You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
More than $760 million from the Inflation Reduction Act’s Green and Resilient Retrofit Program is still caught in legal limbo — but no one seems to have noticed.

When a federal judge put an injunction on the Trump administration’s efforts to freeze Inflation Reduction Act funding back in April, many grantees were able to pick up their clean energy projects where they left off. But not everyone.
Some 100 low-income housing providers that won more than $760 million in grants and loans from the IRA’s Green and Resilient Retrofit Program to make critical safety and energy upgrades to their buildings are still in limbo. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development will not respond to their questions about if or when projects can move forward, and also fired all of the third-party contractors that had been hired to implement the program.
While these developers are certainly not the only ones locked in a bureaucratic standstill — a lawsuit aiming to unlock money from the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund is still wending through the courts, and many states are waiting to hear whether they’ll ever get funding for their home energy retrofit rebate programs — their plight has so far been overlooked, raising the risk that the money could quietly disappear.
The Green and Resilient Retrofit Program addressed a known funding gap for affordable housing preservation. Low-income housing providers operate on tight margins and often struggle to pay for regular maintenance, let alone to make upgrades to their buildings. On top of that, many of the buildings that receive other subsidies from HUD are barred from taking on debt for improvements.
“So what do you do if your building is now 40 years old and it needs upgrades?” Juliana Bilowich, the senior director of housing operations and policy for Leading Age, a nonprofit focused on affordable senior housing, said to me. “There are some housing communities that haven’t had air conditioning for years because the HUD budget won’t support it, or it’s broken and it needs to be upgraded, but there’s no funding they can get to do that.”
That was the case for The Towers, a 20-story senior living center in New Haven, Connecticut, except the building was nearly 60 years old. While its individual apartments have air conditioning, there’s no HVAC system serving the hallways where residents have to wait for the elevator. “The summertime is horrible,” Gus Keach-Longo, the president and CEO of The Towers, told me.
While the building has made cosmetic improvements over the years, it hasn’t done major efficiency or structural work outside of installing LED lightbulbs, Keach-Longo told me. A recent assessment of the building scored it at a 7 out of 100 for energy efficiency. In addition to an HVAC solution, the building needed a new roof and windows.
The Green and Resilient Retrofit Program looked like it could be a lifeline for Towers residents. For one, it was uniquely flexible. The funds could be used for a wide range of projects, as long as they reduced the building’s emissions, improved its energy or water efficiency, or made it more resilient to flooding, extreme heat, or other weather-related hazards.
Billowich called the program a “linchpin” for buildings that didn’t have the ability to go to the bank and get a loan. “This was the way that housing communities were going to be able to continue operating.” Applicants planned to insulate their pipes so they didn’t burst during a cold front, or replace their windows to save money on energy and protect residents from wildfire smoke. The funds could also be leveraged to raise additional money for other kinds of repairs. The resulting energy savings could then be put toward expanding services for residents.
The $1 billion program was divided into three streams of funding. A building owner could get up to $750,000 per property under the “Elements” stream to supplement existing retrofit plans with green upgrades like solar panels. The “Leading Edge” stream supplied up to $10 million for more involved projects and required the building to ultimately meet a green certification, such as Passive House or LEED. The “Comprehensive” stream was designed to facilitate more complicated, full-building retrofits that required significant technical assistance to plan. Grantees could get up to $80,000 per unit, or $20 million total, but they would have to work with HUD-employed contractors that would scope out and oversee the project.
