You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On a billion-dollar mineral push, the north’s grim milestones, and EV charging’s comeback

Current conditions: The Southeastern U.S. is facing flash floods through the end of Thursday • Temperatures in Fez, Morocco, are forecast to hit 108 degrees Fahrenheit • Wildfires continue to rage across southern Europe, sending what Spain’s environment minister called a “clear warning” of the effects of climate change.
President Donald Trump on Wednesday named David Rosner, a centrist Democrat, as the new chairman of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. Since joining the commission in June 2024, Rosner focused the panel on the nation’s growing electricity demand from data centers and pushed for greater automation of the engineering process to connect power plants to the continent’s various grid systems. “Getting grid interconnection moving faster is essential to ensuring reliability,” Rosner told E&E News in March. “We’re starting to learn about these new tools and platforms that just make this work faster, smarter, saves us time, solves the reliability and affordability problems that are facing the country.”
The Bipartisan Policy Center, where Rosner previously worked as a staffer, hailed his promotion as a positive step. “Chairman Rosner’s strong understanding of the energy challenges facing our country, and demonstrated record of bipartisan work to address those challenges, make him well-suited to carry out the responsibilities of FERC chairman,” David R. Hill, the executive vice president of the group’s energy program, said in a statement.

The Energy Department announced at least $925 million in funding for five proposed programs to bolster the country’s domestic supply of minerals. “For too long, the United States has relied on foreign actors to supply and process the critical materials that are essential to modern life and our national security,” Secretary of Energy Chris Wright said in a press release. “The Energy Department will play a leading role in reshoring the processing of critical materials and expanding our domestic supply of these indispensable resources.”
That funding includes:
The Trump administration has made bolstering America’s critical minerals industry one of its signature energy policy priorities. Though as Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin has written, it has also gone out of its way to annihilate sources of domestic demand for these minerals, especially in the wind energy and electric vehicle industries.
In Alaska, an overflowing glacial lake north of Juneau triggered the Mendenhall River to surge to a record height, flooding the state’s capital city. The problem has been growing for years as climate change in the nation’s most rapidly-warming state accelerates the volume of ice melt. In 2023, floodwaters eroded Mendenhall’s banks, causing homes to collapse, according to the Alaska Beacon. In 2024, the news outlet reported, “the flood was the worst yet.” The flood peaked Wednesday afternoon at nearly 17 feet, damaging hundreds of homes.
Across the border, meanwhile, the more than 700 active fires blazing in Canada have already made this the country’s second-worst fire season on record. The largest fire, the Shoe fire in Saskatchewan, has been burning across 1.4 million acres — an area larger than the Grand Canyon National Park in Arizona — since May 7, The New York Times reported.
In an executive order on his first day back in office, Trump singled out the $5 billion National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure program, directing his Department of Transportation to pause and review the funding, with an eye toward cutting it entirely. Earlier this week, the Federal High Administration completed its review and issued a new guidance that, as my colleague Emily Pontecorvo wrote yesterday, “not only preserves it, but also purports to ‘streamline applications,’ ‘slash red tape,’ and ‘ensure charging stations are actually built.’”
“If Congress is requiring the federal government to support charging stations, let’s cut the waste and do it right,” Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy said in a press release. “While I don’t agree with subsidizing green energy, we will respect Congress’ will and make sure this program uses federal resources efficiently.” The statement, Emily noted, is out of sync with the administration’s other actions to throttle the adoption of EVs: “Only time will tell whether the new guidance is truly a win for EV charging, however. It’s a win in the sense that many EV advocates feared the agency would try to kill the program or insert poison pills into the guidance. But it’s unclear whether the changes will speed up NEVI deployment beyond what might have happened had it not been paused.”
A researcher has designed a new centimeter-square device that could help probe the “ignorosphere,” a layer of ultra-thin air that has largely escaped exploration by balloons, aircraft and satellites. The contraption uses technology similar to a weathervane encased in a low-pressure chamber that will spin when exposed to light. “You don’t really believe it until you see it,” Ben Schafer, a physicist at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, told Nature.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The SPEED Act faces near-certain opposition in the Senate.
