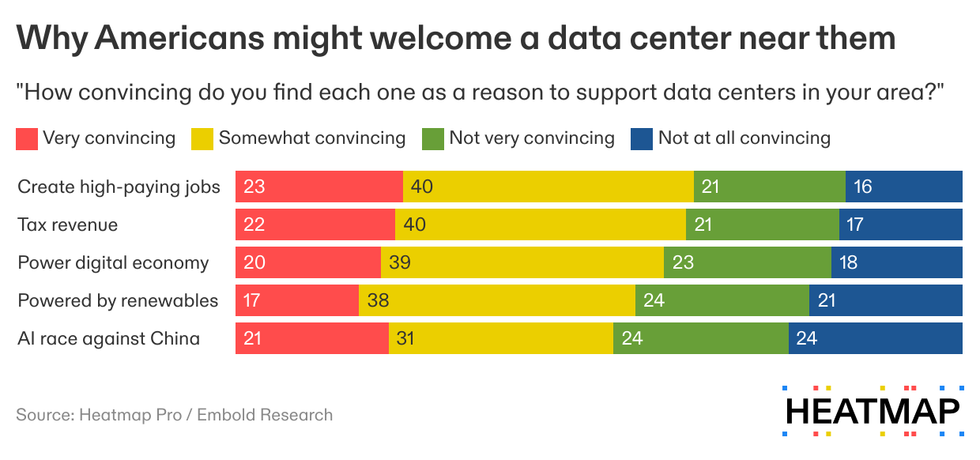
Respondents were far more skeptical of reasons to support data centers that were less tangible or more global. “Many data centers are powered by renewable energy,” was +10% net convincing, while “Data centers are necessary for America to win the AI race against China,” was only +4%. (That question also featured the biggest partisan split. While 61% of Republicans found “the AI race against China” argument convincing, only 45% of Democrats and 40% of independents did.) But when asked about the most convincing reasons to oppose data centers, the idea that they “might require wind or solar farms to be constructed nearby” was only +6% net convincing, while the argument that they could lead to a natural gas power plant being built nearby was +22% net convincing.
Again, tangible, local effects were the most compelling to respondents, as was suggested by the data on specific projects.
The argument that data centers consume too much water was +34% net convincing; while “data centers consume large amounts of electricity, which may increase utility bills,” was +46% net convincing.
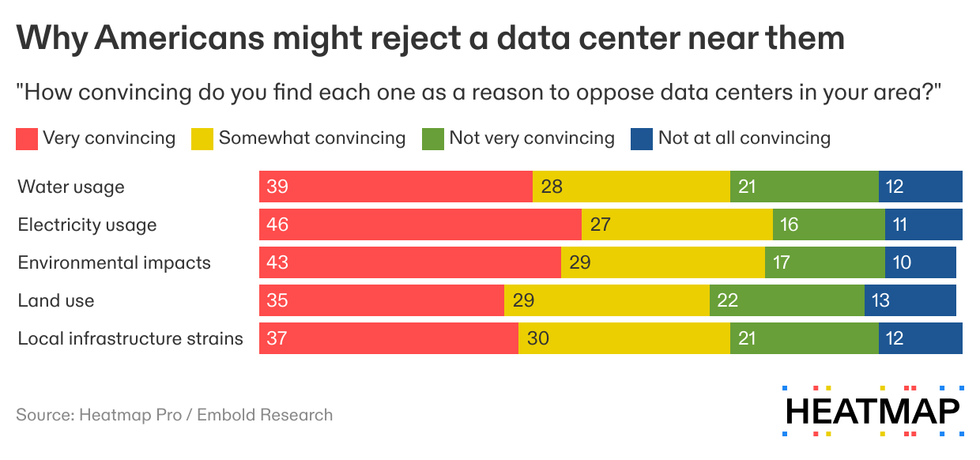
These results are consistent with some of the anti-data-center activism that has popped up in opposition to proposed projects. The city council of Tucson, Arizona, rejected an Amazon project in part due to concerns about effects on drinking water. A $2 billion data center project in Indiana was rejected this week after a public meeting where residents “raised issues around energy usage, environmental impact, and public health,” Data Center Dynamics reported.
Earlier this year, another Indiana data center project was rejected after “residents cited a number of concerns, including noise, power and water consumption and the impact on property values,” Lakeshore Public Media reported.
These concerns should be familiar to anyone who follows the fight around renewable siting. All of these concerns — construction impacts, sightliness and property values, taking up agricultural land — are commonly brought up when local communities oppose a solar or wind farm.