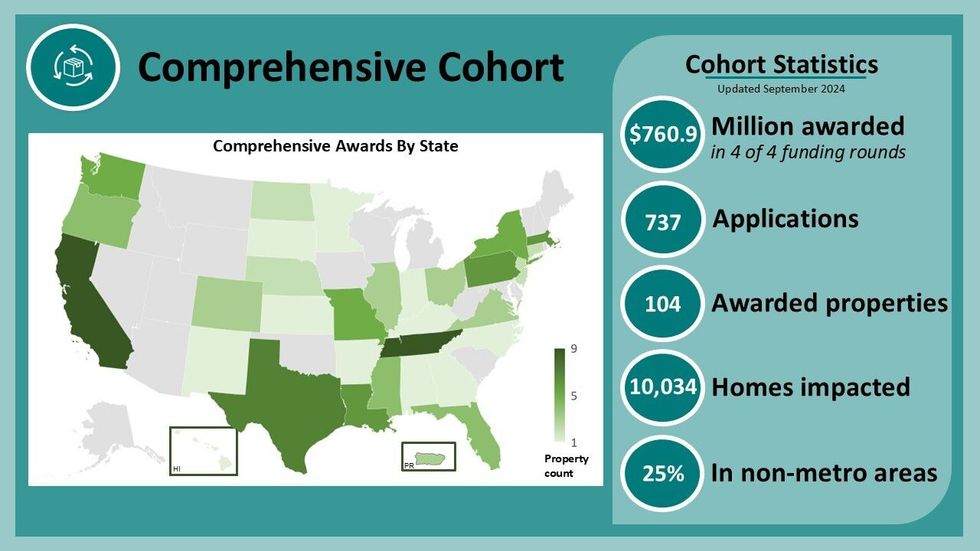
The Towers applied for a Comprehensive grant and was one of just a few properties to win the full $20 million. But since signing a contract for the award last July, Keach-Longo said his team has “heard almost nothing.” They were supposed to be assigned a Multifamily Assessment Contractor, or MAC, the term for the HUD-employed contractor that would oversee the project, but the Biden administration never got to it. When the Trump administration came in, it halted the program as part of the larger IRA funding freeze. On February 12, HUD terminated its contracts with all five of the companies it had selected to serve as MACs, including big consulting firms like Deloitte and Ernst and Young. HUD did not respond to emailed questions for this story.
Margaret Salazar, the CEO of REACH Community Development in Oregon, has also been “stuck in a holding pattern” regarding her organization’s two Comprehensive awards. “We want to do right by what we’ve communicated with residents that we are making these repairs. We want to involve them in the process. And now we’re hanging out there without any path forward,” she told me.
When the funding freeze first went into effect in March, an affordable housing operator in the Boston area called the Codman Square Neighborhood Development Corporation, which had won an Elements grant, joined a lawsuit filed by five other nonprofits that challenged Trump’s pause. In April, the district court judge overseeing the case issued a preliminary injunction barring HUD and other agencies from maintaining any program-wide freezes.
The agency complied, in part. HUD sent a letter to awardees notifying them of the injunction and resumed processing reimbursements for Elements and Leading Edge grants. Ron Budynas, the chief operating officer for an affordable senior housing provider called Wesley Living, which won 10 separate awards from the program, told me he’s been able to proceed with his three Elements projects. He’s already completed one, upgrading an apartment complex in Lexington, Tennessee, with high efficiency heat pumps, and is now working on the others, installing solar and battery backup systems at two other properties in Tennessee.
His remaining seven are Comprehensive projects, however, and are “a whole different story,” he said. “Every time I’ve written to the [Green and Resilient Retrofit Program] staff, the only answer I get back from them on the Comprehensive grants is ’we’re still waiting for direction from headquarters.’”
Budynas was much further along than Keach-Longo at The Towers by the time Trump came into office. He said he was already working with a MAC and had completed a capital needs assessment on five of the properties; the next step was to scope out the work. He told me he contacted HUD after the court’s injunction and asked whether his team could put together the scope for one project to move it forward, but the agency told him no, since the program rules say that the MAC has to do it — even though it had fired all of the MACs.
Then the reconciliation bill that Congress passed earlier this month rescinded $138 million from the program — money set aside for administrative costs and technical assistance, i.e. to pay for the MACs. “How do we go forward if the MAC has to do the scope and they don’t have any money to pay the MAC?” Budynas said. Six of the seven Wesley Living properties that won Comprehensive awards receive HUD subsidies that preclude them from using other types of financing, “so there’s no way for us to update those properties if the Comprehensive doesn’t go forward,” he said.
It’s unclear whether any of this will be addressed in the lawsuit, since the only plaintiff in the case that challenged HUD — Codman Square — has been able to progress with its Elements award. I reached out to Democracy Forward, the nonprofit legal organization that is representing the plaintiffs, but it declined to comment.
Beth Neitzel, a partner at the law firm Foley Hoag, which is not involved in the case, told me this might be an unfortunate gray area for the Comprehensive award winners. She said the lawyers could argue that HUD is violating the terms of the injunction, but the government could respond that no one in the case is being injured by its actions.