The House of Representatives has approved the SPEED Act, a bill that would bring sweeping changes to the nation’s environmental review process. It passed Thursday afternoon on a bipartisan vote of 221 to 196, with 11 Democrats in favor and just one Republican, Brian Fitzpatrick of Pennsylvania, against.
Thursday’s vote followed a late change to the bill on Wednesday that would safeguard the Trump administration’s recent actions to pull already-approved permits from offshore wind farms and other renewable energy projects.
Prior to that tweak, the bill would have limited the Trump administration’s ability to alter or revoke a federal permitting decision after the fact. The new version, adopted to secure votes from Republican representatives in Maryland and New Jersey, carves out an exception for agency actions taken between January 20 and the day the law takes effect.
"Last-minute changes to the SPEED Act undercut the bill’s intent to provide certainty to American business,” Rich Powell, the CEO of the Clean Energy Buyers Association said in a press release after the bill passed. “We hope the Senate will now take this language and strengthen those protections for existing and new projects needed to maintain grid reliability and meet growing electricity demand.”
At a high level, the SPEED Act would hasten federal permitting by restricting the evidence that federal agencies consider during the environmental review process and limiting the amount of time a court can deliberate over challenges to federal decisions. It would also disallow courts from vacating permits or issuing injunctions against projects if it finds that a federal agency violated NEPA. The changes would apply to permits of all kinds, including for oil and gas drilling, solar and wind farms, power lines, and data centers.
Environmental groups were generally against the bill. “Far from helping build the clean energy projects of the future, the SPEED Act will only result in an abundance of contaminated air and water, dirty projects, and chronic illnesses with fewer opportunities to hold polluters accountable in court,” Stephen Sciama, senior legislative council for Earthjustice Action, said in a press release on Thursday.
But proponents, such as the conservative energy group Clearpath Action, argue the bill will enable American industry to “invest and build with confidence” by cutting unnecessary red tape, improving coordination across agencies, and setting clearer rules and timelines for judicial review.
In House floor testimony on Thursday morning, Republican Bruce Westerman of Arkansas, the SPEED Act’s lead sponsor, said the bill had the backing of more than 375 industry groups and businesses, and bipartisan support in both the House and Senate. “The SPEED act will deliver the energy and infrastructure Americans need,” he said.
The bill lost at least one significant industry supporter after Wednesday’s changes, however. The American Clean Power Association, which had previously joined the American Petroleum Institute and others in a letter urging the House to pass the bill, withdrew its support, calling the new language a “poison pill” that “injects permit uncertainty, and creates a pathway for fully permitted projects to be canceled even after the Act’s passage.”
The Solar Energy Industries Association also denounced the bill’s passage.
Contrary to Westerman’s assertion, the bill’s fate in the Senate is far from certain. “Even if the House passes this bill today, it is going nowhere in the Senate,” Democratic Representative Jared Huffman of California asserted on the floor on Thursday. “What a missed opportunity to tackle a serious issue that Democrats were very interested in working on in good faith.”
Some Senate Democrats came out in opposition of the bill even before the late-breaking amendments. Senators Brian Schatz of Hawaii, Sheldon Whitehouse of Rhode Island, and Martin Heinrich of New Mexico told my colleague Jael Holzman that the bill did not do enough to ensure the buildout of transmission and affordable clean energy, but that they “will continue working to pass comprehensive permitting reform that takes real steps to bring down electricity costs.”
Some see getting the SPEED Act through the House as merely a starting point for a more comprehensive and fair permitting deal. Democratic Representative Adam Gray of California told Politico’s Joshua Siegel Thursday that he was voting in favor of the bill despite the last minute changes due to his faith that the Senate will hammer out a version that provides developers of all energy stripes the certainty they need.
His Californian colleague Representative Scott Peters, on the other hand, voted against the bill, but committed to getting a deal done with the Senate. “We need to get permitting reform done in this Congress,” he said on the House floor Thursday.
Federal energy regulators directed the country’s largest grid to make its rules make sense.
Federal energy regulators don’t want utilities and electricity market rules getting in the way of data centers connecting directly to power plants.