The Heatmap Pro poll of 3,741 American registered voters was conducted by Embold Research via text-to-web responses from August 22 to 29, 2025. The survey included interviews with Americans in all 50 states and Washington, D.C. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 1.7 percentage points.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The seminal global climate agreement changed the world, just not in the way we thought it would.
Ten years ago today, the world’s countries adopted the Paris Agreement, the first global treaty to combat climate change. For the first time ever, and after decades of failure, the world’s countries agreed to a single international climate treaty — one that applied to developed and developing countries alike.
Since then, international climate diplomacy has played out on what is, more or less, the Paris Agreement’s calendar. The quasi-quinquennial rhythm of countries setting goals, reviewing them, and then making new ones has held since 2015. A global pandemic has killed millions of people; Russia has invaded Ukraine; coups and revolutions have begun and ended — and the United States has joined and left and rejoined the treaty, then left again — yet its basic framework has remained.
Perhaps you can tell: I am not among those who believe that the treaty has been a failure, although it would be difficult — in this politically arid moment — to call it a complete success. Yet the ensuing decade has seen real progress in limiting global temperature rise. When negotiators gathered to finalize the agreement, it seemed likely that global average temperatures could rise by 4 degrees Celsius by 2100, as compared to their pre-industrial level. Today, a rise from 2.5 to 3 degrees Celsius seems more likely.
And for a document that is often described as non-binding, or even as hortatory, Paris has had a surprisingly material influence on global politics in the ensuing years. During the negotiations, the small-island states — the three dozen or so countries most affected by near-term sea-level rise — successfully got the final text to recognize a “stretch goal” of limiting warming to just 1.5 degrees above pre-industrial levels. They also tasked the United Nations’ advisory scientific body to prepare a special report on the virtues of avoiding 1.5 degrees of warming. When that report was released in 2018, it catalyzed a new wave of global climate action, spawning the European Green Deal — and eventually the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act.
Yet there is at least one way that Paris did not go as imagined.
Cast your mind back to Paris 10 years ago, right as diplomats filed in and began to applaud the final text’s completion. “This is a tremendous victory for all of our citizens — not for any one country or any one bloc, but for everybody here who has worked so hard to bring us across the finish line,” John Kerry, then the U.S. secretary of state, declared to his fellow diplomats.
It was a strange kind of victory. After decades in which western liberals had attempted to secure a globally binding climate treaty — an agreement that would limit each country’s greenhouse gas emissions — the world finally won a non-binding alternative. Under the Paris Agreement, each country would pledge to cut its emissions by as much as it could manage. Countries would then meet regularly to review these pledges, encourage each other to get more ambitious, and gradually ratchet the world into a lower-carbon future.
Kerry was reasonably direct about how such a mechanism would work: capital markets. “We are sending literally a critical message to the global marketplace,” he said. “Many of us here know that it won’t be governments that actually make the decision or find the product, the new technology, the saving grace of this challenge. It will be the genius of the American spirit.”
He was right, in a way: The Paris Agreement did send a signal to the global marketplace— and it did so in part because governments did shape policy and investment outcomes, not because they resisted doing so. But it did not reveal the genius of the American spirit, per se.
In the years running up to and following the Paris Agreement, China rolled out a series of important policies to boost its new energy sectors — a roadmap encouraging “new energy vehicle” sales in 2012, billions of consumer subsidies beginning in 2014, and a domestic content mandate for electric-vehicle batteries in 2015. These programs — along with canny decisions made by Chinese entrepreneurs and engineers, and no small amount of demand pull from companies and policies in the West — have transformed the world’s approach to decarbonization. They have begun to change even what decarbonization means — in the United States, in the western democracies, and around the world.
Ten years ago, Kerry could assume that any eventual solution to climate change would be geopolitically neutral, if not advantageous to the United States. But in 2025, to a degree that commentators still hesitate to describe, the climate story has become the China story. Across a range of sectors, how a country approaches its near-term decarbonization goals depends on how it understands and relates to the Chinese government and Chinese companies.
Consider the power sector, which generates just under a third of all greenhouse gas emissions globally. For many countries, the best way to cut carbon pollution — and to add more power generation to the grid — will be to build new utility-scale solar and battery projects. That will all but require working with Chinese firms, which dominate 80% of the solar supply chain. (They command up to 98% market share for some pieces of equipment, according to the International Energy Agency.)