“I don’t know if that will carry the day. It seems pretty clear they are violating the terms of the preliminary injunction by not unfreezing that fund,” Neitzel said. “But there is that potential wrinkle that they will argue that’s not an issue here because nobody here has standing to challenge that.” As a matter of law, she added, it’s irrelevant that HUD fired the contractors overseeing the program since the program itself was congressionally mandated.
Meanwhile the grantees wait, and the consequences of the delay stack up. Salazar, of REACH in Oregon, told me the organization missed out on an opportunity to get additional funding from the Portland Housing Bureau because it hadn’t been able to scope out the project with its MAC.
“This isn’t just money on the line. This is the future of these affordable housing communities,” Bilowich said. “That is a blue issue, that’s a red issue, that’s everybody’s issue. And so we need a solution, and this was the most efficient and cost-effective solution that everybody had come up with.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The new climate politics are all about affordability.
During the August recess, while members of Congress were back home facing their constituents, climate and environmental groups went on the offensive, sending a blitz of ads targeting vulnerable Republicans in their districts. The message was specific, straightforward, and had nothing to do with the warming planet.
“Check your electric bill lately? Rep. Mark Amodei just voted for it to go up,” declared a billboard in Reno, Nevada, sponsored by the advocacy group Climate Power.
“They promised to bring down prices, but instead our congressman, Derrick Van Orden, just voted to make our monthly bills go up,” a YouTube ad told viewers in Wisconsin’s 3rd district. “It removes clean energy from the electric grid, creating a massive rate hike on electricity,” the voiceover says, while the words “VAN ORDEN’S PLAN: ELECTRICITY RATE HIKE” flash on screen. The ad, paid for by Climate Power, the League of Conservation Voters, and House Majority Forward, a progressive campaign group, was shown more than a million times from August 13 to 27, according to Google’s ad transparency center.
Both were part of a larger, $12 million campaign the groups launched over the recess in collaboration with organizations including EDF Action and Climate Emergency Advocates. Similar billboards and digital ads targeted Republicans in more than a dozen other districts in Arizona, California, Colorado, Iowa, Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Texas. There were also TV spots, partnerships with Instagram influencers, bus stop posters, and in-person rallies outside district offices — all blaming Republicans in Congress for the increasing cost of food, healthcare, and energy.

As others have observed, including Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin back in March, rising utility rates and the broader cost of living crisis are becoming a political liability for Republicans and President Trump. Clean energy advocates are attempting to capitalize on that, trying to get Americans to connect the dots between their mounting electricity bills and their representatives in Congress who voted to cut support for renewable energy.
Some of this is run-of-the-mill politicking, but it’s not only that. It also represents a strategic shift in how the climate movement talks about the energy transition.
It’s not new for green groups to make the argument that renewable energy can save people money. Relying on “free” wind and sun rather than fuels that are subject to price volatility has always been part of the sell, and the plummeting cost of solar panels and wind turbines have only made that pitch more compelling.
But it is new for the affordability argument to come first — above job creation, economic development, reducing pollution, and, of course, tackling climate change.
For most of the past four years, the climate movement has gone all in on trying to build an association in the American mind between the transition to clean energy and jobs. “When I think of climate change, I think of jobs,” then-candidate Joe Biden said during one of his 2020 campaign speeches.
It made sense at the time, Daniel Aldana Cohen, a sociologist at the University of California, Berkeley, told me. Just two years earlier, the Sunrise Movement had emerged as a political force with a headline-grabbing rally in Nancy Pelosi’s office demanding “green jobs for all.” The group was joined by then-newly elected Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, who soon introduced her framework for a Green New Deal that would offer a “just transition” for fossil fuel workers, ensuring them a place in the new clean energy economy.
The fossil fuel industry had seeded divisions between labor and environmental groups for decades by arguing that regulations kill jobs, and Democrats would have to upend that narrative if they wanted to make progress on climate. But the rationale was also more pressing: Unemployment was skyrocketing due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and whoever won the presidency would be responsible for rebuilding the U.S. workforce.
Fast forward to the end of Biden’s first year in office, however, and the unemployment rate had snapped back to pre-pandemic levels. Meanwhile, inflation was rising fast. Even though the Democrats managed to name their climate bill the “Inflation Reduction Act,” the administration and the climate movement continued talking about it in terms of jobs, jobs, jobs.