That was the consensus message from both Republican and Democratic commissioners on the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission Thursday, when it issued its long-awaited order on co-location in PJM Interconnection, the country’s largest electricity market, covering the Mid-Atlantic and Midwest.
The question is a holdover from last year, when Amazon struck a deal with independent power producer Talen Energy to co-locate an Amazon Web Services data center with the Susquehanna nuclear plant in Pennsylvania. Amazon eventually amended the deal to a more traditional power purchase agreement after failing to win regulatory approval for a behind-the-meter arrangement. Constellation, which owns a number of nuclear power plants in the PJM territory, had asked FERC to force PJM to adopt co-location rules and prevent what it saw as utilities obstructing co-location projects.
More broadly, though, the dispute is between independent power plants and their owners and utilities who build and operate the transmission grid. The latter want the former to essentially pay full freight for grid services for co-located power plants, even if they are largely or exclusively serving a single customer — such as, let’s say, a data center. Even co-located loads still incur substantial grid costs, utilities have argued, which should be paid for in their entirety.
Co-location has become attractive lately as a way to get data centers online faster and limit expensive grid upgrades that could drive up costs for everyone on the grid. Up until now, though, PJM didn’t really have a way to determine the distribution of costs and responsibilities when some or all of a new demand source is served by a co-located generator — and it wasn’t really in a particular rush to set one up, FERC said.
“The Commission finds that PJM’s tariff does not appear to sufficiently address the rates, terms and conditions of service that apply to co-location arrangements,” FERC said in its order. “The absence of this information may leave generators and load unable to determine what steps they can take to set up co-location arrangements of various configurations, and how to do so in an acceptable way.”
The commission was unanimous in its order, showing that despite the increased partisanship of regulatory politics in Donald Trump’s Washington, FERC is still operating under its traditional consensus-based approach. The consensus also shows the high level of dissatisfaction across the political spectrum with rising electricity prices, and specifically with PJM, which has combined rising prices with a clogged interconnection process and concerns about reliability.
“If a new large load wants to connect directly with a power plant and operate in a way that lowers grid costs, we should let it. If the current rules don’t let this work in a way that’s fair for everyone,” said Commissioner David Rosner, a Democrat. “We should change those rules so we can deliver the savings that consumers need and ensure reliable electricity for everybody.”
In its order, the commission asked PJM to come up with new arrangements that will allow transmission costs to scale with actual usage of the transmission system.
To do so, the new rules will have to reflect the actual usage of the transmission system of a co-located data center or other large load, Rosner explained.
He gave the example of a 1,000-megawatt data center co-located with a new 900-megawatt power plant. Its draw from the grid would be 100 megawatts, but “under PJM status quo rules,” Rosner said, “the data center needs to take the full 1,000 megawatts of front-of-meter transmission service from the grid, despite being directly connected to the co-located power plant.”
With the new options FERC is mandating PJM come up with, “the data center will now have the option to purchase what we call firm contract demand to take just 100 megawatts of firm service,” Rosner said, which will help cut costs across the board, he added.
The order also touches on the other hottest subject in grid policy today: flexibility. Because PJM will no longer be required to plan transmission or assure it has capacity for directly-connected loads, Rosner said, a big customer will have to accept the risk of being curtailed “if its usage exceeds what it’s contracted for in advance.”
The renewables industry cheered the order, especially the message that PJM needs to embrace flexibility and enable new generation and load to get online quickly.
“PJM needs to heed FERC’s message that grid flexibility enables speed, affordability, and reliability. As PJM proposes new rules to enable fast-tracking large load interconnections, it should prioritize the advanced energy technologies that are quickest to build and enable flexibility,” Jon Gordon, policy director at Advanced Energy United, said in a statement.
Independent power producers — i.e. the companies that own that power plants — also seemed happy with what the commission had to say. Talen, Constellation Energy, and Vistra Energy, all of whom have substantial footprints in PJM, saw their share prices rise at least 3% in early Thursday trading.