It is much the same story in the grid-scale battery industry. China produces more than three-quarters of the world’s batteries, and it refines most of the minerals that go into those batteries. Its batteries are at least 20% cheaper than those made in Europe or North America. Most of the world’s top battery firms are Chinese — in part because they have more experience than anyone else; the country’s firms have manufactured 70% of all lithium-ion batteries ever produced. Nearly two dozen countries have bought at least $500 million in Chinese-made batteries this year, according to the think tank Ember.
What if a country wants to build wind turbines, not batteries? Even then, it will have to work to buy non-Chinese products. Although European and American firms have long led among turbine makers, six of the top 10 wind turbine manufacturers are now in mainland China, according to BloombergNEF. And for the first time since analysts’ rankings began in 2013, none of the world’s top three turbine makers are North American or European.
Transportation generates another 13% of global climate emissions. If a country wants to tackle that sector, then it will find itself (again) working with China — which made more than 70% of the world’s EVs in 2024. Thanks to the country’s sprawling battery and electronics-making ecosystem, its home-grown automakers — BYD, Geely, Xiaomi, and others — can produce more affordable, innovative, and desirable EVs at greater scale and at lower cost than automakers anywhere else. “The competitive reality is that the Chinese are the 700-pound gorilla in the EV industry,” Jim Farley, the CEO of Ford, said recently. As the scholar Ilaria Mazzocco put it in a recent report: “Chinese companies are ubiquitous in the value chain for EVs and battery components, meaning that for most countries, climate policy is now at least in part linked to policy toward China, and more specifically trade with China.”
That insight — that climate policy is now linked to policy toward China — will apply more and more, even when countries wish to tackle the remaining third of emissions that come from energy-related sources. Earlier this year, China approved a plan to build roughly 100 low-carbon industrial parks by 2030, where its firms will develop new ways to capture carbon, make steel, and refine chemicals without carbon pollution. (The Trump administration revoked funding for similar low-carbon projects in the U.S. earlier this year.) At the same time, China is building more conventional nuclear reactors than the rest of the world combined, and it may be pulling ahead of the United States in the race to develop commercial fusion.
This wasn’t inevitable. It happened because Chinese politicians, executives, and engineers decided to make it happen — choices owing as much to the government’s focus on energy security as to its concern for the global environmental commons. But it was also the result of American business leaders and politicians squandering this country’s leadership in climate technologies — and especially the result of choices made by Trump administration officials, who at nearly every opportunity have regarded batteries and electric vehicles as a technological sideshow to the more profitable oil and gas sector.
It was the Trump administration, after all, that licensed and then eventually gave U.S.-funded research on flow batteries to a Chinese company in 2017. It was the Trump administration that gutted fuel economy and clean car rules in 2018 and 2019, setting the American car industry back compared to its Chinese and European competitors. And it was the Trump administration and congressional Republicans that killed electric vehicle tax credits earlier this year, further choking off investment.
For progressives, this all might suggest a pleasant parable: China embraced the energy transition, and America didn’t, and now America is paying for it. Nowadays, commentators often invoke China’s clean energy dominance to inspire awe at its accomplishments. And how can you not, in truth, be impressed? China’s industrial miracle — its move to the frontier of global technological development — is the most important story of the past quarter century. The scale of the Chinese consumer market and the success of Chinese industrial policy (or, at least, its success so far) has wrenched world history in new directions. And Chinese companies have done humanity a great service by bringing down the cost of solar panels, batteries, and EVs on the supply side, even if they did so at first with demand-side assistance from policies in California or Europe.
But climate advocates in North America and Europe cannot be completely sanguine about what this development means globally. For environmentalists and other western liberals who have worked in decarbonization for decades, it will in particular require some rhetorical and political adjustment. We cannot pretend that we are playing by the 1990s’ rules, nor that environmental activism is but one part of a post-1970s progressive coalition, which is free to make demands and ignore inconvenient trade-offs. Basic questions of decarbonization policy now have patent geopolitical significance, which environmental groups attempt to side-step at their own peril.
Yet it isn’t only Americans or Europeans who must answer these questions. China’s dominance of decarbonization technology means that for the time being, every country on Earth must address this dynamic. When the scholar Mazzocco looked at how six countries around the world are approaching Chinese EVs, she found an uneven landscape, she told me on a recent podcast. Costa Rica, which has long embraced climate policy, has welcomed Chinese-made EVs; Brazil opened its doors to them but has now begun to close it.