Cohen co-directs the Climate and Community Institute, a progressive think-tank founded in 2020, and admitted that “from the very start, we would just model every policy with jobs numbers,” partly because modeling the effects of policies on cost of living was a lot more complicated. Now he sees two issues with that approach. For one, it was always going to take time for new manufacturing jobs to materialize — much longer than an election cycle. For another, when unemployment is low, “everybody experiences inflation, but extremely few people experience a good new green job,” Cohen said.
During a recent panel hosted by the Institute for Policy Studies, Ben Beachy, who was a special assistant to Biden for climate policy, expressed some regret about the jobs push. “It wasn't addressing one of the biggest economic concerns of most people at that point, which was the rent is too damn high,” he said. But Beachy also defended the strategy, noting that all of the policies addressing cost of living in Biden’s big climate bill, like money for housing, public transit, and childcare, had been stripped out to appease West Virginia Democrat Joe Manchin. “So we were left without a strong policy leg to stand on to say, this is going to lower your costs.”
When the moderator asked what message Beachy thinks climate candidates should run on today, Beachy replied, “affordability, affordability, affordability.”
Jesse Lee, a senior advisor at Climate Power who also worked as a senior communications advisor in the Biden White House, echoed Beachy’s account of what went wrong post-IRA. The cost of living crisis makes it almost impossible to talk about anything else now, he told me. “If you don't start off talking about that, you’ve lost people before you’ve even begun,” he told me.
Average U.S. electricity rates jumped 10% in just the year from 2021 to 2022, and have continued to rise faster than inflation. All evidence suggests the trend will continue. Utilities have already requested or received approval for approximately $29 billion in rate increases this year, according to the nonprofit PowerLines, compared to roughly $12 billion by this time last year. And these increases likely don’t reflect the expected costs associated with ending tax credits for wind and solar, hobbling wind and solar development, and keeping aging, expensive coal plants online.
In mid-July, Climate Power issued a strategy document advising state and local elected officials how to talk about clean energy based on the group’s polling. A post-election poll found that “more than half of Americans (51%) say the main goal of US energy policies should be to lower energy prices,” and that 85% “believe policymakers should do more to lower energy costs.” A more recent poll found that telling voters that “cutting clean energy means America produces less energy overall, and that means families will pay even more to keep the lights on,” was the most persuasive among a variety of arguments for clean energy.
This tracks with our own Heatmap Pro opinion polling, which found that the top perceived benefit of renewables in the U.S. is “lower utility bills” — though while 75% of Democrats believe that argument, only 56% of Republicans do. An affordability frame also aligns with academic research on clean energy communication strategies, which has found that emphasizing cost savings is a more effective and enduring message than job creation, economic development, or climate change mitigation.
The pivot to affordability isn’t just apparent in district-level campaigns to hold Republicans accountable. Almost every press release I’ve received from the climate group Evergreen Action this month has mentioned “soaring power bills” or “Trump’s energy price hike” in reference to various actions the administration has taken to hamstring renewables. Even clean energy groups, which at first attempted to co-opt Trump’s “energy dominance” frame, can no longer parrot it with a straight face. After Trump issued a stop work order on Orsted’s offshore Revolution Wind project, which is 80% built, the American Clean Power Association accused the administration of “raising alarms about rising energy prices while blocking new supply from reaching the grid.”
Several people I spoke to for this story pointed to the example of Mikie Sherill, the Democrat running for governor in New Jersey, who last week vowed to freeze utility rates for a year if elected. She immediately followed that statement with a promise to “massively expand cheaper, cleaner power generation,” including solar and batteries.
Dan Crawford, the senior vice president of Echo Communications Advisors, a climate-focused strategy firm, declared in a recent newsletter that Democrats should “become the party of cheap electricity.” He mused that we may be at an inflection point “where the old politics of clean-vs.-polluting makes way for a new debate of cheap-vs.-expensive.”
Debate is probably too tame a term — the claim to affordability is becoming a full-on messaging war. Last week, President Trump took to social media to declare that states that get power from wind and solar “are seeing RECORD BREAKING INCREASES IN ELECTRICITY AND ENERGY COSTS,” — a claim that has no basis in reality. The Trump administration is leaning heavily on affordability arguments to justify keeping coal plants open. In defense of canceling Revolution Wind, Interior Secretary Doug Burgum told Fox News that “this is part of our drive to make sure we’ve got affordable, reliable energy for every American … These are the highest electric prices in the country coming off of these projects.” On Thursday, Energy Secretary Chris Wright posted a news story about his agency rescinding a loan for an offshore wind transmission project, writing that “taxpayers will no longer foot the bill for projects that raise electricity prices and ultimately don't work.”