Thursday’s order comes as “large load interconnection” — i.e. data centers hooking up to the grid — dominates the energy regulatory discussion. Secretary of Energy Chris Wright has asked FERC to come up with new rules early next year to speed up interconnection without jacking up consumer electricity prices. At the same time, PJM’s market is under stress, with another capacity auction this week resulting in yet another round of record-setting payments to generators — plus, this time, a failure to secure its typical margin over and above its minimum projected capacity needed to ensure future reliability.
PJM is working on its own new set of rules to connect large loads without large price impacts, a process that has so far resulted in not much, as the market’s board has yet to agree on a proposal to bring to FERC.
Beating up on PJM was a bipartisan affair Thursday morning.
“The order recognizes that PJM existing transmission services are insufficient in that they do not recognize the controllable nature of co-location arrangement’s,” the commission’s Republican Chair Laura Swett said in her statement at Thursday’s meeting.
“Flexible options for co-located load means carving a path for minimizing expensive and time-intensive network upgrades in circumstances where they’re not needed,” Commissioner Lindsay See, another Republican appointee, said.
Rosner’s statement echoed his colleagues’, arguing that the existing PJM rates and contracts are “unjust and unreasonable” because they do not “contain provisions addressing with sufficient clarity or consistency the rates, terms and conditions of service that apply to interconnection customers serving co-located load and eligible customers taking transmission service on behalf of co-located load.”
He also addressed the electricity market’s board directly: “In my opinion, PJM board, tomorrow, once you’ve read this order, would be a great day to file this with us,” Rosner said.
Current conditions: Flooding continues in the Pacific Northwest as the Pineapple Express atmospheric river dumps another 4 inches of rain on Oregon • A warm front with temperatures in the 60s Fahrenheit is heading for the Northeast • Temperatures in Paraguay are surging past 90 degrees.
The Trump administration plans to dismantle the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Colorado. Founded in 1960, The New York Times credited the center with “many of the biggest scientific advances in humanity’s understanding of weather and climate.” But in a post on X late Tuesday evening, Russell Vought, the director of the White House’s Office of Management and Budget, called the institute “one of the largest sources of climate alarmism in the country,” and said the administration would be “breaking up” its operations. It’s just the latest attempt by the White House to salt the Earth for federal climate science. As I wrote in August, the administration went as far as rewriting existing climate reports.
The latest capacity auction in PJM Interconnection, where power generators in the nation’s largest electricity market bid to provide power when the grid is especially stressed, ended at the legally-mandated cap of $333.44 per megawatt. This adds up to some $16.4 billion, a record-setting figure following the past two auctions, which brought in $16.1 billion and $14.7 billion.
This auction covers 2027 through 2028, and is the last that will be subject to the price cap. Despite the dizzying spending, it failed to procure enough power to meet PJM’s preferred 20% reserve margin for a severe demand event. The auction procured 145,777 megawatts of capacity, 6,623 megawatts short of the target, giving the grid a 14.8% margin. Much of that projected demand will come from data centers, which, as Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote, have stressed the grid operator nearly to the breaking point.

Global coal use is set to start declining over the next five years as renewables and liquified natural gas gobble up its market share, the International Energy Agency projected in its latest annual forecast Wednesday. Demand is on track to inch upward 0.5% this year to a record 8,845 million tons before dropping 3% by 2030. Analysts warned Bloomberg that coal has remained “stubbornly strong” given high levels of consumption in China and India, and the Paris-based IEA cautioned that its five-year outlook “is subject to significant uncertainties that could impact it materially.”
Among the factors that look increasingly certain: That the Trump administration won’t allow any more U.S. coal plants to shut down. On Tuesday, the Department of Energy ordered the 730-megawatt TransAlta Centralia Generation in Washington to remain past its retirement at the end of this month, despite the state’s ban on coal operations. There’s just one big problem with that plan, as Matthew wrote last month. Old coal plants keep breaking down.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Nuno Loureiro, a professor of nuclear science and the director of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center, died Tuesday after being shot multiple times in his home near Boston the night before. Police statements made no mention of a suspect or motives, but Loureiro’s coveted position as one of the United States’ leading fusion scientists stoked speculation that the killing was politically motivated. Prominent influencers including the Trump adviser Laura Loomer falsely claimed that Loureiro, who was from Portugal, was Jewish and a vocal activist for the Israeli government. But The Jerusalem Post reported that Israeli intelligence officials are investigating potential links between the murder and the Iranian government, though the newspaper cautioned that the assessment “has not yet been verified.” As of now, there is no clear evidence of who killed Loureiro or why. His death shocked the field of research in which he was lauded as a leader. A former colleague in Portugal who started working at the same laboratory with Loureiro years ago in Lisbon and “knew him well” told me, “Everyone here is in shock.”