Most major countries have some form of domestic automaking industry; no country will be able to sit back and passively allow Chinese exports to drive their local automakers out of business. At the same time, China’s manufacturing primacy is already making conventional export-driven growth less attractive for countries. And that will only be the beginning of the dilemmas to come. As long as going green requires buying and integrating Chinese technologies into critical infrastructure, environmental policymakers will be wagering decarbonization’s success on some of the world’s highest stakes geopolitical bets.
Environmentalists have long insisted climate change is a national security issue, but are we ready to think and act like it is? Do Western anxieties about a large and globalized war — either a Chinese invasion of Taiwan, a Russian invasion of the EU, or both — reflect a reasonable response to a real and growing menace, or an elite panic driven by our declining economic primacy? If China were to invade Taiwan, what would that mean for climate and energy policy — not only in the West, but around the world? Would American or European environmentalists even get a vote on that question — and if they do, how would they balance emissions reduction against other goals? If the unthinkable happens, we will all be called to account.
A decade ago, I remember watching the live stream of the world’s diplomats applauding their own success in Paris and realizing that I would be seeing that video in documentaries and news reels for the rest of my life. How will I see it then? I wondered. Would it strike me as the naivete of a simpler time, an era when liberal internationalism still seemed possible? Or would it really reflect a turning point, the moment when the world took the climate challenge seriously, pragmatically, and began to decarbonize in earnest? A decade later, I still don’t know. Perhaps the answer is both.
The electric vehicle-maker’s newly unveiled, lidar-equipped, autonomy-enabled R2 is scheduled to hit the road next year.
When Rivian revealed the R2 back in the spring of 2024, the compelling part of the electric SUV was price. The vehicle looked almost exactly like the huge R1S that helped launch the brand, but scaled down to a true two-row, five-seat ride that would start at $45,000. That’s not exactly cheap, but it would create a Rivian for lots of drivers who admired the company’s sleek adventure EV but couldn’t afford to spend nearly a hundred grand on a vehicle.
But at the company’s “Autonomy and AI Day,” held on Thursday at Rivian’s Palo Alto office in the heart of Silicon Valley, company leaders raised the expectations for their next vehicle. R2 wouldn’t just be the more affordable Rivian — it would be the AI-defined car that vaults them into the race to develop truly self-driving cars.
First, the hardware. Rivian said that the R2 will come with 11 camera and five radar units spread around the vehicle to improve the car’s ability to comprehend the world around it. But the crucial, headline-grabbing addition is a lidar, or light-based radar, unit. Lidar shoots laser pulses and measures the time it takes for the reflected light to return, thereby building a three-dimensional picture of the environment it surveys.
Those twirling bobs you might have seen on the top of Waymo’s driverless cars as they roam the streets, mapping the world around them, are lidar. The technology’s ability to see the world in detail across distances is necessary for the upper levels of automotive autonomy — the ones where the car can basically do it all and the humans can take their hands off the wheel and their eyes off the road.
Lidar units to date have been large and expensive, which is one reason they’re seen in pods that protrude from the top of a vehicle. Rivian, however, figured out how to mount one within the vehicle, in the area at the top of the front windshield near the rear-view mirror. The forward-facing lidar gives the vehicle 300 meters of forward vision. Demos the company showed during autonomy day revealed just how much more a constellation of cameras, radar, and lidar can see than a system without lidar, especially in dark or foggy conditions.
The other “wow” reveal on Thursday was that the R2 will process all that camera data on a chip that Rivian built from scratch to handle the AI and autonomous driving workload of its vehicles, rather than sourcing chips from some other tech company. CEO R.J. Scaringe said during his presentation to open the event that this kind of vertical integration was meant to allow the company to keep pace with the AI race as opposed to having to work with whatever third-party components it could get.
The result is a leap forward in capability over what Rivian offered with the R1S SUV and R1T pickup truck. Those vehicles had a hand-free system that let the EVs drive themselves with minimal human oversight on a little more than 100,000 miles of roads that were well-marked and well-mapped. James Philbin, the vice president of autonomy and AI, promised on Thursday that the lidar and processing improvements would allow hands-free driving on more than 3 million miles of roads — basically anywhere that the lines on the highway are clear enough for the R2’s cameras to see. And what’s next, Rivian promises, is true autonomy. The SUV will drive itself entirely from point to point when the conditions allow, and as the AI continuously improves over time, you might eventually see driverless Rivians out there competing with the likes of Waymo.