Clean energy proponents aren’t just going up against Trump — the fossil fuel industry has leaned on affordability as a rhetorical strategy for a long time, Joshua Lappen, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Notre Dame studying the energy transition, told me. Lappen, who lives in California, said cost has been at the forefront of conflicts over climate policy in the state for a while. At the moment, it’s driving a fight over oil refinery closures that threaten to drive up gas prices even more. “I took a trip over the weekend and drove through the Central Valley,” Lappen told me, “and there are placards zip-tied to every gas pump at Chevron stations that are highlighting that state climate policy is increasing the cost of gas.”
I asked Lee, of Climate Power, how the climate movement could make a convincing case when clean energy has become so politically charged. He’s not worried about that right now. “I don’t think we necessarily need to win a debate about what’s cheaper,” he said. “All we have to do is say, Hey, we're in favor of more energy, including wind and solar, and it's nuts, nuts to be taking wind and solar and batteries off the table when we have an energy crisis and when utility rates have gone up 10%.”
That may work for now, at least at the national level. Americans tend to blame whoever is in office for the economic pains of the moment, even though presidents have little influence on prices at the pump and it can take years for policy changes to make their way into utility rates.
But there’s a difference between defensively blaming rising energy costs on the administration’s efforts to block renewable, and making a positive case for the energy transition on the same grounds. While there is an argument for the latter, it’s a lot harder to convey.
The factors pushing up energy prices, such as necessary grid modernization and disaster-related costs, likely aren’t going away, whether or not we build offshore wind farms. Meanwhile, the savings that large-scale wind and solar projects offer won’t be experienced as a reduction in rates — they won’t be experienced at all because they’re measured against a counterfactual world where renewables don’t get built. That’s a lot trickier to communicate in a pithy campaign. People may end up blaming the wind farms either way.
This dilemma is a hallmark of the so-called “mid-transition,” Lappen told me. The term was coined by his advisor, the energy engineer and sociologist Emily Grubert, and Sara Hastings-Simon, a public policy professor at the University of Calgary. The two argue that the mid-transition is a period where fossil fuel systems persist alongside the growing clean energy sector.
“Comparisons of the new system to the old system are likely to rest on experience of a world less affected by climate change, such that concerns about lower reliability, higher costs, and other challenges might be perceived as inherent to zero-carbon systems, versus energy systems facing consequences of climate change and long-term underinvestment,” they write.
To Cohen, advocates need to go a lot further than rhetoric to link clean energy with affordability. “We need to rebuild the brand and then rebuild the investment priorities of climate action so that working class communities see and literally touch direct, tangible benefits in their life,” he said. He described a “green economic populism” with much more public investment in helping renters access green technologies that will lower their bills, for example, or fixing up homes that have deferred maintenance so that they can eventually make energy efficiency improvements.
It’s not about abandoning industrial policy or research and development, Cohen told me, but rather about a shift in emphasis. He pointed to Sherill’s approach. “She's not just saying, oh, clean energy will automatically lower bills if you just unleash it. She's like, I'm going to assertively use the government to guarantee a price freeze, and then I’m going to backfill that with clean energy policies to bring down prices over time.”
To be fair, the IRA did contain policies that would have produced more tangible benefits. The $7 billion Solar for All program would have delivered the benefits of solar — i.e. energy bill savings — to low-income residents all over the country. The remainder of the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund, of which Solar for All was a part, was set to make a range of other green home upgrades more accessible to the working class, and the Green and Resilient Retrofit Program would have done the same for low-income housing developments and senior living centers. Electric school bus grants and urban tree-planting programs would have brought cleaner, cooler air to communities.
These were huge new programs that were never going to produce results in the span of two years, and now the Trump administration has made every effort to ensure they never do. Whether they would have paid political dividends eventually, we’ll never know. But a successful energy transition may depend on giving it another shot.