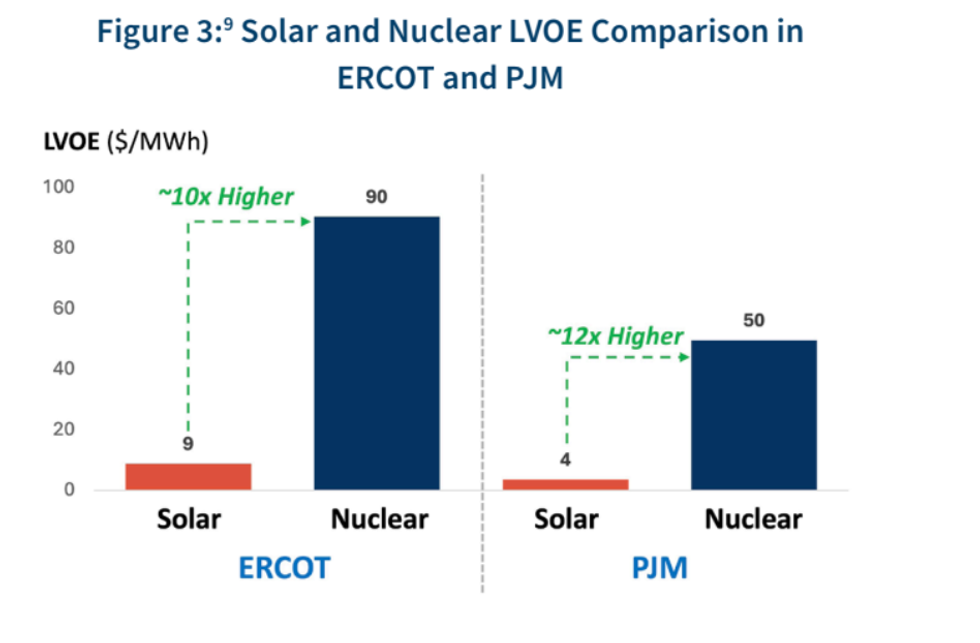
Back in June, Matthew wrote a good piece explaining why the commonly used metric known as levelized cost of energy was “wrong.” Essentially, LCOE represents the energy output of a given source in terms of its construction and operating expenses — the lower the LCOE, the more efficient it is operationally. But the metric fails to capture all the other things that make an energy source valuable, such as the frequency with which it operates, how long it lasts, or how much infrastructure is required to make use of it. When Ontario Power Generation assessed the cost of building new nuclear reactors at its Darlington station, the LCOE showed solar and batteries costing far less. But a full systems analysis found that nuclear reactors would last longer, require fewer transmission upgrades, and would not need back-up generation. A report published this morning by the consultancy FTI has proposed two new metrics instead: Levelized value of energy, or LVOE, “which reflects the total value a project can create for its owners, and Levelized Net Benefit (LNB), which quantifies the broader value a project can deliver to the overall system.” While the LCOE for solar is roughly 40% lower than nuclear power in both Texas’ ERCOT grid system and PJM, a chart from the report shows that nuclear has an LVOE roughly 10 times greater.
Record rainfall last month has revived an ancient lake in an unusual place. When ice covered the Sierra Nevada between 128,000 and 186,000 years ago, a lake 100 miles long and 600 feet deep sat in what is today the Mojave Desert in eastern California. That lake, called Lake Manly, has returned. As the science site Phys.org reported, “now Death Valley, one of the hottest places on Earth and the lowest point in North America, has a desert lake framed by snow-capped mountains.” But the “marvel” is likely to disappear soon.