All this stuff costs money, of course. The Rivian Autonomy+ package would add $2,500 or a monthly fee of $50 to the purchase price. But the fact that this tech is coming to a car that starts in the $40,000s is telling. It is how many people will get their first taste of true vehicle autonomy.
Thursday’s event wasn’t all about self-driving, either. Rivian also built an AI software assistant for the cabin that can be summoned with a “Hey Rivian” and perform all kinds of in-car functions, such as changing the driving mode or adjusting the climate control. The achievement here is one of natural language. In Rivian’s demos, the assistant could ably fulfill the driver’s wishes with a command like “make it a little toastier in here” as opposed to formal instructional language like “turn the driver’s temperature to 70 degrees and set the seat heater to level one.”
At times this feels unnecessary, like AI looking for something to do to justify its existence. It doesn’t take that many button-pushes to alter the climate, after all. I admit, though, that having test-driven Rivians on road trips this summer, one of their weak points is my struggle to remember exactly which menu contains which controls. AI, in a way, helpfully solves a problem created by the modern EV that has amazing capability, but routes that capability through a large touchscreen that’s annoying (and dangerous) to navigate while driving.
Rivian is playing catch up with Tesla when it comes to autonomy, of course, as Elon Musk’s company has been touting its Full Self Driving feature for years and is now building the Cybercab, which is meant to be a car that humans will never drive. But Tesla has struggled to meet its timelines and targets for autonomous systems, giving rivals like Rivian a window to develop their own technology.
And so, what’s clear after Rivian’s event is that car companies, especially EV makers, are going to be key players in this autonomy and AI age. Nowhere was it written that electric vehicles had to be synonymous with self-driving vehicles. Battery-powered cars could be dumb and not smart, ruled by buttons instead of touchscreens. It just so happens that EVs are finally coming of age during the simultaneous ascent of artificial intelligence — and that the leading EV-only startups are Silicon Valley tech companies, or at least started out that way.
Tesla has forgotten about acting like a car company and staked its future on being the one that will crack true self-driving and reap the windfall. Rivian, which hadn’t made nearly as much noise about AI and autonomy before this week, has put forth a compelling case for its in-house autonomous systems and AI models, ones that will continue to improve as they’re trained on data provided by thousands of R2s hitting the road starting in 2026.
The market is reeling from a trio of worrisome data center announcements.
The AI industry coughed and the power industry is getting a cold.
The S&P 500 hit a record high on Thursday afternoon, but in the cold light of Friday, several artificial intelligence-related companies are feeling a chill. A trio of stories in the data center and semiconductor industry revealed dented market optimism, driving the tech-heavy NASDAQ 100 down almost 2% in Friday afternoon trading, and several energy-related stocks are down even more.
Here’s what’s happening:
Taken together, the three stories look like an AI slowdown, at least compared to the most optimistic forecasts for growth. If so, expectations of how much power these data centers need will also have to come down a bit. That has led to notable stock dips for companies across the power sector, especially independent power producers that own power plants, many of whose shares have risen sharply in the past year or two.
Shares in NRG were down around 4.5% on the day on Friday afternoon; nuclear-heavy Constellation Energy was down over 6%; Talen Energy, which owns a portfolio of nuclear and fossil fuel plants, was down almost 3% and Vistra was down 2%. Shares in GE Vernova, which is expanding its gas turbine manufacturing capacity to meet high expected demand for power, were down over 3.5%.
It’s not just traditional power companies that are catching this AI chill — renewables are shivering, as well. American solar manufacturer First Solar is down over 5%, while solar manufacturing and development company Canadian Solar is down over almost 9%.
Shares of Blue Owl, the investment firm that is helping to fund the big tech data center buildout, were down almost 4%.
The fates of all these companies are deeply intertwined. As Heatmap contributor Advait Arun wrote recently, ”The commercial potential of next-generation energy technologies such as advanced nuclear, batteries, and grid-enhancing applications now hinge on the speed and scale of the AI buildout.” Many AI-related companies are either invested in or lend to each other, meaning that a stumble that looks small initially could quickly cascade.
The power industry has seen these types of AI-optimism hiccups before, however. In January, several power companies swooned after Chinese AI company DeepSeek released an open source, compute-efficient large language model comparable to the most advanced models developed by U.S. labs.
Constellation’s stock price, for example, fell as much as 20% in response to the “DeepSeek Moment,” but are up over 45% this year, even factoring in today’s fall. GE Vernova shares have doubled in value this year.
So it looks like the power sector will still have something to celebrate at the end of this year, even if the celebrations are slightly less warm than they might have been.