On fusion’s big fundraise, nuclear fears, and geothermal’s generations uniting
Current conditions: New Orleans is expecting light rain with temperatures climbing near 90 degrees Fahrenheit as the city marks the 20th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina • Torrential rains could dump anywhere from 8 to 12 inches on the Mississippi Valley and the Ozarks • Japan is sweltering in temperatures as high as 104 degrees.
The Environmental Protection Agency is preparing to propose a new Clean Water Act rule that would eliminate federal protections for many U.S. waterways, according to an internal presentation leaked to E&E News. If finalized, the rule would establish a two-part test to determine whether a wetland received federal regulations: It would need to contain surface water throughout the “wet season,” and it would need to be touching a river, stream, or other body of water that flows throughout the wet season. The new language would require fewer wetland permits, a slide from the presentation showed, according to reporter Miranda Willson. Two EPA staffers briefed on the proposal confirmed the report.
The new rule follows the 2023 Supreme Court decision in Sackett v. EPA, which said that only waterways “with a ‘continuous surface connection’ to a ‘relatively permanent’ body of water” fell under the Clean Water Act’s protections, according to E&E News. What “relatively permanent” means, however, the court didn’t say, nor did Biden’s EPA. The two EPA staffers, who were granted anonymity to avoid retribution, “said they believed the proposal was not based in science and could worsen pollution if finalized,” Willson wrote.
Investors are hot on the Massachusetts Institute of Technology spinoff promising to make fusion energy a reality. Commonwealth Fusion Systems netted an eye-popping $863 million in its latest fundraising round. In a press release Thursday, the company said that its “oversubscribed round of capital is the largest amount raised among deep tech and energy companies since” its $1.8 billion financing deal in 2021. Commonwealth Fusion will use the funds to complete its demonstration project and further develop its proposed first power plant in Virginia. To date, the company said, it has raised close to $3 billion, “about one-third of the total capital invested in private fusion companies worldwide.” It’s a sign that investors recognize Commonwealth Fusion “is making fusion power a reality,” CEO Bob Mumgaard said.
The fusion industry has ballooned over the past six years. “It is finally, possibly, almost time” for the technology to arrive, Heatmap’s Katie Brigham wrote last year, noting: “For the ordinary optimist, fusion energy might invoke a cheerful Jetsons-style future of flying cars and interplanetary colonization. For the cynic, it’s a world-changing moment that’s perpetually 30 years away. But investors, nuclear engineers, and physicists see it as a technology edging ever closer to commercialization and a bipartisan pathway towards both energy security and decarbonization.”
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
A record 75 gigawatts of new generating capacity hooked up to the U.S. power grid last year, a 33% surge from the previous year, thanks to new federal regulations aimed at streamlining the process. That’s according to new data from the consultancy Wood Mackenzie published Thursday. The report found that the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s Order No. 2023, issued in July 2023, along with other reforms by independent system operators, have had a “considerable impact on processing interconnection agreements, by driving improvements through reducing speculative projects and clearing queue backlogs.” While connections increased, regional grid operators received 9% fewer new project entries and saw a 51% uptick in non-viable projects since 2022.
Solar and storage technologies made up 75% of all interconnection agreements in 2024, equaling about 58 gigawatts. Wood Mackenzie projected that the sectors will retain a similar market share in 2025. Natural gas saw an increase in interconnection requests since 2022, adding 121 gigawatts of capacity. New gas applications are already breaking annual records this year. But overall the number of gas projects that successfully hook up to the grid is down 25% since 2022.
Almost 200 people have left the Nuclear Regulatory Commission since President Donald Trump’s inauguration in January, according to new estimates published Thursday in the Financial Times. Of the 28 officials in senior leadership positions, nearly half are working in an “acting” capacity, and only three of the five NRC commissioner roles are filled. “It is an unprecedented situation with some senior leaders having been forced out and many others leaving for early retirement or worse, resignation,” Scott Morris, the former NRC deputy executive director of operations, who retired in May, told the newspaper. “This is really concerning for the staff and is one of the factors causing many key staff and leaders to leave the agency they love ... creating a huge brain drain of talent.”
The exodus comes as Trump is pressing the agency to dramatically overhaul and speed up its review and approval process for new reactors. Supporters of the president’s effort say the NRC has stymied the nuclear industry for decades, and a future buildout of new reactors requires clearing house. But skeptics of the burn-it-all-down approach warn that the atomic energy industry’s success in avoiding major accidents since the 1979 partial meltdown at Three Mile Island is owed to NRC oversight, and that the agency’s processes have actually protected nuclear developers by avoiding frivolous lawsuits and not-in-my-backyard types.
Geothermal giant Ormat has reigned over the global industry of harvesting energy from hot underground reservoirs for the past 60 years. Now a new generation of companies is promising to tap the Earth’s heat even in places without water by using fracking technology to drill much deeper, vastly expanding the potential for geothermal. And Ormat has placed a big bet on one. On Thursday, the company inked a strategic partnership with Houston-based Sage Geosystems. As part of the deal, Sage will build its first commercial power plant at an existing Ormat facility in Nevada or Utah, significantly speeding up the timeline for the debut generating station. Sage CEO Cindy Taff told me the plant could be online by next year. “Ormat’s chosen a winner,” Yakov Feygin, a researcher at the Center for Public Enterprise who co-authored a report on next-generation geothermal, told me.
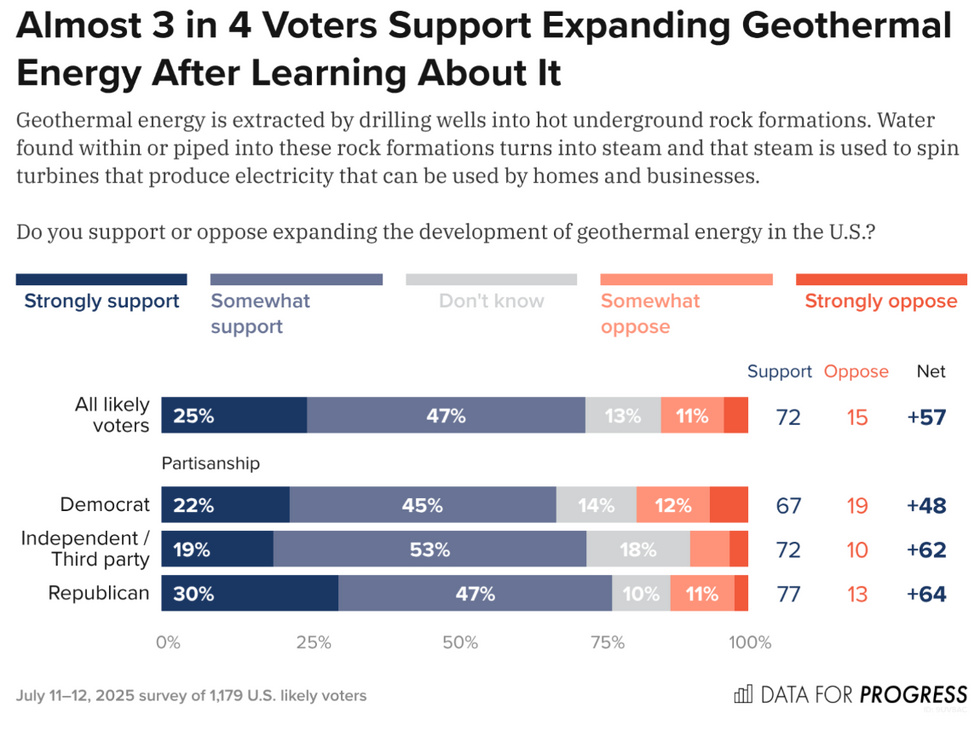
A majority of U.S. voters are still unfamiliar with geothermal power, according to a new poll from Data for Progress I reported on this week. When exposed to details about how the technology works, however, support grows among voters across the political spectrum. Republicans in particular are supportive.
The Grammy- and Oscar-award winning New Orleans jazz and funk singer Jon Batiste released a new song to mark the 20th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina, the catastrophic storm that flooded his home city. Dubbed “Petrichor,” a word that describes the scent of earth after rain, the lyrics unfold like a haunting hymn over a driving beat. “Help me, Lord / They burning the planet down / No more second linin' in the street / They burning the planet down, Lord / Help me, Lord / No more plants for you to eat.” In an interview published in The Guardian, Batiste said the song was meant to be a statement. “You got to bring people together. People power is the way that you can change things in the world,” he said. “It’s a warning, set to a dance beat.”
How the Migratory Bird Treaty Act could become the administration’s ultimate weapon against wind farms.
The Trump administration has quietly opened the door to strictly enforcing a migratory bird protection law in a way that could cast a legal cloud over wind farms across the country.
As I’ve chronicled for Heatmap, the Interior Department over the past month expanded its ongoing investigation of the wind industry’s wildlife impacts to go after turbines for killing imperiled bald and golden eagles, sending voluminous records requests to developers. We’ve discussed here how avian conservation activists and even some former government wildlife staff are reporting spikes in golden eagle mortality in areas with operating wind projects. Whether these eagle deaths were allowable under the law – the Bald and Golden Eagle Protection Act – is going to wind up being a question for regulators and courts if Interior progresses further against specific facilities. Irrespective of what one thinks about the merits of wind energy, it’s extremely likely that a federal government already hostile to wind power will use the law to apply even more pressure on developers.
What’s received less attention than the eagles is that Trump’s team signaled it could go even further by using the Migratory Bird Treaty Act, a separate statute intended to support bird species flying south through the U.S. from Canada during typical seasonal migration periods. At the bottom of an Interior press release published in late July, the department admitted it was beginning a “careful review of avian mortality rates associated with the development of wind energy projects located in migratory flight paths,” and would determine whether migratory birds dying because of wind farms qualified as “‘incidental’ takings” – harm or death – under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act.
While not stated explicitly, what this means is that the department appears to be considering whether to redefine these deaths as intentional under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act, according to Ben Cowan, a lawyer with the law firm Troutman Pepper Locke.
I reached out to Cowan after the eagle investigation began because his law firm posted a bulletin warning that developers “holding active eagle permits” might want to prepare for “subpoenas that may be forthcoming.” During our chat earlier this month, he told me that the eagle probe is likely going to strain financing for projects even on private lands that wouldn’t require any other forms of federal sign-off: “Folks don’t want to operate if they feel there’s a significant risk they might take an eagle without authorization.”
Cowan then voiced increasing concern about the migratory bird effort, however, because the law on this matter could be a quite powerful – if legally questionable – weapon against wind development.
Unlike the Endangered Species Act or the eagle protection law, there is currently no program on the books for a wind project developer to even obtain a permit for incidental impacts to a migratory bird. Part of the reason for the absence of such a program is the usual federal bureaucratic struggle that comes with implementing a complex statute, with the added effect of the ping-pong of federal control; the Biden administration started a process for permitting “incidental” impacts, but it was scrapped in April by the Trump team. Most protection of migratory birds under the law today comes from voluntary measures conducted by private companies and nonprofits in consultation with the federal government.
Hypothetically, hurting a migratory bird should be legally permissible to the federal government. That’s because the administration loosened implementation of the law earlier this year with an Interior Department legal opinion that stated the agency would only go after harm that was “intentional” – a term of art under the statute.
This is precisely why Cowan is fretting about migratory birds, however. Asked why the wind industry hasn’t publicly voiced more anxiety about this potential move, he said industry insiders genuinely hope this is “bluster” because such a selective use of this law “would be so beyond the pale.”
“It’s basically saying the purpose of a wind farm is to kill migratory birds, which is very clearly not the case – it’s to generate renewable electricity,” Cowan told me, adding that any effort by the Interior Department would inevitably result in lawsuits. “I mean, look at what this interpretation would mean: To classify it as intentional take would say the purpose of operating a wind farm would be to kill a bird. It’s obviously not. But this seems to be a way this administration is contemplating using the MBTA to block the operation of wind farms.”
It’s worth acknowledging just how bonkers this notion is on first blush. Is the federal government actually going to decide that any operating wind farm could be illegal? That would put entire states’ power supplies – including GOP-heavy states like Iowa – in total jeopardy. Not to mention it would be harmful overall to take operating capacity offline in any fashion at a moment when energy demand is spiking because of data centers and artificial intelligence. Even I, someone who has broken quite a few eye-popping stories about Trump’s war on renewables, struggle to process the idea of the government truly going there on the MBTA.
And yet, a door to this activity is now open, like a cleaver hanging over the industry’s head.
I asked the Interior Department to clarify its timeline for the MBTA review. It declined to comment on the matter. I would note that in mid-August, the Trump administration began maintenance on a federal dashboard for tracking regulations such as these and hasn’t updated it since. So we’ll have to wait for nothing less than their word to know what direction this is going in.